2. 山东黄金集团有限公司, 济南 255014;
3. 山东省地质矿产勘查开发局, 济南 255013
2. Shandong Gold Group Co. LTD, Jinan 255014, China;
3. Shandong Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration and Development, Jinan 255013, China
0 引言
邯邢式矽卡岩铁矿成矿围岩类型主要为中基性侵入岩[1],矿体一般呈透镜状产于中基性侵入岩体与碳酸盐围岩的接触带。该类型矿床主要分布在华北克拉通内隆起区边缘的坳陷带,包括山东莱芜张家洼、淄博金岭、济南及河北沙河的白涧铁矿等[2]。研究表明矽卡岩型铁矿的矿化类型与岩浆岩的成分有着密切的联系[3-4],而含矿岩体的成因和来源目前还存在多种认识[5-11],因此探讨成矿岩体的成因特征对了解矽卡岩铁矿床成因具有重要作用。
鲁西矽卡岩型铁矿床主要分布在鲁西隆起区的东部和北部莱芜、淄博等地区,其形成于燕山晚期,属于“邯邢式”铁矿,主要产于侵入体与寒武-奥陶系的接触带上。众多学者从不同角度对与铁矿床有关的中基性岩浆岩进行了研究[5-6, 10-16],并认为其岩浆起源于上地幔纯橄榄岩熔体的部分熔融并受到陆壳物质的混染作用,但对于地壳物质的来源存在不同的认识:1)三叠纪扬子板块与华北陆块碰撞俯冲,扬子地壳物质部分熔融并交代华北岩石圈地幔[15-16];2)华北太古宙地壳物质和岩石圈地幔拆沉进入地幔[6, 17-18];3)古太平洋俯冲板块形成的熔体和岩石圈地幔熔体混合[13]。鉴于此,本文对鲁西金岭矽卡岩型铁矿区内与成矿密切相关的侵入体进行了详细的岩石学、地球化学和锆石U-Pb年代学研究,并探讨了成矿岩体岩浆源区特征及其动力学背景等问题,以期为探讨鲁西金岭矽卡岩型铁矿的成因机制提供佐证。
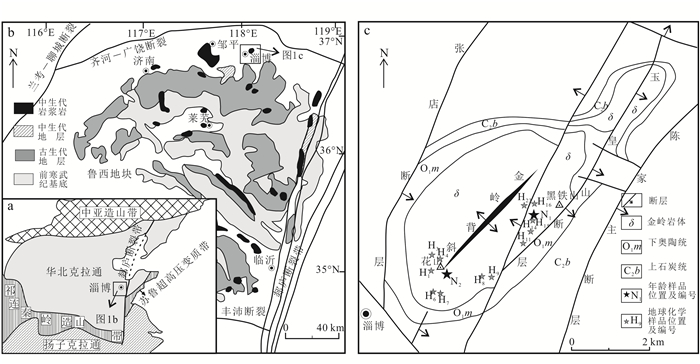
1 区域地质背景和样品描述鲁西地块位于华北克拉通东部,郯庐断裂带以西、兰考-聊城断裂以东、北部以齐河—广饶断裂为界、东南与苏鲁超高压变质带相接[13, 16](图 1a、b)。研究区位于鲁西地块东北缘,齐河—广饶断裂南侧,区内出露地层主要为下奥陶统马家沟组灰岩和上石炭统本溪组砂页岩(图 1c)。区内断裂构造发育,以NE向和NWW向断裂为主,并发育由SW向NE倾伏的背斜构造,该NNE向金岭短轴背斜构造是金岭铁矿的控矿背斜构造[1](图 1c)。研究区内岩浆活动以中基性岩浆岩为主,由辉石闪长岩-黑云母闪长岩组成,其分布在花山-黑铁山一带,出露面积约70 km2。闪长岩侵入体形态和展布方向受金岭短轴背斜控制[12],呈NE向展布并侵入到下奥陶统灰岩中形成矽卡岩型铁矿床[16]。
样品采自山东省淄博市张店区黑铁山和花山一带(图 1c),主要岩性为黑云母(辉石)闪长岩。其中,年代学样品(N1和N2)采样位置分别位于黑铁山西南侧3 km人工采坑内和花山南侧联通路路边人工露头处,GPS坐标分别为36°50′32″N、118°7′ 58″E,36°49′12″N、118°6′53″E。黑云母(辉石)闪长岩风化面深灰色,新鲜面灰黑色,中细粒结构,块状构造(图 2a、b),主要组成矿物有角闪石(35%)、斜长石(45%)、黑云母(10%)、辉石(5%)和石英(<5%),辉石多被角闪石包裹(图 2c、d)。
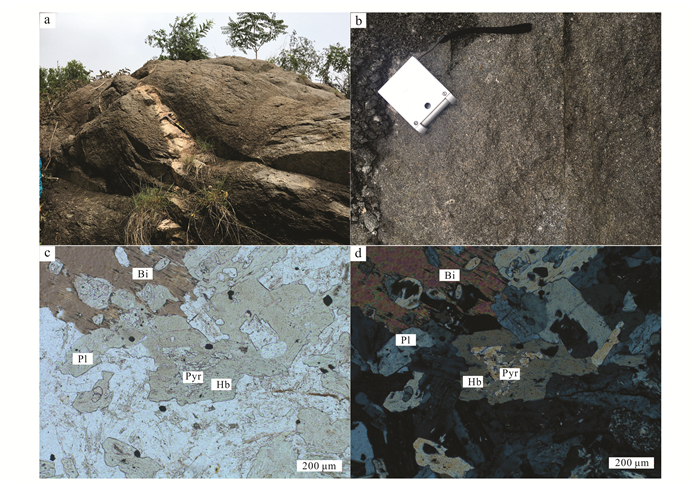
|
| Bi.黑云母;Pl.斜长石;Pyr.辉石;Hb.角闪石。 图 2 金岭闪长岩体野外照片(a、b)及显微照片(c、d) Figure 2 Photograph of outcrops(a、b) and photomicrographs (c、d) of the Jinling diorite |
|
|
对闪长岩样品(N1、N2)进行锆石U-Pb年龄测定。锆石的挑选工作在河北省廊坊区域地质调查研究所实验室完成,锆石的透射光、反射光和阴极发光(CL)图像的采集和LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄测定工作均在北京燕都中实测试技术有限公司完成。锆石U-Pb定年工作在NewWaveUP213深紫外激光器和布鲁克M90 ICP-MS联机下进行。213 nm激光器对锆石进行剥蚀的深度为20~40 μm,激光斑束为40 μm。由于测得的普通铅含量较低,以现代地壳的平均铅同位素组成作为普通Pb组成进行校正。同位素比值及年龄误差均为1σ。采用ISPLOT软件对数据结果进行处理[21]。
2.2 岩石地球化学测试样品全岩分析在澳实分析检测(广州)有限公司完成。主量元素采用X射线荧光光谱法(XRF)测定,所采用的仪器为荷兰PANalytical生产的Axios仪器;稀土元素采用美国生产的Agilent 7700x电感耦合等离子体-质谱仪(ICP-MS)进行分析测试;除稀土以外的微量元素采用美国生产的电感耦合等离子体-原子发射光谱(Varian VISTA ICP-AES)和电感耦合等离子体-质谱分析方法(Perkin Elmer Elan 6 000 ICP-MS)完成。主量元素分析精度和准确度优于5%,微量和稀土元素分析精度和准确度为5%~10%。
3 分析结果 3.1 锆石U-Pb定年结果金岭闪长岩样品N1和N2锆石阴极发光图像特征见图 3。N1闪长岩样品中锆石多为短柱状或粒状,晶形一般,颗粒大小不均,多数为80~120 μm,锆石阴极发光图像显示锆石成分较为复杂:锆石N1-2、N1-3、N1-4、N1-7、N1-8、N1-9、N1-11、N1-15具有较小的变质边和清晰的核幔结构(图 3a),其Th和U的质量分数分别为w(Th)=22.50×10-6~396.40×10-6和w(U)= 20.00×10-6~1 753.00×10-6,样品的Th/U值为0.03~1.41,其变化范围较大;其余锆石显示条痕状条带,Th和U的质量分数分别为w(Th)=149.70×10-6~677.90×10-6和w(U)= 132.00×10-6~421.00×10-6,样品的Th/U值为1.13~1.69(表 1),具有中基性岩浆锆石的特点。选择变质边和环带清晰的代表性锆石共20个颗粒进行锆石U-Pb年龄测定,8颗锆石表面年龄为(2 505.0±6.0)~(2 554.0±11.0)Ma(图 3a),上交点年龄为(2 529.6±4.2)Ma(图 4a),12颗锆石表面年龄为(127.0±1.0)~(132.0±0.8)Ma,对12颗锆石进行加权平均年龄计算结果为(129.17±0.96)Ma(MSWD=2.4)(图 4a),属于早白垩世。该年龄代表金岭铁矿区闪长岩岩体的结晶年龄。
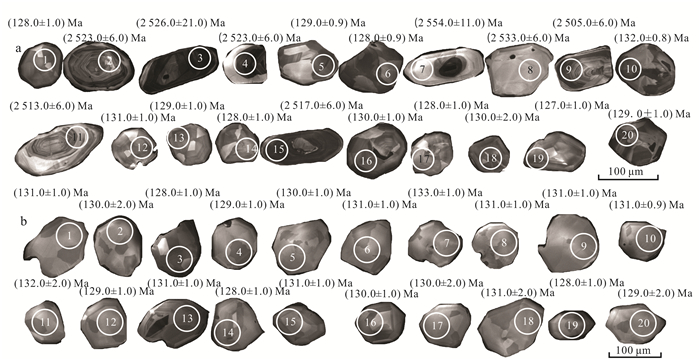
|
| a.N1; b.N2。 图 3 金岭闪长岩锆石CL图 Figure 3 Cathodoluminescence images of zircons of the Jinling diorite |
|
|
| 测点 | w(Th)/10-6 | w(U)/10-6 | Th/U | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | |||||||||||
| 207Pb/ 206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/ 235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | 207Pb/206Pb | 1σ | 207Pb/235U | 1σ | 206Pb/238U | 1σ | |||||
| N1-1 | 210.20 | 174.00 | 1.21 | 0.049 1 | 0.001 0 | 0.135 5 | 0.002 7 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 2 | 153.0 | 32.0 | 129.0 | 2.0 | 128.0 | 1.0 | |
| N1-2 | 377.20 | 359.00 | 1.05 | 0.166 5 | 0.001 1 | 10.722 4 | 0.083 8 | 0.466 6 | 0.003 0 | 2 523.0 | 6.0 | 2 499.0 | 7.0 | 2 468.0 | 13.0 | |
| N1-3 | 209.70 | 1 753.00 | 0.12 | 0.166 8 | 0.002 0 | 10.335 7 | 0.095 1 | 0.449 5 | 0.003 5 | 2 526.0 | 21.0 | 2 465.0 | 9.0 | 2 393.0 | 16.0 | |
| N1-4 | 396.40 | 1 052.00 | 0.38 | 0.166 5 | 0.001 0 | 9.438 0 | 0.080 8 | 0.410 9 | 0.003 4 | 2 523.0 | 6.0 | 2 382.0 | 8.0 | 2 219.0 | 15.0 | |
| N1-5 | 395.60 | 234.00 | 1.69 | 0.049 3 | 0.000 8 | 0.137 0 | 0.002 2 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 1 | 162.0 | 24.0 | 130.0 | 2.0 | 129.0 | 0.9 | |
| N1-6 | 653.00 | 416.00 | 1.57 | 0.048 4 | 0.000 7 | 0.134 2 | 0.001 9 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 1 | 118.0 | 21.0 | 128.0 | 2.0 | 128.0 | 0.9 | |
| N1-7 | 27.60 | 20.00 | 1.41 | 0.169 6 | 0.002 1 | 11.018 1 | 0.148 7 | 0.473 1 | 0.004 6 | 2 554.0 | 11.0 | 2 525.0 | 13.0 | 2 497.0 | 20.0 | |
| N1-8 | 22.50 | 33.00 | 0.68 | 0.167 5 | 0.001 1 | 10.489 2 | 0.086 8 | 0.454 0 | 0.003 3 | 2 533.0 | 6.0 | 2 479.0 | 8.0 | 2 413.0 | 15.0 | |
| N1-9 | 180.60 | 536.00 | 0.34 | 0.164 7 | 0.001 0 | 9.261 7 | 0.074 3 | 0.407 9 | 0.003 2 | 2 505.0 | 6.0 | 2 364.0 | 7.0 | 2 205.0 | 15.0 | |
| N1-10 | 677.90 | 421.00 | 1.61 | 0.048 1 | 0.000 6 | 0.137 1 | 0.001 7 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 1 | 105.0 | 18.0 | 130.0 | 2.0 | 132.0 | 0.8 | |
| N1-11 | 138.10 | 244.00 | 0.57 | 0.165 5 | 0.001 1 | 9.896 4 | 0.080 8 | 0.433 1 | 0.002 8 | 2 513.0 | 6.0 | 2 425.0 | 8.0 | 2 320.0 | 13.0 | |
| N1-12 | 202.40 | 154.00 | 1.31 | 0.049 8 | 0.001 0 | 0.140 7 | 0.002 8 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 2 | 185.0 | 30.0 | 134.0 | 2.0 | 131.0 | 1.0 | |
| N1-13 | 149.70 | 132.00 | 1.13 | 0.048 7 | 0.001 3 | 0.134 1 | 0.003 3 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 2 | 134.0 | 40.0 | 128.0 | 3.0 | 129.0 | 1.0 | |
| N1-14 | 198.70 | 159.00 | 1.25 | 0.049 6 | 0.001 3 | 0.137 1 | 0.003 7 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 175.0 | 46.0 | 130.0 | 3.0 | 128.0 | 1.0 | |
| N1-15 | 38.10 | 1 172.00 | 0.03 | 0.165 9 | 0.001 0 | 9.478 3 | 0.076 1 | 0.414 4 | 0.002 7 | 2 517.0 | 6.0 | 2 385.0 | 7.0 | 2 235.0 | 12.0 | |
| N1-16 | 314.20 | 232.00 | 1.35 | 0.050 7 | 0.001 5 | 0.140 6 | 0.004 0 | 0.020 4 | 0.000 2 | 228.0 | 47.0 | 134.0 | 4.0 | 130.0 | 1.0 | |
| N1-17 | 155.60 | 138.00 | 1.13 | 0.050 2 | 0.001 6 | 0.136 6 | 0.004 0 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 205.0 | 50.0 | 130.0 | 4.0 | 128.0 | 1.0 | |
| N1-18 | 213.50 | 159.00 | 1.34 | 0.050 3 | 0.001 8 | 0.138 4 | 0.005 0 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 2 | 207.0 | 61.0 | 132.0 | 4.0 | 130.0 | 2.0 | |
| N1-19 | 361.00 | 221.00 | 1.63 | 0.050 6 | 0.001 9 | 0.137 2 | 0.005 1 | 0.020 0 | 0.000 2 | 223.0 | 65.0 | 131.0 | 5.0 | 127.0 | 1.0 | |
| N1-20 | 378.90 | 302.40 | 1.30 | 0.100 0 | 0.000 0 | 0.100 0 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 0 | 0.000 0 | 206.0 | 42.0 | 132.0 | 3.0 | 129.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-1 | 57.80 | 63.00 | 0.92 | 0.051 5 | 0.001 8 | 0.143 1 | 0.004 9 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 2 | 261.0 | 59.0 | 136.0 | 4.0 | 131.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-2 | 37.60 | 52.00 | 0.72 | 0.052 6 | 0.002 1 | 0.144 1 | 0.005 4 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 2 | 313.0 | 64.0 | 137.0 | 5.0 | 130.0 | 2.0 | |
| N2-3 | 262.30 | 203.00 | 1.29 | 0.050 6 | 0.001 0 | 0.139 4 | 0.002 8 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 223.0 | 32.0 | 133.0 | 3.0 | 128.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-4 | 64.40 | 64.00 | 1.01 | 0.053 5 | 0.001 9 | 0.145 7 | 0.004 8 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 2 | 348.0 | 55.0 | 138.0 | 4.0 | 129.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-5 | 42.40 | 57.00 | 0.74 | 0.053 4 | 0.002 0 | 0.147 9 | 0.005 3 | 0.020 4 | 0.000 2 | 346.0 | 61.0 | 140.0 | 5.0 | 130.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-6 | 41.80 | 58.00 | 0.72 | 0.053 8 | 0.001 9 | 0.148 6 | 0.004 8 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 2 | 363.0 | 53.0 | 141.0 | 4.0 | 131.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-7 | 40.90 | 56.00 | 0.73 | 0.052 3 | 0.002 0 | 0.146 6 | 0.005 2 | 0.020 8 | 0.000 2 | 299.0 | 60.0 | 139.0 | 5.0 | 133.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-8 | 43.00 | 56.00 | 0.76 | 0.051 3 | 0.001 8 | 0.142 5 | 0.004 9 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 2 | 254.0 | 58.0 | 135.0 | 4.0 | 131.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-9 | 52.90 | 64.00 | 0.83 | 0.049 1 | 0.001 9 | 0.135 5 | 0.004 7 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 2 | 151.0 | 61.0 | 129.0 | 4.0 | 131.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-10 | 372.10 | 276.00 | 1.35 | 0.048 7 | 0.000 8 | 0.136 7 | 0.002 3 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 1 | 134.0 | 26.0 | 130.0 | 2.0 | 131.0 | 0.9 | |
| N2-11 | 38.50 | 52.00 | 0.74 | 0.048 1 | 0.001 8 | 0.134 8 | 0.005 0 | 0.020 7 | 0.000 2 | 103.0 | 63.0 | 128.0 | 4.0 | 132.0 | 2.0 | |
| N2-12 | 48.90 | 61.00 | 0.80 | 0.049 3 | 0.001 7 | 0.134 5 | 0.004 4 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 2 | 162.0 | 55.0 | 128.0 | 4.0 | 129.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-13 | 233.50 | 203.00 | 1.15 | 0.049 3 | 0.000 9 | 0.139 7 | 0.002 7 | 0.020 6 | 0.000 2 | 160.0 | 30.0 | 133.0 | 2.0 | 131.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-14 | 57.70 | 72.00 | 0.80 | 0.053 1 | 0.001 9 | 0.143 6 | 0.004 7 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 335.0 | 55.0 | 136.0 | 4.0 | 128.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-15 | 60.30 | 81.00 | 0.75 | 0.050 5 | 0.001 7 | 0.140 5 | 0.004 5 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 2 | 217.0 | 56.0 | 134.0 | 4.0 | 131.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-16 | 134.00 | 120.00 | 1.12 | 0.051 3 | 0.001 3 | 0.142 0 | 0.003 7 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 2 | 253.0 | 42.0 | 135.0 | 3.0 | 130.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-17 | 41.00 | 54.00 | 0.75 | 0.046 1 | 0.003 0 | 0.129 1 | 0.008 2 | 0.020 3 | 0.000 3 | 387.0 | 142.0 | 123.0 | 7.0 | 130.0 | 2.0 | |
| N2-18 | 37.40 | 48.00 | 0.78 | 0.051 5 | 0.001 8 | 0.143 3 | 0.004 9 | 0.020 5 | 0.000 3 | 265.0 | 56.0 | 136.0 | 4.0 | 131.0 | 2.0 | |
| N2-19 | 66.10 | 74.00 | 0.89 | 0.049 3 | 0.001 6 | 0.134 8 | 0.004 3 | 0.020 1 | 0.000 2 | 160.0 | 55.0 | 128.0 | 4.0 | 128.0 | 1.0 | |
| N2-20 | 36.10 | 49.00 | 0.74 | 0.048 2 | 0.002 0 | 0.131 9 | 0.005 2 | 0.020 2 | 0.000 3 | 107.0 | 66.0 | 126.0 | 5.0 | 129.0 | 2.0 | |
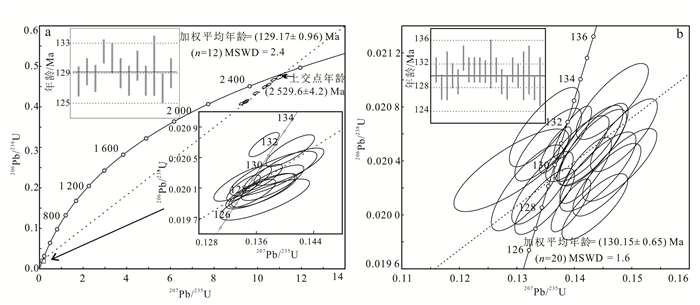
|
| 图 4 金岭闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年结果 Figure 4 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb concordia plots and recalculated weighted mean 206Pb/238U ages of the Jinling diorite |
|
|
N2闪长岩样品中锆石多为短柱状,晶形较好,颗粒大小不均,多数为80~120 μm,锆石阴极发光图像显示条痕状条带特征(图 3b),其Th和U的质量分数分别为36.10×10-6~372.10×10-6和48.00×10-6~276.00×10-6,样品的Th/U值为0.72~1.35(表 1),均大于0.40,具有典型中基性岩浆锆石的特征。选择条痕状清晰的20颗颗粒进行锆石U-Pb年龄测定,其表面年龄为(128.0±1.0)~(133.0±1.0)Ma,20颗锆石颗粒加权平均年龄为(130.15±0.65)Ma(图 4b),属于早白垩世。该年龄代表金岭铁矿区闪长岩体的结晶年龄。
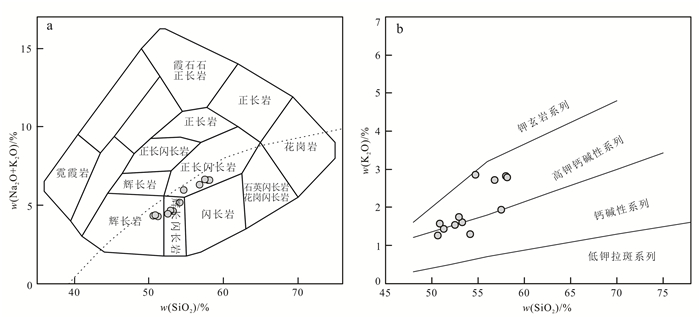
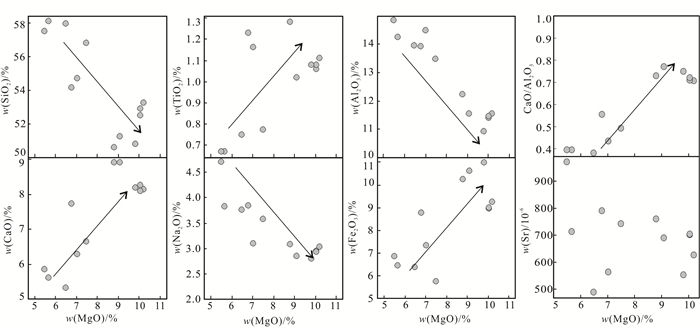
3.2 主量元素和微量元素 3.2.1 主量元素金岭铁矿区闪长岩地球化学分析结果见表 2。闪长岩w(SiO2)为50.62%~58.12%,平均为54.22%,3个样品w(SiO2)<52.00%,地球化学特征上表现基性岩浆岩特征,其余样品属于中性岩浆岩;w(Al2O3)为10.92%~14.82%,平均为12.82%,具有高铝质特点;w(Na2O)和w(K2O)分别为2.80%~4.71%和1.26%~2.86%,Na2O/K2O值为1.08~2.96,具有相对富钠的特征。在w(Na2O +K2O)-w(SiO2)图解(图 5a)中,样品落在了辉长岩-辉长闪长岩-正长闪长岩范围内。在w(K2O)-w(SiO2)图解(图 5b)中,多数样品落入了高钾钙碱性系列,少数样品落在了钙碱性系列。样品的里特曼指数为1.95~2.96,小于3.30,具有钙碱性系列岩浆演化趋势。w(MgO)变化较大,为5.49%~10.20%,平均为8.08%,Mg#值为58.00~70.00,具有高Mg闪长岩Mg#的特点;A/CNK为0.51~0.74,为准铝质岩石。样品w(MgO)与w(SiO2)、w(Na2O)、w(Al2O3)呈负相关,而与w(Fe2O3)、w(TiO2)、w(CaO)和CaO/Al2O3呈正相关(图 6)。
| 样品 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | H2O+ | 烧失量 | 总计 | K2O+Na2O | A/CNK |
| H1 | 57.97 | 0.75 | 13.93 | 7.08 | 0.14 | 6.48 | 5.31 | 3.76 | 2.82 | 0.33 | 1.18 | 1.86 | 101.61 | 6.58 | 0.74 |
| H3 | 58.12 | 0.67 | 14.24 | 7.17 | 0.11 | 5.67 | 5.62 | 3.82 | 2.79 | 0.29 | 1.13 | 1.12 | 100.75 | 6.61 | 0.73 |
| H4 | 56.80 | 0.77 | 13.47 | 6.39 | 0.11 | 7.49 | 6.64 | 3.58 | 2.71 | 0.32 | 1.19 | 1.25 | 100.72 | 6.29 | 0.64 |
| H6 | 53.25 | 1.11 | 11.53 | 10.28 | 0.16 | 10.20 | 8.15 | 3.03 | 1.60 | 0.50 | 1.14 | 0.84 | 101.79 | 4.63 | 0.53 |
| H7 | 52.91 | 1.06 | 11.39 | 9.94 | 0.17 | 10.05 | 8.08 | 2.94 | 1.74 | 0.48 | 1.53 | 1.03 | 101.32 | 4.68 | 0.53 |
| H8 | 52.51 | 1.08 | 11.46 | 10.01 | 0.16 | 10.05 | 8.27 | 2.93 | 1.54 | 0.50 | 1.61 | 0.69 | 100.81 | 4.47 | 0.53 |
| H9 | 51.24 | 1.02 | 11.54 | 11.79 | 0.18 | 9.09 | 8.90 | 2.85 | 1.43 | 0.48 | 1.36 | 1.83 | 101.71 | 4.28 | 0.51 |
| H11 | 57.49 | 0.67 | 14.82 | 7.61 | 0.12 | 5.49 | 5.86 | 4.71 | 1.93 | 0.31 | 1.35 | 1.05 | 101.41 | 6.64 | 0.72 |
| H14 | 54.71 | 1.16 | 14.46 | 8.16 | 0.12 | 7.03 | 6.29 | 3.09 | 2.86 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 2.22 | 101.06 | 5.95 | 0.74 |
| H15 | 50.62 | 1.28 | 12.21 | 11.39 | 0.20 | 8.80 | 8.91 | 3.08 | 1.26 | 0.58 | 0.71 | 1.17 | 100.21 | 4.34 | 0.54 |
| H16 | 50.83 | 1.08 | 10.92 | 12.22 | 0.21 | 9.81 | 8.18 | 2.80 | 1.58 | 0.49 | 0.46 | 1.24 | 99.82 | 4.38 | 0.51 |
| H23 | 54.16 | 1.23 | 13.92 | 9.73 | 0.14 | 6.79 | 7.73 | 3.85 | 1.30 | 0.46 | 0.00 | 0.24 | 99.55 | 5.15 | 0.64 |
| 样品 | Mg# | N2O/K2O | σ | CaO/Al2O3 | Rb | Sr | Ba | Cs | Y | Zr | Hf | Nb | Ta | Th | U |
| H1 | 64.00 | 1.33 | 2.80 | 0.38 | 64.60 | 488.00 | 1 020.00 | 0.87 | 14.40 | 115.00 | 2.80 | 6.80 | 0.50 | 4.18 | 1.03 |
| H3 | 61.00 | 1.37 | 2.79 | 0.39 | 55.10 | 713.00 | 994.00 | 0.78 | 13.20 | 128.00 | 3.30 | 6.60 | 0.40 | 4.21 | 0.93 |
| H4 | 70.00 | 1.32 | 2.75 | 0.49 | 51.70 | 742.00 | 1 095.00 | 0.78 | 15.30 | 125.00 | 3.20 | 7.30 | 0.60 | 3.82 | 0.88 |
| H6 | 66.00 | 1.89 | 2.03 | 0.71 | 35.30 | 626.00 | 781.00 | 1.55 | 20.90 | 117.00 | 30.00 | 7.50 | 0.50 | 2.18 | 0.56 |
| H7 | 66.00 | 1.69 | 2.08 | 0.71 | 40.80 | 701.00 | 911.00 | 1.53 | 20.00 | 93.00 | 2.50 | 6.70 | 0.40 | 2.20 | 0.58 |
| H8 | 66.00 | 1.90 | 1.95 | 0.72 | 34.70 | 704.00 | 807.00 | 1.70 | 20.40 | 98.00 | 2.60 | 6.80 | 0.40 | 2.07 | 0.53 |
| H9 | 60.00 | 1.99 | 2.03 | 0.77 | 30.50 | 690.00 | 671.00 | 1.00 | 18.60 | 72.00 | 2.00 | 5.10 | 0.30 | 2.15 | 0.62 |
| H11 | 59.00 | 2.44 | 2.96 | 0.40 | 43.60 | 971.00 | 1 080.00 | 0.80 | 16.70 | 93.00 | 2.60 | 7.10 | 0.30 | 2.85 | 0.57 |
| H14 | 63.00 | 1.08 | 2.86 | 0.43 | 65.90 | 563.00 | 812.00 | 1.51 | 21.70 | 137.00 | 3.60 | 8.50 | 0.40 | 4.47 | 1.39 |
| H15 | 60.00 | 2.44 | 2.22 | 0.73 | 22.40 | 760.00 | 579.00 | 0.87 | 19.10 | 76.00 | 2.10 | 6.40 | 0.30 | 2.00 | 0.48 |
| H16 | 61.00 | 1.77 | 2.19 | 0.75 | 27.90 | 553.00 | 706.00 | 0.56 | 19.30 | 77.00 | 2.10 | 5.40 | 0.20 | 2.12 | 0.46 |
| H23 | 58.00 | 2.96 | 2.29 | 0.56 | 26.60 | 790.00 | 787.00 | 0.91 | 21.00 | 104.00 | 2.60 | 10.00 | 0.40 | 1.96 | 0.51 |
| 样品 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | |
| H1 | 46.10 | 81.80 | 8.99 | 33.00 | 5.97 | 1.60 | 4.88 | 0.61 | 3.22 | 0.59 | 1.55 | 0.21 | 1.17 | 0.16 | |
| H3 | 28.50 | 59.90 | 7.02 | 26.80 | 5.21 | 1.55 | 4.12 | 0.52 | 2.77 | 0.49 | 1.24 | 0.18 | 1.03 | 0.15 | |
| H4 | 27.70 | 58.20 | 7.08 | 28.30 | 5.17 | 1.82 | 4.77 | 0.60 | 3.17 | 0.61 | 1.53 | 0.21 | 1.24 | 0.18 | |
| H6 | 27.30 | 61.50 | 7.94 | 33.90 | 7.23 | 2.15 | 6.87 | 0.84 | 4.62 | 0.81 | 2.06 | 0.28 | 1.55 | 0.24 | |
| H7 | 28.40 | 63.50 | 8.15 | 34.50 | 7.44 | 2.22 | 6.87 | 0.86 | 4.54 | 0.81 | 2.02 | 0.27 | 1.50 | 0.22 | |
| H8 | 27.10 | 61.50 | 8.02 | 34.70 | 7.24 | 2.29 | 7.03 | 0.91 | 4.71 | 0.83 | 2.08 | 0.28 | 1.57 | 0.22 | |
| H9 | 24.90 | 54.60 | 6.95 | 29.80 | 6.30 | 2.01 | 5.68 | 0.77 | 4.04 | 0.73 | 1.82 | 0.24 | 1.33 | 0.19 | |
| H11 | 33.00 | 68.10 | 8.29 | 33.90 | 6.44 | 2.11 | 5.61 | 0.66 | 3.42 | 0.63 | 1.68 | 0.23 | 1.27 | 0.18 | |
| H14 | 39.90 | 77.60 | 8.55 | 35.10 | 6.86 | 1.96 | 5.99 | 0.83 | 4.50 | 0.86 | 2.14 | 0.29 | 1.68 | 0.25 | |
| H15 | 25.20 | 55.80 | 7.13 | 31.60 | 6.42 | 2.11 | 6.21 | 0.79 | 4.07 | 0.69 | 1.85 | 0.25 | 1.43 | 0.20 | |
| H16 | 20.30 | 47.70 | 6.41 | 27.90 | 6.00 | 1.90 | 5.86 | 0.76 | 4.14 | 0.73 | 1.98 | 0.27 | 1.55 | 0.21 | |
| H23 | 28.00 | 60.20 | 7.37 | 32.30 | 6.40 | 2.10 | 5.95 | 0.82 | 4.43 | 0.81 | 2.10 | 0.28 | 1.69 | 0.25 | |
| 样品 | Co | Ni | Cr | Ga | Sc | V | ∑REE | Rb/Sr | Ba/Rb | Zr/Hf | La/Sm | Nb/Ta | (La/Yb)N | δEu | |
| H1 | 19.00 | 137.00 | 350.00 | 19.10 | 16.00 | 142.00 | 189.69 | 0.13 | 15.79 | 41.07 | 7.72 | 13.60 | 26.56 | 0.91 | |
| H3 | 23.00 | 134.00 | 300.00 | 19.60 | 14.00 | 128.00 | 139.33 | 0.08 | 18.04 | 38.79 | 5.47 | 16.50 | 18.65 | 1.02 | |
| H4 | 24.00 | 192.00 | 440.00 | 20.30 | 17.00 | 146.00 | 140.40 | 0.07 | 21.18 | 39.06 | 5.36 | 12.17 | 15.06 | 1.12 | |
| H6 | 43.00 | 235.00 | 570.00 | 16.80 | 24.00 | 195.00 | 157.05 | 0.06 | 22.12 | 39.00 | 3.78 | 15.00 | 11.87 | 0.93 | |
| H7 | 43.00 | 237.00 | 600.00 | 17.50 | 23.00 | 192.00 | 161.08 | 0.06 | 22.33 | 37.20 | 3.82 | 16.75 | 12.76 | 0.95 | |
| H8 | 43.00 | 233.00 | 570.00 | 16.70 | 23.00 | 195.00 | 158.26 | 0.05 | 23.26 | 37.69 | 3.74 | 17.00 | 11.64 | 0.98 | |
| H9 | 44.00 | 184.00 | 410.00 | 16.90 | 27.00 | 227.00 | 139.17 | 0.04 | 22.00 | 36.00 | 3.95 | 17.00 | 12.62 | 1.03 | |
| H11 | 24.00 | 99.00 | 270.00 | 20.90 | 14.00 | 140.00 | 165.34 | 0.04 | 24.77 | 35.77 | 5.12 | 23.67 | 17.52 | 1.07 | |
| H14 | 29.00 | 170.00 | 370.00 | 19.20 | 20.00 | 218.00 | 186.26 | 0.12 | 12.32 | 38.06 | 5.82 | 21.25 | 16.01 | 0.93 | |
| H15 | 42.00 | 144.00 | 380.00 | 17.80 | 25.00 | 247.00 | 143.55 | 0.03 | 25.85 | 36.19 | 3.93 | 21.33 | 11.88 | 1.02 | |
| H16 | 44.00 | 202.00 | 490.00 | 16.60 | 27.00 | 267.00 | 125.50 | 0.05 | 25.30 | 36.67 | 3.38 | 27.00 | 8.83 | 0.98 | |
| H23 | 34.00 | 105.00 | 280.00 | 18.70 | 21.00 | 198.00 | 152.45 | 0.03 | 29.59 | 40.00 | 4.38 | 25.00 | 11.17 | 1.04 | |
| 注:主量元素质量分数单位为%;微量和稀土元素质量分数单位为10-6。Mg#=100(w(MgO)/40.31)/(w(MgO)/40.31+w(TFeO)/71.85)。H2O+为结构水。 | |||||||||||||||
|
| 图 6 金岭闪长岩MgO和主量元素氧化物以及微量元素关系图 Figure 6 MgO variation diagrams of representative major element oxides and minor elements of the Jinling diorite |
|
|
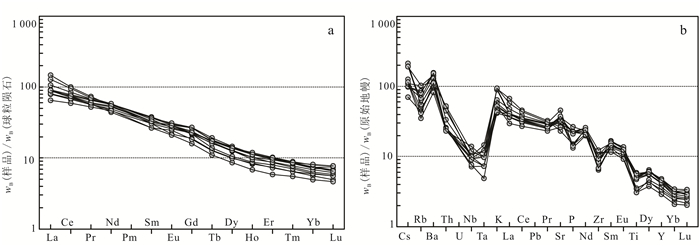
闪长岩稀土元素质量分数为(125.50~189.69)×10-6,轻稀土质量分数为(110.21~177.46)×10-6,重稀土质量分数为(10.35~17.41)×10-6,(La/Yb)N=8.83~26.56,轻重稀土元素分馏程度中等。δEu为0.91~1.12,表现出弱的Eu负异常到Eu正异常。在球粒陨石标准化的稀土元素配分曲线上(图 7a),闪长岩样品富集轻稀土元素,相对亏损重稀土元素。在原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 7b)中,样品富集大离子亲石元素(Ba、K、Sr)和高场强元素Nd,相对亏损高场强元素(Rb、Nb、Ta、Zr),指示了与俯冲作用相关的微量元素地球化学特征[26-27]。所有样品具有较高的w(Sr)((488.00~971.00)×10-6,地壳平均w(Sr)为325.00×10-6[28])及低的w(Yb)((1.03~1.69)×10-6),具有埃达克质岩石的地球化学特征。其w(Ni)为(99.00~237.00)×10-6,w(Cr)为(270.00~600.00)×10-6,w(Co)为(19.00~44.00)×10-6,暗示其岩浆源区可能为幔源。Nb/Ta值为12.17~27.00,Zr/Hf值为35.77~41.07,Rb/Sr值为0.03~0.13,Ba/Rb值为12.32~29.59,其相关比值也暗示闪长岩幔源岩浆源区的特征。而变化较小的La/Sm值(3.38~7.72)表明其地壳混染作用在岩浆演化过程中影响较小或没有影响[26, 29-30]。
《山东省区域地质志》[31]中,根据金岭地区闪长岩与其他地质体的接触关系,将其侵位时代确定为中生代燕山晚期;文献[32]中,根据黑云母闪长岩中角闪石和黑云母的K-Ar同位素年龄将金岭地区闪长岩的形成时代确定为129~112 Ma;杨承海等[16]利用LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年方法对其侵位时代进行了研究,其加权平均年龄为(132.8±4.2)Ma,属于早白垩世晚期。本文对金岭地区闪长岩体进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,闪长岩的阴极发光图像和Th/U值显示具有典型的岩浆成因,所测得的年龄可以代表岩体的形成时代。样品N1和N2加权平均年龄分别为(129.17±0.96)和(130.15±0.65)Ma,与杨承海等[16]所测得的结果一致,为早白垩世晚期。
4.2 岩石成因金岭闪长岩矿物组成主要为角闪石和黑云母以及少量的石英和辉石,具有中基性侵入岩的矿物组合特征;此外,岩体中含有幔源型矿物Ca石榴石和Cr石榴石[1]、纯橄岩包体和辉石包体[12, 14, 33-34],岩相学特征暗示金岭闪长岩岩浆源区 具有幔源岩浆特征。黑云母和角闪石矿物的出现以及辉石被角闪石包围的特点(图 2c、d),表明岩浆体系具有富水特征。金岭岩浆岩样品w(SiO2)较低,MgO、Ni、Co、Cr质量分数和Mg#较高,并具有高Sr低Yb的特点。另外,样品的Nb/Ta值为12.17~27.00,明显高于壳源岩浆的Nb/Ta值(11.00),而与幔源岩浆的Nb/Ta值(17.50)相符[35];Zr/Hf值(35.77~41.07)接近于原始地幔值(36.27),远高于大陆地壳值(11.00)[26];Rb/Sr值为0.03~0.13(原始地幔的Rb/Sr值为0.03[36]),Ba/Rb值为12.32~29.59 (原始地幔Ba/Rb值为11.00[37])。金岭闪长岩矿物学特征和岩石地球化学特征均暗示其岩浆具有幔源岩浆的特征。
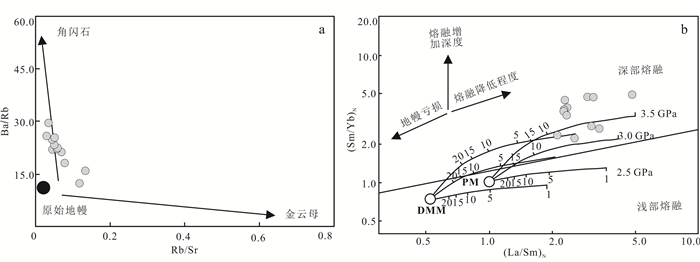
在Ba/Rb-Rb/Sr图解(图 8a)中,金岭闪长岩样品明显表现出与角闪石相关的演化趋势,暗示其源区可能存在角闪石矿物[38-39]。此外,样品的SiO2、Al2O3、TiO2、Na2O、Fe2O3、CaO、Sr质量分数和CaO/Al2O3与MgO质量分数的线性关系(图 6),说明闪长岩岩浆源区可能存在橄榄石、单斜辉石的分离结晶作用[13]。在(Sm/Yb)N-(La/Sm)N图解(图 8b)中,金岭岩体样品落在了3.0 GPa和3.5 GPa刻线附近,表明其岩浆源区深度应大于91 km,且源区可能含有斜方辉石、单斜辉石、石榴石、铬尖晶石等矿物。金岭闪长岩的岩相学和岩石地球化学特征均暗示其岩浆可能来源于含辉石、铬尖晶石地幔橄榄岩的部分熔融。金岭地区闪长岩富集大离子亲石元素(Ba、K、Sr)和高场强元素Nd,明显亏损高场强元素(Rb、Nb、Ta、Zr)和元素性质不活泼的不相容元素P和Ti,上述特征指示了与俯冲作用相关的微量元素地球化学特征,而强不相容元素(Ba、Sr)显著富集和高场强元素(Nb、Ta)明显亏损,表明其岩浆源区可能为俯冲流体交代的岩石圈地幔或是受到陆壳物质混染。
研究表明,受俯冲影响的岩浆源区87Sr/86Sr值较低、εNd(t)值较高[15, 41-42],而且金岭闪长岩具有较高的Sr质量分数,暗示其可能受俯冲流体的影响;金岭闪长岩高87Sr/86Sr值(0.704 75~0.705 78)和低εNd(t)值(-3.95~-6.45)[10, 16], 表明岩体岩浆源区应受到地壳物质的混染。因此,金岭岩体岩浆源区应受到地壳物质的混染。
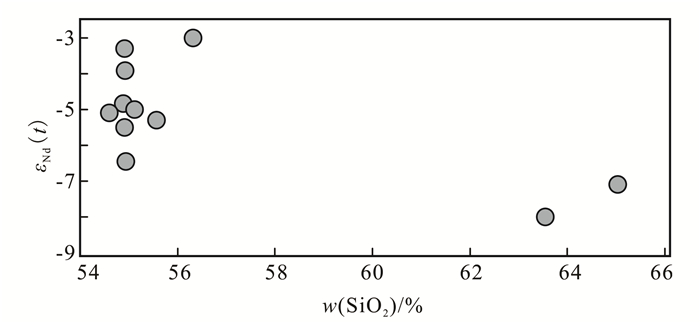
样品N1存在约2.5 Ga的捕获锆石,证明金岭闪长岩岩浆源区受到古老下地壳物质的混染作用,其Pb同位素特征和较老的Nd模式年龄也反映其岩石圈地幔受改造的物质应主要为华北克拉通基底[7, 10, 16]。目前,对于鲁西地幔源区的地壳物质加入存在两种不同的认识:1)通过拆沉作用华北古老下地壳物质加入到地幔源区[17-18];2)幔源岩浆底侵促使上部下地壳物质熔融形成花岗质熔体,花岗质熔体与地幔起源的玄武质熔体岩浆混合[5]。金岭闪长岩中w(SiO2)与εNd(t)大致呈线性负相关关系(图 9),表明下地壳起源的花岗质熔体与地幔起源的玄武质熔体的岩浆混合作用在高镁闪长岩的形成过程中起主要作用,而锆石Hf同位素特征[10]和Os同位素特征[43]也表明金岭闪长岩的岩浆演化模式不同于拆沉模式,而符合壳幔岩浆混合的成因模式。总之,金岭闪长岩岩浆源区是富集地幔起源的基性(玄武质岩浆)岩浆与华北古老下地壳熔融形成的壳源酸性(花岗质)岩浆混合过程的产物。
中国东部广泛分布拉张的沉积盆地[44]、变质核杂岩[45-48]、A型花岗岩和碱性岩[49],表明中国东部在晚中生代时期处于拉张的构造环境。该伸展构造环境可能属于三叠纪华北板块和扬子板块的碰撞后拉张[50],也可能是受到太平洋板片俯冲的影响[51-52]或是两者之间共同作用的影响。但新的资料[52-54]显示,晚中生代中国东部伸展构造环境是太平洋板片俯冲之后的板片后撤作用引起的。因此,金岭闪长岩侵位构造背景可能为太平洋板片俯冲后后撤引起的伸展构造。
5 结论1) 鲁西金岭闪长岩位于华北克拉通东南部,主要由辉石闪长岩-黑云母闪长岩组成。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年表明金岭闪长岩结晶年龄为(129.17±0.96)和(130.15±0.65)Ma,是早白垩世晚期岩浆活动的产物。
2) 金岭闪长岩含有约2.5 Ga的捕获锆石,同时具有与幔源岩浆相似的Nb/Ta、Zr/Hf、Rb/Sr和Ba/Rb值,并富集大离子亲石元素(Ba、K、Sr)和高场强元素Nd,明显亏损高场强元素(Rb、Nb、Ta、Zr)和元素性质不活泼的不相容元素P和Ti。
3) 金岭闪长岩岩浆源区是富集地幔起源的基性(玄武质岩浆)岩浆与华北古老下地壳熔融形成的壳源酸性(花岗质)岩浆混合过程的产物,形成于太平洋板块俯冲后后撤引起的伸展构造环境。
致谢: 样品测试工作得到了吉林大学地球科学学院大青山工作组的大力支持,显微照片采集过程中得到山东省地质科学院韩代成高级工程师和宋英昕助理工程师的热忱帮助,在此表示感谢。| [1] |
黄有德, 李绥远. 中国东部地区夕卡岩型铁矿成矿控制和富集条件[J].
矿产与地质, 1983(3): 129-142.
Huang Youde, Li Suiyuan. Ore-Controlling and Enrichment Condition of Skarn Iron Deposit in Eastern China[J]. Journal of Mining and Geology, 1983(3): 129-142. |
| [2] |
赵一鸣. 中国主要富铁矿床类型及地质特征[J].
矿床地质, 2013, 32(4): 685-704.
Zhao Yiming. Main Genetic Types and Geological Characteristics of Iron-Rich Ore Deposits in China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(4): 685-704. |
| [3] |
毛景文.
湖南柿竹园钨锡钼铋多金属矿床地质与地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998: 1-214.
Mao Jingwen. Deposit Geology and Chemistry of the Polymetallic W Sn Mo Bi in Shizhuyuan, Hunan Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1998: 1-214. |
| [4] | Kwak T A P. W-Sn Skarn Deposits and Related Metamorphic Skarns and Granitoids[J]. Elsevier, 1987, 52: 559. |
| [5] |
陈斌, 陈长健, 贺敬博, 等. 华北东部中生代高镁埃达克质岩浆的起源:岩石学和Nd-Sr-Os同位素证据[J].
科学通报, 2013, 58(20): 1941-1953.
Chen Bin, Chen Changjian, He Jingbo, et al. Origin of Mesozoic High-Mg Adakitic Rocks from Northeastern China:Petrological and Nd-Sr-Os Isotopic Constraints[J]. ChineseScience Bulletin, 2013, 58(20): 1941-1953. |
| [6] |
王浩, 徐兆文, 李海勇, 等. 邹平雪山二长岩年代学和Sr-Nd同位素研究及成因探讨[J].
南京大学学报(自然科学), 2015, 51(1): 73-86.
Wang Hao, Xu Zhaowen, Li Haiyong, et al. Geochronology, Sr-Nd Isotope and Genesis of the Xueshan Monzonite, Zouping County, Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Nanjing University(Natural Sciences), 2015, 51(1): 73-86. |
| [7] |
杨承海, 许文良, 杨德彬, 等. 鲁西上峪辉长-闪长岩的成因:年代学与岩石地球化学证据[J].
中国科学:地球科学, 2008, 31(1): 44-55.
Yang Chenghai, Xu Wenliang, Yang Debin, et al. Petrogenesis of Shangyu Gabbro-Diorites in Western Shandong:Evidence from Chronology and Petro-Geochemistry[J]. Chinese Science:Earth Science, 2008, 31(1): 44-55. |
| [8] | Guo F, Fan W M, Wang Y J, et al. Late Mesozoic Mafic Intrusive Complexes in North China Block:Constraints on the Nature of Subcontinental Lithospheric Mantle[J]. Physics & Chemistry of the Earth Part A Solid Earth & Geodesy, 2001, 26(9/10): 759-771. |
| [9] | Lan T G, Fan H R, Santosh M, et al. Crust-Mantle Interaction Beneath the Luxi Block, Eastern North China Craton:Evidence from Coexisting Mantle-and Crust-Derived Enclaves in a Quartz Monzonite Pluton[J]. Lithos, 2013, 177: 1-16. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.05.017 |
| [10] | Jin Z, Zhang Z, Hou T, et al. Genetic Relationship of High-Mg Dioritic Pluton to Iron Mineralization:A Case Study from the Jinling Skarn-Type Iron Deposit in the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 957-979. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.039 |
| [11] | Xie Q, Zhang Z, Hou T, et al. Petrogenesis of the Zhangmatun Gabbro in the Jinan Complex, North China Craton:Implications for Skarn-Type Iron Mineralization[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 113: 1197-1217. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.040 |
| [12] |
许文良, 王冬艳, 高山, 等. 鲁西中生代金岭闪长岩中纯橄岩和辉石岩包体的发现及其意义[J].
科学通报, 2003, 48(8): 790-797.
Xu Wenliang, Wang Dongyan, Gao Shan, et al. The Discovery and Significance of Xenoliths of Dunite and Pyroxenite in Jinling Mesozoic Diorite in Western Shandong Province[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(8): 790-797. |
| [13] |
宁培松, 龙群, 程婷, 等. 鲁西地块晚中生代中-基性岩地球化学和Sr-Nd-Pb同位素组成特征[J].
地球科学与环境学报, 2013, 35(4): 62-76.
Ning Peisong, Long Qun, Cheng Ting, et al. Geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopic Composition of Late Mesozoic Intermediate-Basic Rock in Western Shandong Block[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences & Environment, 2013, 35(4): 62-76. |
| [14] |
王冬艳, 许文良, 兰翔, 等. 鲁西中生代辉长-闪长岩中辉石岩捕虏体的岩石成因[J].
吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2004, 34(2): 167-173.
Wang Dongyan, Xu Wenliang, Lan Xiang, et al. Petrogenesis of Pyroxenite Xenoliths in Mesozoic Gabbro-Diorite from Western Shandong Province, China[J]. Journal of Jiling University(Earth Science Edition), 2004, 34(2): 167-173. |
| [15] |
巫祥阳, 徐义刚, 马金龙, 等. 鲁西中生代高镁闪长岩的地球化学特征及其成因探讨[J].
大地构造与成矿学, 2003, 27(3): 228-236.
Wu Xiangyang, Xu Yigang, Ma Jinlong, et al. Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic High-Mg Diorites from Western Shandong[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2003, 27(3): 228-236. |
| [16] |
杨承海, 许文良, 杨德彬, 等. 鲁西中生代高Mg闪长岩的成因:年代学与岩石地球化学证据[J].
地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2006, 31(1): 81-92.
Yang Chenghai, Xu Wenliang, Yang Debin, et al. Petrogenesis of Mesozoic High-Mg Diorites in Western Shandong:Evidence from Chronology and Petro-Geochemistry[J]. Earth Science:Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2006, 31(1): 81-92. |
| [17] | Lan T G, Fan H R, Hu F F, et al. Multiple Crust-Mantle Interactions for the Destruction of the North China Craton:Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf Isotopic Evidence from the Longbaoshan Alkaline Complex[J]. Lithos, 2012, 122: 87-106. |
| [18] | Yang Q L, Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F. Slab-Mantle Inte-raction in Continental Subduction Channel:Geochemical Evidence from Mesozoic Gabbroic Intrusives in Southeastern North China[J]. Lithos, 2012, 155(1): 442-460. |
| [19] | Zhang H F, Sun M, Zhou X H, et al. Geochemical Constraints on the Origin of Mesozoic Alkaline Intrusive Complexes from the North China Craton and Tectonic Implications[J]. Lithos, 2005, 69(6): 297-317. |
| [20] |
郝兴中. 鲁西地区铁矿成矿规律与预测研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014.
Hao Xingzhong. Study on Metallogenic Regularities and Prognosis of Iron Deposits in Western Shandong Province[D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1014249417.htm |
| [21] | Ludwig K R. Users Manual for Isoplot/Ex Rev. 2.49[M]. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Centre Special Publication, 2001: 1-56. |
| [22] | Mackenzie-W S. TheInterpretation of Igneous Rocks[M]. London: Allen and Unwin, 1979: 1-450. |
| [23] | Rickwood P C. Boundary Lines with in Petrologic Diagrams Which Use Oxides of Major and Minor Elements[J]. Lithos, 1989, 22(4): 247-263. DOI:10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5 |
| [24] | Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements:Meteorite Studies[M]//Henderson P.Rare Earth Element Geochemistry.Amsterdam:Elsevier, 1984:63-114. |
| [25] | Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts; Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 |
| [26] |
刘永江, 刘宾强, 冯志强, 等. 大兴安岭中北段老道口闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及构造意义[J].
吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2016, 46(2): 482-498.
Liu Yongjiang, Liu Binqiang, Feng Zhiqiang, et al. SIMS Zircon U-Pb Age, Petrogeochemistry and Its Tectonic Implication of Laodaokou Diorite in the Mid-North Part of Great Xing'an Range[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2016, 46(2): 482-498. |
| [27] | Kelemen P B, Shimizu N, Dunn T. Relative Deple-tion of Niobium in Some Arc Magmas and the Continental Crust:Partitioning of K, Nb, La and Ce During Melt/Rock Reaction in the Upper Mantle[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1993, 120(3/4): 111-134. |
| [28] | Rudnick R L, Fountain D M. Nature and Composi-tion of the Continental Crust:A Lower Crustal Perspective[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(3): 267-310. DOI:10.1029/95RG01302 |
| [29] |
郭锋, 范蔚茗, 王岳军, 等. 大兴安岭南段晚中生代双峰式火山作用[J].
岩石学报, 2001, 17(1): 161-168.
Guo Feng, Fan Weiming, Wang Yuejun, et al. Petrogenesis of the Late Mesozoic Bimodal Volcanic Rocks in the Southern Da Hinggan Mts, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2001, 17(1): 161-168. |
| [30] |
张玉涛, 张连昌, 英基丰, 等. 大兴安岭北段塔河地区早白垩世火山岩地球化学及源区特征[J].
岩石学报, 2007, 23(11): 2811-2822.
Zhang Yutao, Zhang Lianchang, Ying Jifeng, et al. Geochemistry and Source Characteristics of Early Cretaceous Volcanic Rocks in Tahe, North Da Hinggan Mountain[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(11): 2811-2822. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.012 |
| [31] |
山东省地质矿产局第四地质研究院.
山东省区域地质[M]. 济南: 山东省地图出版社, 2003: 331-350.
NO.4 Institute Of Geological Research Institute of Shandong Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Regional Geology of Shandong Province[M]. Jinan: Map Publishing House of Shandong Province, 2003: 331-350. |
| [32] | 山东省地矿局地质综合研究队和实验室. 山东省岩浆岩研究报告[J]. 济南:山东省地图出版社, 1985: 1-50. |
| [33] |
陈立辉, 周新华. 鲁西中生代闪长岩中的深源超镁铁质岩捕虏体及其富硅交代特征[J].
中国科学:地球科学, 2003, 33(8): 734-744.
Chen Lihui, Zhou Xinhua. The Characteristics of Silica Enrichment and Deep Source Ultramafic Rocks Xenoliths in Mesozoic Diorite from Western Shandong Province[J]. China Science:Earth Science, 2003, 33(8): 734-744. |
| [34] |
许文良, 王冬艳, 王清海, 等. 鲁西中生代闪长岩中两类幔源捕虏体的岩石学和地球化学[J].
岩石学报, 2003, 19(4): 623-636.
Xu Wenliang, Wang Dongyan, Wang Qinghai, et al. Petrology and Geochemistry of Two Types of Mantle-Derived Xenoliths in Mesozoic Diorite from Western Shandong Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2003, 19(4): 623-636. |
| [35] | Green T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an Indicator of Geochemical Processes in the Crust-Mantle System[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3): 347-359. |
| [36] | Ionov D A, Griffin W L, O'Reilly S Y. Volatile-Bearing Minerals and Lithophile Trace Elements in the Upper Mantle[J]. Chemical Geology, 1997, 141(3/4): 153-184. |
| [37] | Mcdonough W F, Sun S S. The Composition of the Earth[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3/4): 223-253. |
| [38] | Adam J, Green T H, Sie S H. Proton Microprobe Determined Partitioning of Rb, Sr, Ba, Y, Zr, Nb and Ta Between Experimentally Produced Amphiboles and Silicate Melts with Variable F Content[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 109(1/2/3/4): 29-49. |
| [39] | Latourrette T, Hervig R L, Holloway J R. Trace Element Partitioning Between Amphibole, Phlogopite, and Basanite Melt[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 135(1/2/3/4): 13-30. |
| [40] | Vaughan A P M, Leat P T, Dean A A, et al. Crustal Thickening Along the West Antarctic Gondwana Margin During Mid-Cretaceous Deformation of the Triassic Intra-Oceanic Dyer Arc[J]. Lithos, 2012, 142: 130-147. |
| [41] | Yang C H, Xu W L, Yang D B, et al. Petrogenesis of Shangyu Gabbro-Diorites in Western Shandong:Geochronological and Geochemical Evidence[J]. Science in China:Series D:Earth Sciences, 2008, 51(4): 481-492. DOI:10.1007/s11430-008-0029-0 |
| [42] | Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of Some Modern arc Magmas by Melting of Young Subducted Lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347: 662-665. DOI:10.1038/347662a0 |
| [43] | Chen B, Jahn B M, Suzuki K. Petrological and Nd-Sr-Os Isotopic Constraints on the Origin of High-Mg Adakitic Rocks from the North China Craton:Tectonic Implications[J]. Geology, 2012, 41(1): 91-94. |
| [44] | Wang Y, Houseman G A, Lin G, et al. Mesozoic Lithospheric Deformation in the North China Block:Numerical Simulation of Evolution from Orogenic Belt to Extensional Basin System[J]. Tectonophysics, 2005, 405(1/2/3/4): 47-63. |
| [45] | Wang K, Burov E, Gumiaux C, et al. Formation of Metamorphic Core Complexes in Non-Over-Thickened Continental Crust:A Case Study of Liaodong Peninsula(East Asia)[J]. Lithos, 2015, 238: 86-100. DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.09.023 |
| [46] | Yang L Q, Deng J, Wang Z L, et al. Thermochro-nologic Constraints on Evolution of the Linglong Metamorphic Core Complex and Implications for Gold Mineralization:A Case Study from the Xiadian Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 165-178. DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.006 |
| [47] | Ji M, Liu J, Hu L, et al. Evolving Magma Sources During Continental Lithospheric Extension:Insights from the Liaonan Metamorphic Core Complex, Eastern North China Craton[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 47/648: 48-62. |
| [48] | Zhu G, Chen Y, Jiang D, et al. Rapid Change from Compression to Extension in the North China Craton During the Early Cretaceous:Evidence from the Yunmengshan Metamorphic Core Complex[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 656(1): 91-110. |
| [49] |
王德滋, 赵广涛, 邱检生. 中国东部晚中生代A型花岗岩的构造制约[J].
高校地质学报, 1995(2): 13-21.
Wang Dezi, Zhao Guangtao, Qiu Jiansheng. The Tectonic Constraint on the Late Mesozoic A-Type Granitoids in Eastern China[J]. Geological Journal of Universitiesf, 1995(2): 13-21. |
| [50] | Yang Q L, Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F. Modification of Subcontinental Lithospheric Mantle Above Continental Subduction Zone:Constraints from Geochemistry of Mesozoic Gabbroic Rocks in Southeastern North China[J]. Lithos, 2012, 146/147(8): 164-182. |
| [51] | Kawamoto N, Smit J. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of Late Jurassic Shoshonitic Lamprophyre Dikes from the Liaodong Peninsula, NE China[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2010, 100(3): 127-151. |
| [52] | Ma L, Jiang S Y, Dai B Z, et al. Multiple Sources for the Origin of Late Jurassic Linglong Adakitic Granite in the Shandong Peninsula, Eastern China:Zircon U-Pb Geochronological, Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopic Evidence[J]. Lithos, 2013, 162(1): 251-263. |
| [53] | Liang C, Liu Y, Neubauer F, et al. Structures, Ki-nematic Analysis, Rheological Parameters and Temperature-Pressure Estimate of the Mesozoic Xingcheng-Taili Ductile Shear Zone in the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2015, 78: 27-51. DOI:10.1016/j.jsg.2015.06.007 |
| [54] | Liang C, Liu Y, Neubauer F, et al. Structural Cha-racteristics and LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Zircon Geochronology of the Deformed Granitic Rocks from the Mesozoic Xingcheng-Taili Ductile Shear Zone in the North China Craton[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 650: 80-103. DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2014.05.010 |