0 引言
吴福元等[1]对辽东半岛的年代学研究进行了总结,认为辽东地区岩浆作用可划分为3期,即三叠纪、侏罗纪和早白垩世,其中早白垩世的岩浆活动最为剧烈。辽东地区中生代岩浆作用与华北克拉通破坏、减薄有关已是一个不争的事实[2],但其时限、机制、演化过程等方面仍然存在争议。徐义刚等[3-5]认为其时限在空间上是不连续、不均匀的。许文良等[6-7]认为华北克拉通的破坏、减薄在三叠纪就已开始。Gao等[8]通过对辽西中侏罗世高镁埃达克岩的研究,认为华北的克拉通破坏、减薄至少在中侏罗世已经开始。姜耀辉等[9]认为华北克拉通破坏、减薄应存在两期,分别为155 Ma与130~120 Ma。Zhang等[10]在辽西阜新地区发现110 Ma来自软流圈地幔的玄武岩,Zheng等[5, 11]也发现该玄武岩携带的地幔橄榄岩特征与华北克拉通东部的新生代玄武岩基本相同,由此认为华北克拉通破、减薄在110 Ma之前已经发生。而路凤香等[12]则认为华北地区晚白垩世至新生代软流圈来源玄武岩的发现才是岩石圈破坏减薄的直接标志。破坏、减薄的机制也是目前激烈争论的问题,包括拆沉作用[8, 13-22],热侵蚀作用[19, 23-27],橄榄岩、熔体相互作用[28-32],机械拉张作用[2],岩浆提取作用[33],岩石圈地幔水化模型[34]等。关于华北克拉通破坏、减薄动力学的探讨仍就众说纷纭,包括地幔柱[35-38]、扬子板块和华北板块的拼合[39]、太平洋板块的俯冲[40]、多方位板块俯冲[41-43]等。笔者通过对辽东半岛岫岩王家堡子地区早白垩世二长花岗岩的岩石学特征、U-Pb年代学特征及岩石地球化学特征进行讨论,反演了其岩浆成因及形成构造环境,以期为中生代华北克拉通减薄、破坏时空分布及破坏的机制、过程和动力学的研究提供新的证据。
1 区域地质特征辽东半岛位于华北克拉通东部,胶—辽—吉造山/活动带中段(图 1a),北侧以辽阳—通化断裂,南侧以鸭绿江断裂分别与龙岗地块、狼林地块以断层接触相邻[44-46]。中生代后,岩浆作用强烈,形成了大面积的岩浆岩(图 1b)。辽宁省地质矿产局①对其进行了归类与总结,发现该区几乎囊括了所有类型的侵入岩,岩体间接触关系复杂、规模不等。研究区位于辽东岫岩县王家堡子地区,区内南辽河群广泛发育,自上而下为盖县岩组、大石桥岩组、高家峪岩组和里尔峪岩组。盖县岩组主要为一套变质石英砂岩-二云片岩组合;大石桥岩组主要为一套大理岩组合;高家峪岩组主要为一套含石墨的大理岩、变粒岩组合;里尔峪岩组主要为一套含硼的电气变粒岩、浅粒岩及黄铁、磁铁变粒岩组合。区内广泛发育中生代的侵入岩与岩脉,主要出露于研究区北部区域,依次为早三叠世石英岩,晚三叠世似斑状二长花岗岩、闪长岩,晚侏罗世二长花岗岩及早白垩世似斑状二长花岗岩、二长花岗岩,岩脉岩性为闪长玢岩与花岗岩(图 1 c、d)。
① 辽宁省地质矿产局.中华人民共和国辽宁省区域地质志.沈阳:辽宁省自然资源厅,2014.
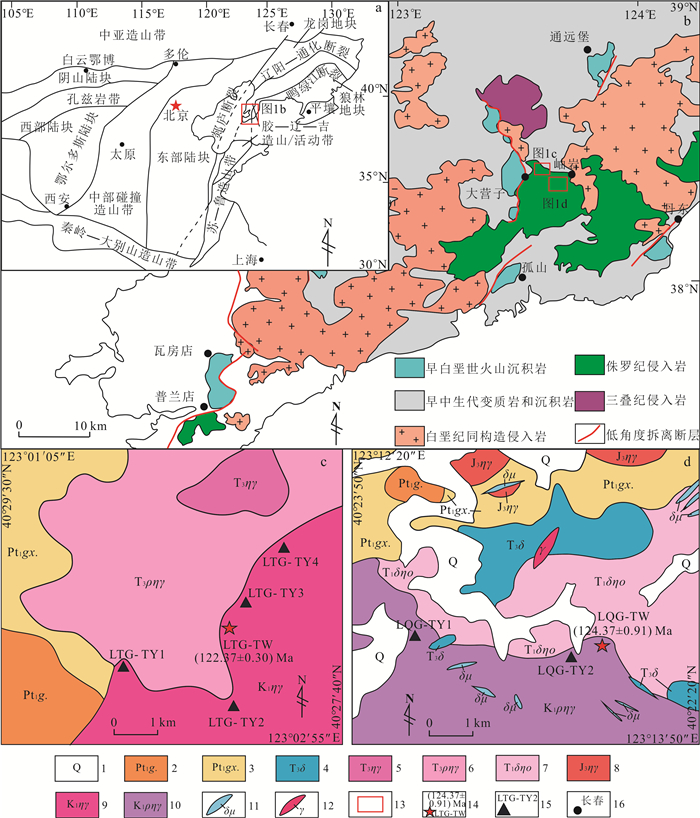
|
| 1.第四系;2.高家峪岩组;3.盖县岩组;4.晚三叠世闪长岩;5.晚三叠世二长花岗岩;6.晚三叠世似斑状二长花岗岩;7.早三叠世闪长二长石英岩;8.晚侏罗世二长花岗岩;9.早白垩世二长花岗岩;10.早白垩世似斑状二长花岗岩;11.闪长玢岩脉;12.花岗岩脉;13.工作区;14.同位素年龄样品采集位置及本次测得的年龄;15.地球化学样品采集位置及样号;16.地名。 图 1 研究区大地构造位置图(a),辽东地区(b)、王家堡子龙潭沟及周边地区(c)和王家堡子罗圈沟及周边地区(d)地质简图 Fig. 1 Sketch map showing tectonic sitting of the study area (a) and simplified geological map of Liaodong Peninsula (b), Wangjiabaozi Longtangou and its surrounding areas (c), Wangjiabaozi Luoquangou and its surrounding areas (d) |
|
|
研究区内二长花岗岩岩体分布广泛,且侵位年代贯穿整个中生代,其中最早的可追溯至晚三叠世,最晚则为早白垩世。本次研究主要针对侵位于早白垩世的二长花岗岩,即龙潭沟岩体与罗圈沟岩体,选取8件新鲜岩石样品进行全岩地球化学分析与锆石U-Pb定年研究。
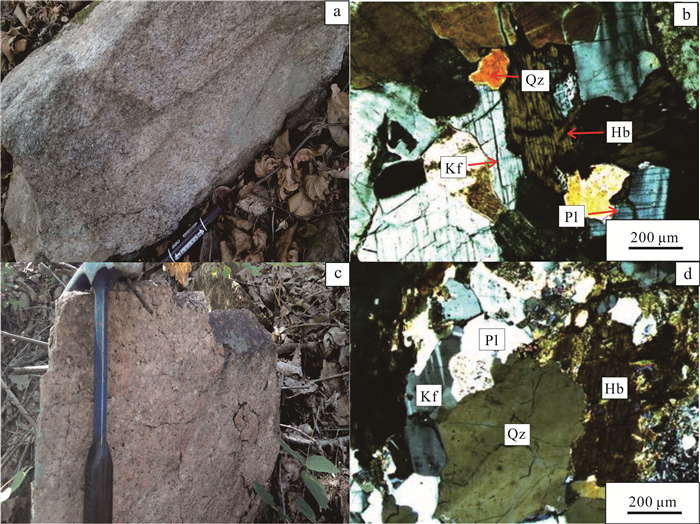
中细粒黑云角闪二长花岗岩(龙潭沟岩体):岩体位于岫岩县西北部龙潭沟附近,岩体表面呈浅灰白色,新鲜面为肉红色,中细粒花岗结构,块状构造(图 2a)。主要矿物成分有斜长石、钾长石、石英、角闪石和黑云母, 其中:斜长石多为半自形—他形,少数为不规则粒状,被钾长石交代呈孤岛状、港湾状,绢云母化,粒径多在0.35~3.00 mm之间,体积分数约为36%;钾长石呈他形粒状充填于其他矿物颗粒间,粒径多在0.3~2.2 mm之间,体积分数约为31%;石英呈不规则粒状,具波状消光,粒径多在0.5~2.0 mm之间,体积分数约为22%;角闪石呈短柱状,粒径多在0.5~1.0 mm之间,体积分数约为5%;黑云母呈片状,绿泥石化,粒径多在0.5~1.5 mm之间,体积分数约为5%(图 2b)。

|
| a.龙潭沟岩体典型岩石宏观照片;b.龙潭沟岩体显微构造照片;c.罗圈沟岩体典型岩石宏观照片;d.罗圈沟岩体显微构造照片。Qz.石英;Pl.斜长石;kf.钾长石;Hb.黑云母。 图 2 岫岩地区早白垩世侵入岩岩体典型岩石宏观及显微构造照片 Fig. 2 Macroscopic and microstructural photographs of typical rocks of Early Cretaceous invasive rock masses in Xiuyan area |
|
|
似斑状中细粒角闪黑云二长花岗岩(罗圈沟岩体):岩体位于岫岩县西北部罗圈沟附近,岩体表面呈灰白色,新鲜面为浅肉红色,似斑状中细粒花岗结构,块状构造,局部具就位叶理(图 2c)。矿物成分主要有斜长石、钾长石、石英、黑云母和角闪石,其中:斜长石为更长石成分,半自形—自形,环带构造发育,有的绢云母化、钠黝帘石化,核部蚀变强烈,粒径多在1.0~5.0 mm之间,体积分数约为35%;钾长石多呈他形粒状,有的充填于其他矿物颗粒间,粒径多在0.5~5.0 mm之间,体积分数约为33%;石英为他形粒状或粒状集合体,毕姆纹和亚颗粒发育,粒径多在0.8~2.5 mm之间,体积分数约为24%;黑云母为片状或片状集合体,绿泥石化,粒径多在0.5~3.0 mm之间,体积分数约为5%;角闪石呈柱粒状或柱状集合体,粒径多在0.3~1.2 mm之间,体积分数约为3%(图 2d)。
3 样品采集和测试方法本次采集了6个地球化学分析样品:LTG-TY1(123°01′45″E,40°28′10″N)、LTG-TY2(123°02′22″E,40°27′55″N)、LTG-TY3(123°02′31″E,40°28′46″N)、LTG-TY4(123°02′37″E,40°29′05″N),LQG-TY1(123°12′34″E,40°22′55″N)、LQG-TY2(123°13′21″E,40°22′40″N);2个同位素年龄样品:LTG-TW(123°02′18″E,40°28′35″N)与LQG-TW(123°13′32″E,40°22′48″N)。
锆石U-Pb同位素由LA-ICP-MS法测试。锆石单矿物分选在河北省廊坊区域地质调查研究院地质实验室完成。将挑好的锆石置于环氧树脂内固定、抛光,将制好的靶样进行透、反射光照相并采集阴极发光(CL)图像。锆石制靶和阴极发光照相由北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成。根据锆石CL图像判断锆石成因,结合透、反射照片,选择无包体、无裂隙的锆石微区圈定激光剥蚀区域。LA-ICP-MS测试在中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所国土资源部成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室完成。激光剥蚀系统为Geo Las Pro,ICP-MS为Agilent 7500,激光剥蚀直径为30 μm。对分析数据的离线处理(包括对样品和空白信号的选择、仪器灵敏度漂移校正、元素含量及U-Th-Pb同位素比值和年龄计算)采用9.0版本的ICPMS Data Cal序完成[47-49]。U-Pb同位素测试中采用锆石标准GJ-1作外标进行同位素分馏校正,每分析5~10个样品点,分析2次GJ-1。对于与分析时间有关的U-Th-Pb同位素比值漂移,利用GJ-1的变化采用线性内插的方式进行了校正。锆石U-Pb谐和图绘制和加权平均计算采用3.0版本的Isoplot[50]完成。
岩石主量元素、微量和稀土元素的分析测试由国土资源部沈阳矿产资源监督检测中心完成。主量元素使用X射线荧光光谱仪(XRF-1500)完成分析测试,其中FeO质量分数通过湿化学方法测试。微量元素、稀土元素分析使用等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)Element Ⅱ测试完成。
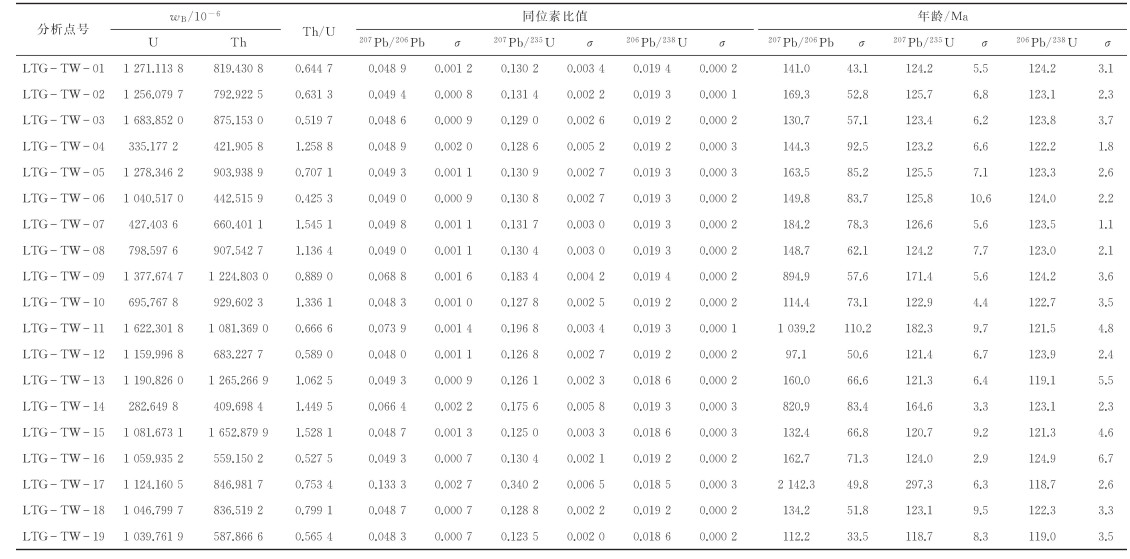
4 锆石U-Pb同位素测定结果龙潭沟岩体年龄样品中,锆石颗粒呈自形短柱状-长柱状或双锥状,粒径为100~180 μm,长宽比为1:1~2:1,通过阴极发光图(图 3a)可见,锆石均呈现清晰明显的岩浆锆石所特有的振荡环带结构,是典型的岩浆结晶型锆石结构。19个测点U质量分数为(282.649 8~1 683.852 0)×10-6,Th质量分数为(409.698 4~1 652.879 9)×10-6,Th/U=0.425 3~1.545 1(表 1),应属于岩浆锆石。在U-Pb谐和图(图 3b)上,所有测点数据均落在一致线上,并分布集中。206Pb/238U=124~118 Ma(表 1),加权平均值为(122.37 ± 0.30) Ma,MSWD=3.1。由此可知,龙潭沟岩体岩浆侵位年龄为早白垩世。
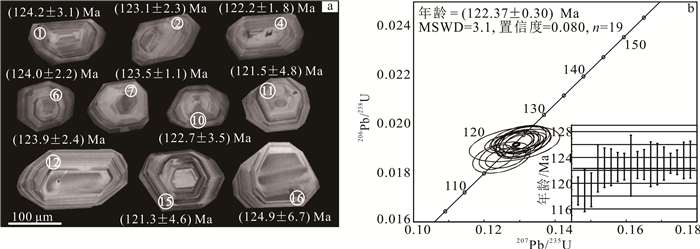
|
| 图 3 龙潭沟岩体部分锆石阴极发光图、测点位置(a)及U-Pb谐和图(b) Fig. 3 CL images, testing point locations (a) and U-Pb concordia diagrams (b) of some zircons of Longtangou pluton |
|
|
 |
罗圈沟岩体年龄样品中,锆石颗粒呈自形短柱状-长柱状或双锥状,粒径为100~180 μm,长宽比为1:1~2:1,通过阴极发光图(图 4a)可见,锆石均呈现清晰明显的岩浆锆石所特有的振荡环带结构,是典型岩浆结晶型锆石结构。21个测点U质量分数为(148.348 7~426.271 2)×10-6,Th质量分数为(126.372 8~423.905 4)×10-6,Th/U=0.778 4~1.464 8(表 2),应属于岩浆锆石。在U-Pb谐和图(图 4b)上,所有测点数据均落在一致线上,并分布集中。206Pb/238U=129~121 Ma(表 2),加权平均值为(124.37±0.91) Ma,MSWD=3.1。由此可知,罗圈沟岩体岩浆侵位年龄为早白垩世。
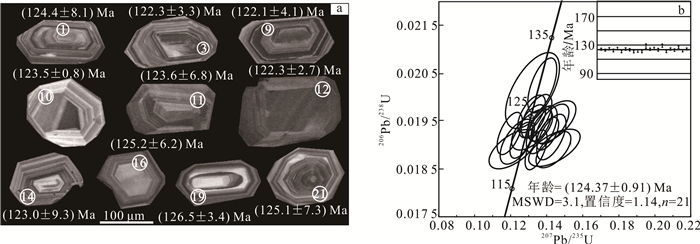
|
| 图 4 罗圈沟岩体部分锆石阴极发光图、测点位置(a)及U-Pb谐和图(b) Fig. 4 CL images, testing point locations (a) and U-Pb concordia diagrams (b) of some zircons of Luoquangou pluton |
|
|
 |
龙潭沟岩体与罗圈沟岩体岩石样品地球化学主量元素分析结果见表 3。
 |
龙潭沟岩体岩石样品K2O/Na2O值为1.00~1.27。岩石里特曼指数(σ)为2.05~2.53,属钙碱性系列。w(K2O)-w(SiO2)图解(图 5a)中,样品落入高钾(钙碱性)系列区域;铝质指数A/CNK为1.00~1.10,属于准铝质岩石(图 5b);Mg#=20.00~47.00。

|
| 图 5 龙潭沟岩体与罗圈沟岩体w(K2O)-w(SiO2)图解(a)和铝饱和指数图解(b) Fig. 5 w(K2O)-w(SiO2) diagram(a)and A/NK-A/CNK diagram(b) of Longtangou and Luoquangou plutons |
|
|
罗圈沟岩体岩石样品K2O/Na2O值为1.04和1.19。岩石里特曼指数(σ)为2.04和2.59,属钙碱性系列。w(K2O)-w(SiO2)图解(图 5a)中,样品落入高钾(钙碱性)系列区域;铝质指数A/CNK为0.83和0.98,属于过铝质岩石(图 5b);Mg#为54.00和56.00。
5.2 痕量元素及主要参数特征龙潭沟岩体与罗圈沟岩体岩石样品地球化学痕量元素分析结果见表 3。
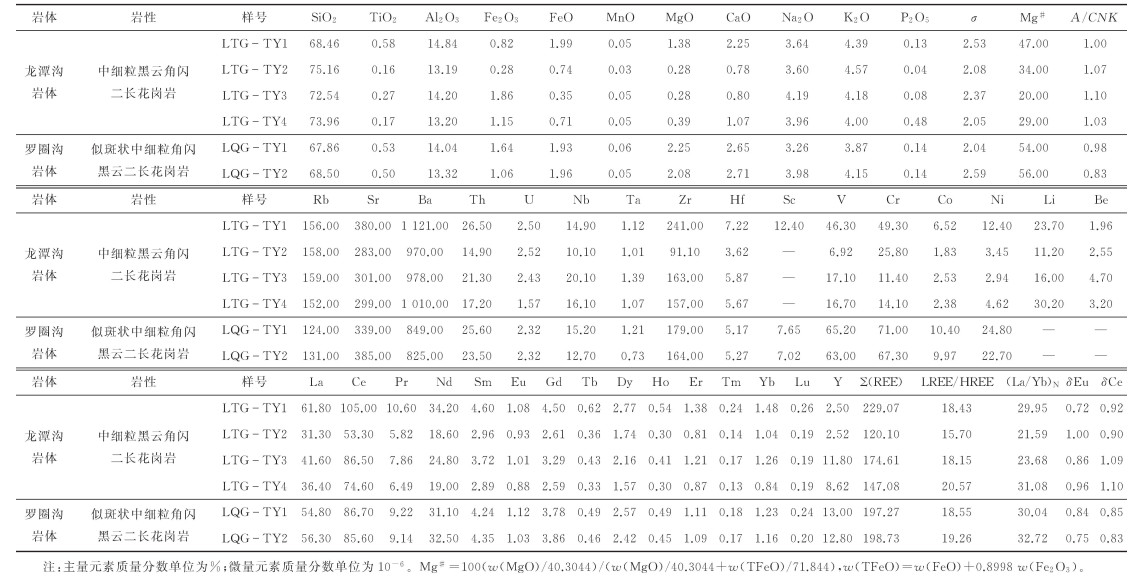
龙潭沟岩体岩石样品w(∑REE)=120.10×10-6~229.07×10-6,LREE/HREE=15.70~20.57,(La/Yb)N=21.59~31.08,表明轻重稀土存在一定程度的分馏,且轻稀土富集、重稀土亏损。球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(图 6a)中,曲线均呈明显的右倾趋势。Eu异常系数为0.72~1.00,Ce异常系数为0.90~1.10,并且在原始地幔微量元素标准化蛛网图(图 6b)上可以看出,富集大离子亲石元素(LILE,如Rb、Ba、Th等),相对亏损高强场元素(HFSE,如Nb、Ta、Ti等)。
|
| 图 6 龙潭沟岩体与罗圈沟岩体REE配分型式(a)与微量元素蛛网图(b) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized rare earth element patterns (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element patterns (b) of Longtangou and Luoquangou plutons |
|
|
罗圈沟岩体岩石样品w(∑REE)为197.27×10-6和198.73×10-6,LREE/HREE为18.55和19.26,(La/Yb)N为30.04和32.72,表明轻重稀土存在一定程度的分馏,且轻稀土富集,重稀土亏损。球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式图(图 6a)中,曲线均呈明显的右倾趋势。Eu异常系数为0.75和0.84,Ce异常系数为0.83和0.85,并且在原始地幔微量元素标准化蛛网图(图 6b)上可以看出,富集大离子亲石元素(LILE,如Rb、Ba、Th等),相对亏损高强场元素(HFSE,如Nb、Ta、Ti等)。
6 讨论 6.1 岩浆成因关于花岗岩浆来源,地学界众说纷纭,包括壳源、幔源、壳幔混合来源。张旗等[51]提出花岗岩都是壳源成因,大致分为洋壳、陆壳以及两者之间过渡的3种源区。研究区龙潭沟岩体与罗圈沟岩体岩石样品具有高SiO2质量分数,低Mg、Co、Cr、Ni质量分数的特征,与Patiño Douce等[52-53]通过实验得出下地壳物质15%~20%部分熔融产物的地球化学特征一致,且富集LREE和LILE,亏损HFSE,即为地壳物质部分熔融形成的岩浆所具有的特征。龙潭沟岩体与罗圈沟岩体岩石样品Ba/Nb分别为48.66~96.04(平均70.67)和55.86、64.96(平均60.41)(幔源岩石Ba/Nb值约9.0,壳源岩石Ba/Nb值约54,据文献[52-53]),由此也表明研究区早白垩世花岗岩浆应为地壳物质熔融的产物。龙潭沟岩体与罗圈沟岩体均具有高Al2O3、K2O质量分数,低Na2O、MnO和CaO质量分数的特征,与Chappell等[54]提出的I型花岗岩特征一致,岩石中未见富铝矿物,可见少量角闪石,因此笔者认为研究区龙潭沟岩体与罗圈沟岩体为高钾钙碱性I型花岗岩。
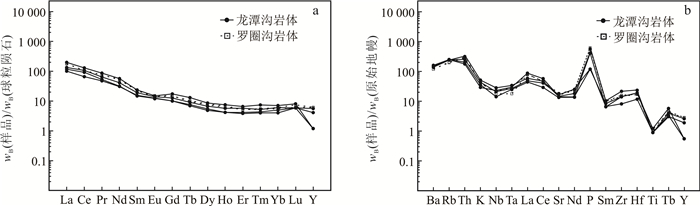
在埃达克岩判别图解(图 7a)中,龙潭沟岩体落入埃达克岩区域,而罗圈沟岩体落入埃达克岩与经典岛弧岩石的共同区域,又因二者岩石样品具有高Sr质量分数(龙潭沟岩体:283.00×10-6~380.00×10-6,罗圈沟岩体:339.00×10-6、385.00×10-6),低Y(龙潭沟岩体:2.50×10-6~11.80×10-6,罗圈沟岩体:12.80×10-6、13.00×10-6)、Yb(龙潭沟岩体:0.84×10-6~1.48×10-6,罗圈沟岩体:1.16×10-6、1.23×10-6)、MgO(龙潭沟岩体:0.28%~1.38%,罗圈沟岩体:2.08%、2.25%)质量分数,高Al2O3(龙潭沟岩体:13.19%~14.84%、罗圈沟岩体:13.32%、14.04%)质量分数,富集LILE及LREE,Eu呈负异常,亏损HREE等地球化学特征,与Defant等[55]提出的典型埃达克岩地球化学特征相似,但较其更富K质量分数,低Al2O3质量分数,HREE配分相对平坦,与中国东部广泛发育的高Sr低Yb质量分数花岗岩一致(张旗等[56]称之为C型埃达克岩),是来自岩石圈地幔的玄武质岩浆底侵到加厚的具克拉通性质的陆壳底部,导致古老的下地壳基性岩部分熔融的产物。在埃达克岩成因图解(图 7b)中,龙潭沟岩体落入加厚下地壳与俯冲洋壳区域,罗圈沟岩体落入俯冲洋壳区域。龙潭沟与罗圈沟岩体表现出较低的稀土质量分数与MgO、MnO质量分数,较高的Na2O及Ba质量分数,与洋壳特征相似,但值得注意的是二者Cr(11.40×10-6~49.30×10-6、67.30×10-6和71.00×10-6)、Ni(2.94×10-6~12.40×10-6、22.70×10-6和24.80×10-6)Co(1.83×10-6~6.52×10-6、9.97×10-6和10.40×10-6)质量分数远远小于洋壳的丰度(w(Cr)=190×10-6、w(Ni)=160×10-6、w(Co)=44×10-6,),更接近陆壳(w(Cr)=88×10-6、w(Ni)=71×10-6、w(Co)=20×10-6),并富集轻稀土元素和大离子亲石元素(Rb、Ba、Th等),亏损高场强元素(Ta、Nb、Ti等),具有活动大陆边缘环境岩浆岩的特征,其中亏损Ta、Nb是陆壳的标志性特征。由此表明,龙潭沟与罗圈沟岩体岩浆的形成应是洋壳俯冲导致陆壳物质部分熔融的结果。实验表明,大洋中脊拉斑玄武岩(MORB)的Mg#值为60,其部分熔融产生的熔体Mg#值不超过45,而一旦受到橄榄岩的混染就会发生明显的升高。龙潭沟岩体Mg#=20.00~47.00(平均值为32.50),罗圈沟岩体Mg#=54.00和56.00(平均值为55.00),表明罗圈沟岩体岩浆遭受过橄榄岩的混染,而龙潭沟岩体岩浆则没有。综上所述,洋壳俯冲导致陆壳加厚,洋壳的俯冲作用带来水和热,使得被加厚的陆壳底部基性岩部分熔融产生龙潭沟岩体岩浆。而罗圈沟岩体岩浆则是俯冲洋壳导致地幔物质上涌,使得玄武质下地壳发生部分熔融,并且岩浆受到了地幔橄榄岩的混染。
|
| 图 7 研究区埃达克岩判别图解(a)与埃达克岩成因图解(b) Fig. 7 Identification discrimination diagram of adakite (a) and genesis diagram (b) in the study area |
|
|
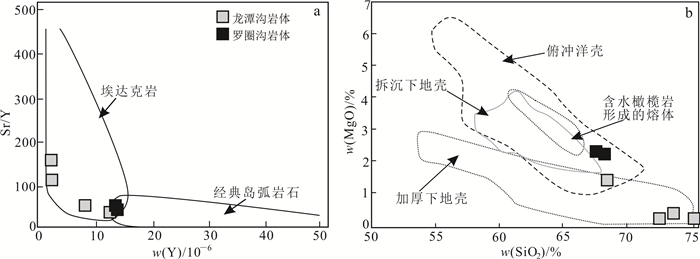
辽东燕山期岩浆活动构造背景仍然存在争议,包括:1)与古太平洋板块俯冲作用有关[57];2)是华北克拉通下地壳拆沉作用的产物[8];3)陆内拉伸作用的结果[58]。由研究区构造判别图解(图 8)可知,龙潭沟岩体与罗圈沟岩体岩浆为碰撞环境中的产物,研究区岩石组合符合黑云母花岗岩-二长花岗岩-花岗闪长岩的安第斯山型活动大陆边缘火山弧钙碱性-高钾钙碱性I型花岗岩岩石组合的特征。由此可知,研究区早白垩世应处于构造挤压的活动大陆边缘环境下。Gao等[8]通过对辽西中生代火成岩的研究,认为华北克拉通晚中生代岩浆活动是扬子板块与华北板块之间的陆-陆碰撞导致下地壳拆沉作用的结果,但拆沉作用的总体背景应该是伸展的,这与研究区所处的构造环境不同。并且区内同时代软流圈地幔来源的玄武岩分布极其有限,这与下地壳拆沉理论十分矛盾。杨进辉等[59]对辽东半岛小黑山岩体的U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学、Sr-Nd同位素和锆石铪同位素组成进行了研究,认为华北东部侏罗纪花岗质岩浆作用是古太平洋板块向西俯冲导致地壳增厚,进而引发下地壳物质部分熔融的结果。吴福元等[20-22]指出华北克拉通东部晚中生代处于构造挤压的大陆活动边缘环境之中,岩浆活动应与古太平洋板块的俯冲有关。由此表明研究区早白垩世岩浆活动应是古太平洋板块俯冲作用的结果。
|
| WPG.板内花岗岩;VAG.火山弧花岗岩;Syn-COLG.同碰撞花岗岩;ORG.洋脊花岗岩。 图 8 研究区构造环境判别图解 Fig. 8 Identification discrimination diagram of tectonic environment |
|
|
张旗等[53]提出华北地区在晚中生代是一个高原。山东蒙阴和辽宁复县金伯利岩(470 Ma)的发现表明岩石圈当时厚度约为200 km[60-61],然而由新生代玄武岩中的幔源包体研究获得的岩石圈厚度为80~120 km[62]。上述表明自古生代以来华北克拉通发生了近百公里的破环与减薄。岩石圈的拉伸是引起岩石圈减薄的主要原因,翟国明等[63]提出,华北板块东部由挤压构造向伸展构造转折始于150~140 Ma,结束于110~100 Ma。张颖等[64]提出,在早白垩世时期,因太平洋板块漂移方向的改变使得华北东部处于伸展环境中。Zhang等[10]在辽西阜新地区发现110 Ma来自软流圈地幔的玄武岩,Zheng等[5, 11]发现其携带的地幔橄榄岩的特征基本相同于华北克拉通东部新生代玄武岩,由此认为华北的克拉通破坏与减薄在110 Ma之前已经发生。刘杰勋等[65]通过对岫岩地区帽盔山二长花岗岩、荒地花岗闪长岩和朝阳苏长辉长岩进行了岩相学、地球化学、LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年的研究提出,在早白垩世时期,辽东岫岩地区处于非造山的伸展环境。张允平[66]也提出欧亚大陆东部广泛发育晚侏罗世—早白垩世的小型断陷盆地群、变质核杂岩、碱性-过碱性岩浆岩体及相关的喷出岩,说明欧亚大陆东部在此期间应处于非造山的伸展环境。另外,研究区内多处被发现变质核杂岩和拆离断层构造也是曾发生过大规模伸展作用的有利证据。本次研究在岫岩王家堡子发现早白垩世(122 Ma)的岩体处于挤压环境,因此笔者认为研究区的构造背景由构造挤压向拉伸环境的转变应在122~110 Ma之间完成,是华北板块东部构造背景转变的具体体现。
7 结论1) 研究区二长花岗岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年结果表明,龙潭沟岩体侵位年龄为(122.37±0.30) Ma,罗圈沟岩体侵位年龄为(124.37±0.91) Ma,均为早白垩世侵位的岩体。
2) 根据对各岩体年代学、岩石地球化学特征可知,岫岩王家堡子地区早白垩世洋壳俯冲导致陆壳加厚,洋壳的俯冲作用带来水和热,使得被加厚的陆壳底部基性岩发生部分熔融产生龙潭沟岩体岩浆;而罗圈沟岩体岩浆则是俯冲洋壳导致地幔物质上涌,使得玄武质下地壳发生部分熔融,并且岩浆受到了地幔橄榄岩的混染。
3) 辽东岫岩王家堡子地区早白垩世岩浆活动形成于碰撞挤压的活动大陆边缘环境中。
致谢: 中国地质大学(北京)肖荣阁老师、董国臣老师、刘翠老师在论文编写过程中提出了宝贵意见,在此表示衷心感谢!
| [1] |
杨进辉, 吴福元. 华北东部三叠纪岩浆作用与克拉通破坏[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2009, 39(7): 910-921. Yang Jinhui, Wu Fuyuan. Triassic Magmatism and Its Relation to Decratonization in the Eastern North China Craton[J]. Science in China:Series D, 2009, 39(7): 910-921. |
| [2] |
吴福元, 徐义刚, 高山, 等. 华北岩石圈减薄与克拉通破坏研究的主要学术争论[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(6): 1145-1174. Wu Fuyuan, Xu Yigang, Gao Shan, et al. Lithospheric Thinning and Destruction of the North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(6): 1145-1174. |
| [3] |
徐义刚. 华北岩石圈减薄的时空不均一特征[J]. 高校地质学报, 2004, 10(3): 324-331. Xu Yigang. Lithospheric Thinning Beneath North China:A Temporal and Spatial Perspective[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2004, 10(3): 324-331. |
| [4] |
Zheng J P, Giriffn W L, O'Reilly S Y, et al. Mineral Chemistry of Peridotites from Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic Lithosphere:Constrain on Mantle Evolution Beneath Eastern China[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2006, 47: 2233-2256. DOI:10.1093/petrology/egl042 |
| [5] |
Zheng J P, Giriffn W L, O'Reilly S Y, et al. Mechanism and Timing of Lithosphere Modification and Replacement Beneath the Eastern North China Craton:Peridotites Xenoliths from the 100Ma Fuxin Basalts and a Region Synthesis Geochim[J]. Cosmoehim Aeta, 2007, 71: 5203-5225. |
| [6] |
许文良, 杨承海, 杨德彬, 等. 华北克拉通东部中生代高Mg闪长岩:对岩石圈减薄机制的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(2): 120-129. Xu Wenliang, Yang Chenghai, Yang Debin, et al. Mesozoic High-Mg Diorites in Eastern North China Craton:Constraints on the Mechanism of Lithospheric Thinning[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(2): 120-129. |
| [7] |
韩宝福, 加加美宽雄, 李惠民. 河北平泉光头山碱性花岗岩的时代、Nd-Sr同位素特征及其对华北早中生代壳幔相互作用的意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(6): 1375-1388. Han Baofu, Kagami Hiroo, Li Huimin. Age and Nd-Sr Isotopic Geochemistry of the Guangtoushan Alkaline Granite, Hebei Province, China:Implications for Early Mesozoic Crust-Mantle Interaction in North China Block[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2004, 20(6): 1375-1388. |
| [8] |
Gao S, Rudniek R L, Yuan H L, et al. Recycling Lower Continental Crust in the North China Craton[J]. Nature, 2004, 432(6): 892-897. |
| [9] |
姜耀辉, 蒋少涌, 赵葵东, 等. 辽东半岛煌斑岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其对中国东部岩石圈减薄开始时间的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2005, 50(19): 2161-2168. Jiang Yaohui, Jiang Shaoyong, Zhao Kuidong, et al. SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Age of Lamprophyre in Liaodong Peninsula and Its Restriction on the Starting Time of Lithospheric Thinning in Eastern China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2005, 50(19): 2161-2168. |
| [10] |
Zhang H F, Sun M, Zhou X H, et al. Secular Evolution of the Lithosphere Beneath the Eastern North China Carton:Evidence from Mesozoic Basalts and High-Mg Andesites[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2003, 67(22): 4373-4387. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00377-6 |
| [11] |
许文良, 郑常青, 王冬艳. 辽西中生代粗面玄武岩中地幔和下地壳捕虏体的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质论评, 1999, 45(增刊1): 444-449. Xu Wenliang, Zheng Changqing, Wang Dongyan. Discovery of Mantle and Lower Crust Xenoliths in Mesozoic Rough Basalts in Western Liaoning and Their Geological Significance[J]. Geological Review, 1999, 45(Sup.1): 444-449. |
| [12] |
路凤香, 郑建平, 邵济安, 等. 华北东部中生代晚期-新生代软流圈上涌与岩石圈减薄[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(2): 86-92. Lu Fengxiang, Zheng Jianping, Shao Ji'an, et al. Asthenospheric Upwelling and Lithospheric Thinning in Late Cretaceous-Cenozoic in Eastern North China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(2): 86-92. |
| [13] |
邓晋福, 莫宣学, 赵海玲, 等. 中国东部岩石圈根/去根作用与大陆"活化":东亚型大陆动力学模式研究计划[J]. 现代地质, 1994, 8(3): 349-356. Deng Jinfu, Mo Xuanxue, Zhao Hailing, et al. Lithospheric Rooting/Derooting in Eastern Chinaand Continental Activation:East Asian Continental Dynamics Model Research Program[J]. Geoscience, 1994, 8(3): 349-356. |
| [14] |
邓晋福, 赵海玲, 莫宣学. 中国大陆根柱构造:大陆动力学的钥匙[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996. Deng Jinfu, Zhao Hailing, Mo Xuanxue. The Root Pillar Structure of China Continent:The Key to Continental Dynamics[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996. |
| [15] |
Gao S, Zhang B R, Luo T C, et al. Chemical Composition of the Continental Crust in the Qinling Orogenic Belt and Its Adjacent North China and Yangtze Cratons[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1992, 56(11): 3933-3950. DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(92)90007-6 |
| [16] |
Gao S, Zhang B R, Jin Z M, et al. How Mafic the Low Continental Crust?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 161(1/2): 101-117. |
| [17] |
Gao S, Luo T C, Zhang B R, et al. Chemical Composition of the Continental Crust as Revealed by Studies in East China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(11): 1959-1975. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00121-5 |
| [18] |
Gao S, Rudnick R L, Carlson R W, et al. Re-Os Evidence for Replacement of Ancient Mantle Lithosphere Beneath the North China Craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 198(3/4): 307-322. |
| [19] |
Xu Y G, Blusztajn J, Ma J L, et al. Late Archean to Early Proterozoic Lithospheric Mantle Beneath the Western North China Craton:Sr-Nd-Os Isotopes of Peridotite Xenoliths from Yangyuan and Fansi[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102(1/2): 25-42. |
| [20] |
吴福元, 孙德有. 中国东部中生代岩浆作用与岩石圈减薄[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 1999, 29(4): 313-318. Wu Fuyuan, Sun Deyou. Mesozoic Magmatism and Lithospheric Thinning in Eastern China[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology, 1999, 29(4): 313-318. |
| [21] |
吴福元, 孙德有, 张广良. 论燕山运动的深部地球动力学本质[J]. 高校地质学报, 2000, 6(3): 379-388. Wu Fuyuan, Sun Deyou, Zhang Guangliang. Deep Geodynamics of Yanshain Movement[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2000, 6(3): 379-388. |
| [22] |
吴福元, 葛文春, 孙德有, 等. 中国东部岩石圈减薄研究中的几个问题[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(3): 51-60. Wu Fuyuan, Ge Wenchun, Sun Deyou, et al. Discussions on the Lithospheric Thinning in Eastern China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(3): 51-60. |
| [23] |
Menzies M A, Fan W M, Zhang M. Palaeozoic and Cenozoic Lithoprobe and the Loss of >120 km of Archean Lithosphere, Sino-Korean Craton, China[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1993, 76(1): 71-81. DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1993.076.01.04 |
| [24] |
Menzies M A, Xu Y G. Geodynamics of the North China Craton[C]//Mantle Dynamics and Plate Interactions in East Asia. Washington District of Columbia: American Geophysical Union, 1998: 155-164.
|
| [25] |
Griffin W L, Andi Z, O'Reilly S Y, et al. Phanerozoic Evolution of the Lithosphere Beneath the Sino-Korean Craton[C]//Mantle Dynamics and Plate Interactions in East Asia. Washington District of Columbia: American Geophysical Union, 1998: 107-126.
|
| [26] |
Xu Y G. Thermo-Tectonic Destruction of the Archaean Lithospheric Keel Beneath the Sino-Korean Craton in China:Evidence, Timing and Mechanism[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth Part a Solid Earth and Geodesy, 2001, 26(9/10): 747-757. |
| [27] |
Xu Y G, Huang X L, Ma J L, et al. Crust-Mantle Interaction During the Tectono-Thermal Reactivation of the North China Craton:Constraints from SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Chronology and Geochemistry of Mesozoic Plutons from Western Shandong[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2004, 147(6): 750-767. DOI:10.1007/s00410-004-0594-y |
| [28] |
Zhang H F, Sun M, Zhou X H, et al. Mesozoic Lithosphere Destruction Beneath the North China Craton:Evidence from Major-, Trace-Element and Sr-Nd-Pb Isotope Studies of Fangcheng Basalts[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 144(2): 241-254. DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0395-0 |
| [29] |
Zhang H F, Nakamura E, Sun M, et al. Transformation of Subcontinental Lithospheric Mantle Through Peridotite-Melt Reaction:Evidence from a Highly Fertile Mantle Xenolith from the North China Craton[J]. International Geology Review, 2007, 49(7): 658-679. DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.49.7.658 |
| [30] |
Zhang H F. Transformation of Lithospheric Mantle Through Peridotite-Melt Reaction:A Case of Sino-Korean Craton[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 237(3/4): 768-780. |
| [31] |
张宏福, 英基丰, 徐平, 等. 华北中生代玄武岩中地幔橄榄石捕虏晶:对岩石圈地幔置换过程的启示[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(8): 784-789. Zhang Hongfu, Ying Jifeng, Xu Ping, et al. Mantle Olivine Xenoliths in Mesozoic Basalts in North China:Implications for Lithospheric Mantle Replacement[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(8): 784-789. |
| [32] |
张宏福. 橄榄岩-熔体的相互作用:岩石圈地幔组成转变的重要方式[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(1): 65-75. Zhang Hongfu. Peridotite-melt Interaction:An Important Mechanism for the Compositional Transformation of Lithospheric Mantle[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(1): 65-75. |
| [33] |
Chen B, Jahn B M, Arakawa Y, et al. Petrogenesis of the Mesozoic Intrusive Complexes from the Southern Taihang Orogen, North China Craton:Elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopic Constraints[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 2004, 148(4): 489-501. |
| [34] |
Niu Y L. Generation and Evolution of Basaltic Magmas:Some Basic Concepts and a New View on the Origin of Mesozoic-Cenozoic Basaltic Volcanism in Eastern China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2005, 11(1): 9-46. |
| [35] |
袁学诚. 秦岭岩石圈速度结构与蘑菇云构造模型[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 1996, 26(3): 209-215. Yuan Xuecheng. Velocity Structure of Lithosphere and Mushroom Cloud Tectonic Model in Qinling Mountains[J]. Scientia in China:Series D, 1996, 26(3): 209-215. |
| [36] |
路凤香, 郑建平, 李伍平, 等. 中国东部显生地幔演化的主要样式:"蘑菇云"模型[J]. 地学前缘, 2000, 7(1): 97-107. Lu Fengxiang, Zheng Jianping, Li Wuping, et al. Main Patterns of Phanerozoic Slow Evolution in Eastern China:Mushroom Cloud Model[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2000, 7(1): 97-107. |
| [37] |
Zhao Z F, Zheng Y F, Wei C S, et al. Zircon Isotope Evidence for Recycling of Subducted Continental Crust in Post-Collisional Granitites from the Dabie Terrane in China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(22): 21-61. |
| [38] |
洪大卫, 王涛, 童英, 等. 华北地台和秦岭-大别-苏鲁造山带的中生代花岗岩与深部地球动力学过程[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(3): 231-256. Hong Dawei, Wang Tao, Tong Ying, et al. Mesozoic Granitoids from North China Block and Qinling-Dabie-Sulu Orogenic Belt and Their Deep Dynamic Process[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(3): 231-256. |
| [39] |
Gao S, Rudnick R L, Carlson R W, et al. Re-Os Evidence for Replacement of Ancient Mantle Lithosphere Beneath the North China Craton[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 198(3/4): 307-322. |
| [40] |
Sun W D, Ding X, Hu Y H, et al. The Golden Transformation of the Cretaceous Plate Subduction in the West Pacific[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 262(3/4): 533-542. |
| [41] |
Zhang H F, Sun M, Zhou X H, et al. Secular Evolution of the Lithosphere Beneath the Eastern North China Carton:Evidence from Mesozoic Basalts and High-Mg Andesites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2003, 67(22): 4373-4387. DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(03)00377-6 |
| [42] |
翟明国, 朱日祥, 刘建明, 等. 华北东部中生代构造体制转折的关键时限[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2003, 33(10): 913-920. Zhai Mingguo, Zhu Rixiang, Liu Jianming, et al. The Key Time Limit of Mesozoic Tectonic System Transition in Eastern North China[J]. Science in China:Series D, 2003, 33(10): 913-920. |
| [43] |
Zhai M G, Fan Q C, Zhang H F, et al. Lower Crustal Processes Leading to Mesozoic Lithospheire Thinning Beneath Eastern North China:Underplating, Replacement and Delarnination[J]. Lithos, 2007, 16(3): 36-54. |
| [44] |
Michel Faure, Lin W, Patrick Monié, et al. Palaeoproterozoic Arc Magmatism and Collision in Liaodong Peninsula (North-East China)[J]. Terra Nova, 2004, 16(2): 75-80. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-3121.2004.00533.x |
| [45] |
万渝生, 宋彪, 刘敦一, 等. 鞍山东山风景区3.8~2.5 Ga古老岩带的同位素地质年代学和地球化学[J]. 地质学报, 2001, 75(3): 363-370. Wan Yusheng, Song Biao, Liu Dunyi, et al. Geochronology and Geochemistry of 3.8~2.5 Ga Ancient Rock Belt in the Dongshan Scenic Park, Anshan Area[J]. Acta Geology Sinica, 2001, 75(3): 363-370. |
| [46] |
刘福来, 刘平华, 王舫, 等. 胶-辽-吉古元古代造山/活动带巨量变沉积岩系的研究进展[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(10): 2816-2846. Liu Fulai, Liu Pinghua, Wang Fang, et al. Progresses and Overviews of Voluminous Meta-Sedimentary Series Within the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Orogenic/Mobile Belt, North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(10): 2816-2846. |
| [47] |
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In Situ Analysis of Major and Trace Elements of Anhydrous Minerals by LA-ICP-MS Without Applying an Internal Standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1/2): 34-43. |
| [48] |
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and Oceanic Crust Recycling-Induced Melt-Peridotite Interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb Dating, Hf Isotopes and Trace Elements in Zircons of Mantle Xenoluths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51(1/2): 537-571. |
| [49] |
Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Zong K Q, et al. Reappraisement and Refinement of Zircon U-Pb Isotope and Trace Element Analyses by LA-ICP-MS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(15): 1535-1546. DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4 |
| [50] |
Ludwig K R. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.0:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[M]. City of Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003: 1-20.
|
| [51] |
张旗, 王焰, 熊小林, 等. 埃达克岩和花岗岩:挑战与机遇[M]. 北京: 中国大地出版社, 2008. Zhang Qi, Wang Yan, Xiong Xiaolin, et al. Adakite and Granite:Challenges and Opportunities[M]. Beijing: China Earth Press, 2008. |
| [52] |
Patiño Douce A E. Experimental Generation of Hybrid Silicic Melts by Reaction of High-Al Basalt with Metamorphic Rocks[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1995, 100(B8): 15623-15639. DOI:10.1029/94JB03376 |
| [53] |
Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration Melting of Metabasalt at 8-32 kbar:Implications for Continental Growth and Crust-Mantle Recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4): 891-931. DOI:10.1093/petrology/36.4.891 |
| [54] |
Chappell B W, White A J R, Williams I S, et al. Lachlan Fold Belt Granites Revisited:High and Low Temperature Granites and Their Implications[J]. Journal of the Geological Society of Australia, 2015, 47(1): 123-138. |
| [55] |
Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of Some Modern Arc Magmas by Melting of Young Subducted Lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347: 662-665. DOI:10.1038/347662a0 |
| [56] |
张旗, 钱青, 王二七, 等. 燕山中晚期的中国东部高原:埃达克岩的启示[J]. 地质科学, 2001, 36(2): 248-255. Zhang Qi, Qian Qing, Wang Erqi, et al. An East China Plateau in Mid-Late Yanshanian Period:Implication from Adakites[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2001, 36(2): 248-255. |
| [57] |
吴福元, 杨进辉, 张艳斌, 等. 辽西东南部中生代花岗岩时代[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(2): 315-325. Wu Fuyuan, Yang Jinhui, Zhang Yanbin, et al. Emplacement Ages of the Mesozoic Granites in Southeastern Part of the Western Liaoning Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(2): 315-325. |
| [58] |
Li X H, Chung S L, Zhou H W, et al. Jurassic Intraplate Magmatism in Southern Hunan-Eastern Guangxi:40Ar/39Ar Dating, Geochemistry, Sr-Nd Isotopes and Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of SE China[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 2002, 226(1): 193-215. |
| [59] |
杨进辉, 吴福元, 柳小明. 辽东半岛小黑山岩体成因及其地质意义:锆石U-Pb年龄和铪同位素证据[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2007, 26(1): 29-43. Yang Jinhui, Wu Fuyuan, Liu Xiaoming. Petrogenesis and Geological Significance of the Jurassic Xiaoheishan Pluton in the Liaodong Peninsula, East China:Insitu Zircon U-Pb Dating and Hf Isotopic Analysis[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2007, 26(1): 29-43. |
| [60] |
路凤香, 韩柱国, 郑建平, 等. 辽宁复县地区古生代岩石圈地幔特征[J]. 地质科技情报, 1991, 10(增刊1): 2-20. Lu Fengxiang, Han Zhuguo, Zheng Jianping, et al. Characteristics of Paleozoic Lithospheric Mantle in Fuxian Area, Liaoning Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1991, 10(Sup.1): 2-20. |
| [61] |
郑建平. 中国东部地幔置换作用与中新生代岩石圈减薄[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1999. Zheng Jianping. Mantle Replacement in Eastern China and Mesozoic-Cenozoic Lithospheric Thinning[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1999. |
| [62] |
Fan Q C, Hooper P R. The Mineral Chemistry of Ultramafic Xenoliths of Eastern China:Implications for Upper Mantle Composition and the Paleogeotherms[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1989, 30(5): 1117-1158. DOI:10.1093/petrology/30.5.1117 |
| [63] |
翟明国, 孟庆任, 刘建明, 等. 华北东部中生代构造体制转折峰期的主要地质效应和形成动力学探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(3): 285-297. Zhai Mingguo, Meng Qingren, Liu Jianming, et al. Geological Features of Mesozoic Tectonic Regime Inversion in Eastern North China and Implication for Geodynamics[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(3): 285-297. |
| [64] |
张颖, 黄智龙, 罗泰义, 等. 云南个旧西区贾沙辉长-二长岩体SIMS锆石U-Pb定年及地球化学研究[J]. 地球化学, 2013, 42(6): 523-543. Zhang Ying, Huang Zhilong, Luo Taiyi, et al. The Geochemistry and SIMS U-Pb Zircon Dating of the Jiasha Gabbric-Monzonitic Intrusion in Gejiu District, Yunnan Province[J]. Geochimica, 2013, 42(6): 523-543. |
| [65] |
刘杰勋, 郭巍, 朱凯. 辽东岫岩地区早白垩世侵入岩的年代学、地球化学及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(9): 2889-2900. Liu Jiexun, Guo Wei, Zhu Kai. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Geological Significance of the Early Cretaceous Intrusive Rocks from Xiuyan Area, Eastern Liaoning Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(9): 2889-2900. |
| [66] |
张允平. 东北亚地区晚侏罗-白垩纪构造格架主体特点[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(5): 1267-1284. Zhang Yunping. Main Characteristics of Late Jurassic-Cretaceous Tectonic Framework in Northeast Asia[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(5): 1267-1284. |


