2. 中国地质大学(北京)地球科学与资源学院, 北京 100083;
3. 西北大学地质学系, 西安 710069;
4. 内蒙古自治区地质调查院, 呼和浩特 010020
2. School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China;
3. Department of Geology, Northwest University, Xi'an 710069, China;
4. Institute of Geological Survey of Inner Mongolia, Hohhot 010020, China
0 前言
“蛇绿岩(ophiolite)”最开始是定义较混淆的地质术语,不同的学者从不同的角度来描述蛇绿岩[1]。蛇绿岩主要由橄榄岩及少量基性岩浆岩组成[2]。1972年,在美国召开的Pengrose会议重新确定蛇绿岩是形成于大洋中脊的具有分层性的一套古大洋地壳和上地幔残片的组合,之后一直以这一定义为标准确定蛇绿岩[3-4]。而后也有学者发现有相当一部分的蛇绿岩并不是形成于大洋中脊环境。如Miyashiro[5]利用地球化学手段对塞浦路斯Troodos蛇绿岩进行研究,认为其形成环境为薄大洋地壳的岛弧环境。而后许多地质学者对蛇绿岩进行进一步的研究,结果表明Pengrose式蛇绿岩的概念已经不能满足研究的需要[1]。因此,一些学者开始寻求更为完善的且涵盖所有确立的蛇绿岩类型定义的方案。在以往的蛇绿岩研究中,对蛇绿岩的分类方案都没有突出其形成的构造环境。如MORB型和SSZ型蛇绿岩[6],斜方辉石型、单斜辉石型和斜长石型蛇绿岩[7],科迪勒拉型和特提斯型蛇绿岩[8-9]以及方辉橄榄岩型和二辉橄榄岩型蛇绿岩[10]等等。在国内,也有许多学者对蛇绿岩进行了详细的研究,多依据蛇绿岩所表现出来的地球化学特征进行分类,主要有低铝型和高铝型蛇绿岩[11],高熔型、中熔型和低熔型蛇绿岩[12],科迪勒拉型、东地中海型和西地中海型蛇绿岩[12],V型LREE富集型、烟斗型LREE亏损型和平坦型蛇绿岩[13],快速扩张型、中速扩张型、中慢速扩张型以及极慢速扩张型蛇绿岩[14]等等。另外蛇绿岩还分为与俯冲作用有关和与俯冲作用无关两种类型[15]。
内蒙古自治区横跨华北板块北缘和兴蒙造山带两大构造单元,其内分布4条蛇绿岩带[16-17],由北向南分别为:1)二连浩特—贺根山一线[18-21];2)交其尔—锡林浩特一线[22-27];3)索伦敖包—林西一线[28-29];4)温都尔庙—西拉木伦河一线[30-36]。内蒙古西乌珠穆沁旗迪彦庙蛇绿岩位于二连浩特—贺根山蛇绿岩带与交其尔—锡林浩特蛇绿岩带一线之间,该蛇绿岩自李英杰等[37]报道以来已经受到越来越多的重视。本文通过该蛇绿岩带内辉长岩地球化学特征及锆石U-Pb年代学对迪彦庙蛇绿岩进行研究,为兴蒙造山带大地构造格架和地壳演化的研究提供依据。
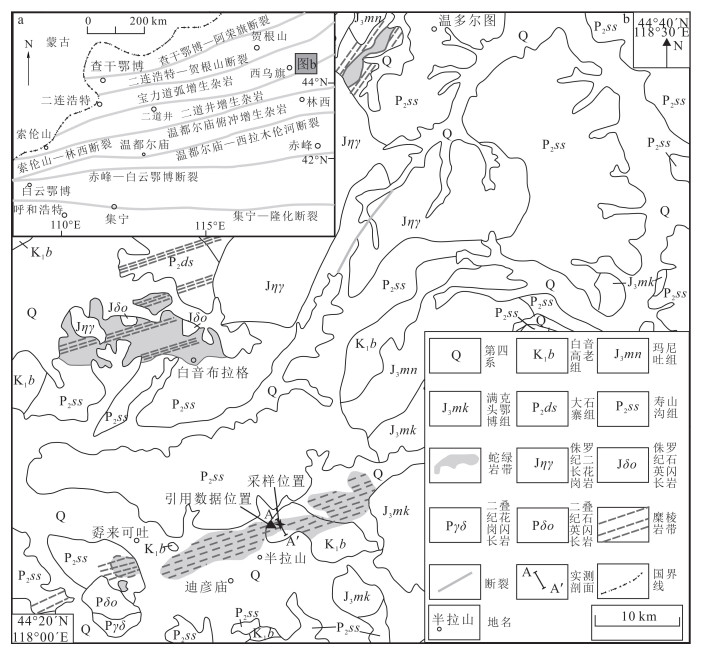
1 区域地质概况迪彦庙位于内蒙古西乌珠穆沁旗(西乌旗)境内,其大地构造位于中亚造山带中段的锡林浩特晚古生代褶皱带[22, 38],温都尔庙—西拉木伦河断裂以北,二连浩特—贺根山断裂以南(图 1a)。该地区构造演化经历了古生代开始的古亚洲洋多阶段俯冲、地壳增生、多地体聚合,中生代的蒙古—鄂霍茨克洋闭合和晚古生代开始的来自古太平洋板块对欧亚大陆板块俯冲作用的影响。迪彦庙地区发育较老的古生界蛇绿岩,呈北东向展布;中生代火山岩分布较广泛。区内地层具有北东向展布特征,主要为下白垩统白音高老组(K1b)、上侏罗统玛尼吐组(J3mn)、上侏罗统满克头鄂博组(J3mk)、中二叠统大石寨组(P2ds)及中二叠统寿山沟组(P2ss)(图 1b)。其中,上侏罗统满克头鄂博组、玛尼吐组和下白垩统白音高老组之间呈整合接触关系,而满克头鄂博组角度不整合覆盖于中二叠统寿山沟组之上。区内岩浆岩主要为侏罗纪二长花岗岩、石英闪长岩,二叠纪花岗闪长岩、石英闪长岩。区内发育北东向韧性剪切带,分布情况与蛇绿岩带基本一致。
西乌旗迪彦庙蛇绿岩带分布于孬来可吐—迪彦庙,呈近北东东向分布,部分地带被第四系覆盖,蛇绿岩带长约28 km,宽1~3 km(图 1b),出露的主要岩性为:蛇纹石化方辉橄榄岩、层状辉长岩、中粗粒-细粒均质块状辉长岩、细碧岩、玄武岩、角斑岩、石英角斑岩、硅质岩[37]。本文所研究的辉长岩为该带中的层状辉长岩,选取的地球化学及年代学样品为变质程度较低的辉长岩。
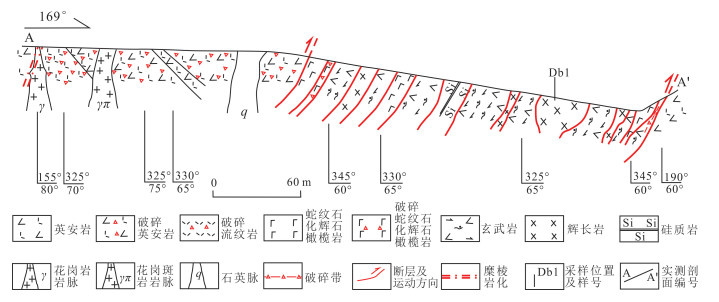
笔者在迪彦庙地区对蛇绿岩带进行了剖面实测,如图 2所示。其野外露头分布如图 3所示。带内主要出露的岩性有蛇纹石化辉石橄榄岩、辉长岩、硅质岩和玄武岩等,岩石受后期构造影响表现为强烈破碎。在蛇绿岩带周围发育有英安岩、流纹岩以及花岗岩脉。
|
| 图 2 迪彦庙蛇绿岩剖面图 Fig. 2 Profile of Diyanmiao ophiolite |
|
|
|
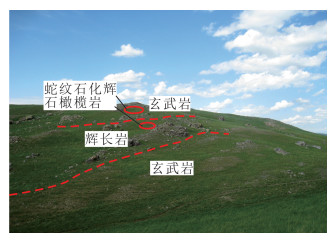
| 图 3 迪彦庙蛇绿岩野外露头分布情况 Fig. 3 Distribution of Diyanmiao ophiolite |
|
|
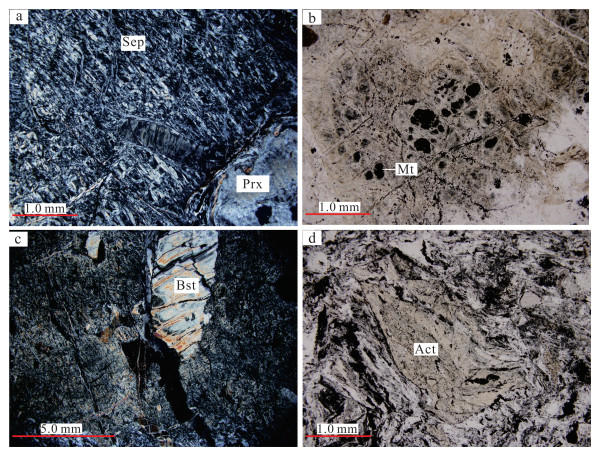
蛇纹石化辉石橄榄岩:野外观察为细小的碎粒组成,碎粒颜色为黑-灰绿色,粒状变晶结构,块状构造。主要矿物由蛇纹石和辉石组成。见有滑石化、蛇纹石化等蚀变现象,从而使岩石整体表现绿色或蓝绿色。镜下为平行纤维状结构、变余斑状结构、网格状结构,块状构造。主要由蛇纹石和辉石组成(图 4a),蛇纹石呈平行纤维状集合体,定向排列,体积分数为75%~80%,析出粉末状、粒状磁铁矿(图 4b),体积分数为10%;辉石呈1~2 mm短柱状,被纤维状蛇纹石交代,呈绢石假像(图 4c),部分辉石发生阳起石化现象(图 4d),体积分数为10%~15%。
|
| a.主要由蛇纹石和辉石组成,蛇纹石呈平行纤维状集合体;b.蛇纹石化辉石橄榄岩析出的磁铁矿或者铁质;c.辉石呈绢石假象;d.辉石发生阳起石化蚀变现象。Sep.蛇纹石;Prx.辉石;Mt.磁铁矿;Bst.绢石;Act.阳起石。 图 4 研究区蛇纹石化辉石橄榄岩显微特征 Fig. 4 Microscopic characteristics of serpentinization pyroxene peridotite in the study area |
|
|
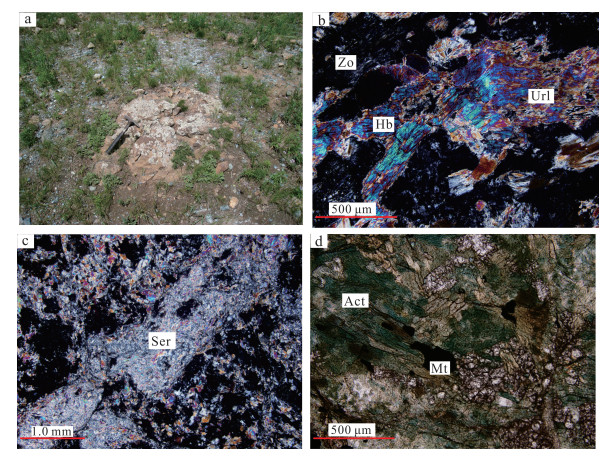
辉长岩:该辉长岩为本次研究对象,采样位置见图 2(Db1)。岩石风化面为深灰色,新鲜面为暗灰绿色(图 5a)。岩石具细中粒辉长结构,似层状构造。主要矿物成分为斜长石和辉石。斑晶为长石,暗色矿物略高于浅色矿物含量。岩石蚀变强烈,部分发生片理化现象。镜下特征为呈现变余细粒辉长结构,块状构造。主要由辉石、斜长石及角闪石组成。斜长石粒径为1 mm左右,部分斜长石见有黝帘石化及绢云母化等蚀变现象(图 5b、c),但保留斜长石板状外形,体积分数为50%~60%;辉石粒径1~2 mm,短柱状,发生次闪石所交代,但大部分保留短柱状外形,部分发生阳起石化蚀变现象(图 5d),体积分数为35%~40%;角闪石粒径为1~2 mm长柱状,体积分数为5%~10%。
|
| a.辉长岩野外露头,周围小颗粒为蛇纹石化辉石橄榄岩;b.斜长石发生黝帘石化现象,辉石被次闪石所交代;c.斜长石发生绢云母化蚀变;d.斜长石发生阳起石化蚀变现象,并有磁铁矿析出。Zo.黝帘石;Url.次闪石;Hb.角闪石;Ser.绢云母;Act.阳起石;Mt.磁铁矿。 图 5 研究区辉长岩岩石学特征 Fig. 5 Petrology characteristics of gabbro in the study area |
|
|
硅质岩:岩石质地坚硬,为隐晶质或半晶质的矿物组成。镜下观察主要为隐晶质结构,块状构造。
玄武岩:岩石风化面为灰色,新鲜面为灰绿色、深灰色,斑状结构,岩石呈致密状,具块状构造,局部见气孔状构造。斑晶为橄榄石、辉石、斜长石等,大小不等,一般粒径为2~3 cm;基质为隐晶质或半晶质的,由微晶和玻璃质组成。部分岩石发生构造破碎。
英安岩:岩石风化面灰色,新鲜面深灰色,斑状结构,块状构造。部分岩石发生破碎,呈碎裂状。斑晶主要为长石及少量石英,石英多熔蚀状;基质主要为长石微晶,呈隐晶质结构。岩石较破碎,具有褐铁矿化。
流纹岩:岩石新鲜面为土黄色,具流纹状结构、基质隐晶-玻璃质结构,块状、流纹状构造。斑晶主要为长石、石英,基质较细;为致密的隐晶质。
糜棱岩化花岗岩:岩石风化面浅灰色,新鲜面浅肉红色,细粒花岗结构,发育糜棱岩化构造。主要矿物成分为石英和长石,矿物颗粒细小。石英并被压扁、拉长,具明显的细条带状和纹层状构造,线理发育。原岩为花岗岩,矿物成分主要为长石、石英及黑云母。长石呈灰白色,自形—半自形柱状、板状,粒径为3~5 mm,体积分数为60%~65%;石英呈半透明浅灰色,他形粒状,粒径为2~3 mm,体积分数为20%~25%;黑云母呈黑色,半自形—自形片状,粒径为1~3 mm,体积分数为3%~5%;花岗岩为脉状,侵入英安岩中,使英安岩破碎强烈,沿裂隙具有强的褐铁矿化、硅化。
3 测试方法地球化学分析样品的粗碎及磨样工作在河北省廊坊市地科勘探技术服务有限公司进行,整个过程无污染。样品在国家地质测试中心进行全岩主量元素测定,采用的方法为X射线荧光光谱法,校准曲线使用国家级标准物质进行制作完成。基体校正系数及谱线重叠校正系数使用回归法进行计算,其精密度小于10%。微量元素由地球物理地球化学勘查研究所进行测试分析。
年代分析的样品送至河北省廊坊市地科勘探技术服务有限公司,该公司使用常规的磁选技术将样品中的锆石进行分离。锆石样品靶的制作步骤为:首先将需要分析的锆石及标准的锆石TEMORA[39]颗粒放在一起进行粘贴,然后使用环氧树脂制成样品靶,待靶固结后进行打磨和抛光,使锆石颗粒中心部位暴露后停止。为了更好地选择锆石颗粒的测试点位,对锆石样品靶中的锆石颗粒进行显微照相(包括透射光和反射光)。该项工作由北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成。将制作好的锆石样品靶送至天津地质矿产研究所进行Pb、U、Th的同位素测试分析。该套方法所使用的设备为LA-MC-ICP-MS系统。利用动态变焦扩大色散等方法对样品靶中的锆石U-Pb同位素进行测定[40-41]。以标准锆石TEMORA颗粒作为标样,从而计算所采样品的Pb、U和Th含量[42-43]。数据处理采用的程序为ICPMS Data Cal程序[44]以及Isoplot程序[45]。在测试过程中,使用208Pb校正法进行校正[46]。
4 测试结果 4.1 地球化学分析| % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 序号 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | CaO | MgO | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | 烧失量 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 45.53 | 16.35 | 0.80 | 4.31 | 19.54 | 8.58 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 3.81 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 46.84 | 15.25 | 0.40 | 4.58 | 19.47 | 8.71 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 3.65 | |||||||||||||||||
| 3 | 50.48 | 14.26 | 1.01 | 5.58 | 12.23 | 10.92 | 0.65 | 1.86 | 0.30 | 0.03 | 0.15 | 2.34 | |||||||||||||||||
| 4 | 50.28 | 13.31 | 1.87 | 10.13 | 7.68 | 7.19 | 0.10 | 3.92 | 1.82 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 2.29 | |||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 50.35 | 14.63 | 6.13 | 5.05 | 8.00 | 6.64 | 0.21 | 4.15 | 1.32 | 0.10 | 0.18 | 2.70 | |||||||||||||||||
| 6 | 51.47 | 15.52 | 1.51 | 5.44 | 13.26 | 6.13 | 0.10 | 2.80 | 0.78 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 2.21 | |||||||||||||||||
| 7 | 49.14 | 15.31 | 2.67 | 7.70 | 13.04 | 5.22 | 0.12 | 2.76 | 1.41 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 1.93 | |||||||||||||||||
| 8 | 46.53 | 14.41 | 4.44 | 10.07 | 8.66 | 6.78 | 0.13 | 2.49 | 2.22 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 2.71 | |||||||||||||||||
| 9 | 50.02 | 15.72 | 1.37 | 5.01 | 11.77 | 9.79 | 0.51 | 2.37 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 2.47 | |||||||||||||||||
| 10 | 45.94 | 15.19 | 0.84 | 6.42 | 16.94 | 9.86 | 0.02 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.08 | 0.15 | 3.23 | |||||||||||||||||
| 11 | 46.84 | 15.25 | 0.40 | 4.58 | 19.47 | 8.71 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.14 | 4.12 | |||||||||||||||||
| 12 | 45.49 | 17.05 | 0.85 | 3.97 | 17.32 | 10.64 | 0.03 | 0.51 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.14 | 3.54 | |||||||||||||||||
| 13 | 45.53 | 16.35 | 0.80 | 4.31 | 19.54 | 8.58 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 4.42 | |||||||||||||||||
| 注:序号1、2数据引自李英杰等[37];序号3数据来自本文;序号4—13数据引自白卉等[47]。 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 序号 | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | ∑REE | LREE | HREE | LREE/HREE | δEu | (La/Yb)N | (La/Sm)N | (Gd/Yb)N | Y | Ni | Cr | V | Zr | Ta | Sr | Nb | U | Th | Ti | Hf |
| 1 | 0.16 | 0.48 | 0.11 | 0.72 | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.50 | 0.14 | 1.07 | 0.23 | 0.69 | 0.12 | 0.77 | 0.12 | 5.68 | 2.04 | 3.64 | 0.56 | 1.33 | 0.15 | 0.27 | 0.54 | 6.01 | 822 | 144 | 4.51 | 0.44 | 70.1 | 1.11 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 1 138.75 | 0.20 | |
| 2 | 0.34 | 0.65 | 0.12 | 0.65 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.40 | 0.11 | 0.79 | 0.18 | 0.53 | 0.09 | 0.59 | 0.09 | 5.01 | 2.23 | 2.78 | 0.80 | 1.50 | 0.41 | 0.73 | 0.56 | 4.74 | 748 | 136 | 2.23 | 0.50 | 59.9 | 1.45 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 839.08 | 0.12 | |
| 3 | 0.58 | 1.39 | 0.27 | 1.61 | 0.73 | 0.42 | 1.06 | 0.27 | 1.92 | 0.45 | 1.48 | 0.25 | 1.80 | 0.22 | 12.45 | 5.00 | 7.45 | 0.67 | 1.46 | 0.23 | 0.51 | 0.49 | 11.29 | 178.38 | 853.07 | 184.03 | 28.75 | 0.08 | 228.5 | 0.18 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 1 778.74 | 1.55 |
| 注:序号1、2数据引自李英杰等[37];序号3数据来自本文。微量元素和稀土元素质量分数单位为10-6。 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
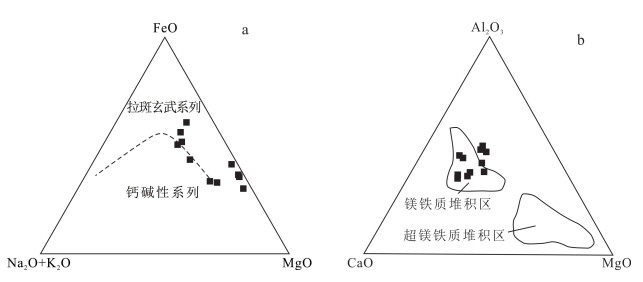
辉长岩SiO2质量分数为45.49%~51.47%,表明所有岩石类型均为基性岩;Al2O3质量分数较高,为13.31%~17.05%,平均为15.28%,高于中国辉长岩的平均质量分数14.52%[48],反映岩石中主要为富Al的斜长石和单斜辉石[49];K2O质量分数为0.01%~0.65%,低于中国辉长岩的平均质量分数1.18%[48];Na2O质量分数为0.30%~4.15%,平均为1.73%,低于中国辉长岩的平均质量分数2.97%[48];CaO质量分数较高,为7.68%~19.54%,揭示辉长岩少碱性长石和富钠斜长石,富含基性斜长石;MgO变化幅度较小,为5.22%~ 10.92%,不存在高镁橄榄石;P2O5质量分数为0.03%~ 0.23%。在FeO-(Na2O+K2O)-MgO图(图 6a)中,辉长岩具有钙碱性-拉斑玄武系列的过渡趋势,以拉斑玄武系列为主;在Al2O3-CaO-MgO图(图 6b)中,辉长岩全部落入镁铁质堆积区及附近。从辉长岩的主量元素特征来看,西乌旗迪彦庙蛇绿岩中的辉长岩属于高铝、低钾、低钠的拉斑玄武系列。
|
| 图 6 迪彦庙蛇绿岩带中辉长岩FeO-(Na2O+K2O)-MgO(a)和Al2O3-CaO-MgO(b)分析图解 Fig. 6 Diagram of FeO-(Na2O+K2O)-MgO (a) and Al2O3-CaO-MgO (b) for gabbro from Diyanmiao ophiolite belt |
|
|
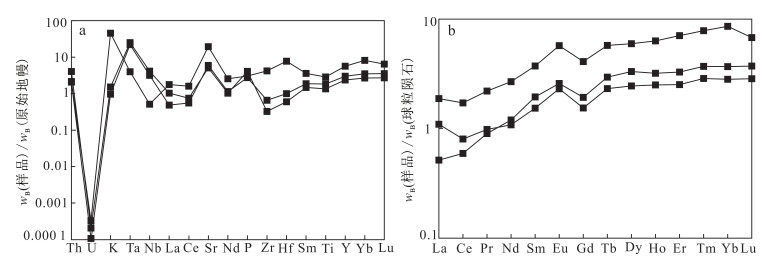
微量元素方面,Th、U、Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf的质量分数分别为0.09×10-6~0.17×10-6、0.01×10-6~0.04×10-6、0.18×10-6~1.45×10-6、0.08×10-6~0.50×10-6,2.23×10-6~28.75×10-6,0.12×10-6~1.55×10-6。从微量元素蛛网图(图 7a)中可以看出,Nb、Zr、Hf、Ti元素相对亏损,K、Ta、Sr元素相对富集。
|
| 图 7 迪彦庙蛇绿岩带中辉长岩微量元素蛛网图(a)及稀土元素配分曲线图(b) Fig. 7 Primative mantle-normalized trace element patterns (a) and chondrite-normalized REE distribution patterns (b) for gabbro from Diyanmiao ophiolite belt |
|
|
辉长岩的稀土元素总量(w(∑REE))较小,为5.01×10-6~12.45×10-6、平均为7.71×10-6;w(∑LREE)为2.04×10-6~5.00×10-6,平均为3.09×10-6;w(∑HREE)为2.78×10-6~7.45×10-6,平均为4.62×10-6;LREE/HREE为0.56~0.80。重稀土元素比轻稀土元素较为富集,表现为(La/Yb)N<1,为0.15~0.41,平均为0.26,(La/Sm)N为0.27~0.73,(Gd/Yb)N为0.49~0.56。在稀土元素配分曲线(图 7b)中,辉长岩显示明显的Eu正异常(δEu为1.33~1.50,平均为1.43)。与绝大多数蛇绿岩中的辉长岩具有相类似的稀土元素配分曲线[50]。
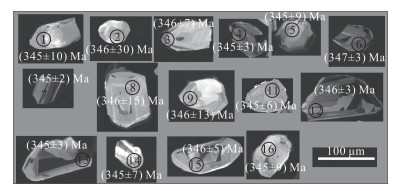
4.2 年代学分析选取测年所用的锆石为淡黄色-无色透明短柱状、中长柱状晶体,大小为30 μm× 20 μm~80 μm×100 μm。从锆石的阴极发光图像(图 8)中来看,锆石颜色主要为灰白色,振荡环带模糊,个别较清晰。从锆石的内部特征来看,锆石具有明暗相间的条带结构、较宽的振荡环带、扇形分带结构以及内部结构相对均匀且无明显分带或环带结构等4种特征。吴元保等[51]研究表明,上述4种锆石的内部特征表明其成因为岩浆锆石。对样品Db1分析测试了20个点,但存在3个异常点数据,在数据分析时已经剔除,其结果见表 3。
|
| 图 8 迪彦庙蛇绿岩带内辉长岩代表性锆石CL图像特征 Fig. 8 CL images of representative zircons for gabbro from Diyanmiao ophiolite belt |
|
|
| 点号- | wB/10 —6 | 同位素比值 | 年龄/Ma | ||||||||||||||
| Pb | U | 206 Pb/238 U | σ | 207 Pb/235 U | σ | 207 pb/206 pb | σ | 208 pb/232 Th | σ | 232 Th/238 U | σ | 206 Pb/238 U | σ | 207 Pb/235 U | σ | ||
| 1 | 1.203 | 18.309 | 0.054 9 | 0.001 6 | 0.861 1 | 0.173 1 | 0.113 7 | 0.036 1 | 0.016 5 | 0.001 2 | 0.881 6 | 0.015 5 | 345 | 10 | 631 | 127 | |
| 2 | 0.598 | 8.522 | 0.055 1 | 0.004 7 | 1.619 7 | 0.511 6 | 0.213 2 | 0.083 7 | 0.057 4 | 0.010 3 | 0.245 1 | 0.006 5 | 346 | 30 | 978 | 309 | |
| 3 | 1.124 | 18.365 | 0.055 1 | 0.001 0 | 1.695 1 | 0.111 1 | 0.223 3 | 0.015 2 | 0.013 8 | 0.002 3 | 0.235 7 | 0.001 9 | 346 | 7 | 1 007 | 66 | |
| 4 | 5.396 | 98.990 | 0.054 9 | 0.000 4 | 0.405 2 | 0.019 4 | 0.053 5 | 0.002 5 | 0.010 8 | 0.000 3 | 0.471 3 | 0.004 3 | 345 | 3 | 345 | 17 | |
| 5 | 1.430 | 23.093 | 0.055 0 | 0.001 5 | 0.851 8 | 0.177 5 | 0.112 2 | 0.025 6 | 0.028 5 | 0.003 2 | 0.357 4 | 0.002 4 | 345 | 9 | 626 | 130 | |
| 6 | 4.817 | 86.397 | 0.055 2 | 0.000 4 | 0.406 0 | 0.020 8 | 0.053 3 | 0.002 7 | 0.010 9 | 0.000 2 | 0.567 9 | 0.002 7 | 347 | 3 | 346 | 18 | |
| 7 | 12.439 | 214.027 | 0.054 9 | 0.000 4 | 0.404 6 | 0.012 0 | 0.053 4 | 0.001 6 | 0.010 8 | 0.000 1 | 0.853 4 | 0.002 3 | 345 | 2 | 345 | 10 | |
| 8 | 0.457 | 8.443 | 0.055 1 | 0.002 4 | 0.599 3 | 0.311 3 | 0.078 9 | 0.041 7 | 0.010 9 | 0.004 9 | 0.280 0 | 0.004 1 | 346 | 15 | 477 | 248 | |
| 9 | 0.828 | 14.480 | 0.055 2 | 0.002 1 | 0.705 5 | 0.226 9 | 0.092 8 | 0.050 1 | 0.016 2 | 0.003 0 | 0.350 7 | 0.003 1 | 346 | 13 | 542 | 174 | |
| 10 | 2.213 | 20.499 | 0.077 0 | 0, it)l 1 | 2.347 6 | 0.105 6 | 0.221 3 | 0.009 5 | 0.076 8 | 0.002 5 | 0.395 1 | 0.008 2 | 478 | 7 | 1 227 | 55 | |
| 11 | 1.389 | 24.809 | 0.054 9 | 0.001 0 | 0.582 9 | 0.120 0 | 0.077 0 | 0.018 4 | 0.009 3 | 0.001 0 | 0.584 6 | 0.012 0 | 345 | 6 | 466 | 96 | |
| 12 | 2), 603 | 47.021 | 0.055 1 | 0.000 5 | 0.407 1 | 0.044 7 | 0.053 6 | 0.006 1 | 0.013 6 | 0.000 5 | 0.428 7 | 0.001 9 | 346 | 3 | 347 | 38 | |
| 13 | 6.913 | 114.021 | 0.055 0 | 0.000 4 | 0.406 6 | 0.019 2 | 0.053 6 | 0.002 5 | 0.010 3 | 0.000 1 | 1.164 7 | 0.001 6 | 345 | 3 | 346 | 16 | |
| 14 | 2.130 | 32.832 | 0.054 9 | o, it)i i | 1.088 4 | 0.110 8 | 0.143 7 | 0, t)U 4 | 0.019 6 | 0.001 4 | 0.609 5 | 0.012 5 | 345 | 7 | 748 | 76 | |
| 15 | 1.816 | 31.853 | 0.055 1 | 0.000 7 | 0.405 3 | 0.064 6 | 0.053 4 | 0.009 5 | 0.011 7 | 0.000 4 | 0.664 5 | 0.002 1 | 346 | 5 | 345 | 55 | |
| 16 | 0.798 | 14.073 | 0.055 0 | 0.001 5 | 1.148 9 | 0.172 8 | 0.151 6 | 0.025 5 | 0.006 4 | 0.002 5 | 0.330 % | 0.003 1 | 345 | 9 | 777 | 117 | |
| 17 | 5.423 | 195.420 | 0.026 4 | 0.000 2 | 0.184 4 | 0.012 3 | 0.050 7 | 0.003 4 | 0.006 1 | 0.000 1 | 0.703 5 | 0.003 5 | 168 | 1 | 172 | 11 | |
从表 3中可以看出,测点w(U)为8.443× 10-6~214.027×10-6,w(Pb)为0.457×10-6~12.439×10-6。206Pb/238U值为0.026 4~ 0.077 0,大多数锆石的206Pb/238U值集中于0.054 9~ 0.055 2之间。从所分析的数据来看,除了10和17测点的锆石脱离主锆石群,其余的锆石年龄都比较集中,锆石206Pb/238U年龄集中分布于345~347 Ma之间,其中,10号测点的锆石年龄明显偏高,为(478±7) Ma,而17测点的206Pb/238U年龄明显偏低,为(168±1) Ma,这两个锆石颗粒明显与主锆石群不谐和。从图 9中可以看出,辉长岩的加权平均年龄为(345.3±2.3) Ma(MSWD=0.079)。因此,本文将迪彦庙蛇绿岩带内辉长岩的结晶年龄确定为(345.3±2.3) Ma,为早石炭世。
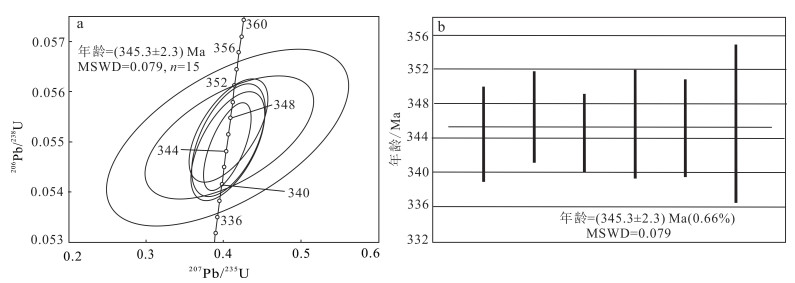
|
| 图 9 迪彦庙蛇绿岩带内辉长岩锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图(a)和加权平均年龄图(b) Fig. 9 Concordia diagrams of U-Pb ages of zircons for gabbro from Diyanmiao ophiolite belt (a) and weighted average age (b) |
|
|
从微量元素来看,迪彦庙蛇绿岩带中辉长岩富集K、Ta、Sr等大离子亲石元素以及相对亏损Nb和Ti等高场强元素,显示出具有俯冲带幔源特点[52],也表明岩浆或源区受地壳物质混染的影响[53]。其中Nb、Hf等的相对亏损也反映出辉长岩曾经受地壳物质混染的影响[54];Ti和Nb的负异常也表明辉长岩具有俯冲带的岩浆岩特征[55]。Nb/U值与源区物质有关,迪彦庙蛇绿岩中辉长岩的Nb/U值变化范围较大,为4.50~111.00,平均为54.62,高于中国东部地壳(中国东部地壳Nb/U值为9.6)[56],对此合理的解释应该是地幔源区受俯冲流体的交代作用而产生的。辉长岩的Nb/La值为0.31~6.93,平均值为3.84,高于大陆地壳平均值(Nb/La的大陆地壳平均值0.7),而结晶分异作用不会导致Nb/La降低[56],表明辉长岩的成因可能为受到俯冲作用产生的流体交代,而并非结晶分异作用所致。
5.2 辉长岩形成时代本次工作在迪彦庙蛇绿岩带中的辉长岩获得的LA-ICP-MS锆石年龄为(345.3±2.3) Ma,其形成时代与二连浩特—贺根山蛇绿岩吻合(表 4),且在苏尼特左旗至西乌旗一带发育一套石炭纪闪长岩、石英闪长岩、英云闪长岩及花岗岩组合[26, 66-70]。综上所述,二连浩特—贺根山蛇绿岩带为一条石炭纪的蛇绿岩带。这些年代学资料也佐证了迪彦庙蛇绿岩中的辉长岩形成时代为早石炭世。
| 序号 | 位置 | 岩性 | 测试方法 | 年龄/Ma | 文献 |
| 1 | 朝克山蛇绿岩 | 辉长岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法 | 295±15 | [21] |
| 2 | 小坝梁蛇绿岩 | 辉长岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法 | 354±7 | [57] |
| 3 | 斜长花岗岩 | 333±4 | |||
| 4 | 二连浩特东部蛇绿岩 | 辉长岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法 | 354.2±4.5 | [58] |
| 5 | 353.3±3.7 | ||||
| 6 | 梅劳特乌拉蛇绿岩 | 辉长岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法 | 308.5±2.2 | [59] |
| 7 | 迪彦林场蛇绿岩 | 辉绿岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法 | 331±2 | [60] |
| 8 | 辉长岩 | 356±5 | |||
| 9 | 贺根山蛇绿岩 | 辉长闪长岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法 | 341±3 | [61] |
| 10 | 二连浩特东部蛇绿岩 | 斜长花岗岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法 | 356~348 | [62] |
| 11 | 迪彦林场蛇绿岩 | 辉长岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法 | 361~340 | [63] |
| 12 | 迪彦庙蛇绿岩 | 玄武岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法 | 333.4±8.5 | [64] |
| 13 | 白音呼舒 | 花岗岩 | SHRIMP锆石U-Pb法 | 309.2±1.6 | [65] |
蛇绿岩在板块构造的研究中应用较为广泛[71],其主要类型有MORB型及SSZ型[72],可发育于大洋中脊及消减带等环境中[73-78]。李英杰等[37]将该处的橄榄岩定为方辉橄榄岩,从他们所研究的方辉橄榄岩以及玄武岩的岩石地球化学特征来看,可能与SSZ构造环境中复杂的源区有关。
根据地球化学特征,辉长岩具有高铝、低钛和磷的特点,类似于活动大陆边缘或岛弧环境下形成的岩石;从辉长岩主量元素来看,与洋脊拉斑玄武岩(N-MORB)类似;辉长岩的稀土配分模式图和微量元素蛛网图与N-MORB类似;但大离子亲石元素比洋中脊稍高,高场强元素比洋中脊稍低,显示弱亏损,呈现出俯冲带岛弧拉斑玄武岩的特征,暗示少量俯冲流体的参与,该辉长岩兼具有洋中脊和岛弧的双重性质。与N-MORB相比,迪彦庙辉长岩的轻稀土及重稀土元素的数值低,表明地幔楔可能以熔融为主。结合区域上对兴蒙造山带内的蛇绿岩的研究[21, 50, 79-82],笔者认为迪彦庙辉长岩的形成环境为弧前环境,为SSZ型。
6 结论1) 西乌旗迪彦庙蛇绿岩中的辉长岩属于高铝、低钾、低钠的拉斑玄武系列;稀土元素表现为重稀土元素比轻稀土元素较为富集,与绝大多数蛇绿岩中的辉长岩具有相类似的稀土元素配分曲线。
2) 迪彦庙蛇绿岩带内辉长岩的年龄为(345.3±2.3) Ma,为早石炭世。
3) 综合分析,辉长岩可能为受到俯冲作用所产生的流体交代而成,而并非结晶分异作用所致;形成环境为弧前环境。
致谢: 狄永军副教授、周志广副教授在论文完成过程中给予了指导与帮助,李瑞杰硕士、陈诚硕士、董金元硕士、李洪斌高级工程师在野外地质调查工作中给予了帮助,卢俊浩硕士、邱骏挺硕士、袁远博士、李鹏举博士等在论文撰写过程中给予了帮助,其他同门师兄弟在室内工作给予了帮助,在此一并表示感谢。
| [1] |
Coleman R G. Ophiolites[M]. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1977: 1-229.
|
| [2] |
Steinmannn G. Die Ophiolitischen Zonen in den Mediterranean Kettengebirgen (The Ophiolitic Zones in the Mediterranean Mountain Chains)[J]. Translated by Daniel B, Gerald M F. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2003, 373: 77-91. |
| [3] |
张旗. 蛇绿岩的分类[J]. 地质科学, 1990, 25(1): 54-61. Zhang Qi. Classification of Ophiolites[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1990, 25(1): 54-61. |
| [4] |
臧遇时, 杨高学, 赵金凤. 蛇绿岩的定义、分类及其发展[J]. 西北地质, 2013, 46(2): 12-17. Zang Yushi, Yang Gaoxue, Zhao Jinfeng. The Definition Classification and Development of Ophiolites[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2013, 46(2): 12-17. |
| [5] |
Miyashiro A. The Troodos Complex Was Probably Formed in an Island Arc[J]. Earth Planetary Science Letters, 1973, 19: 218-224. DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(73)90118-0 |
| [6] |
Pearce J A. Basalt Geochemistry Used to Investigate Past Tectonic Environments on Cyprus[J]. Tectonophysics, 1975, 25(1/2): 41-67. |
| [7] |
Church W R, Riccio L. Fractionation Trend of the Bay of Islands Ophiolite of Newfoundland:Polycyclic Cumulate Sequences in Ophiolites and Their Classification[J]. Canadian Earth Sciences, 1977, 14(5): 1156-1165. DOI:10.1139/e77-105 |
| [8] |
Moores E M. Origin and Emplacement of Ophiolites[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Space Physics, 1982, 20(4): 735-760. DOI:10.1029/RG020i004p00735 |
| [9] |
Coleman R G. The Diversity of Ophiolites[J]. Geologicen Mijnbouw, 1984, 63(2): 144-150. |
| [10] |
Boudier F, Nicolas A. Harzburgite and Lherzolite Subtypes in Ophiolitic and Oceanic Environments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1985, 76(1/2): 84-92. |
| [11] |
朱宝清, 王来生, 王连晓. 西准噶尔西南地区古生代蛇绿岩[J]. 中国地质科学院西安地质矿产研究所所刊, 1987, 17: 3-64. Zhu Baoqing, Wang Laisheng, Wang Lianxiao. Paleozoic Ophiolite in Southwest of Western Junggar[J]. Bulletin of the Xi'an Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, the Chinese Academy of Geologica Sciences, 1987, 17: 3-64. |
| [12] |
王希斌, 鲍佩声. 中国大陆造山带中地幔橄榄岩体的熔融残余类型及其构造形变[J]. 地球学报, 1990, 11(1): 49-52. Wang Xibin, Bao Peisheng. Types of Melting Residue and Structural Deformation of the Mantle Peridotite Bodies in Orogenic Belts of China[J]. Axta Geoscienca Sinica, 1990, 11(1): 49-52. |
| [13] |
王希斌, 鲍佩声, 戎合. 中国蛇绿岩中变质橄榄岩的稀土元素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 1995, 11(增刊1): 24-41. Wang Xibin, Bao Peisheng, Rong He. Rare Earth Elements Geochemistry of the Mantle Peridotite in the Ophiolite Suites of China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1995, 11(Sup. l): 24-41. |
| [14] |
肖序常. 从扩张速率试论蛇绿岩的类型划分[J]. 岩石学报, 1995, 11(增刊1): 10-23. Xiao Xuchang. Discussion on the Classification of Ophiolites by Spreading Rate[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1995, 11(Sup. l): 10-23. |
| [15] |
Dilek Y, Furnes H. Ophiolite Genesis and Global Tectonics:Geochemical and Tectonic Fingerprinting of Ancient Oceanic Lithosphere[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2011, 123(3/4): 387-411. |
| [16] |
张旗, 周国庆, 王焰. 中国蛇绿岩的分布、时代及其形成环境[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 19(1): 1-8. Zhang Qi, Zhou Guoqing, Wang Yan. The Distribution of Time and Space of Chinese Ophiolites, and Their Tectonic Settings[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2003, 19(1): 1-8. |
| [17] |
梁日喧. 内蒙古中段蛇绿岩特征及地质意义[J]. 中国区域地质, 1994, 1: 37-45. Liang Rixuan. The Features of Ophiolites in the Gentral Sector of Inner Mongolia and Its Ecological Significance[J]. Regional Geology of China, 1994, 1: 37-45. |
| [18] |
Hsu K J, Wang Q, Hao J. Geologic Evolution of the Neomonides:A Working Hypothesis[J]. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 1991, 84(1): 1-31. |
| [19] |
Şengör A M C, Natalin B A, Burtman V S. Evolution of the Altaid Tectonic Collage and Paleozoic Crustal Growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 1993, 364: 299-307. DOI:10.1038/364299a0 |
| [20] |
包志伟, 陈森煌, 张桢堂. 内蒙古贺根山地区蛇绿岩稀土元素和Sr-Nd同位素研究[J]. 地球化学, 1994, 23(4): 339-349. Bao Zhiwei, Chen Senhuang, Zhang Zhentang. Study on Ree and Sm-Nd Isotopes of Hegenshan Ophiolite, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geochimica, 1994, 23(4): 339-349. |
| [21] |
Miao L C, Fan W M, Liu D Y, et al. Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Hegenshan Ophiolitic Complex:Implications for Late-Stage Tectonic Evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling Orogenic Belt, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(5/6): 348-370. |
| [22] |
Tang K D. Tectonic Development of the Paleozoic Foldbelts at the Northern Margin of the Sino-Korean Craton[J]. Tectonics, 1990, 9(2): 249-260. DOI:10.1029/TC009i002p00249 |
| [23] |
唐克东. 中朝板块北侧褶皱带构造演化及成矿规律[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1992. Tang Kedong. Tectonic Evolution and Metallogenic Regularity of the Fold Belt in the North and North China Plate[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 1992. |
| [24] |
陈斌, 徐备. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗地区古生代两类花岗岩类的基本特征和构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 1996, 12(4): 546-561. Chen Bin, Xu Bei. The Main Characteristics and Tectonic Implications of Two Kinds of Paleozoic Granitoids in Sunidzuqi, Central Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1996, 12(4): 546-561. |
| [25] |
郝旭, 徐备. 内蒙古锡林郭勒杂岩的原岩年代和变质年代[J]. 地质论评, 1997, 43(1): 101-105. Hao Xu, Xu Bei. Sm-Nd, Rb-SrIsotopic Geochronology of the Xilin Gol Complex, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Geological Review, 1997, 43(1): 101-105. |
| [26] |
Chen B, Jahn B, Wilde S, et al. Two Contrasting Paleosoic Magmatic Belts in Northern Inner Mongolia, China:Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 328(1/2): 157-182. |
| [27] |
黄金香, 赵志丹, 张宏飞, 等. 内蒙古温都尔庙和巴彦敖包-交其尔蛇绿岩的元素与同位素地球化学:对古亚洲洋东部地幔域特征的限制[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(12): 2889-2900. Huang Jinxiang, Zhao Zhidan, Zhang Hongfei, et al. Elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb Isotopic Geochemistry of the Wenduermiao and Bayanaobao-Jiaoqier Ophiolites, Inner Mongolia:Constraints for the Characteristics of the Mantle Domain of Eastern Paleo-Asian Ocean[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(12): 2889-2900. |
| [28] |
陶继雄, 苏茂荣, 宝音乌力吉, 等. 内蒙古达尔罕茂明安联合旗满都拉地区索伦山蛇绿混杂岩的特征及构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(12): 1238-1242. Tao Jixiong, Su Maorong, Baoyin Wuliji, et al. Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of the Sonol Mountain Ophiolitic Mélang in the Mandula Area, Darhan Muminggan, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletn of China, 2004, 23(12): 1238-1242. |
| [29] |
王荃, 刘雪亚, 李锦轶. 中国华夏与安加拉古陆间的板块构造[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1991. Wang Quan, Liu Xueya, Li Jinyi. Plate Tectonic Between Cathaysia and Angara[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 1991. |
| [30] |
邵济安.内蒙古中部早古生代蛇绿岩及其在恢复地壳演化历史中的意义[C]//《中国北方板块构造论文集》编委会.中国北方板块构造论文集: 第一集.北京: 地质出版社, 1986: 158-172. Shao Ji'an. The Early Protozoic Ophiolite in Middle Inner Mongolia and Its Implications for Reconstruct Crust Evolution[C]//CPPTNC Editorial Committee. Contributions to the Project of Plate Tectonics in Northern China: No 1. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1986: 158-172. |
| [31] |
邵济安. 中朝板块北缘中段地壳演化[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1991. Shao Ji'an. Crust Evolution in the Middle Part of the Northern Margin of Sion-Korean Plate[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 1991. |
| [32] |
王东方. 内蒙古温都尔庙地区古板块会聚带的岩石化学和地球化学[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 1986, 27(2): 111-123. Wang Dongfang. The Petrology and Geochemistry of Convergent Zone of Old Plate at the Ondor Sum District, Neimongol[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturaliun Universitatis Pekinensis, 1986, 27(2): 111-123. |
| [33] |
许传诗. 内蒙古温都尔庙地区蛇绿岩变质作用的研究[J]. 河北地质学院学报, 1987, 10(1): 1-26. Xu Chuanshi. On the Metamorphism of Wenduermiao Ophiolite, Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Hebei College of Geology, 1987, 10(1): 1-26. |
| [34] |
许传诗. 内蒙古温都尔庙地区蛇绿岩微量元素特征及其岩石学成因意义[J]. 河北地质学院学报, 1990, 13(1): 1-8. Xu Chuanshi. Features of Trace Elements of Ophiolites in Wenduermiao Area, Nei Mongol and Their Significance in Rock Genesis[J]. Journal of Hebei College of Geology, 1990, 13(1): 1-8. |
| [35] |
牛树银, 胡晓, 孙爱群. 华北地台北侧的古板块构造演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 1993, 12(1): 17-21. Niu Shuyin, Hu Xiao, Sun Aiqun. Evolution of the Paleoplate Tectonics on North Side of North China Platform[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 1993, 12(1): 17-21. |
| [36] |
刘敦一, 简平, 张旗, 等. 内蒙古图林凯蛇绿岩中埃达克岩SHRIMP测年:早古生代洋壳消减的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2003, 77(3): 317-330. Liu Dunyi, Jian Ping, Zhang Qi, et al. SHRIMP Dating of Adakites in the Tulinkai Ophiolite, Inner Mongolia:Evidence for the Early Paleozoic Subduction[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2003, 77(3): 317-330. |
| [37] |
李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等. 内蒙古西乌珠穆沁旗迪彦庙蛇绿岩的识别[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(4): 1282-1290. Li Yingjie, Wang Jinfang, Li Hongyang, et al. Recognition Diyanmiao Ophiolite in Xi Ujimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(4): 1282-1290. |
| [38] |
唐克东, 张允平. 内蒙古缝合带的构造演化[M]. 北京: 北京科学技术出版社, 1991. Tang Kedong, Zhang Yunping. Tectonic Evolution of Suture Zone in Inner Mongolia[M]. Beijing: Beijing Science and Technology Press, 1991. |
| [39] |
Black L P, Kamo S L, Allen C M, et al. Improved 206Pb/238U Microprobe Geochronology by the Monitoring of a Trace-Element-Related Matrix Effect; SHRIMP, ID-TIMS, ELA-ICP-MS and Oxygen Isotope Documentation for a Series of Zircon Standards[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 205(1/2): 115-140. |
| [40] |
李怀坤, 陆松年, 李惠民, 等. 侵入下马岭组的基性岩床的锆石和斜锆石U-Pb精确定年:对华北中元古界地层划分方案的制约[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(10): 1396-1404. Li Huaikun, Lu Songnian, Li Huimin, et al. Zircon and Beddeleyite U-Pb Precision Dating of Basic Rock Sills Intruding Xiamaling Formation, North China[J]. Geological Bulletn of China, 2009, 28(10): 1396-1404. |
| [41] |
李怀坤, 朱士兴, 相振群, 等. 北京延庆高于庄组凝灰岩的锆石U-Pb定年研究及其对华北北部中元古界划分新方案的进一步约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(7): 2131-2140. Li Huaikun, Zhu Shixing, Xiang Zhenqun, et al. Zircon U-Pb Dating on Tuffbed from Gaoyuzhuang Formation in Yanqing, Beijing:Further Constraints on the New Subdivision of the Mesoproterozoic Stratigraphy in the Northern North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(7): 2131-2140. |
| [42] |
Jackson S E, Pearson N J, Griffin W J, et al. The Application of Laser Ablation-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry to in Situ U-Pb Zircon Geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 211(1/2): 47-69. |
| [43] |
Black L P, Kamo S L, Allen C M, et al. A New Zircon Standard for Phanerozoic U-Pb Geochronology[J]. Chemical Geology, 2003, 200(1/2): 155-170. |
| [44] |
Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and Oceanic Crust Recycline-Induced Melt-Peridotite Interactions in the Trans-North China Orengen:U-Pb Dating, Hf Isotopes and Trace Elements in Zircons from Mantle Xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2009, 51(1/2): 537-571. |
| [45] |
Ludwing K R. Users Manual for Isoplot/Ex:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Centre Special Publication, 2001, 1a: 1-55. |
| [46] |
Andersen T. Correction of Common Lead in U-Pb Analyses That do not Report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192(1/2): 59-79. |
| [47] |
白卉, 张红晨, 贺秋利, 等. 内蒙古迪彦庙蛇绿岩辉长岩岩石学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2012, 21(6): 531-534. Bai Hui, Zhang Hongchen, He Qiuli, et al. Lithology of Gabbro of the Diyanmiao Ophiolite in Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Resources, 2012, 21(6): 531-534. |
| [48] |
邱家骧. 岩浆岩岩石学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1985. Qiu Jiaxiang. Magmatic Petrology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1985. |
| [49] |
赵莉, 张招崇, 王福生, 等. 一个开放的岩浆房系统:攀西新街镁铁-超镁铁质层状岩体[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(6): 1565-1578. Zhao Li, Zhang Zhaochong, Wang Fusheng, et al. Open-System Magma Chamber:An Example from the Xinjie Mafic-Ultramafic Layered Intrusion in Panxi Region, SW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2006, 22(6): 1565-1578. |
| [50] |
张旗, 周国庆. 中国蛇绿岩[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. Zhang Qi, Zhou Guoqing. Ophiolite in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. |
| [51] |
吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. Wu Yuanbao, Zheng Yongfei. The Study of Zircon Genesis Mineralogy and Constraints of the Interpretation on Its U-Pb Age[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. |
| [52] |
Keppler H. Constraints from Partitioning Experiments on the Composition of Subductoin-Zone Fluids[J]. Nature, 1996, 380: 237-240. DOI:10.1038/380237a0 |
| [53] |
孟繁聪, 薛怀民, 李天福, 等. 苏鲁造山带晚中生代地幔的富集特征:来自辉长岩的地球化学证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(6): 1583-1592. Meng Fancong, Xue Huaimin, Li Tianfu, et al. Enriched Characteristics of Late Mesozoic Mantke Under the Sulu Orogenic Belt:Geochemical Evidence from Gabbro in Rushan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005, 21(6): 1583-1592. |
| [54] |
周长勇, 吴福元, 葛文春, 等. 大兴安岭北部塔河堆晶辉长岩体的形成时代、地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(3): 763-775. Zhou Changyong, Wu Fuyuan, Ge Wenchun, et al. Age, Geochemistry and Petrogenesis of the Cumulate Gabbro in Tahe, Northern Da Hinggan Mountain[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005, 21(3): 763-775. |
| [55] |
蔡克大, 袁超, 孙敏, 等. 阿尔泰塔尔浪地区斜长角闪岩和辉长岩的形成时代、地球化学特征和构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(5): 877-888. Cai Keda, Yuan Chao, Sun Min, et al. Geochemical Characteristics and Ages of the Amplibolites and Gabbors in Tarlang Area:Implications for Tectonic Evolution of the Chinese Altai[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(5): 877-888. |
| [56] |
Zhao Z H, Zhou L D. REE Geochemistry of Some Alkali-Rich Intrusive Rocks in China[J]. Science in China:Series D, 1997, 40(2): 145-158. DOI:10.1007/BF02878373 |
| [57] |
Jian P, Kröner A, Windley B F, et al. Carboniferous and Cretaceous Mafic-Ultramafic Massifs in Inner Mongolia (China):A SHRIMP Zircon and Geochemical Study of the Previously Presumed Integral "Hegenshan Ophiolite"[J]. Lithos, 2012, 142(2): 48-66. |
| [58] |
Zhang Z C, Li K, Li J F, et al. Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Eastern Ophiolitic Complex:Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of the Inner Mongolia-Daxinganling Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 97: 279-293. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.06.008 |
| [59] |
李英杰, 王金芳, 李红阳, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗梅劳特乌拉蛇绿岩的识别[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(5): 1461-1470. Li Yingjie, Wang Jinfang, Li Hongyang, et al. Recognition of Meilaotewula Ophiolite in Xi U jimqin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(5): 1461-1470. |
| [60] |
Song S G, Wang M M, Xu X, et al. Ophiolites in the Xing'an-Inner Mongolia Accretionary Belt of the CAOB:Implications for Two Cycles of Seafloor Spreading and Accretionary Orogenic Events[J]. Tectonics, 2015, 34(10): 2221-2248. DOI:10.1002/2015TC003948 |
| [61] |
黄波, 付冬, 李树才, 等. 内蒙古贺根山蛇绿岩形成时代及构造启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(1): 158-176. Huang Bo, Fu Dong, Li Shucai, et al. The Age and Tectonic Implications of the Hegenshan Ophiolite in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(1): 158-176. |
| [62] |
Yang J F, Zhang Z C, Chen Y, et al. Ages and Origin of Felsic Rocks from the Eastern Erenhot Ophiolitic Complex, Southeastern Centera Asian Orogenic Belt, Inner Mongolia China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 144(3/4): 126-140. |
| [63] |
Li Y J, Wang G H, Santosh M, et al. Supra-Subduction Zone Ophiolites from Inner Mongolia, North China:Implications for the Tectonic History of the Southeaetern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2018, 59(3): 126-143. |
| [64] |
李英杰, 王金芳, 王根厚, 等. 内蒙古迪彦庙蛇绿岩带达哈特前弧玄武岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(2): 469-482. Li Yingjie, Wang Jinfang, Wang Genhou, et al. Discovery and Significance of the Dahate Fore-Arc Basalts from the Diyanmiao Ophiolite in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(2): 469-482. |
| [65] |
王金芳, 李英杰, 李红阳, 等. 贺根山缝合带白音呼舒奥长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(4): 857-872. Wang Jinfang, Li Yingjie, Li Hongyang, et al. Zircon U-Pb Ages and Geochemical Characteristics of Baiyinhushu Trondhjemite in Hegenshan Suture Zone and Their Tectonic Implications[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(4): 857-872. |
| [66] |
陈斌, 赵国春, Simon Wilde. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗南两类花岗岩同位素年代学及其构造意义[J]. 地质论评, 2001, 47(4): 361-367. Chen Bin, Zhao Guochun, Simon Wilde. Subduction-and Collision-Related Granitoids from Southern Sonidzuoqi, Inner Mongolia:Isotopic Ages and Tectonic Implications[J]. Geological Review, 2001, 47(4): 361-367. |
| [67] |
鲍庆中, 张长捷, 吴之理, 等. 内蒙古白音高勒地区石炭纪石英闪长岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学及其意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2007, 37(1): 15-23. Bao Qingzhong, Zhang Changjie, Wu Zhili, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb Zircon Geochronology of a Carboniferous Quartz-Diorite in Baiyingaole Area, Inner Mongolia and Its Implications[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2007, 37(1): 15-23. |
| [68] |
刘建峰, 迟效国, 张兴洲, 等. 内蒙古西乌旗南部石炭纪石英闪长岩地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(3): 365-376. Liu Jianfeng, Chi Xiaoguo, Zhang Xingzhou, et al. Geochemical Characteristic of Carboniferous Quartz-Diorite in the Southern Xiwuqi Area, Inner Mongolia and Its Tectonic Significance[J]. Acta Geologeica Sinica, 2009, 83(3): 365-376. |
| [69] |
Chen B, Jahn B M, Tian W. Evolution of the Solonker Suture Zone:Constraints from Zircon U-Pb Ages, Hf Isotopic Ratios and Whole-Rock Nd-Sr Isotope Compositions of Subduction and Collision-Related Magmas and Forearc Sediments[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 34(3): 245-257. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.05.007 |
| [70] |
张拴宏, 赵越, 刘建民, 等. 华北板块北缘晚古生代-早中古生代岩浆活动期次、特征及构造背景[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2010, 29(6): 824-842. Zhang Shuanhong, Zhao Yue, Liu Jianmin, et al. Geochronology, Geochemistry and Tectonic Setting of the Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic Magmatism in the Northern Margin of the North China Block:Apreliminary Review[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2010, 29(6): 824-842. |
| [71] |
Kidd R G W. A Model for the Process of Formation of the Upper Oceanic Crust[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1977, 50(1): 149-183. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-246X.1977.tb01328.x |
| [72] |
Pearce J A, Lippard S J, Roberts S. Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of Supra-Subduction Zone Ophiolites[J]. Geolgical Society London Special Publications, 1984, 16(1): 77-94. DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1984.016.01.06 |
| [73] |
Robinson P T, Zhou M F, Hu X F, et al. Geochemical Constraints on the Origin of the Hengenshan Ophiolite, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1999, 17(4): 423-442. DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00016-4 |
| [74] |
Nozaka T, Liu Y. Petrology of the Hegenshan Ophiolite and Its Implication for the Tectonic Evolution of Northern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 202(1): 89-104. |
| [75] |
Dilek Y, Robinson P T. Ophiolites in Earth History: Introduction[C]//Dilek, Robinson P T. Ophiolites in Earth History. London: Geological Society, 2003: 1-8. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Yildirim_Dilek/publication/249551225_Ophiolites_in_Earth_history_Introduction/links/5681b41e08ae051f9aec5824.pdf?origin=publication_detail
|
| [76] |
Dilek Y, Furnes H. Structure and Geochemistry of Tethyan Ophiolites and Their Petrogenesis in Subduction Rollback Systems[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113(1/2): 1-20. |
| [77] |
Dilek Y, Furnes H. Ophiolites and Their Origins[J]. Elements, 2014, 10(2): 93-100. DOI:10.2113/gselements.10.2.93 |
| [78] |
Stern R J, Ali K A, Liegeois J P, et al. Distribution and Signify-Cance of Pre-Neoproterozoic Zircons Injuvenile Neoproterozoic Igneous Rocks of the Arabian-Nubianshield[J]. American Journal of Science, 2010, 310(9): 791-811. DOI:10.2475/09.2010.02 |
| [79] |
Li J Y. Permian Geodynamic Setting of Northeast China and Adjacent Regions:Closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean and Subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 26(3/4): 207-224. |
| [80] |
王树庆, 许继峰, 刘希军, 等. 内蒙朝克山蛇绿岩地球化学:洋内弧后盆地的产物?[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(12): 2869-2879. Wang Shuqing, Xu Jifeng, Liu Xijun, et al. Geochemistry of the Chaokeshan Ophiolite:Product of Intra-Oceanic Back-Arc Basin?[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(12): 2869-2879. |
| [81] |
周国庆. 蛇绿岩研究新进展及其定义和分类的再讨论[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 44(1): 1-24. Zhou Guoqing. Ophiolite:Some Key Aspects Regarding Its Definition and Classification[J]. Journal of Nanjing University (Natural Sciences), 2008, 44(1): 1-24. |
| [82] |
王成, 任利民, 张晓军, 等. 内蒙古崇根山蛇绿岩前弧玄武岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 1-11. Wang Cheng, Ren Limin, Zhang Xiaojun, et al. Discovery and Significance of the Fore-Arc Basalts from the Chonggenshan Ophiolitein Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 1-11. |