扩展功能
文章信息
- 卜祥风, 谢友浩
- BU Xiang-feng, XIE You-hao
- 具有可调式液力惯容器的蓄能悬架H∞控制
- H∞ Control for Inerter Suspension with a Variable-inertance Hydraulic Inerter
- 公路交通科技, 2018, 35(12): 118-123
- Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Denelopment, 2018, 35(12): 118-123
- 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2018.12.017
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2017-04-24
2. 安徽猎豹汽车有限公司, 安徽 滁州 239000
2. Anhui Leopaard Automobile Co., Ltd., Chuzhou Anhui 239000, China
2002年,剑桥大学Smith教授根据机电相似理论提出了“惯容器”的概念,并制作了齿轮齿条式惯容器样机,通过试验发现其具有高摩擦、背隙影响大等问题[1]。Parageorgiou提出了滚珠丝杠式惯容器,虽然较好地解决了背隙大的问题,但同时增大了摩擦力[2]。2011年,王富正[3]提出了油缸马达液力惯容器,由于这种惯容器能够输出较大的惯容力,被广泛应用于车辆蓄能悬架中。
陈龙等[4-8]设计了定惯容系数的油缸马达液力惯容器,并将其应用到车辆蓄能悬架中,组成“惯容器-弹簧-阻尼”(ISD)悬架。汪若尘[9-11]将ISD被动悬架与半主动悬架结合,提出了两级串联式ISD半主动悬架,并基于模糊控制策略研究了ISD半主动悬架的动态性能。仿真与试验结果均表明,ISD半主动悬架比ISD被动悬架拥有更好的减振效果。张孝良[12-14]还进行了惯容与阻尼串联式ISD悬架实车道路试验。结果表明,ISD悬架与传统悬架相比,明显降低了偏频处的功率谱密度峰值,并且显著提高了车辆行驶平顺性。
以上研究中均使用了定惯容系数液力惯容器,少见可变惯容系数的液力惯容器在悬架中的应用,且传统定惯容系数液力惯容器在飞轮换向时反向冲击较大,影响惯容器工作效能。引入液压单向桥可以解决飞轮换向冲击问题,同时引入比例阀改变液压马达流量从而改变惯容器的惯容系数,形成可调式液力惯容器。将可调式液力惯容器应用到蓄能悬架系统中,满足车辆不同行驶工况的需求,以期取得更好地减振效果。
1 可调式液力惯容器图 1为定惯容油缸马达液力惯容器的结构示意图。它的工作原理是:当随动端1受到向左的推力时,活塞随之向左运动。活塞左腔的液流受挤压从左端口流出,流经双向定量液压马达6时推动飞轮5顺时针旋转,然后从右端口流入活塞右腔,反之亦然。
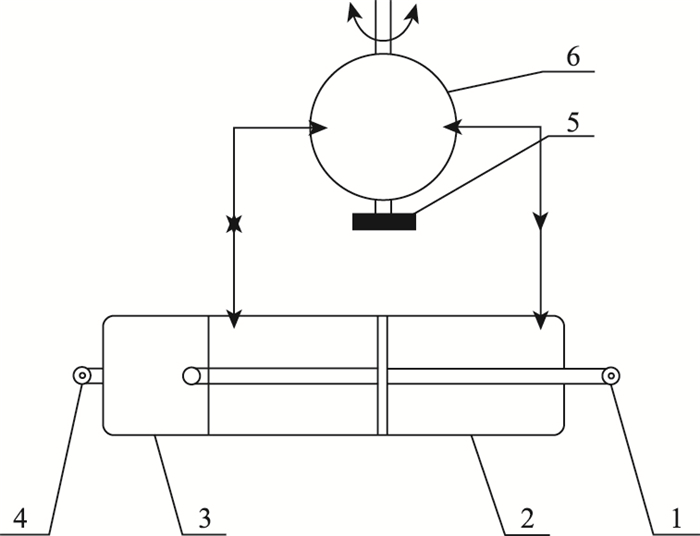
|
| 图 1 定惯容油缸马达液力惯容器 Fig. 1 Fixed-inertance cylinder-motor hydraulic inerter 1—随动端;2—液压缸缸体;3—液压缸上罩壳;4—固定端;5-飞轮; 6-双向定量液压马达 |
| |
图 2为可调式油缸马达液力惯容器。它在定惯容液力惯容器的基础上增加了由液压单向阀5,6,7,8组成的单向整流桥,使得无论活塞向左还是向右运动,飞轮9都顺时针旋转不用改变方向,从而避免了飞轮因频繁换向造成的转速波动、冲击、迟滞等问题。另外在液压马达10的两端并联比例阀11,调整比例阀11的开度可以改变液压马达10的流量,从而改变飞轮9的转速。文献[15-17]研究表明,液力惯容器的惯容系数随飞轮转速正比变化,所以通过控制比例阀11的开度就可以改变液力惯容器的惯容系数,从而调节惯容器对外输出力的大小。
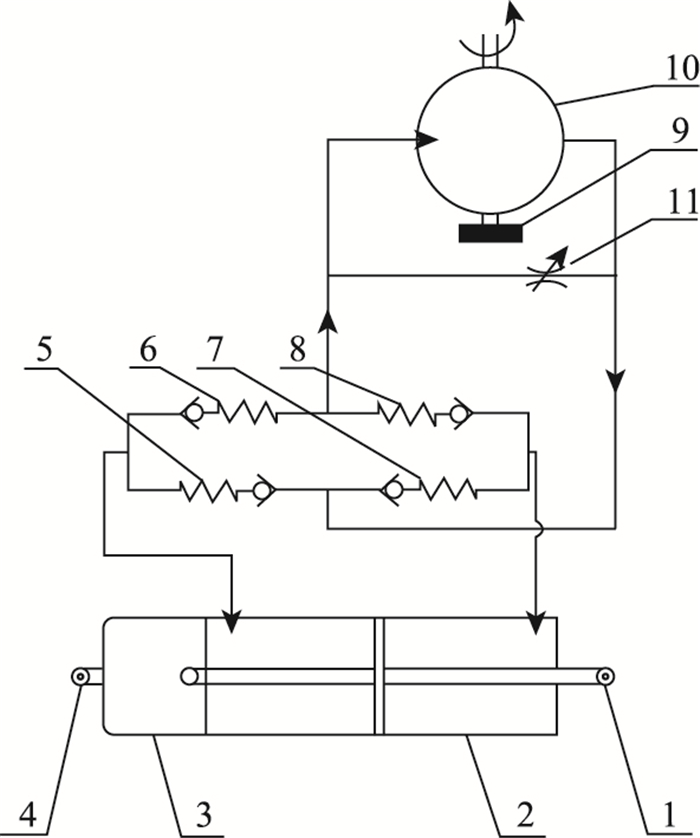
|
| 图 2 可调式油缸马达液力惯容器 Fig. 2 Variable-inertance cylinder-motor hydraulic inerter 1—随动端;2—液压缸缸体;3—液压缸上罩壳;4—固定端;5—液压单向阀1;6—液压单向阀2;7—液压单向阀3;8—液压单向阀4;9—飞轮;10—液压马达;11—比例阀 |
| |
2 车辆蓄能悬架动力学 2.1 蓄能悬架动力学建模
如图 3所示,可调式液力惯容器与传统被动悬架相结合,形成一种蓄能悬架。其中,m2为车身质量;m1为车轮质量;k2为悬架弹簧刚度;k1为轮胎刚度;c2为悬架阻尼系数;b为惯容器惯容系数,x2为车身位移;x1为车轮位移;q为路面位移。

|
| 图 3 蓄能悬架模型 Fig. 3 Model of inerter suspension |
| |
以可调式液力惯容器为对象,通过控制比例阀的开度来改变惯容器的惯容系数,从而调节惯容器的输出力。为了便于仿真和计算,可以将图 3中可调式液力惯容器简化成蓄能悬架简化模型(图 4)中所示的一个力F作为控制器的输出。实际应用时把控制器输出力F与车身-车轮相对加速度相除,使数值逼近试验所得惯容器的惯容系数,从而驱动比例阀打开一定的开度实现对惯容器惯容系数的控制。
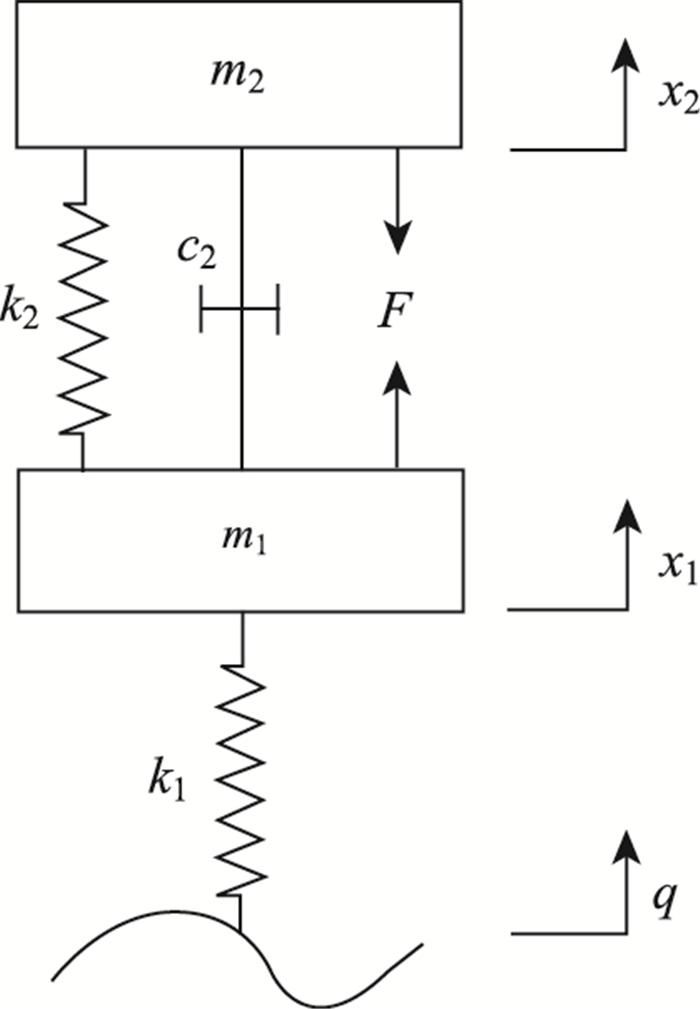
|
| 图 4 蓄能悬架简化模型 Fig. 4 Simplified model of inerter suspension |
| |
由图 4蓄能悬架的简化模型和牛顿第二运动定律得到系统的动力学模型:
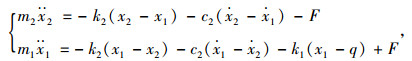
|
(1) |
式中,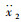
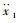
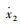
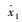
系统的状态变量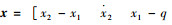
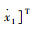
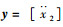
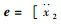
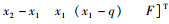
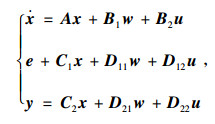
|
(2) |
式中,w为外部输入;u为控制输入;
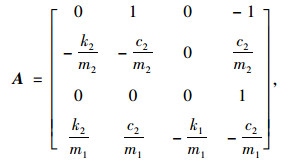
|
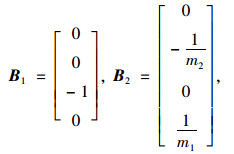
|
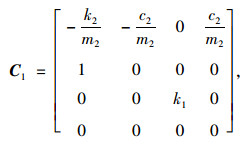
|
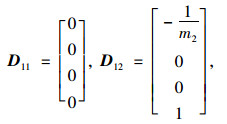
|
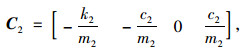
|
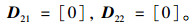
|
设系统(2)的输出反馈控制器k(S)为:

|
(3) |
式中,xk∈R为控制器的状态;Ak, Bk, Ck, Dk为待求的控制器参数矩阵。
根据文献[18]的变量替换法,令:
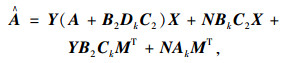
|
(4) |
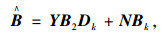
|
(5) |
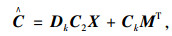
|
(6) |
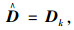
|
(7) |
式中,X, Y∈Rn×n对称矩阵,M和N为满秩矩阵,且MNT=I-XY,I为单位矩阵,则系统(2)的H∞最优输出反馈控制器的求解可以归结为凸优化问题:
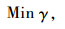
|
(8) |
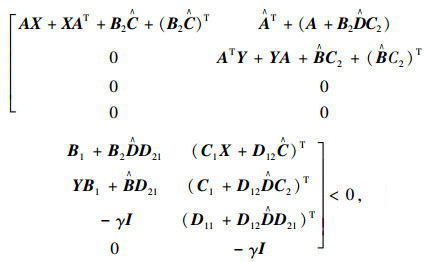
|
(9) |
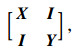
|
(10) |
式中γ为待求的常数。
系统(2)的H∞最优输出反馈控制器的求解步骤如下。
(1) 求凸优化问题(4)的可行性解X,Y,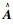
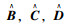
(2) 对矩阵I-XY进行奇异值分解,可得满秩矩阵M和N。
(3) 求解控制器的参数矩阵:
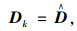
|
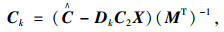
|
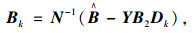
|
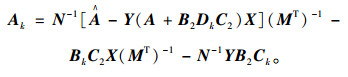
|
仿真选用某型轿车后悬架,各部件参数具体数值如表 1所示。
| 参数 | 数值 |
| 车轮质量/kg | 317.5 |
| 车身质量/kg | 45.5 |
| 轮胎刚度/(kN·m -1) | 192 |
| 悬架弹簧刚度/(kN·m -1) | 22 |
| 悬架阻尼系数/(kN·s·m -1) | 2.4 |
3.2 频域响应分析
在Matlab/Simulink环境下对蓄能悬架进行数值仿真,得到蓄能悬架的频率响应特性,并与相应的被动悬架进行比较。
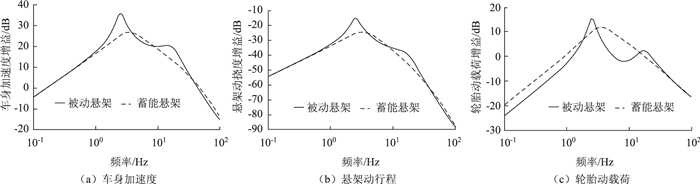
图 5为蓄能悬架和被动悬架在路面随机输入下,车身加速度、悬架动行程和轮胎动载荷的幅频特性曲线。
|
| 图 5 系统频域响应 Fig. 5 Frequency domain response of system |
| |
由图 5可知,在车身加速度方面,蓄能悬架在人体最敏感的2 Hz附近低频范围相比于被动悬架幅值下降明显,削减了被动悬架车身主振型的共振峰,取得了明显的减振效果。同样,在20 Hz附近的高频范围内,蓄能悬架的幅值也有所降低,削减了车轮主振型的共振峰。只在3~10 Hz的中高频带,蓄能悬架幅值略有升高。蓄能悬架动行程的改善效果和趋势与车身加速度类似。蓄能悬架的轮胎动载荷幅值在0.1~1.5 Hz的低频带和3~15 Hz的中高频带有所升高,但同样在2 Hz和20 Hz附近削减了共振峰,提高了安全性。
3.3 时域响应分析在Simulink环境下建立蓄能悬架与相应被动悬架的时域仿真模型,取积分白噪声的时域模型作为路面输入模型,其输入方程为:
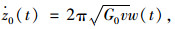
|
(11) |
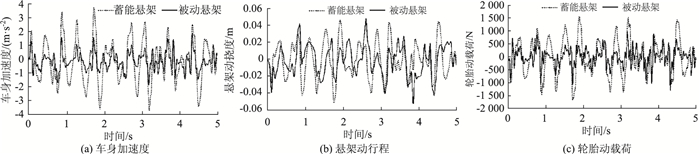
式中,G0为路面不平度系数;w(t)为Gauss白噪声;v为行车速度。选取G0=5×10-6 m3/cycle,v=30 m/s,得到C级路面下,蓄能悬架和被动悬架在车身加速度、悬架动挠度和轮胎动载荷的时域仿真对比,见图 6。相应的均方根值列于表 2。
|
| 图 6 系统时域响应 Fig. 6 Time domain response of system |
| |
随机激励下蓄能悬架与被动悬架系统响应均方根值如表 2所示。
| 悬架类型 | 指标 | 数值 |
| 蓄能悬架 | 车身加速度均方根值/(m·s-2) | 0.623 5 |
| 悬架动行程均方根值/m | 0.017 9 | |
| 轮胎动载荷均方根值/N | 332.926 3 | |
| 被动悬架 | 车身加速度均方根值/(m·s-2) | 1.488 7 |
| 悬架动行程均方根值/m | 0.020 7 | |
| 轮胎动载荷均方根值/N | 681.874 1 |
由表 2可知,蓄能悬架的车身加速度均方根值比被动悬架改善了58.12%,体现了良好的减振效果。在悬架动行程和车轮动载荷两项上,蓄能悬架比被动悬架也分别改善了13.53%和51.17%。可见,蓄能悬架相比于传统被动悬架不仅取得了良好的汽车平顺性,也获得了更好的操纵稳定性,提高了行车安全性。时域仿真对比从一个侧面表明所设计的H∞输出反馈控制器是正确的、有用的。
4 结论(1) 可调式油缸马达液力惯容器应用到蓄能悬架系统中,通过调节惯容器的输出力,可以起到良好的减振效果。与传统被动悬架相比,蓄能悬架在行车平顺性和操纵安全性方面都有很大改善。
(2) 蓄能悬架系统的H∞控制策略是可行的,能适时、正确地调节惯容器输出力,使蓄能悬架系统起到良好的减振效果。
| [1] |
SMITH M C. Synthesis of Mechanical Networks:The Inerter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2002, 47(10): 1648-1662. |
| [2] |
PAPAGEORGIOU C, HOUGHTON N E, SMITH M C. Experimental Testing and Analysis of Inerter Devices[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement and Control, 2009, 131(1): 1-11. |
| [3] |
WANG F, HONG M, LIN T. Designing and Testing a Hydraulic Inerter[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C:Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2011, 225(1): 66-72. |
| [4] |
陈龙, 杨晓峰, 汪若尘, 等. 基于二元件ISD结构隔振机理的车辆被动悬架设计与性能研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2013, 32(6): 90-95. CHEN Long, YANG Xiao-feng, WANG Ruo-chen, et al. Design and Performance Study of Vehicle Passive Suspension Based on Two-element Inerter-spring-damper Structure Vibration Isolation Mechanism[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(6): 90-95. |
| [5] |
陈龙, 杨晓峰, 汪若尘, 等. 改进的ISD三元件车辆被动悬架性能的研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2014, 36(3): 340-345. CHEN Long, YANG Xiao-feng, WANG Ruo-chen, et al. A Study on the Performances of Vehicle Passive Suspension with Modified Inerter-spring-damper Three-element Structure[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2014, 36(3): 340-345. |
| [6] |
孙晓强, 陈龙, 汪少华, 等. 非线性惯容器-弹簧-阻尼悬架系统隔振性能分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 2013(23): 38-45. SUN Xiao-qiang, CHEN Long, WANG Shao-hua, et al. Analysis of Vibration Isolation Performance for Nonlinear Inerter-spring-damper Suspension[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2013(23): 38-45. |
| [7] |
孙晓强, 陈龙, 汪少华, 等. 2级串联式ISD悬架非线性建模与参数优化[J]. 农业机械学报, 2014, 45(6): 7-13. SUN Xiao-qiang, CHEN Long, WANG Shao-hua, et al. Nonlinear Modeling and Parameter Optimization of Two-stage Series-connected ISD Suspension[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(6): 7-13. |
| [8] |
陈龙, 沈钰杰, 杨晓峰, 等. 基于惯容器-弹簧结构体系的车辆悬架结构设计与试验[J]. 振动与冲击, 2014(22): 83-87. CHEN Long, SHEN Yu-jie, YANG Xiao-feng, et al. Design and Experiment of Vehicle Suspension Based on Inerter-spring Structure[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014(22): 83-87. |
| [9] |
汪若尘, 孟祥鹏, 施德华, 等. 车辆惯容器-弹簧-阻尼器半主动悬架模糊控制[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013, 44(12): 1-5. WANG Ruo-chen, MENG Xiang-peng, SHI De-hua, et al. Fuzzy Control of Vehicle ISD Semi-active Suspension[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(12): 1-5. |
| [10] |
汪若尘, 陈兵, 张孝良, 等. 车辆蓄能悬架系统仿真与试验[J]. 农业机械学报, 2012, 43(12): 1-4. WANG Ruo-chen, MENG Xiang-peng, ZHANG Xiao-liang, et al. Simulation and Experiment of Vehicle Inerter Suspension System[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2012, 43(12): 1-4. |
| [11] |
汪若尘, 陈兵, 孙泽宇, 等. 基于LMI的两级串联式ISD半主动悬架H∞控制[J]. 车辆与动力技术, 2013(3): 21-25. WANG Ruo-then, CHEN Bing, SUN Ze-yu, et al. H∞ Control for the Semi-active Suspension System in Model Two-stage Series-connected ISD Based on the LMI Method[J]. Vehicle & Power Technology, 2013(3): 21-25. |
| [12] |
张孝良, 陈龙, 聂佳梅, 等. 2级串联型ISD悬架频响特性分析与试验[J]. 江苏大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 33(3): 255-258. ZHANG Xiao-liang, CHEN Long, NIE Jia-mei, et al. Analysis and Experiment of Frequency Response Characteristics of Two-stage Series-connected ISD Suspension[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University:Natural Science Edition, 2012, 33(3): 255-258. |
| [13] |
张孝良, 张华新, 蒋涛. 惯容与阻尼串联式ISD悬架实车道路试验[J]. 汽车工程, 2016, 38(11): 1391-1395. ZHANG Xiao-liang, ZHANG Hua-xin, JIANG Tao. Vehicle Road Test of ISD Suspension with Inerter and Damper Connected in Series[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2016, 38(11): 1391-1395. |
| [14] |
张孝良, 聂佳梅, 汪若尘, 等. 基于惯容-弹簧-阻尼结构体系的被动天棚阻尼悬架系统[J]. 农业机械学报, 2013, 44(10): 10-14, 9. ZHANG Xiao-liang, NIE Jia-mei, WANG Ruo-chen, et al. Passive Skyhook-damping Suspension System Based on Inerter-spring-damper Structural System[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2013, 44(10): 10-14, 9. |
| [15] |
陈龙, 任皓, 汪若尘, 等. 液力式惯容器力学性能仿真与试验研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2014, 33(12): 87-92. CHEN Long, REN Hao, WANG Ruo-chen, et al. Simulations and Tests for Mechanical Properties of a Hydraulic Inerter[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2014, 33(12): 87-92. |
| [16] |
毛明, 王乐, 陈轶杰, 等. 惯容器及惯容器-弹簧-阻尼器悬架研究进展[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(3): 525-534. MAO Ming, WANG Le, CHEN Yi-jie, et al. Research Progress in Inerter and Inerter-spring-damper Suspension[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(3): 525-534. |
| [17] |
谭德昕, 刘献栋, 单颖春. 惯容器在车辆减振系统中的应用研究综述[J]. 汽车工程学报, 2011, 1(4): 342-347. TAN De-xin, LIU Xian-dong, SHAN Ying-chun. Review on the Inerter and Its Applications in Vehicle Damping System[J]. Chinese Journal of Automotive Engineering, 2011, 1(4): 342-347. |
| [18] |
俞立. 鲁棒控制-线性矩阵不等式处理方法[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2002. YU Li. Robust Control-linear Matrix Inequality Approach[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2002. |
 2018, Vol. 35
2018, Vol. 35
