2. 延长油田股份有限公司 志丹采油厂, 陕西 延安 717500
2. Zhidan Oil Production Plant of Yanchang Oilfield Co., Ltd., Yan'an 717500, Shaanxi Province, China
志丹油田纸坊北油区位于鄂尔多斯盆地中部陕西省志丹县境内,该区开发的主力层位为三叠系延长组长6、长7、长8和长9油藏. 研究区的长6—长9油藏为岩性油藏,构造特征对其成藏影响作用较弱(图 1),储层物性差,表现为低渗-超低渗储层特征[1]. 该区目前的试油试产数据表明,仅仅从宏观方面对油藏进行有利区预测开发效果较差,而且本区的试油试产资料证明该区的物性对储层的产量影响较大,故亟需对研究区的储层物性与油气成藏时限的关系进行研究与厘定,这对于该区有利油气勘探的区带与圈闭评价,具有重要意义. 前人对鄂尔多斯盆地延长组的储层成岩与成藏耦合关系进行了大量研究,但是研究成果观点各不相同[2-5]. 因此需要在对主要含油气层段致密储层成岩现象、成岩作用类型、成岩演化特征综合对比的基础上,结合不同区块内现今油气富集聚集的状态,进一步分析成岩演化差异性. 故本文以志丹油田纸坊北油区长6—长9油藏为研究对象,主要通过成岩作用阶段对储层物性参数孔隙度的影响,定量研究储层孔隙度的演化规律与油气充注时间的耦合关系,进一步认识整个纸坊北油气成藏过程及油气藏分布规律,以期为下一步的建产方向提供依据[6].
|
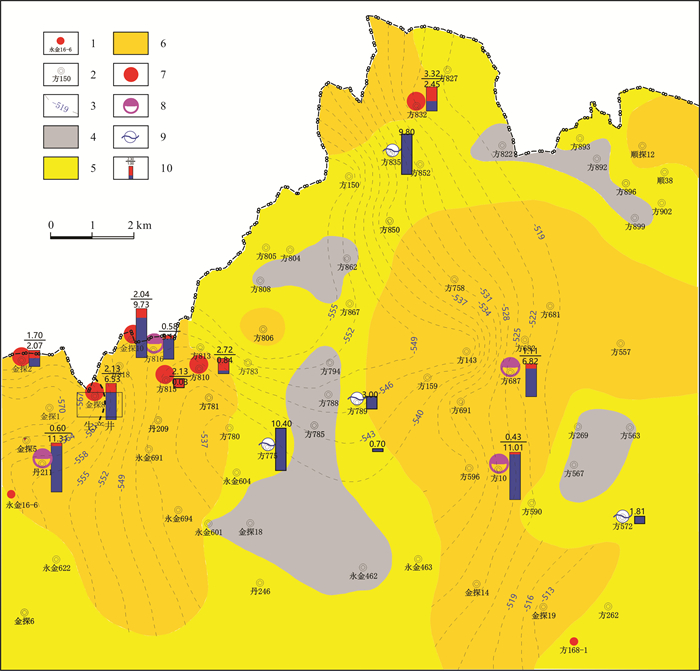
图 1 志丹油田纸坊北油区长9砂体顶面构造与砂厚及试油产量叠合图 Fig.1 Superposition map of top structure, sand thickness and test oil yield of Chang 9 sandbody in North Zhifang area 1—生产井位置(production well);2—探井位置(exploratory well);3—构造等值线(structure contour);4—砂岩尖灭区(sandstone pinch-out area);5—有利二类区(favorable second-class area);6—有利一类区(favorable first-class area);7—工业油流井(industrial oil flow well);8—低产油流井(low- yield oil flow well);9—纯水井(pure water well);10—产量柱子(yield column) |
本研究先利用经验公式恢复储层原始孔隙度,在此基础上,定量计算压实作用对储层孔隙的影响;然后根据成岩演化序列中胶结物形成的时间顺序及其含量的差异性,定量计算不同胶结物对储层孔隙的影响,同理确定溶蚀作用对储层孔隙增加的影响;最终结合成岩演化史,还原砂岩储层的孔隙致密化的过程.
1.1 砂岩原始孔隙度恢复为了确定研究区长6—长9储层目前原生孔隙度的剩余量和次生孔隙度的形成量,首先要对目的层长6—长9储层的原始孔隙度进行恢复,然后在此基础上评价不同成岩作用或事件对目的层孔隙度演化的贡献值. 计算原始孔隙度最常用的方法是Beard等[7]利用分选系数建立的经验公式,本研究利用该公式对目的层的原始孔隙度恢复进行了计算(表 1).
|
|
表 1 纸坊北地区延长组储层分选系数及原始孔隙度恢复计算结果 Table 1 Reservoir sorting coefficient and primary porosity recovery of Yanchang Formation in North Zhifang area |
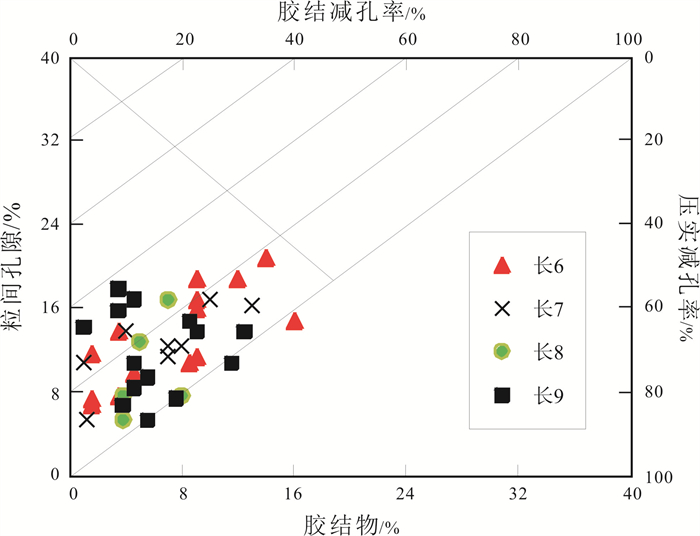
通过对大量的常规薄片及铸体薄片[8]鉴定统计分析(图 2、表 2),可以看出研究区从上到下压实作用对孔隙度的影响逐渐增加;胶结作用对孔隙度的影响逐渐降低. 由此可见强烈的压实作用是纸坊北地区长6—长9储层致密的主要原因.
|
图 2 纸坊北地区胶结减孔率和压实减孔率交汇图 Fig.2 Crossplot of cementation porosity reduction rate and compaction porosity reduction rate in North Zhifang area |
|
|
表 2 纸坊北地区不同层位压实作用和胶结作用对孔隙度的影响对比 Table 2 Effects of compaction and cementation on porosity at different horizons in North Zhifang area |
溶蚀作用对储层孔隙度具有积极的贡献[9-11]. 从表 3中可以看出,溶蚀作用对研究区长9储层的孔隙度贡献量最大,对长8储层的贡献量最小.
|
|
表 3 纸坊北地区各层位溶蚀作用对孔隙度的影响对比 Table 3 Comparison of the effect of dissolution on porosity at different horizons in North Zhifang area |
经岩心分析化验,研究区内含有较多的塑形矿物,如长石、云母及岩屑. 这些物质的存在使得储层在压实过程中原生孔隙受到较大的影响. 从表 4中可以看出压实作用带来的减孔程度从长6到长9油层组依次增加;在压实作用存在的同时,绿泥石矿物也同步充填孔隙,使得储层孔隙度进一步减少;随着埋深进一步增加,少量石英加大边形成,孔隙进一步减少,而且碳酸盐胶结和伊利石充填使孔隙进一步减少[12-13]. 随后发生溶蚀作用,溶解作用对孔隙度改善作用显著.
|
|
表 4 纸坊北地区长6—长9油层组孔隙度变化及计算、实测值 Table 4 Porosity variation, calculated and measured values of Chang 6-Chang 9 oil reservoirs in North Zhifang area |
根据研究区长6—长9储层内流体包裹体含烃量的不同,采用西安石油大学陕西省油气成藏地质学重点实验室ZEISS双通道荧光-透射光显微镜对石英宿主矿物内流体包裹体观察,可以分辨出盐水包裹体、含液态烃包裹体和液态烃包裹体3类包裹体.
有机包裹体的荧光颜色可间接地反映有机质的演化程度,也即随着有机质从低成熟向高成熟过渡,其荧光颜色由浅黄(亮黄)色→褐黄色→棕色→暗蓝色→蓝灰色→无荧光变化[14-15]. 在显微荧光技术下研究区目的层烃类包裹体多发黄绿色,由此可证明纸坊北地区长6—长9油层组有机质成熟度已达到中等水平.
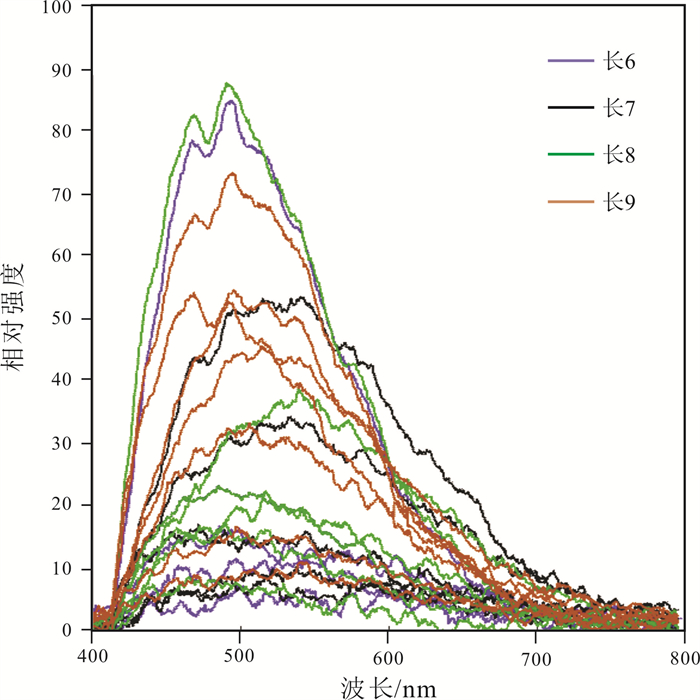
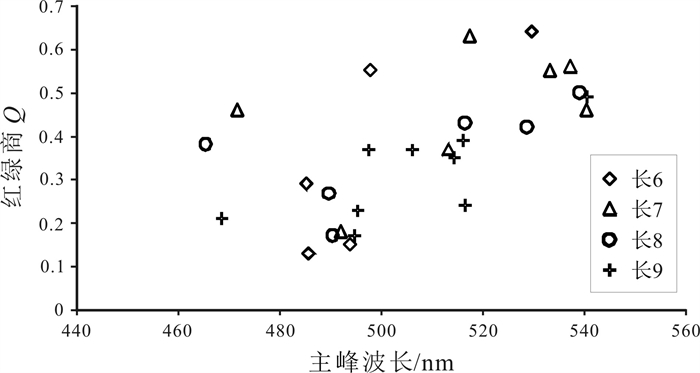
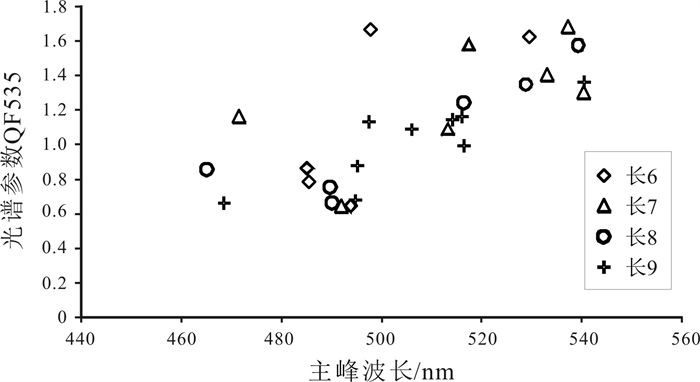
通过对纸坊北地区液态烃包裹体的荧光光谱分析发现,目的层位主峰波长在465~541 nm之间,红绿商在0.17~0.64之间,光谱参数QF535在0.64~1.68之间,反映研究区有机质成熟度中等;且从长6—长9油层组λ、Q和QF535没有明显的分界,同样数值上没有明显的中断,分布连续. 由此反映了纸坊北地区长6—长9时期油气充注是一个虽然漫长但是连续的过程,成藏时期为同一期(图 3、4、5).
|
图 3 纸坊北地区长6—长9油层组烃类包裹体荧光光谱特征 Fig.3 Fluorescence spectrum characteristics of hydrocarbon inclusions from Chang 6-Chang 9 oil reservoirs in North Zhifang area |
|
图 4 纸坊北地区烃类包裹体荧光光谱主峰波长与红绿商交汇图 Fig.4 Main peak wavelength vs. red-green quotient of fluorescence spectrum of hydrocarbon inclusions in North Zhifang area |
|
图 5 纸坊北地区烃类包裹体荧光光谱主峰波长与光谱参数QF535交汇图 Fig.5 Main peak wavelength vs. spectral parameters QF535 of fluorescence spectrum of hydrocarbon inclusions in North Zhifang area |
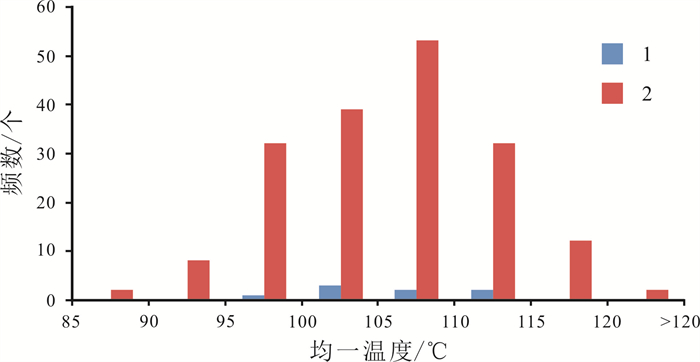
流体包裹体的宿主矿物主要为石英,其次是碳酸盐岩胶结物. 本次研究主要针对石英宿主矿物的流体包裹体,一类发育于石英颗粒的次生加大边,一类发育于石英颗粒愈合微裂隙内[16]. 流体包裹体均一法测温与冰点温度的测定主要以能反映油气充注信息的与烃类包裹体相伴生的盐水包裹体为测温对象. 通过观察发现,流体包裹体的均一温度主要分布在85~120 ℃,均一温度峰值分布在95~115 ℃(图 6),而冰点温度主要分布在-4~-2 ℃之间.
|
图 6 纸坊北地区长6—长9油层组不同产状内烃类包裹体伴生盐水包裹体均一温度直方图 Fig.6 Homogenization temperature histogram of hydrocarbon inclusions associated with brine inclusions of Chang 6-Chang 9 oil reservoirs in North Zhifang area 1—加大边(enlarged edge);2—愈合微裂隙(healed microfracture) |
烃类包裹体为烃源岩不同演化阶段形成的“黑匣子”,记录了不同阶段油气演化的原始信息,是油气源追踪的可靠且有效的地质载体和手段,因此烃类包裹体在油气成藏研究领域得到越来越广泛的重视[17-18].
单个流体包裹体激光拉曼光谱分析在西安石油大学陕西省油气成藏地质学重点实验室完成,检测仪器型号为LABHR-VISLabRAM HR800研究级显微激光拉曼光谱仪. 实验条件:Ar+激光器波长为532 nm,Yag晶体倍频固体激光器扫描范围100~4 200 cm-1;实验室温度25 ℃,湿度50%.
纸坊北地区烃类流体包裹体的激光拉曼光谱分析结果表明,研究区存在两种类型的液态烃类激光拉曼光谱:荧光类型和饱和烃类型. 其具有以下特征:1)大多数液态烃包裹体的拉曼光谱没有显著的峰值,主要为一个3 000 cm-1的宽缓的荧光拉曼峰或者2个(2 000 cm-1和3 000 cm-1)宽缓的荧光拉曼峰,因此无法从其中得出有价值的液态烃包裹体的有机组分信息;2)仍然有小部分烃类流体包裹体的荧光拉曼光谱图中显示有显著的拉曼峰值,证明此烃类流体包裹体内含有饱和烃. 研究区内这类液态烃包裹体的拉曼光谱有一个显著的峰值(2 720~2 980 cm-1区域),但是由于荧光的干扰,也有一个3 000 cm-1的宽缓的荧光拉曼峰或者2个(2 000 cm-1和3 000 cm-1)宽缓的荧光拉曼峰为背景.
2.4 油气充注期次确定流体包裹体技术已被证实在含油气盆地的运移期次研究中是一个有效的手段. 根据流体包裹体均一温度,结合精细埋藏史恢复和热史分析,可以确定不同期次油气注入的绝对时间[18-26]. 通过研究发现,与烃类流体包裹体相伴生的盐水包裹体的均一温度在80~140 ℃均有发现,且整体上无明显间断. 结合各个层位烃类流体包裹体荧光光谱特征,可以断定:研究区长6—长9油层组内油气充注是一个历史漫长且持续的过程;研究区长6—长9油藏的形成时间在距今110~130 Ma之间. 由此说明研究区油气的主要充注时间为早白垩世.
3 储层致密史与成藏史耦合关系以上根据研究区不同层位的成岩作用及其对孔隙度的影响程度,研究了不同层位储层孔隙演化史,然后根据流体包裹体的岩相学特征、均一温度测定和荧光光谱分析,并结合精细埋藏史恢复和热史分析[17, 19-29],推断了研究区长6—长9油藏石油充注的期次和时间,在此基础上分析了纸坊北地区长6—长9油藏的成岩-成藏耦合关系.
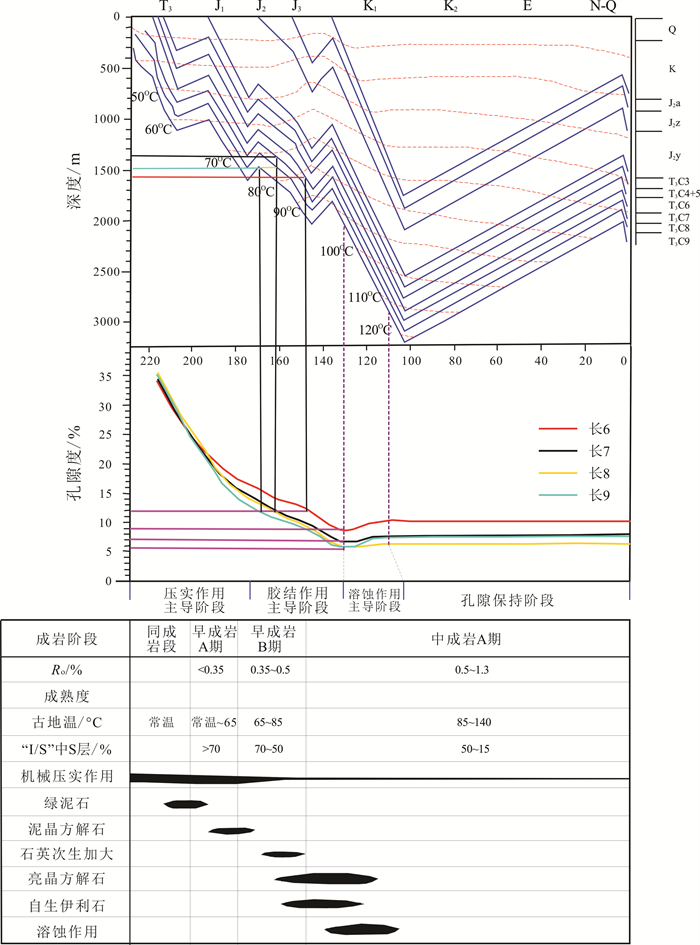
根据上述研究确定的储层孔隙度演化史和成藏时间的耦合关系可知:研究区长9储层大约在中侏罗世(168 Ma)开始致密,此时长9油藏埋深大约为1 500 m;长8和长7储层大约在中侏罗世(162 Ma开始致密),此时长8油藏埋深大约为1 500 m,长7油藏埋深约1 380 m;长6储层大约在晚侏罗世(148 Ma)开始致密,此时长6油藏埋深大约为1 580 m. 从成岩作用与成藏的耦合图(图 7)中还可以发现,研究区大约在早白垩世(130~110 Ma)进入生排烃高峰,此时研究区大量油气开始生成富集,但是此时的储层孔隙度已经致密化(长8、长9降至5.5%,长7降至7%,长6降至9%). 由此可见研究区长6—长9油藏为“先致密,后成藏”的成岩-藏耦合关系.
|
图 7 志丹油田纸坊北地区长6—长9油藏成岩-成藏耦合关系图 Fig.7 Coupling relationship between diagenesis and accumulation of Chang 6-Chang 9 reservoirs in North Zhifang area |
(1)基于铸体薄片资料的砂岩储层孔隙度演化定量计算结果表明:研究区长6—长9油层组压实减孔率介于49.80%~61.64%,胶结减孔率介于26.87%~31.65%,强烈的压实作用是研究区长6—长9油层组储层致密的主要原因.
(2)流体包裹体研究表明:研究区长6—长9油藏的形成时间在110~130 Ma之间,主成藏期为早白垩世.
(3)根据储层的成藏史与储层埋深及储层孔隙度的关系,推断纸坊北地区长6—长9油藏为“先致密、后成藏”的成岩—成藏关系.
| [1] |
郑川江, 李玉蓉, 王成龙, 等. 志丹油田三曹湾区域长6油气藏成藏条件及富集规律[J]. 非常规油气, 2019, 6(5): 1-10. Zheng C J, Li Y R, Wang C L, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and enrichment regularity of Chang-6 reservoirs in Sancaowan region of Zhidan Oilfield[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2019, 6(5): 1-10. |
| [2] |
邓秀芹, 刘新社, 李士祥. 鄂尔多斯盆地三叠系延长组超低渗透储层致密史与油藏成藏史[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2009, 30(2): 156-161. Deng X Q, Liu X S, Li S X. The relationship between compacting history and hydrocarbon accumulating history of the super-low permeability reservoirs in the Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2009, 30(2): 156-161. |
| [3] |
刘明洁, 刘震, 刘静静, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地上三叠统延长组机械压实作用与砂岩致密过程及对致密化影响程度[J]. 地质论评, 2014, 60(3): 655-665. Liu M J, Liu Z, Liu J J, et al. The relationship between the mechanical compaction and the densification process of sandstones and the affect degree of compaction to the Densifying of Yanchang Formation, Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2014, 60(3): 655-665. |
| [4] |
罗晓容, 张刘平, 杨华, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长81段低渗油藏成藏过程[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(6): 770-778, 837. Luo X R, Zhang L P, Yang H, et al. Oil accumulation process in the low-permeability Chang-81 Member of Longdong area, the Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2010, 31(6): 770-778, 837. |
| [5] |
白玉彬, 罗静兰, 王少飞, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地吴堡地区延长组长8致密砂岩油藏成藏主控因素[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(4): 1159-1168. Bai Y B, Luo J L, Wang S F, et al. The distribution of Chang-8 tight sandstone oil reservoir of Yanchang Formation in Wubao area, central south of Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40(4): 1159-1168. |
| [6] |
方欣欣, 郭迎春, 王朋, 等. 致密油成藏研究进展与待解决的重要科学问题[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(1): 43-56. Fang X X, Guo Y C, Wang P, et al. The progress of research on tight oil accumulation and several scientific issues requiring further study[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(1): 43-56. |
| [7] |
Beard D C, Weyl P K. Influence of texture on porosity and permeability of unconsolidated sand[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1973, 57(2): 349-369. |
| [8] |
张创, 孙卫, 高辉, 等. 基于铸体薄片资料的砂岩储层孔隙度演化定量计算方法——以鄂尔多斯盆地环江地区长8储层为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(2): 365-375. Zhang C, Sun W, Gao H, et al. Quantitative calculation of sandstone porosity evolution based on thin section data: A case study from Chang 8 reservoir of Huanjiang area, Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(2): 365-375. |
| [9] |
张月华, 王一刚. 构造期溶蚀作用对储层的改造及其意义[J]. 石油学报, 1991, 12(1): 17-22. Zhang Y H, Wang Y G. The dissolution in the period of structure formation in the reworking of the gas reservoir and its geological significance in Sichuan region[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1991, 12(1): 17-22. |
| [10] |
贺艳祥, 张伟, 胡作维, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区长8油层组砂岩中长石的溶解作用对储层物性的影响[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2010, 21(3): 482-488. He Y X, Zhang W, Hu Z W, et al. Affect of feldspar dissolution to properties of sandstone reservoir of Chang-8 oil layer in Jiyuan area, Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2010, 21(3): 482-488. |
| [11] |
王永田, 付兴亮, 王一航, 等. 长石溶蚀作用特征及对储层的影响——以鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区长4+5油层组为例[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版), 2017, 14(15): 9-13, 50. Wang Y T, Fu X L, Wang Y H, et al. The feature of feldspar dissolution and its influence on reservoirs: By taking Chang 4+5 reservoir of Jiyuan area in Ordos Basin for example[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 14(15): 9-13, 50. |
| [12] |
董丽红, 李欣伟, 杜彦军, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地坪北地区延长组长8、长9油层沉积特征研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2017, 26(6): 577-582, 595. Dong L H, Li X W, Du Y J, et al. Study on the sedimentary characteristics of the oil-bearing layers C-8 and C-9 of Yanchang Formation in Pingbei area, Ordos Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2017, 26(6): 577-582, 595. |
| [13] |
马立元, 邱桂强, 李超, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地镇泾地区延长组异常压力演化及其成藏意义[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(4): 503-511. Ma L Y, Qiu G Q, Li C, et al. The evolution of abnormal pressure of Yanchang Formation in Zhenjing area of Ordos Basin and its reservoir-forming significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(4): 503-511. |
| [14] |
孙樯, 谢鸿森, 郭捷, 等. 含油气沉积盆地流体包裹体及应用[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 2000, 30(1): 42-45. Sun Q, Xie H S, Guo J, et al. Fluid inclusions in sedimentary basins generating petroleum and their application[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2000, 30(1): 42-45. |
| [15] |
邵晓州, 李勇, 张文选, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陕北地区长8致密砂岩流体包裹体特征与石油成藏[J/OL]. 中国地质: 1-15. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=DIZI20200620000, 2020-06-23. Shao X Z, Li Y, Zhang W X, et al. The fluid inclusion characteristics and petroleum accumulation of Chang 8 tight sandstone in Northern Shaanxi, Ordos Basin[J/OL]. Geology in China: 1-15. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=DIZI20200620000, 2020-06-23. |
| [16] |
王思航, 陈义才, 张军帮, 等. 苏北盆地富民油田阜一段储层流体包裹体特征及成藏时期研究[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2014, 4(5): 1-5. Wang S H, Chen Y C, Zhang J B, et al. Reservoir fluid inclusion characteristics and accumulation period research of Fu-1 segment in Fumin Oilfield of North Jiangsu Basin[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2014, 4(5): 1-5. |
| [17] |
葛云锦. 碳酸盐岩烃类包裹体形成机制及其对油气成藏的响应[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2010. Ge Y J. Trapping mechanism of hydrocabon inclusion in carbonate and its response to hydrocarbon accumulation[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2010. |
| [18] |
王建华, 葛云锦, 杜克锋, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中部三叠系延长组下组合有机流体活动与关键成藏期次[J]. 能源与环保, 2020, 42(5): 55-60. Wang J H, Ge Y J, Du K F, et al. Organic fluid activity and key accumulation period of the Triassic Lower Yanchang Formation, central Ordos Basin[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2020, 42(5): 55-60. |
| [19] |
徐相涛, 张辉, 郭毅. 博湖坳陷油气成藏期次综合分析[J]. 石油天然气学报(江汉石油学院学报), 2006, 28(3): 220-223. Xu X T, Zhang H, Guo Y. Comprehensive analysis of hydrocarbon accumulation stages in Bohu Depression[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2006, 28(3): 220-223. |
| [20] |
张学军, 邹育良, 霍秋立. 流体包裹体在松辽盆地成藏期次研究中的应用[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2008, 13(4): 50-55. Zhang X J, Zou Y L, Huo Q L. Application of fluid inclusions to period research on oil and gas accumulation in Songliao Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2008, 13(4): 50-55. |
| [21] |
刘曼丽, 徐文, 黄兰, 等. 流体包裹体技术在松南气田成藏期次研究中的应用[J]. 海洋石油, 2013, 33(3): 46-49. Liu M L, Xu W, Huang L, et al. Study on hydrocarbon accumulation phases in Songnan gas field with fluid inclusion technique[J]. Offshore Oil, 2013, 33(3): 46-49. |
| [22] |
曹青, 赵靖舟, 柳益群. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部上古生界流体包裹体特征及其意义[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 43(5): 749-756. Cao Q, Zhao J Z, Liu Y Q. The characteristics of fluid inclusions in Upper Paleozoic of southeast area at Ordos Basin and their significance[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 43(5): 749-756. |
| [23] |
谭万仓. 群克构造志留系储层包裹体特征与油气成藏过程[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2018, 37(4): 38-43. Tan W C. Fluid inclusion characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation process for Silurian reservoirs in Qunke structure[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2018, 37(4): 38-43. |
| [24] |
刘润川, 任战利, 马侃, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部延长组油气成藏期次研究[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(6): 1263-1274. Liu R C, Ren Z L, Ma K, et al. Classification of hydrocarbon accumulation phases of Yanchang Formation in southern Ordos Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(6): 1263-1274. |
| [25] |
李博, 崔军平, 李莹, 等. 伊陕斜坡吴起地区延长组油气成藏期次分析[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(6): 21-28. Li B, Cui J P, Li Y, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation phases of Yanchang Formation in Wuqi area, Yishan slope[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(6): 21-28. |
| [26] |
孙宁亮, 钟建华, 倪良田, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地南部上三叠统延长组物源分析及热演化[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(3): 537-556. Sun N L, Zhong J H, Ni L T, et al. Provenance analysis and thermal evolution of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in the southern Ordos Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(3): 537-556. |
| [27] |
高岗, 梁晓伟, 朱康乐, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7段源储组合特征与油气成藏模式[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(3): 198-205. Gao G, Liang X W, Zhu K L, et al. Characteristics of source-reservoir assemblage and hydrocarbon accumulation model of Chang 7 Member in Ordos Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(3): 198-205. |
| [28] |
康昱, 陈刚, 张卫刚, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬油区铁边城区块长8储层成岩致密化及其与油气成藏关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(2): 64-75. Kang Y, Chen G, Zhang W G, et al. Diagenetic densification of Chang 8 sandstone reservoirs and its relationship with hydrocarbon accumulation in Tiebiancheng area, Jiyuan Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 64-75. |
| [29] |
黄振凯, 郝运轻, 李双建, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7段泥页岩层系含油气性与页岩油可动性评价——以H317井为例[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(1): 210-219. Huang Z K, Hao Y Q, Li S J, et al. Oil-bearing potential, mobility evaluation and significance of shale oil in Chang 7 shale system in the Ordos Basin: A case study of well H317[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(1): 210-219. |
 2023, Vol. 32
2023, Vol. 32

