东北地区是中国的主要能源基地,随着勘探研究程度的逐年提高,松辽盆地、下辽河盆地等大型含油气盆地勘探难度越来越大,亟需新的油气接替区,为国家的能源安全和可持续发展提供能源资源保障. 近些年随着辽西地区油气勘探的逐步深入,尤其是中国地质调查局在该区实施的多口地质调查井都在下侏罗统北票组获得了油气新发现[1-5],证实了下侏罗统北票组泥岩是辽西重要油气勘探层系,亦可能成为保障能源安全的油气接替区[6-10].
2017年中国地质调查局沈阳地质调查中心在牛营子凹陷北缘组织实施辽凌地1(LLD1)井钻探,首次在中元古界推覆体之下(井深1527.91~1722.78 m,未见底)钻遇下侏罗统北票组厚层泥岩(图 1)[3]. 笔者采用气相色谱、气相色谱-质谱技术[11-12],对辽凌地1井中元古界推覆体下的北票组烃源岩进行系统分析,开展生物标志化合物特征的研究,揭示其蕴含的有机质来源、形成环境、有机质热演化程度等地质意义,为辽西地区下侏罗统北票组油气地质条件研究提供支撑[13-14].
|
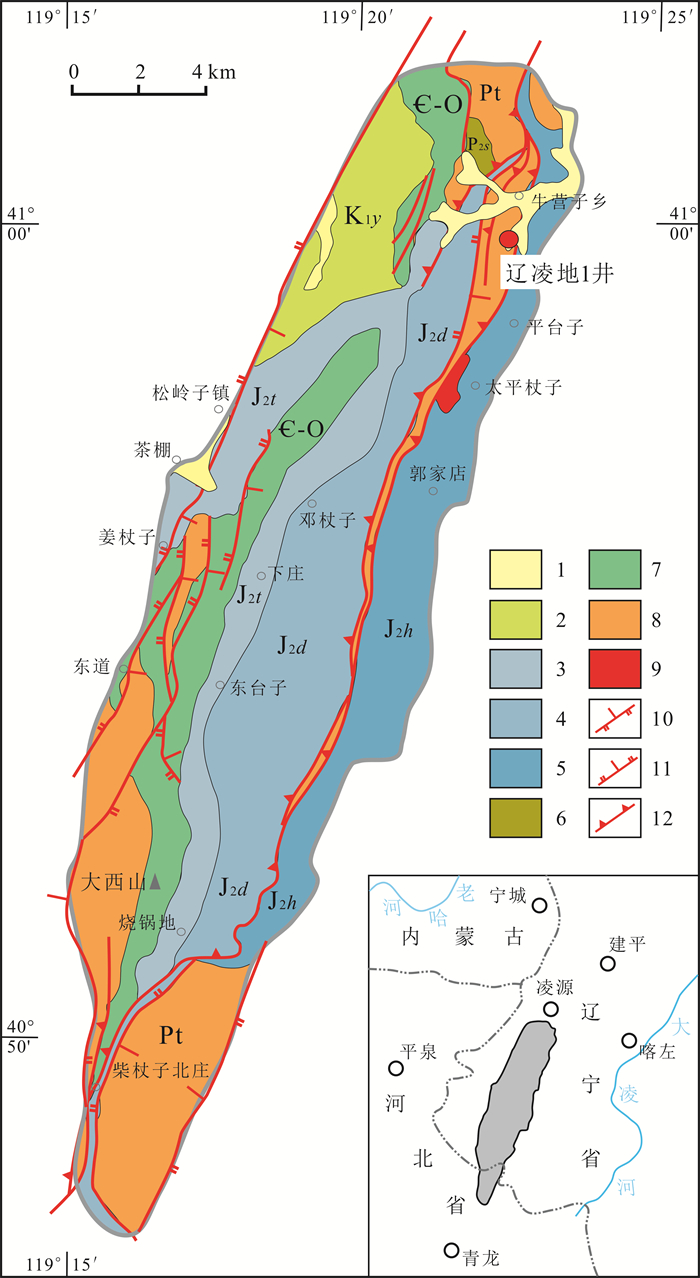
图 1 辽西牛营子凹陷地质略图(据文献[3]修改) Fig.1 Geological sketch map of Niuyingzi sag in western Liaoning (Modified from Reference [3]) 1—第四系(Quaternary);2—白垩系义县组(Cretaceous Yixian fm.);3—侏罗系髫髻山组(Jurassic Tiaojishan fm.);4—侏罗系邓杖子组(Jurassic Dengzhangzi fm.);5—侏罗系海房沟组(Jurassic Haifangou fm.);6—二叠系石盒子组(Permian Shihezi fm.);7—寒武系-奥陶系并层(Cambrian-Ordovician);8—中新元古界并层(Meso-Neoproterozoic);9—侵入岩(intrusive rock);10—逆断层(reverse fault);11—正断层(normal fault);12—逆冲推覆构造(thrust nappe structure) |
辽凌地1井揭露的推覆体下北票组地层大于194.87 m,共发育暗色泥岩12层,累计厚度为102.58 m,单层厚度大于3 m的泥岩累计总厚度为33.69 m,砂岩累计厚度92.42 m,泥地比59.79%,并见多段气测异常:该井段气测录井全烃值大于背景值2倍地层厚度为39 m;全烃最大值为10.78% [3, 15]. 本次共采集1527.91~1722.78 m井段12件暗色泥岩样品,分别进行热解、氯仿抽提、族组成分离、饱和烃色谱、饱和烃色谱-质谱等分析. 上述实验分析均在长江大学地球化学教育部重点实验室完成,测试分析方法见文献[16-17],详细数据见表 1.
|
|
表 1 辽西牛营子凹陷辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩生物标志物化合物参数表 Table 1 Biomarker compound parameters of Beipiao Formation source rocks from LLD1 well in Niuyingzi sag, western Liaoning |
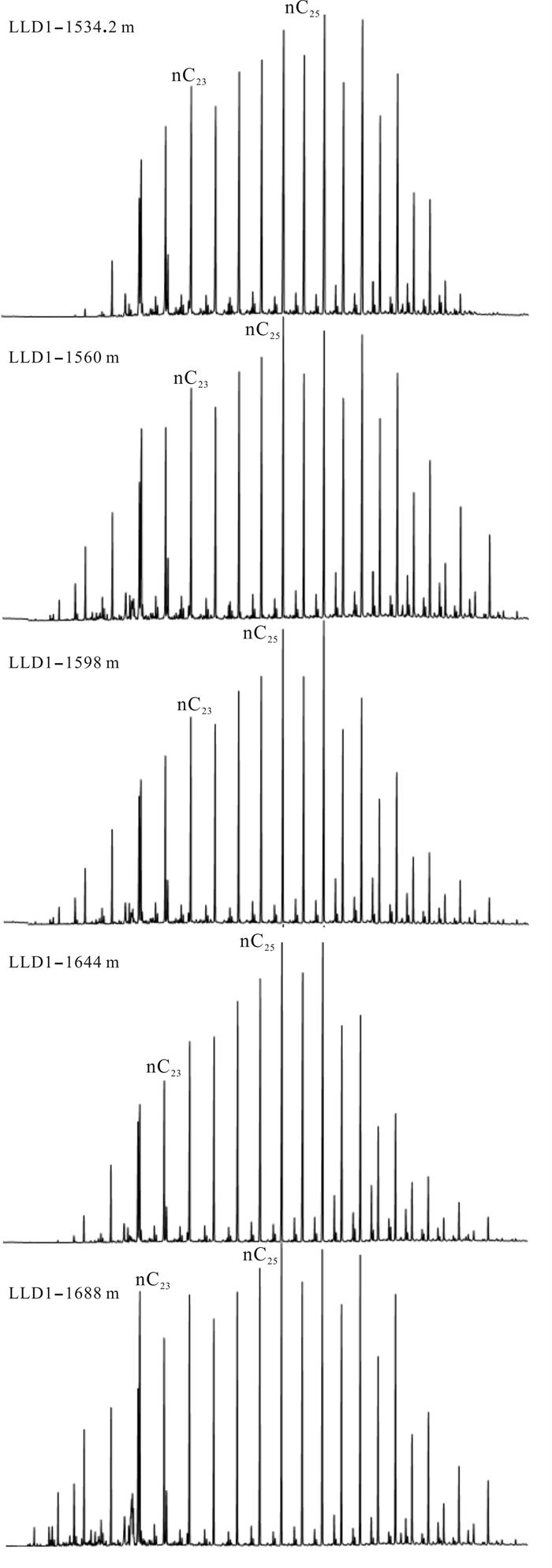
正构烷烃有无奇偶优势通常用CPI(碳优势指数)值或OEP(奇偶优势)值来表征[18-19]. 本次研究的12件LLD1井北票组烃源岩样品正构烷烃OEP值主要为1.07~1.42之间,平均值为1.26;CPI值为1.35~1.71,平均为1.57,说明奇偶优势不明显. 轻重比∑nC21-/∑nC22+变化很大,主要为0.28~0.69,平均值为0.47,主峰碳多为nC23,部分为nC25(表 1),多为后单峰型(图 2). 正构烷烃相关参数间接表征烃源岩成熟度较低,多为未熟—低熟阶段,有机质输入以陆源输入为主,有部分低等生物输入.
|
图 2 辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩质量色谱图(m/z 85) Fig.2 Gas chromatogram of Beipiao Formation source rocks from LLD1 well |
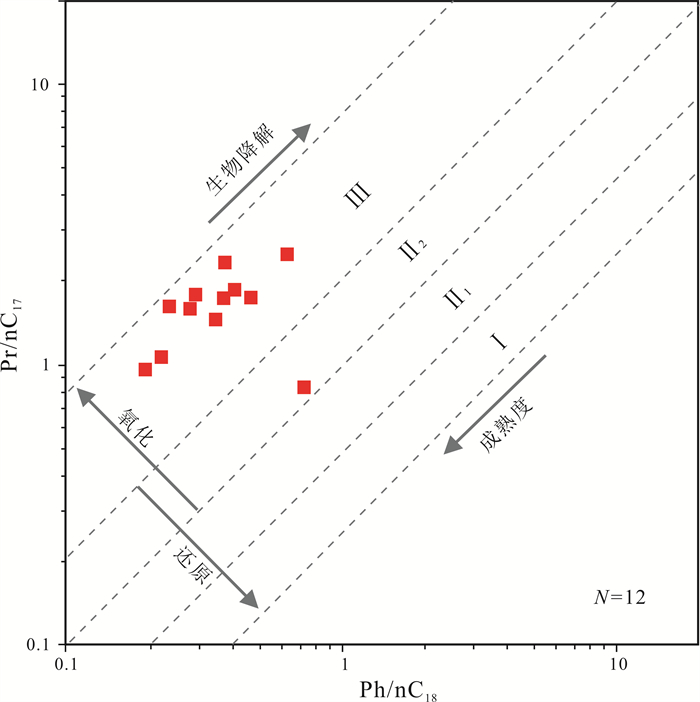
姥鲛烷(Pr)和植烷(Ph)是常用的表征古环境的生物标志化合物[20-21]. 一般而言,Pr/Ph<0.5为强还原性膏盐沉积环境;Pr/Ph=0.5~1.0为还原环境;Pr/Ph=1~2为弱还原—弱氧化环境;Pr/Ph>2者见于偏氧化性环境,如河湖及滨海沼泽或浅湖-海沉积;典型煤系地层有机质以Pr/Ph>2.5为特征,高者可达8以上. LLD1井北票组烃源岩Pr/Ph值为0.94~5.01,平均3.40,具有典型煤系地层有机质特征,形成于偏氧化性环境(表 2). LLD1井北票组烃源岩有机质类型以Ⅲ型为主,且主要集中在偏氧化的沉积环境中(图 3).
|
|
表 2 辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩气相色谱参数表 Table 2 Gas chromatographic parameters of Beipiao Formation source rocks from LLD1 well |
|
图 3 辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩姥植比Pr/nC17-Ph/nC18关系图 Fig.3 The Pr/nC17-Ph/nC18 diagram of Beipiao Formation source rocks from LLD1 well |
三环萜烷和四环萜烷系列是一类重要的生物标志化合物,它们在不同性质烃源岩中的分布和组成特征及浓度变化存在着显著差异[18]. 三环萜烷主要由微生物细胞膜中三环类异戊二烯醇形成,可能与某些菌藻类有一定的成因联系,四环萜烷一般与陆源有机输入有关.
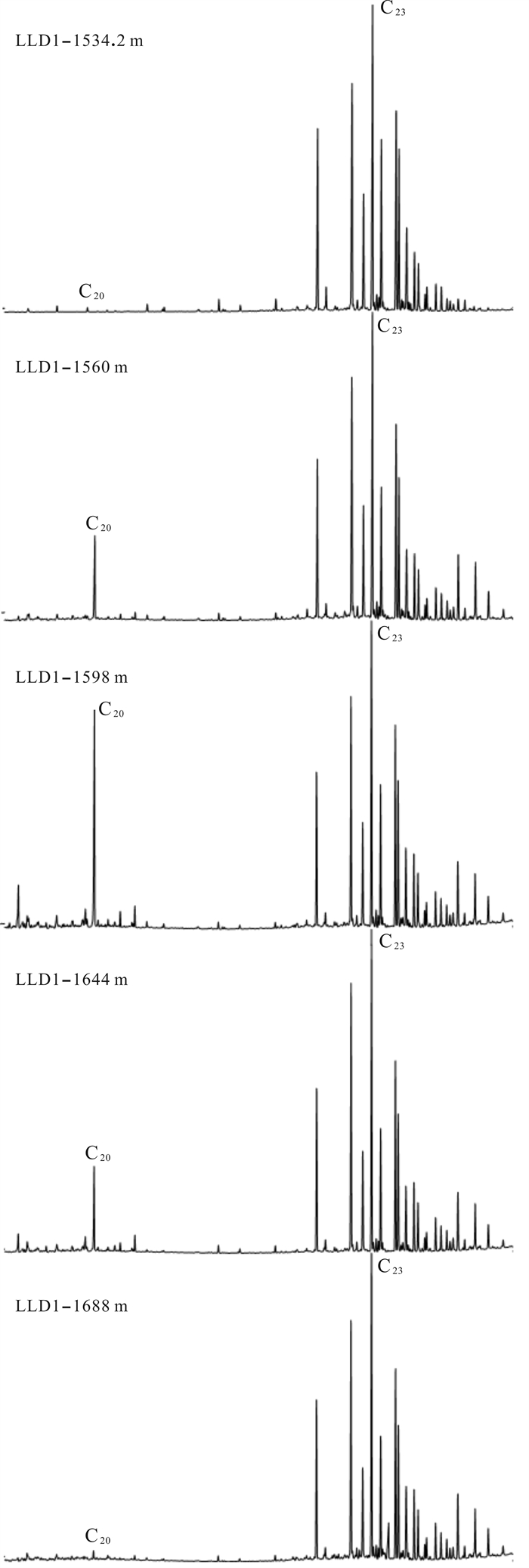
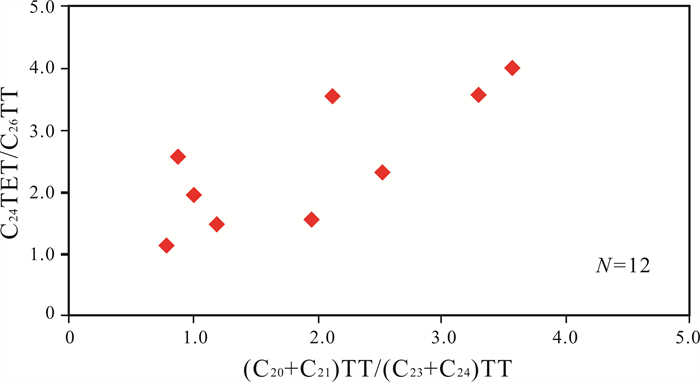
牛营子地区侏罗系烃源岩饱和烃质量色谱图m/z 191中,三环萜烷呈C20或C23为主峰的正态分布,不同深度样品中化合物的分布存在一定的差异,三环萜烷含量普遍偏低(图 4). 从C24TeT/C26TT-(C20+C21)TT/(C23+C24)TT关系图可以看出,两者呈明显线性关系. LLD1井北票组烃源岩中的C24TeT/C26TT-(C20 +C21)TT/(C23+C24)TT值整体偏高,指示一种高等植物来源,部分为低等生物来源,C24-四环二萜/C26三环萜烷比值介于1.15~5.28,平均值为2.76,表明北票组陆源高等植物贡献较为充足(图 5).
|
图 4 辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩质量色谱图(m/z 191) Fig.4 Gas chromatogram of Beipiao Formation source rocks from LLD1 well |
|
图 5 辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩三环萜烷与四环萜烷关系图 Fig.5 The C24TeT/C26TT-(C20+C21)TT/(C23+C24)TT diagram of Beipiao Formation source rocks from LLD1 well |
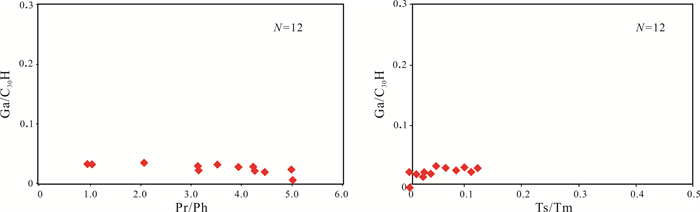
本次研究的LLD1井北票组12件烃源岩中藿烷系列化合物总体上以C30藿烷占绝对优势,C31以上化合物较低,且随碳数增高呈递减型分布,是碎屑岩有机质来源的典型特征(图 4). 伽马蜡烷指数(Ga/C30H)与姥鲛烷/植烷(Pr/Ph)关系图中,伽马蜡烷指数分布在0~0.04,平均值为0.02(图 6),反映当时的沉积环境为淡水环境. Ts/Tm(18αH-22,29,30-三降藿烷/17αH-22,29,30-三降藿烷)整体低于0.5,表征样品成熟度整体偏低.
|
图 6 辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩Ga/C30H-Pr/Ph及Ga/C30H-Ts/Tm关系图 Fig.6 The Ga/C30H-Pr/Ph and Ga/C30H-Ts/Tm diagrams of Beipiao Formation source rocks from LLD1 well |
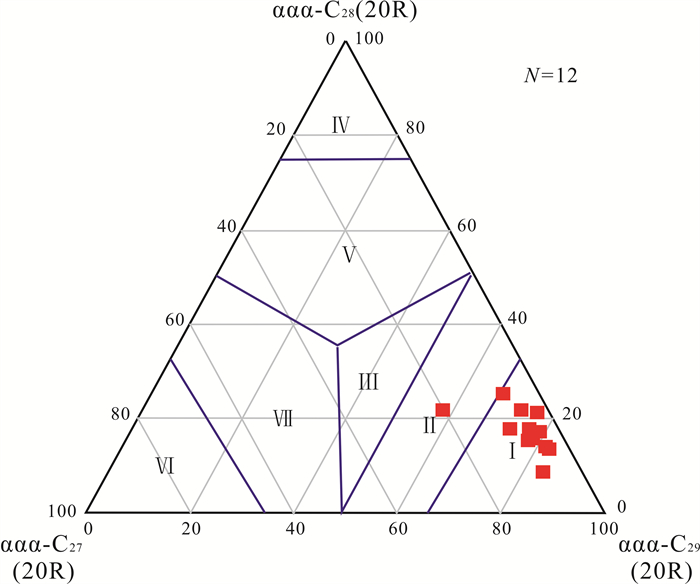
从ααα(R)构型甾烷的C27-C28-C29分布三角图(图 7)可以看出,LLD1井北票组烃源岩有机质以陆源高等植物为主,有少量低等生物输入.
|
图 7 辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩C27-C28-C29-ααα(R)甾烷分布三角图 Fig.7 The C27-C28-C29-ααα(R)diagram of Beipiao Formation source rocks from LLD1 well Ⅰ—陆生植物(terrestrial plant);Ⅱ—陆生植物为主(terrestrial plant dominated);Ⅲ—混合源(mixed source);Ⅳ—藻类(algae);Ⅴ—藻类为主(algae dominated);Ⅵ—浮游植物(phytoplankton);Ⅶ—浮游植物为主(phytoplankton dominated) |
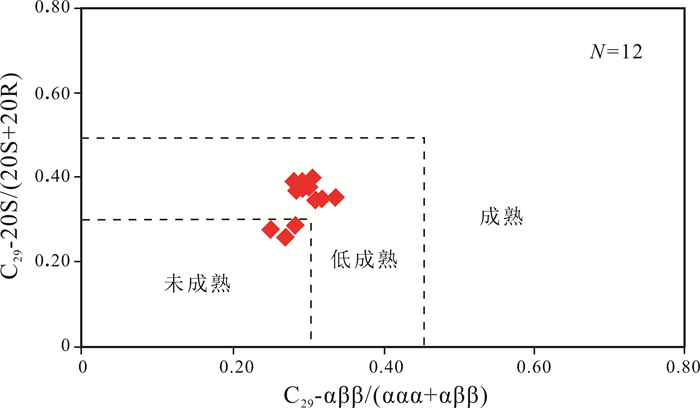
甾烷演化特征可以判断和划分有机质的热演化阶段,尤其是甾烷化合物的立体异构化比值是有效的成熟度指标[13-14]. 随着成熟度的增加,甾烷的α构型向β构型转化和生物构型R向地质构型S转化,表现为甾烷C29-αββ/(αββ+ααα)和C29甾烷ααα20S/(20S+20R)的比值逐渐增加. Peters等[21]将C29甾烷ααα20S/(20S+20R)比值为0.25和0.42分别定义为未成熟与低成熟以及低成熟和成熟的界限. LLD1井北票组样品甾烷C29-αββ/(αββ+ααα)分布于0.25~0.33,平均值0.29,C29-ααα20S/(20S+20R)分布于0.26~0.40,平均值0.34(图 8),总体反映出牛营子凹陷北票组烃源岩处于低成熟阶段,部分为未成熟. 在m/z 217质量色谱图中,样品甾烷呈现C29甾烷占优势的反“L”型,表示为高等植物输入占绝对优势(图 9).
|
图 8 辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩甾烷成熟度参数相关图 Fig.8 The sterane maturity parameter correlation diagram of Beipiao Formation source rocks from LLD1 well |
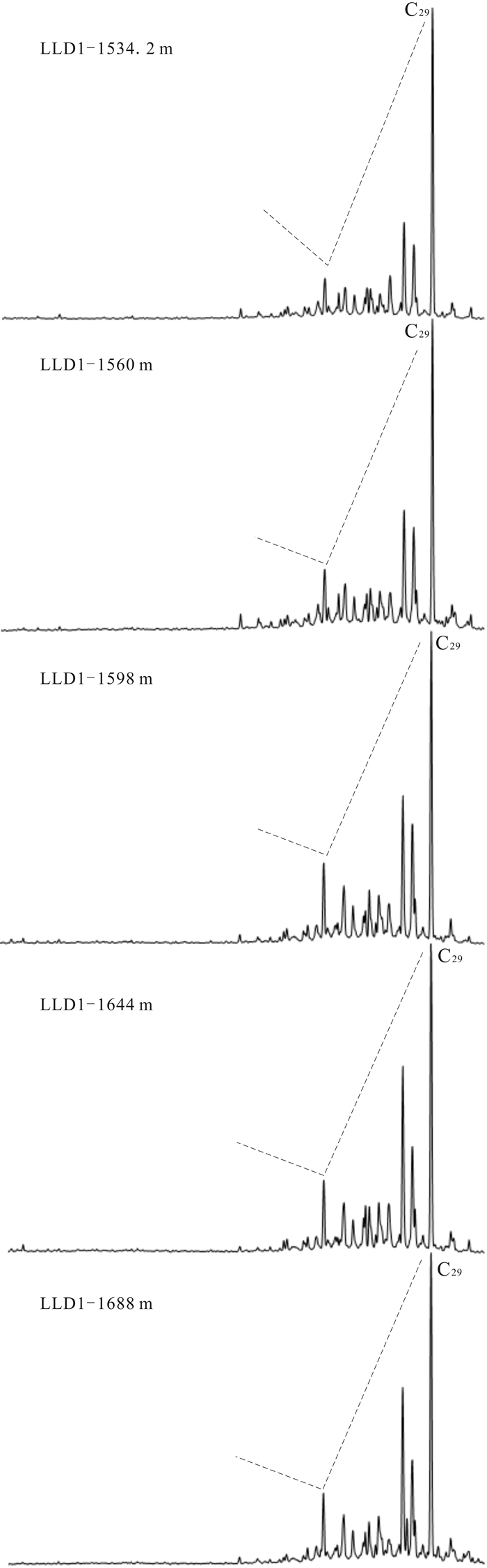
|
图 9 辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩质量色谱图(m/z 217) Fig.9 Gas chromatogram of Beipiao Formation source rocks from LLD1 well |
(1)牛营子凹陷辽凌地1井北票组烃源岩正构烷烃相关参数间接表征烃源岩成熟度较低,多为未熟—低熟阶段,有机质输入以陆源输入为主,有部分低等生物输入. 姥植比分布于0.94~5.01,平均为3.40,具有典型煤系地层有机质特征,形成于偏氧化性环境.
(2)烃源岩中的C24TeT/C26TT-(C20 +C21)TT/(C23+C24)TT值整体偏高,指示一种高等植物来源,部分为低等生物来源. C24-四环二萜/C26三环萜烷比值分布于1.15~5.28,平均值为2.76,表明其陆源高等植物贡献较为充足.
(3)烃源岩中的藿烷系列化合物以C30藿烷占绝对优势,C31以上化合物较低,且随碳数增高呈递减型分布,是碎屑岩有机质来源的典型特征. 伽马蜡烷指数分布于0~0.04,平均值0.02,反映当时的沉积环境为淡水环境. 甾烷C29-αββ/(αββ+ααα)分布于0.25~0.33,平均值0.29,C29-ααα20S/(20S+20R)分布于0.26~0.40,平均值0.34,总体反映出牛营子凹陷北票组烃源岩处于低成熟阶段,部分为未成熟. 在m/z 217质量色谱图中,样品甾烷呈现C29甾烷占优势的反“L”型,表示为高等植物输入占绝对优势.
| [1] |
李永飞, 陈树旺. 辽西地区金岭寺-羊山盆地油气资源调查新发现[J]. 地质通报, 2014, 33(9): 1463-1464. Li Y F, Chen S W. A Newly Discovered oil and gas resources in Jinyang Basin, Western Liaoning[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2014, 33(9): 1463-1464. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.09.023 |
| [2] |
陈树旺, 李永飞. 松辽盆地外围油气地质调查进展[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(4): 401. Chen S W, Li Y F. Progress of the geological survey for oil-gas in surroundings of Songliao Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(4): 401. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.04.015 |
| [3] |
孙求实, 宗文明, 王斯佳, 等. 辽西牛营子凹陷中元古界推覆体下发现早中侏罗世新地层[J/OL]. 中国地质, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20210111.1050.002.html, 2021-01-11. Sun Q S, Zong W M, Wang S J, et al. The new discovery of the Jurassic strata under the middle Proterozoic thrust-nappe in Niuyingzi depression, westhern Liaoning Province[J/OL]. Geology in China, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20210111.1050.002.html, 2021-01-11. |
| [4] |
Sun Q S, Xiao F, Gao X Y, et al. A new discovery of Mesoproterozoic erathem oil, and oil-source correlation in the Niuyingzi area of western Liaoning Province, NE China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 110: 606-620. |
| [5] |
陈树旺, 丁秋红, 郑月娟, 等. 松辽盆地外围新区、新层系——油气基础地质调查进展与认识[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(8): 1147-1158. Chen S W, Ding Q H, Zheng Y J, et al. New areas and series of strata on the periphery of Songliao Basin: The progress and recognition based on foundational geological survey for oil and gas resources[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(8): 1147-1158. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.08.002 |
| [6] |
Zhang T, Sun S L, Sun Q S, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the lower Jurassic black shales in the Jinyang Basin, northeast China: implications for organic matter accumulation[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2019, 360: 012051. |
| [7] |
Sun Q S, Gao X Y, Zong W M, et al. A newly discovered oil-bearing Mesoproterozoic Erathem within the Niu D1 well, Liaoxi depression, Yanliao faulted depression zone, NE China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2020, 94(1): 202-203. |
| [8] |
刘淼, 张渝金, 孙守亮, 等. 辽西金羊盆地北票组孢粉组合及其时代和古气候意义[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(10): 3393-3408. Liu M, Zhang Y J, Sun S L, et al. Palynological assemblages of Beipiao formation in Jinyang Basin of West Liaoning, and their age and Paleoclimatic significances[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(10): 3393-3408. |
| [9] |
孙守亮, 李永飞, 郜晓勇, 等. 辽西金羊盆地下侏罗统北票组页岩气地球化学特征及其成因[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(4): 575-581. Sun S L, Li Y F, Gao X Y, et al. An analysis of the genesis and geochemical characteristics of shale gas in Lower Jurassic Beipiao Formation in Jinyang Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2017, 36(4): 575-581. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.04.011 |
| [10] |
孙守亮, 李永飞, 孙鹏, 等. 辽西金羊盆地岩浆岩对北票组烃源岩演化影响的初步分析[J]. 地质论评, 2019, 65(S1): 175-176. Sun S L, Li Y F, Sun P, et al. Preliminary analysis of the influence of magmatic rocks on the evolution of source rocks of Beipiao Formation in Jinyang Basin, western Liaoning Province[J]. Geological Review, 2019, 65(S1): 175-176. |
| [11] |
孙鹏, 唐友军, 张坤. 辽西金羊盆地北票组一类新的油砂地球化学特征及意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(4): 335-341. Sun P, Tang Y J, Zhang K. A new type of oil sands in the Beipiao Formation of Jinyang Basin, western Liaoning Province: Geochemical characteristics and geological implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(4): 335-341. |
| [12] |
唐友军, 刘客, 孙鹏, 等. 辽西金羊盆地北票组油砂芳烃地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 17(2): 1-8. Tang Y J, Liu K, Sun P, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of aromatic hydrocarbons in oil sand of Beipiao formation in Jinyang Basin in western Liaoning Province[J]. Journal of Yangtze University(Natural Science Edition), 2020, 17(2): 1-8. |
| [13] |
孙守亮, 张涛, 刘淼, 等. 辽西金羊盆地北票组沉积环境与烃源岩成因[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2019, 43(6): 1-12. Sun S L, Zhang T, Liu M, et al. Sedimentary environment and genesis of source rocks of Beipiao Formation in Jinyang Basin, Western Liaoning[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2019, 43(6): 1-12. |
| [14] |
易勇进, 苏培东, 田振兴, 等. 金羊盆地非煤隧道油气成因及运移模式研究[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2020, 31(2): 51-56. Yi Y J, Su P D, Tian Z X, et al. Research on oil and gas genesis and migration model of non coal tunnel in Jinyang Basin[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 2020, 31(2): 51-56. |
| [15] |
孙求实, 袁杰, 宗文明, 等. 广域电磁法在辽西地区牛营子凹陷油气资源潜力评价中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(1): 64-69. Sun Q S, Yuan J, Zong W M, et al. The application of wide field electromagnetic method to the oil and gas exploration of Niuyingzi sag in Liaoxi area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(1): 64-69. |
| [16] |
蒋兴超, 陈树旺, 唐友军, 等. 内蒙古突泉盆地ZK-WJT钻井下侏罗统红旗组生烃潜力[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(8): 1236-1242. Jiang X C, Chen S W, Tang Y J, et al. The evaluation of hydrocarbon production potential of well ZK-WJT in Lower Jurassic Hongqi Formation within Tuquan basin of Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(8): 1236-1242. |
| [17] |
唐友军, 孔雪, 蒋兴超, 等. 内蒙古额济纳旗大狐狸山地区干泉组烃源岩生物标志化合物特征及意义[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(4): 652-660. Tang Y J, Kong X, Jiang X C, et al. Biomarkers of hydrocarbon source rocks of Ganquan Formation in Dahulishan area, Ejin Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2013, 32(4): 652-660. |
| [18] |
卢双舫, 张敏. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008: 201-212. Lu S F, Zhang M. Hydrocarbon geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008: 201-212. |
| [19] |
侯读杰, 冯子辉. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011: 201-242. Hou D J, Feng Z H. Hydrocarbon geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011: 201-242. |
| [20] |
Huang W Y, Meinschein W G. Sterols as ecological indicators[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1979, 43(5): 739-745. |
| [21] |
Peters K E, Moldowan J M. The biomarker guide: interpreting molecular fossils in petroleum and ancient sediments[M]. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice Hall Inc., 1993: 215-225.
|
 2022, Vol. 31
2022, Vol. 31


