2. 福建省地质调查研究院, 福建 福州 350013
2. Fujian Institute of Geological Survey, Fuzhou 350013, China
中国地质调查局2016年印发的《1:50 000区域地质调查工作指南(试行)》中明确指出: 遥感影像图是区域地质调查的重要野外工作图件, 遥感解译应贯穿区域地质调查工作的全过程. 20世纪90年代遥感技术已经在区域地质调查项目中开始推广应用[1-14]. 21世纪以来, 遥感技术突飞猛进, 影像分辨率越来越高. 充分利用遥感影像和遥感解译对提高区域地质调查的质量和效率起到非常重要的作用[15-34], 特别是在中、新生代火山岩区, 利用遥感影像圈定与火山喷发活动相关的环形构造、放射状构造, 对于火山机构的预判和发现起着至关重要的作用[35-44].
内蒙古1:5万牛汾台林场等4区调遥感解译工作采用LandSat-8多光谱数据和资源三号卫星数据. LandSat-8多光谱数据影像编号为LC81220272015291LGN00、LC81220282015291LGN00, 轨道号分别为122/027、122/028(行/列号), 影像采集时相分别为2015/10/18T02: 45: 22. 5500486Z、2015/10/18T02: 45: 46. 4343781Z, 多光谱/全色波段的空间分辨率分别为30/15 m. 影像中云、雪等的覆盖量小于全区面积的5%, 质量精度满足要求. 资源三号卫星高空间分辨率遥感数据, 影像分辨率2 m, 使用3个波段融合(红、绿、蓝), 数据位数: 8 bit. 影像中云、雪等的覆盖量小于全区面积的1%, 质量精度满足要求.
研究区属林区, 森林覆盖率达70%以上, 植被具覆盖厚、分布广、发育密的特征, 对遥感岩性地层解译工作有较大影响, 但对遥感构造解译影响较小. 因此本次遥感解译主要从线性构造、环形构造、火山机构等方面着手, 利用高分辨率遥感数据进行解译工作. 同时, 遥感技术具有地理实体表示的多样化以及多属性、动态变化的特点, 地质信息丰富, 真实客观, 宏观性强. 本次遥感解译工作以人机交互解译为主, 通过目视解译和类比分析解译方法, 分别解译线性构造、环状构造、岩石地层、侵入岩的分布及相互关系, 详细勾绘地质体, 不但可以提高整个工作区地质调查成果质量, 并且可弥补路线地质调查过程中无法涉及地区的相关地质资料收集的不足.
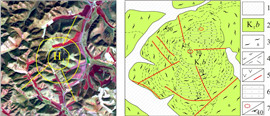
1 线性构造遥感解译与验证通过LandSat-8多光谱数据(采用7/5/3波段进行彩色合成), 解译出29条大小不等线性构造(图 1), 总体构造线方向以NE、NW向为主, NNE向次之. 不同方向构造线切割关系主要表现为: NNE向切割NE向断裂, NW向切割NE向断裂, 但局部表现为NNE向断裂切割NW向断裂, 反映区内NNE向断裂多期活动的特点.

|
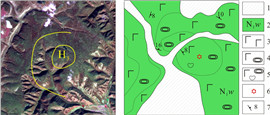
图 1 研究区遥感及解译图(LandSat-8影像, 7/5/4+8波段组合) Fig.1 Remote sensing and interpretation images of the study area (LandSat-8 image, 7/5/4+8 bands combination) 1—第四系(Quaternary); 2—新近系五叉沟组(Neogene Wuchagou fm.); 3—上侏罗统-下白垩统(Upper Jurassic-Lower Cretaceous); 4—下古生界(Lower Paleozoic); 5—早白垩世岩体(Early Cretaceous intrusive rock); 6—第四系界线(boundary of Quaternary); 7—五叉沟组界线(boundary of Wuchagou fm.); 8—岩体界线(boundary of intrusive mass); 9—大石寨组界线(boundary of Dashizai fm.); 10—断层/隐伏断层及编号(fault/concealed fault and number); 11—环状、放射状断裂及编号(ring, radial faults and number) |
通过遥感数据处理、解译, 初步推断详勘目标断层的位置, 而后进行野外测量和验证. 验证手段主要为路线地质调查和剖面测制, 对遥感解译的29条主干断裂(F1—F29)进行了重点验证, 确定了各断层性质、空间展布、产状等, 共验证发现断层11条, 其中10条表现为张性断裂, 仅F1为逆断层, 多条断层宏观表现为密集节理带. 主要线型构造验证情况见表 1. 另外18条验证为河流、冲沟等负地形, 未见明显构造形迹.
|
|
表 1 研究区主要线性构造解译标志、影像特征及验证情况表 Table 1 Image features, interpretation signs and verification of major linear structures in the study area |
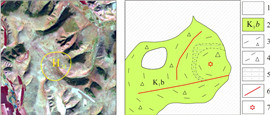
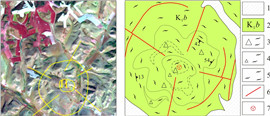
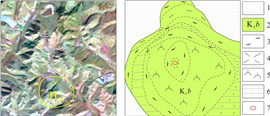
通过遥感解译, 在研究区共解译出29个与火山喷发活动相关的小型环形构造(见图 1). 区内与火山机构相关的环形构造形态复杂多变, 既有单个的环形构造, 也有两个或多个规模相近或悬殊甚大的环形构造互相作用形成的多环复合形态, 包括切接式、套接式、大环包含小环、多环交接式或多环串珠状、链状. 此外, 与环形构造配套的放射性断裂亦发育. 局部可见破碎火山口在地貌上呈凹陷, 火山机构形成的火口湖、围绕环形断裂的小型水洼地或湖泊、环形断裂造成的河流弯曲环绕以及多个或多期次火山喷发形成多个环形构造叠加的复杂形态在区内亦常见.
研究区环状断裂、弧形断裂及放射状断裂较发育, 且时常相伴产出, 与火山机构关系密切, 多分布于火山口边缘. 岩层产状的急变、节理化带、挤压破碎、断层角砾、断层泥、构造透镜体、牵引构造、小褶皱、擦痕等可作为判断依据. 对29个环形构造进行了野外实地验证, 其中H3、H8、H10、H12、H17、H18、H23、H24、H25、H28、H29等11个环形影像验证为火山机构. 野外验证详情见表 2.
|
|
表 2 研究区环形构造解译标志、影像特征及验证情况表 Table 2 Image features, interpretation signs and verification of ring structures in the study area |
由于研究区基岩出露不佳, 草场、植被等覆盖较严重, 对遥感岩性地层解译工作有较大影响, 因此本次遥感解译主要解译了第四系、新近系五叉沟组、古生界及上侏罗统—下白垩统地层的界线, 满克头鄂博组、玛尼吐组、白音高老组的界线在遥感图上无法解译. 以下仅对本区出露较好的岩石地层单元作简单介绍.
遥感解译标志是某一填图单元具代表性的遥感影像特征, 是开展全区地质解译的基础和标准, 在整个解译工作中具有控制和指导作用. 不同的填图单元由于岩石组合不同, 影像特征也在色调、形态、纹理、地貌以及水系上均有不同的特点, 可建立不同的遥感解译标志. 以LandSat-8 7/5/4-8波段经PC融合的假彩色遥感影像底图为基准影像, 通过色、形、纹、貌等特征建立了区内出露较好的岩石地层单元和侵入岩的遥感解译标志(表 3).
|
|
表 3 研究区地层岩石单元及侵入岩遥感解译标志 Table 3 Remote sensing interpretation marks of stratigraphic units and intrusive rocks in the study area |
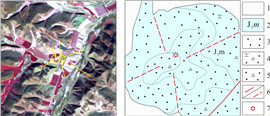
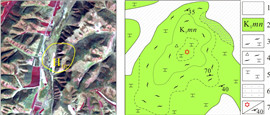
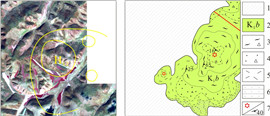
经验证, 测区内新近系五叉沟组(Ν1w)以及第四系冲洪积物解译界线与野外调查界线大致吻合; 解译古生界地层界线与验证的早古生代海勒斯台构造混杂岩界线大致相同; 中生界上侏罗统满克头鄂博组(J3m)、玛尼吐组(J3mn), 中生界下白垩统白音高老组(K1b)在遥感影像上无法区分. 另外, 早白垩世岩体经验证为早白垩世正长花岗岩.
4 地形地貌的解译传统的区域地质调查项目一般采用20世纪测绘的地形图. 此类地形图已经有几十年的历史了, 图中的村庄和道路信息变化较大, 老旧的信息已经很难满足现在智能化填图的要求. 近年来国家发射了一系列高空间分辨率的遥感卫星, 本次工作采用的资源三号卫星影像分辨率为2 m, 可以用来提取道路、水系、等高线、村庄、山峰等地形地貌的数据(表 4).
|
|
表 4 研究区地形地貌类型遥感影像特征及解译情况 Table 4 Remote sensing image features and interpretation of topographic types in the study area |
(1) 运用LandSat-8多光谱数据解译出29条大小不等断裂构造, 总体构造线方向以NE、NW向为主, NNE向次之. 野外验证发现断层11条, 另外18条验证为河流、冲沟等负地形.
(2) 解译出29个与火山喷发活动相关的小型环形构造. 野外验证发现11个火山构造, 整体环形构造在遥感平面图上形态呈圆形, 由弧形影纹、色差界面或环形沟谷、水系组成, 围绕环形构造局部发育线状影纹或水系构成的放射状断裂组合.
(3) 解译了第四系、新近系五叉沟组、古生界及上侏罗统—下白垩统地层的界线. 经实地调查验证, 五叉沟组以及第四系解译界线与野外调查界线大致吻合; 解译古生界地层界线与验证的早古生代海勒斯台构造混杂岩界线大致相同; 早白垩世岩体经验证为早白垩世正长花岗岩.
(4) 资源三号卫星高精度遥感影像适用于提取道路、水系、等高线、村庄、山峰等地形地貌的数据.
(5) 通过内蒙古1:5万牛汾台林场等4幅区调遥感解译验证, 资源三号卫星影像适合应用于地形地貌方面的解译, 而LandSat-8多光谱数据(采用7/5/3波段进行彩色合成)在解译线型构造和环状构造方面表现突出, 能达到区调工作遥感先行的目的.
| [1] |
陈昌礼. 全面推广遥感技术, 加速1:5万区域地质调查进程[J]. 国土资源遥感, 1991(2): 1-6. Chen C L. Spreading remote sensing technology overall and speeding up 1:50000 regional geological survey[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 1991(2): 1-6. |
| [2] |
周维屏. 1:50 000区调地质填图新方法[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1993. Zhou W P. The new methods of 1:50 000 regional geological mapping[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Publishing House, 1993. |
| [3] |
陈松岭. 深层断裂构造的遥感研究及其找矿意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1995, 19(3): 258-265. Chen S L. The application of remote sensing in identifying basement faults and prospecting[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1995, 19(3): 258-265. |
| [4] |
张景发, 王四龙. 鲜水河活动断裂带TM图像中雪及其影响的抑制[J]. 国土资源遥感, 1995(2): 58-63. Zhang J F, Wang S L. The methods of dispelling snow in TM image along Xianshuihe active fault zone[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 1995(2): 58-63. |
| [5] |
张景发, 王四龙, 侯孝强. 活动断裂带中遥感数字图像处理技术─ ─以鲜水河活动断裂带为例[J]. 地震地质, 1996, 18(1): 1-16. Zhang J F, Wang S L, Hou X Q. The technique of TM data image processing in the investigation of active faultzone: Xianshuihe active fault zone as an example[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1996, 18(1): 1-16. |
| [6] |
于学政, 刘刚, 李述靖. 遥感技术在内蒙古苏尼特左旗1:5万区调中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 1995, 9(2): 254-260. Yu X Z, Liu G, Li S J. Application of remote sensing technology to 1:50 000 regional geological surveying in Sonid Zuoqi area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geoscience, 1995, 9(2): 254-260. |
| [7] |
刘登忠. 遥感在天全、灵关地区区调中的应用[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 1995, 22(2): 52-56. Liu D Z. Application of remote sensing to 1:50 000 regional geological mapping in Tianquanand Lingguan, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 1995, 22(2): 52-56. |
| [8] |
刘登忠. 陆相红层盆地1:5万区调中的遥感应用研究[J]. 国土资源遥感, 1996(2): 45-50. Liu D Z. Application of remote sensing to 1:50 000 areal geological mapping in continental red bed basin[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 1996(2): 45-50. |
| [9] |
刘刚, 于学政. 浅谈遥感技术在1:5万区调中的应用[J]. 国土资源遥感, 1997(1): 14-19. Liu G, Yu X Z. The method of 1:50 000 geological mapping using remote sensing technology[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 1997(1): 14-19. |
| [10] |
刘登忠, 李斌山. 四川南江地区1:50 000遥感地质填图效果评价[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 1997, 24(2): 108-112. Liu D Z, Li B S. Comparative evaluation of remote sensing to 1:50 000 regional geological mapping in Nanjiang, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 1997, 24(2): 108-112. |
| [11] |
潘宝玉, 王贵祥. 3S技术集成及其在地质领域中的应用[J]. 山东地质, 1998, 14(4): 50-55. Pan B Y, Wang G X. Threes technical integration and their application in geological field[J]. Geology of Shandong, 1998, 14(4): 50-55. |
| [12] |
马建文, 朱章森, 杨武年, 等. 遥感数字图像处理在高山积雪覆盖地区增强成矿岩石的纹理信息[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 1998, 25(S1): 17-21. Ma J W, Zhu Z S, Yang W N, et al. The texture extraction of mineral bearing rocks using TM image data in high mountain areas with snow cover[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 1998, 25(S1): 17-21. |
| [13] |
周竞平, 吴淦国. 冀西北下双台地区构造及金矿找矿标志的遥感影像特征[J]. 国土资源遥感, 1998(3): 83-85, 96. Zhou J P, Wu G G. The image feature of structure and gold-ore marks of Xia Shuang Tai area of Hebei Province of China[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 1998(3): 83-85, 96. |
| [14] |
刘登忠. 试论遥感技术在红层1:50 000区调填图中的作用[J]. 成都理工学院学报, 1999, 26(2): 119-123. Liu D Z. A Discussion on the role of remote sensing in 1:50 000 geological mapping in red beds[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 1999, 26(2): 119-123. |
| [15] |
张洪涛, 王平. 论地质调查中的科技进步与创新[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(2): 49-54. Zhang H T, Wang P. Scientific and technological progress and innovation in the geological survey of China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(2): 49-54. |
| [16] |
隋志龙, 杨巍然, 张利华. 西藏定结幅区调工作中的断裂构造遥感研究方法探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2002, 26(4): 452-458. Sui Z L, Yang W R, Zhang L H. Discussion on fault research method using remote sensing technology: A example from Dingjie regional geological survey, Xizang[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2002, 26(4): 452-458. |
| [17] |
隋志龙, 李德威, 杨巍然, 等. 藏南拉轨岗日变质核杂岩带的TM影像特征[J]. 地球科学——中国地质大学学报, 2003, 28(6): 680-684. Sui Z L, Li D W, Yang W R, et al. Characteristic from TM image of Laguigangri metamorphic core complex zone in southern Tibet[J]. Earth Science — Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2003, 28(6): 680-684. |
| [18] |
濮国梁, 杨武年, 徐凌, 等. 数字区调新技术新方法——RS_Ortho Mapper系统研制开发[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2003, 39(22): 53- 55, 64. Pu G L, Yang W N, Xu L, et al. New method and technology in digital region geological survey: Development of RS_OrthoMapper system[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2003, 39(22): 53- 55, 64. |
| [19] |
杨武年, 廖崇高, 濮国梁, 等. 数字区调新技术新方法——遥感图像地质解译三维可视化及影像动态分析[J]. 地质通报, 2003, 22(1): 60-64. Yang W N, Liao C G, Pu G L, et al. A new method for digital regional geological survey: 3D visualization of geological interpretation of remote sensing images and image dynamical analysis[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2003, 22(1): 60-64. |
| [20] |
王润生, 熊盛青, 聂洪峰, 等. 遥感地质勘查技术与应用研究[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(11): 1699-1743. Wang R S, Xiong S Q, Nie H F, et al. Remote sensing technology and its application in geological exploration[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(11): 1699-1743. |
| [21] |
王正海, 胡光道, 刘星. 基于影像的多源地学数据融合处理及应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2004, 34(4): 617-620. Wang Z H, Hu G D, Liu X. Merging and applications of multi- sources geological data based on image[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2004, 34(4): 617-620. |
| [22] |
张克信, 孙赜, 于庆文, 等. 基于数字填图系统的遥感等数据在构造-地层分区和地层单位识别中的应用——以1:25万民和县幅、临夏市幅和定西市幅数字地质填图为例[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(7): 965-973. Zhang K X, Sun Z, Yu Q W, et al. Application of remote sensing data to the tectono-stratigraphic division and recognition of stratigraphic units based on the digital mapping system: A case study of 1:250 000 digital geological mapping of the Minhe County, Linxia City and Dingxi City sheets, northwestern China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(7): 965-973. |
| [23] |
田莉. 地质遥感中岩性的识别研究[J]. 科技传播, 2010(19): 220. Tian L. The identification research of lithology in the remote sensing geology[J]. Public Communication of Science & Technology, 2010(19): 220. |
| [24] |
赵珍梅, 马伟, 王润生. 三种高保真遥感影像融合方法效果评价与分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2010, 46(4): 705-710. Zhao Z M, Ma W, Wang R S. Evaluation and analysis of three methods of fusing remote sensing images with high fidelity of spectral information[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2010, 46(4): 705-710. |
| [25] |
吴志春, 郭福生, 刘林清, 等. 遥感技术在区域地质调查中的应用研究——以江西省1:5万陀上幅区调应用为例[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 36(4): 364-374. Wu Z C, Guo F S, Liu L Q, et al. Application of the remote sensing technology in regional geological survey: A case study in Tuoshang, Jiangxi Province by 1:50 000[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology, 2013, 36(4): 364-374. |
| [26] |
吴志春, 郭福生, 刘林清, 等. 应用遥感技术解译相山居隆庵地区水系及线性构造[J]. 东华理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2013, 32(3): 378-383. Wu Z C, Guo F S, Liu L Q, et al. Application of remote sensing technology to interpreting the river system and linear structure of Julong'an area in Xiangshan[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology, 2013, 32(3): 378-383. |
| [27] |
闫颖, 陈有炘, 孟勇, 等. 遥感技术在东天山大黑山地区地质填图中的应用[J]. 西北地质, 2015, 48(2): 231-237. Yan Y, Chen Y X, Meng Y, et al. Application of remote sensing technique in the geologic mapping of Daheishanregion, eastern Tianshan[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2015, 48(2): 231-237. |
| [28] |
张志军, 刘世华, 孔迪, 等. 北巴颜喀拉山1: 5万区域地质调查中的遥感解译应用[J]. 现代地质, 2016, 30(5): 1141-1149. Zhang Z J, Liu S H, Kong D, et al. Application of remote sensing interpretation on 1: 50 000 regional geological survey of North Bayan Hara Mountain[J]. Geoscience, 2016, 30(5): 1141-1149. |
| [29] |
赵炜, 方宏. 高分辨率影像数据在地质构造解译中的应用——以青海省俄昌公仁地区1:50 000区调应用为例[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2016, 38(3): 423-429. Zhao W, Fang H. High resolution image data in the application of the geological structure interpretation: For example Echang of Qinghai Province and the kernel region 1:50 000 area of application[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 38(3): 423-429. |
| [30] |
山克强, 潘明, 林宇. 无人机航空遥感地质解译在岩石地层单元识别中的应用——以1:50 000西南岩溶区填图试点为例[J]. 地质力学学报, 2016, 22(4): 933-942. Shan K Q, Pan M, Lin Y. Application of unmanned air vehicle (UAV) remote sensing data in the recognition of stratigraphic units: A case study of 1:50 000 pilot geological mapping of karst area in southwestern China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2016, 22(4): 933-942. |
| [31] |
李志龙, 王文博. 遥感地质信息解译工作方法研究[J]. 四川有色金属, 2018(2): 9-11. Li Z L, Wang W B. Research on interpretation of remote sensing geological information[J]. Sichuan Nonferrous Metals, 2018(2): 9-11. |
| [32] |
冯雨林, 杨佳佳, 王晓光. 基于GIS技术的水土流失遥感定量评价研究进展[J]. 地质与资源, 2018, 27(3): 279-283. Feng Y L, Yang J J, Wang X G. Research progress of quantitative evaluation on water and soil loss by remote sensing based on GIS[J]. Geology and Resources, 2018, 27(3): 279-283. |
| [33] |
卢辉雄, 聂振龙, 刘敏, 等. 基于RS和GIS的石羊河流域近50年土地覆被类型变化研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(2): 165-171, 179. Lu H X, Nie Z L, Liu M, et al. Research on land cover changes in Shiyang River basin in recent 50 years based on RS and GIS[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(2): 165-171, 179. |
| [34] |
林敏. 地质测绘中遥感技术的应用探索[J]. 四川水泥, 2020(9): 57-58. Lin M. Application of remote sensing technology in geological surveying and mapping[J]. Sichuan Cement, 2020(9): 57-58. |
| [35] |
卢清地. "火山构造-岩性岩相-火山地层"填图方法研究报告[M]. 福州: 福建省地图出版社, 2004. Lu Q D. Research report on mapping method of "volcanic structure- lithology lithofacies-volcanic stratigraphy"[M]. Fuzhou: Fujian Map Publishing House, 2004. |
| [36] |
梁涛, 罗照华, 李文韬, 等. 托云火山群的火山地质特征及其构造意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2005, 23(2): 105-111. Liang T, Luo Z H, Li W T, et al. Geologic features and tectonic implications of the Tuyon volcano group[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2005, 23(2): 105-111. |
| [37] |
许建东, 栾鹏, 樊笑英, 等. 基于遥感影像光谱与纹理分析的地物分类——以长白山天池火山地区为例[J]. 地震地质, 2009, 31(4): 607-616. Xu J D, Luan P, Fan X Y, et al. Analysis of spectrum and texture information on Changbaishan Tianchi volcano caldera and its application[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2009, 31(4): 607-616. |
| [38] |
傅树超, 卢清地. 陆相火山岩区填图方法研究新进展——"火山构造-岩性岩相-火山地层"填图方法[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(11): 1640-1648. Fu S C, Lu Q D. New progress of mapping method in the nonmarine volcanic terrain: "Volcanic construction-lithologic rock facies-volcanic strata" mapping method[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(11): 1640-1648. |
| [39] |
张柳毅, 李霓, 赵勇伟, 等. 腾冲火山区地形地貌特征及断裂制约关系——卫片与DEM解译的认识[J]. 地震地质, 2012, 34(4): 755-767. Zhang L Y, Li N, Zhao Y W, et al. Geomorphic characteristics and fault restriction in the Tengchong volcanic region: Interpretation based on DEM and TM data[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2012, 34(4): 755-767. |
| [40] |
卢清地. 陆相火山地层研究方法——"火山构造-岩性岩相-火山地层"三位一体[J]. 福建地质, 2014, 33(4): 251-261. Lu Q D. Process of nonmarine volcanic sequence research "volcanic structure-lithologic lithofacies-volcanic sequence" trinity research process[J]. Geology of Fujian, 2014, 33(4): 251-261. |
| [41] |
白卉, 曲洪晔. 遥感DEM分析在新生代火山群提取和识别中的应用[J]. 吉林地质, 2017, 36(3): 55-57. Bai H, Qu H Y. Application of remote sensing in the extraction and identification of Cenozoic volcano group based on DEM analysis[J]. Jilin Geology, 2017, 36(3): 55-57. |
| [42] |
林敏. 福建寿山火山喷发盆地火山作用特征及与叶蜡石成矿关系探讨[J]. 福建地质, 2017, 36(4): 251-261. Lin M. Study on the characteristics of volcanism of volcanic eruptive basins and the relation to pyrophyllite ore in Shoushan area, Fujian Province[J]. Geology of Fujian, 2017, 36(4): 251-261. |
| [43] |
林敏, 卢清地, 李玉娟, 等. 陆相火山岩三重填图方法研究进展及应用示例[J]. 福建地质, 2018, 37(2): 165-180. Lin M, Lu Q D, Li Y J, et al. Research progress and application examples of ternary mapping of continental volcanic rocks[J]. Geology of Fujian, 2018, 37(2): 165-180. |
| [44] |
马雨轩, 李江海, 陈耀华. 大兴安岭中段阿尔山地区第四纪火山地貌特征及其构造意义[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 55(2): 289-298. Ma Y X, Li J H, Chen Y H. Geomorphological characteristics of the Quaternary volcanoes and their tectonic implications in Aershan region, central Greater Khingan Range[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2019, 55(2): 289-298. |
| [45] |
Lin M, Yu S Y, Ma C Q, et al. Characteristics of the Hailesitai volcanic province, Inner Mongolia, and inferred magma source and tectonic setting[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55(10): 6841-6859. |
 2022, Vol. 31
2022, Vol. 31