随着我国经济的快速增长,对油气资源的需求越来越大,而剩余的常规油气资源日益减少. 松辽盆地作为我国重要油气产区,半个多世纪的连续开采使得盆地内油气勘探进入高成本、高难度阶段,面临后备油气资源不足的严重威胁[1]. 以页岩油气为代表的非常规油气资源快速兴起,已成为油气资源的重要接替领域[2]. 泥页岩不仅可以作为油气生成的烃源岩,也可以作为储集岩,其中蕴含着大量的油气资源. 松辽盆地白垩系发育沙河子组、青山口组、嫩江组等多套陆相泥页岩,是盆地主要烃源岩层,在地质历史时期生成了大量的烃类[3]. 因此,松辽盆地页岩油具有优越的成藏地质条件,资源潜力大,是未来油气勘探开发的重要接续领域[4].
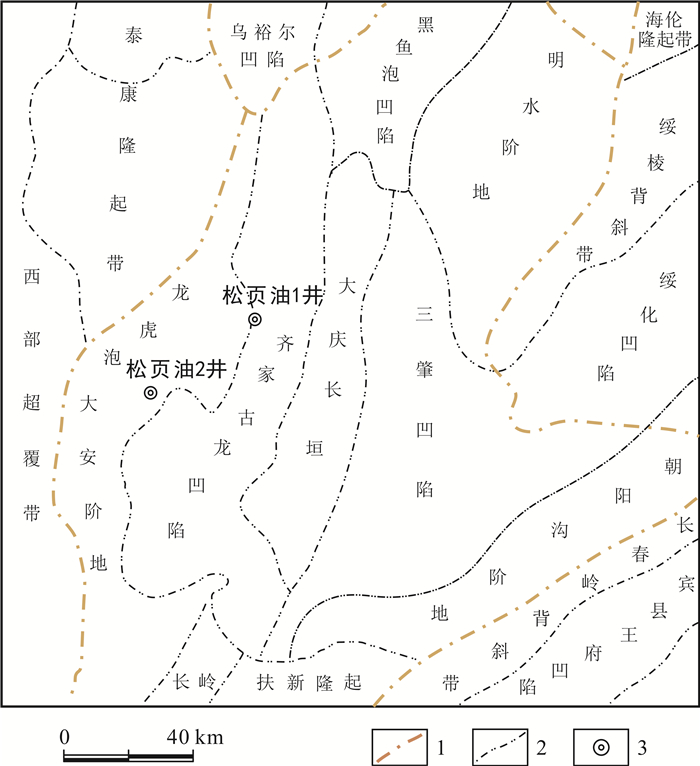
1 区域地质概况齐家-古龙地区位于松辽盆地中央拗陷区(图 1),主要表现为长期继承性发育的深水湖盆凹陷,是松辽盆地北部的主要生油凹陷[5-6],页岩油勘探开发潜力大[7]. 泉三四段沉积时期,盆地主要发育河流相红色砂泥岩互层沉积;青山口组—嫩江组沉积时期,主要为三角洲相和湖泊相沉积[8-9],广泛发育富有机质泥页岩. 上白垩统青山口组、姚家组和嫩江组一段是松辽盆地最主要的含油层系[10],盆地北部嫩江组只有部分区域进入成熟阶段,青山口组大部分区域均进入排油气阶段[11]. 综上分析可知,青山口组是页岩油勘探的重点层系. 页岩油的形成直接受到沉积环境的影响[12-15],因此有必要对齐家-古龙地区青山口组沉积微相特征开展研究.
|
图 1 松辽盆地构造分区及参数井分布(据文献[7]修改) Fig.1 Tectonic division of Songliao Basin with distribution of parameter wells Modified from Reference [7]) 1—一级构造线(first-order tectonic line);2—二级构造线(second-order tectonic line);3—页岩油参数井(parameter well of shale oil) |
松页油1井位于松辽盆地中央拗陷区齐家凹陷南部(图 1),完井井深2 547 m,取心进尺127.20 m,取心层位为泉四段上部—青二三段下部(图 2);松页油2井位于松辽盆地中央拗陷区龙虎泡-大安阶地(图 1),完井井深2 350 m,取心进尺183.37 m,取心层位主要为泉四段上部—青二三段下部(图 3). 本研究主要是通过开展两口页岩油参数井岩心大比例尺观察和描述,结合测井曲线特征,进行泉四段上部—青二三段下部沉积微相特征研究,并优选出有利于页岩油形成的沉积微相类型.
|
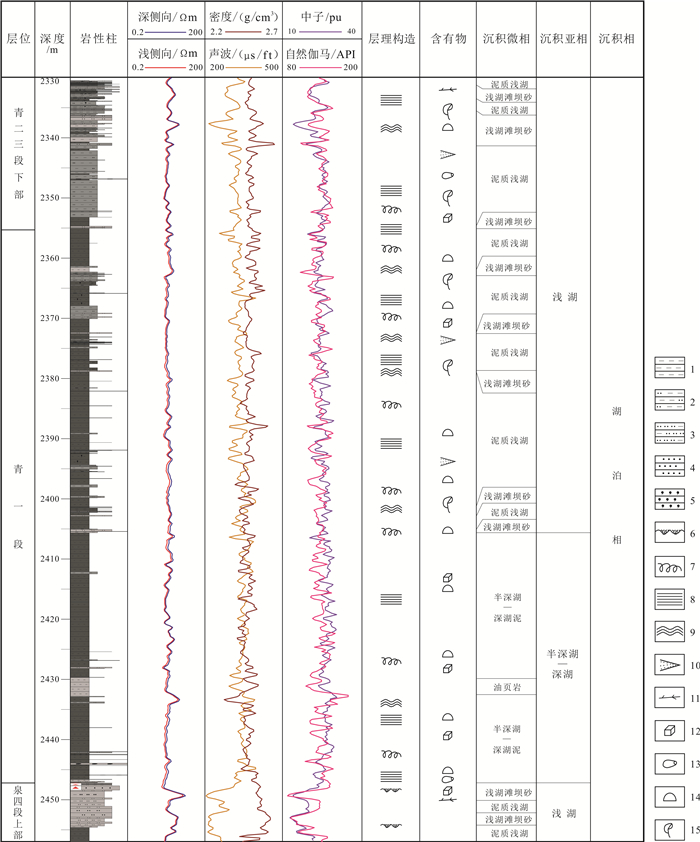
图 2 松页油1井岩心沉积微相分析柱状图 Fig.2 Sedimentary microfacies column of the core from SYY1 well 1—泥岩(mudstone);2—粉砂质泥岩(silty mudstone);3—泥质粉砂岩(argillaceous siltstone);4—细砂岩(fine sandstone);5—介形虫层(ostracoda layer);6—冲刷面(erosion surface);7—生物扰动(bioturbation);8—水平层理(horizontal bedding);9—波状层理(wavy bedding);10—砂质条带(sandy banding);11—碳屑(charcoal debris);12—黄铁矿(pyrite);13—叶肢介(conchostraca);14—介形虫(ostracoda);15—植物碎片(phytoclast) |

|
图 3 松页油2井岩心沉积微相分析柱状图 Fig.3 Sedimentary microfacies column of the core from SYY2 well 1—泥岩(mudstone);2—粉砂质泥岩(silty mudstone);3—泥质粉砂岩(argillaceous siltstone);4—细砂岩(fine sandstone);5—介形虫层(ostracoda layer);6—生物扰动(bioturbation);7—水平层理(horizontal bedding);8—波状层理(wavy bedding);9—砂质条带(sandy strip);10—泥质条带(pelitic strip);11—叶肢介(conchostraca);12—介形虫(ostracoda);13—植物碎片(phytoclast) |
根据岩心岩性、层理构造、化石、含有物、电性特征等[16-19],在松页油1井、松页油2井岩心中识别出1种沉积相——湖泊相,可进一步划分为浅湖、半深湖—深湖2种沉积亚相,以及浅湖滩坝砂、介壳滩、泥质浅湖、半深湖—深湖泥和油页岩5种沉积微相(表 1).
|
|
表 1 松页油1井和松页油2井岩心沉积微相类型划分 Table 1 Classification of sedimentary microfacies of the cores from SYY1 and SYY2 wells |
该亚相是指沉积于枯水期最低水位线至浪基面之间地带的以泥岩和粉砂岩为主的沉积相,多发育水平层理、生物扰动构造,水动力较强时沉积地层中可见波状层理. 在松页油1井、松页油2井岩心中,浅湖亚相主要分布在青二三段下部、青一段上部和泉四段上部地层,可进一步划分为浅湖滩坝砂、介壳滩、泥质浅湖3种沉积微相.
3.1.1 浅湖滩坝砂微相该微相岩性主要为深灰色、灰色粉砂岩、细砂岩、泥质粉砂岩,夹深灰色粉砂质泥岩条带和团块,局部可见介形虫化石、植物茎干化石和碳屑,发育波状(交错)层理、脉状层理(图 4),多呈中厚层状构造. 该微相主要在松页油1井和松页油2井泉四段上部和青二三段下部岩心中可见,且砂岩粒径总体偏细,说明在泉四段晚期和青二三段早期湖盆水位相对较低,由于受到波浪的作用,早期沉积的近岸砂体接受冲刷而在距离湖岸更远的浅湖地区再次沉积下来. 测井曲线上,该微相主要表现为高电阻率、低自然伽马、低声波时差、高密度的特征(图 2、3).

|
图 4 岩心浅湖滩坝砂微相沉积特征 Fig.4 Sedimentary characteristics of cores with shallow lake beach-bar sand microfacies a—松页油1井青二三段浅湖滩坝砂微相发育波状(交错)层理(shallow lake beach-bar sand microfacies with developed wavy/cross bedding in the 2nd-3rd mems. of Qingshankou fm. from SYY1 well);b—松页油2井青一段浅湖滩坝砂微相发育脉状层理和生物扰动构造(shallow lake beach-bar sand microfacies with developed flaser bedding and bioturbated structure in the 1st mem. of Qingshankou fm. from SYY2 well);c—松页油1井泉四段浅湖滩坝砂微相粉砂岩沉积,局部可见碳屑(siltstone of shallow lake beach-bar sand microfacies in the 4th mem. of Quantou fm. from SYY1 well,locally with charcoal debris);d—松页油2井泉四段浅湖滩坝砂微相粉砂岩沉积(siltstone of shallow lake beach-bar sand microfacies in the 4th mem. of Quantou fm. from SYY2 well) |
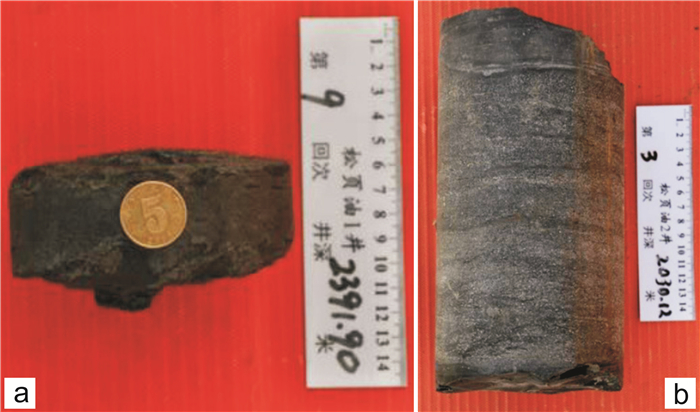
该微相主要表现为一定厚度的介形虫层沉积,介形虫壳体保存较完整,纵向上主要分布在青二三段下部—青一段上部,可能是盆地水体环境变化而导致介形虫集群死亡的结果[20-22]. 介形虫层在松页油1井岩心中局部可见,在松页油2井岩心中更常见,厚度一般在1~50 cm(图 5),主要呈薄层和中厚层状构造. 测井曲线上,该微相主要表现为高电阻率、低自然伽马、低声波时差、高密度的特征(图 2、3).

|
图 5 岩心介壳滩微相沉积特征 Fig.5 Sedimentary characteristics of cores with ostracoda beach microfacies a—松页油1井青一段介壳滩微相(ostracoda beach microfacies in the 1st mem. of Qingshankou fm. from SYY1 well);b—松页油2井青二三段下部介壳滩微相(ostracoda beach microfacies in the lower part of 2nd-3rd mems. of Qingshankou fm. of SYY2 well) |
该微相岩性主要为灰绿色、深灰色、灰黑色泥岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩,以泥质沉积为主,多夹粉砂岩条带和团块,可见介形虫、叶肢介、碳屑和植物化石碎片,发育水平层理、生物扰动构造(图 6),多呈巨厚层状或块状构造,局部层理和裂缝发育处可见黄绿色油斑. 测井曲线上,该微相主要表现出较低电阻率、较高自然伽马、较高声波时差、较低密度的特征(图 2、3).

|
图 6 岩心泥质浅湖微相沉积特征 Fig.6 Sedimentary characteristics of cores with argillaceous shallow lake microfacies a—松页油1井青二三段下部泥质浅湖微相含介形虫化石(ostracoda fossil-bearing argillaceous shallow lake microfacies in the lower part of 2nd-3rd mems. of Qingshankou fm. from SYY1 well);b—松页油2井青二三段下部泥质浅湖微相含介形虫化石团块(ostracoda lump-bearing argillaceous shallow lake microfacies in the lower part of 2nd-3rd mems. of Qingshankou fm. from SYY2 well);c—松页油1井青一段浅湖亚相可见水平层理、波状层理和介形虫层(shallow lake microfacies with horizontal bedding,wave bedding and ostracoda layer in the 1st mem. of Qingshankou fm. from SYY1 well);d—松页油2井青二三段下部泥质浅湖微相发育生物扰动构造(argillaceous shallow lake microfacies with bioturbated structure in the lower part of 2nd-3rd mems. of Qingshankou fm. from SYY2 well) |
该亚相是指沉积在浪基面以下、未受波浪和湖流搅动的静水区深水沉积物. 由于水体安静、水动力弱,故地层多发育水平层理,水体多表现为还原性. 在松页油1井和松页油2井岩心中,半深湖—深湖亚相主要分布在青一段下部,可进一步划分为半深湖—深湖泥、油页岩2种沉积微相.
3.2.1 半深湖—深湖泥微相该微相岩性以深灰色、灰黑色泥岩和粉砂质泥岩为主,局部夹粉砂质条带,含介形虫、叶肢介化石,局部可见植物化石碎片、碳屑、黄铁矿,发育水平层理,巨厚层状或块状构造,泥岩层理、裂缝发育处局部可见油浸现象或黄绿色油斑(图 7a). 测井曲线上,该微相主要表现为低电阻率、高自然伽马、高声波时差、低密度的特征(图 2、3).

|
图 7 岩心半深湖—深湖亚相沉积特征 Fig.7 Sedimentary characteristics of cores with semi-deep-deep lake microfacies a—松页油2井青一段半深湖-深湖泥微相(semi-deep-deep lake mud microfacies in the 1st mem. of Qingshankou fm. from SYY2 well);b—松页油1井青一段油页岩微相(oil shale microfacies in the 1st mem. of Qingshankou fm. from SYY1 well) |
该微相与半深湖—深湖泥微相在岩心特征上相似、不好区分,岩性主要为深灰色泥岩,发育水平层理(图 7b). 本研究主要依据测井曲线特征来识别油页岩微相. 该微相在测井曲线上主要表现为高电阻率、高自然伽马、高声波时差、低密度的特征(图 2、3).
综合分析松页油1井、松页油2井岩心中不同沉积微相的含油性特征可知,泥质浅湖微相、半深湖—深湖泥微相以及油页岩微相均是有利于页岩油形成的沉积微相类型. 这主要是与齐家-古龙凹陷青一段和青二三段下部烃源岩有机质丰度高、有机质类型较好、多处于成熟阶段、生烃潜力较大[4, 23]有关.
4 结论1)通过岩性、电性特征分析,在齐家-古龙地区松页油1井、松页油2井泉四段上部—青二三段下部岩心中,识别出1种湖泊相沉积,划分出浅湖和半深湖—深湖2种沉积亚相,并进一步划分为浅湖滩坝砂、介壳滩、泥质浅湖、半深湖—深湖泥和油页岩5种沉积微相.
2)松页油1井和松页油2井青一段下部主要发育半深湖—深湖亚相,而浅湖亚相主要分布在青一段上部、青二三段下部和泉四段上部层位.
3)泥质浅湖微相、半深湖—深湖泥微相以及油页岩微相均是有利于页岩油形成的沉积微相类型.
致谢: 感谢参与松页油1井、松页油2井科研工作的全体人员.
| [1] |
王成善. 《松辽盆地及外围油气资源地质调查专辑》序[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(3): 219-219. Wang C S. Special Issue on Geological Survey for Oil and Resources in Songliao Basin and its Periphery Areas: Preface[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(3): 219-219. |
| [2] |
王琦. 松辽盆地古龙凹陷青山口组泥页岩油资源评价[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2014: 4-5. Wang Q. The shale oil resource assessment of Gulong Sag Qingshankou Group in Songliao Basin[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2014: 4-5. |
| [3] |
徐兴友, 刘卫彬, 白静, 等. 松辽盆地南部青山口组一段页岩油富集地质特征及资源潜力[J]. 地质与资源, 2021, 30(3): 296-305. Xu X Y, Liu W B, Bai J, et al. Enrichment characteristics and resource potential of shale oil in the First Member of Qingshankou Formation in southern Songliao Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2021, 30(3): 296-305. |
| [4] |
周志, 阎玉萍, 任收麦, 等. 松辽盆地页岩油勘探前景与对策建议[J]. 中国矿业, 2017, 26(3): 171-174. Zhou Z, Yan Y P, Ren S M, et al. Prospects and strategy for shale oil exploration in Songliao Basin, China[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2017, 26(3): 171-174. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2017.03.035 |
| [5] |
王雪. 松辽盆地齐家凹陷与大庆长垣扶杨油层油源[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2006, 33(3): 294-298. Wang X. Oil sources of Fuyang oil formation in Qijia sag and Daqing placanticline, Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2006, 33(3): 294-298. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2006.03.007 |
| [6] |
申家年, 丛永山, 毛立全, 等. 松辽盆地古龙凹陷葡萄花油层超压成因[J]. 地质科学, 2009, 44(2): 502-512. Shen J N, Cong Y S, Mao L Q, et al. Mechanism of Putaohua oil layer's overpressure in the Gulong Sag, Songliao Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2009, 44(2): 502-512. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2009.02.014 |
| [7] |
李士超, 张金友, 公繁浩, 等. 松辽盆地北部上白垩统青山口组泥岩特征及页岩油有利区优选[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(4): 654-663. Li S C, Zhang J Y, Gong F H, et al. The characteristics of mudstones of Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation and favorable area optimization of shale oil in the north of Songliao Basin[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2017, 36(4): 654-663. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.04.019 |
| [8] |
高瑞祺, 蔡希源. 松辽盆地油气田形成条件与分布规律[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997: 12-46. Gao R Q, Cai X Y. Distribution and formation of oil and gas fields in Songliao Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1997: 12-46. |
| [9] |
赵陟君. 松辽盆地构造演化[J]. 内蒙古石油化工, 2015(1): 139-141. Zhao Z J. Tectonic evolution in Songliao Basin[J]. Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry, 2015(1): 139-141. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7981.2015.01.058 |
| [10] |
辛仁臣, 张翼, 张春卉, 等. 松辽盆地中部含油组合高精度层序地层格架分析[J]. 地层学杂志, 2008, 32(4): 389-396. Xin R C, Zhang Y, Zhang C H, et al. High-resolution sequence stratigraphic framework for the middle oil-bearing beds in the Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Stratigraphy, 2008, 32(4): 389-396. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2008.04.006 |
| [11] |
薛海涛, 田善思, 卢双舫, 等. 页岩油资源定量评价中关键参数的选取与校正——以松辽盆地北部青山口组为例[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(1): 70-78. Xue H T, Tian S S, Lu S F, et al. Selection and verification of key parameters in the quantitative evaluation of shale oil: A case study at the Qingshankou Formation, Northern Songliao Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(1): 70-78. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.01.008 |
| [12] |
张文正, 杨华, 杨奕华, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7优质烃源岩的岩石学、元素地球化学特征及发育环境[J]. 地球化学, 2008, 37(1): 59-64. Zhang W Z, Yang H, Yang Y H, et al. Petrology and element geochemistry and development environment of Yanchang Formation Chang-7 high quality source rocks in Ordos Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2008, 37(1): 59-64. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2008.01.008 |
| [13] |
王玉满, 董大忠, 李建忠, 等. 川南下志留统龙马溪组页岩气储层特征[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(4): 551-561. Wang Y M, Dong D Z, Li J Z, et al. Reservoir characteristics of shale gas in Longmaxi Formation of the Lower Silurian, southern Sichuan[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(4): 551-561. |
| [14] |
王阳, 陈洁, 胡琳, 等. 沉积环境对页岩气储层的控制作用——以中下扬子区下寒武统筇竹寺组为例[J]. 煤炭学报, 2013, 38(5): 845-850. Wang Y, Chen J, Hu L, et al. Sedimentary environment control on shale gas reservoir: A case study of Lower Cambrian Qiongzhusi Formation in the Middle Lower Yangtze area[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2013, 38(5): 845-850. |
| [15] |
杨振恒, 李志明, 王果寿, 等. 北美典型页岩气藏岩石学特征、沉积环境和沉积模式及启示[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010, 29(6): 59-65. Yang Z H, Li Z M, Wang G S, et al. Enlightenment from petrology character, depositional environment and depositional model of typical shale gas reservoirs in North America[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(6): 59-65. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2010.06.010 |
| [16] |
王波, 周飞, 石正灏, 等. 柴北缘冷湖构造带古近系沉积体系及演化特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(6): 543-552. Wang B, Zhou F, Shi Z H, et al. The Paleogene sedimentary system and evolution characteristics of Lenghu structural belt in northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(6): 543-552. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.06.006 |
| [17] |
符勇, 黄礼, 白玉彬, 等. 靖边油田L区块长6油层组沉积特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(1): 49-56. Fu Y, Huang L, Bai Y B, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of C-6 reservoir in L block of Jingbian oilfield[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(1): 49-56. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.01.009 |
| [18] |
张志垚, 张昌民, 侯国伟, 等. 东海盆地某凹陷P井区平湖组沉积微相及沉积模式[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(2): 142-151, 160. Zhang Z Y, Zhang C M, Hou G W, et al. Microfacies distribution and sedimentary model of Pinghu Formation in P well area, East China Sea Basin[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(2): 142-151, 160. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.02.005 |
| [19] |
张强, 郭发军, 谢俊, 等. 饶阳凹陷大王庄地区古近系东营组三段沉积微相研究[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(3): 252-259. Zhang Q, Guo F J, Xie J, et al. Sedimentary microfacies of Ed3 in Dawangzhuang area of Raoyang sag[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(3): 252-259. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.03.007 |
| [20] |
方德庆, 张艳芯. 松辽盆地北部青山口组介形类化石保存与沉积环境[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 1995, 19(4): 42-46. Fang Q D, Zhang Y X. Ostracoda fossil preservation and depositional environment in Qingshankou Formatuon in north Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute, 1995, 19(4): 42-46. |
| [21] |
杨平, 孙镇城, 李东明, 等. 柴达木盆地中、新生代介形类爆发与绝灭事件[J]. 古地理学报, 2000, 2(3): 69-74. Yang P, Sun Z C, Li D M, et al. Ostracoda extinction and explosion events of the Mesozoic-Cenozoic in Qaidam Basin, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2000, 2(3): 69-74. |
| [22] |
潘树新, 梁苏娟, 史永苏, 等. 松辽盆地上白垩统青山口组介形虫群集性死亡事件成因[J]. 古地理学报, 2010, 12(4): 409-414. Pan S X, Liang S J, Shi Y S, et al. Origin of ostracod extinction event of the Upper Cretaceous Qingshankou Formation in Songliao Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2010, 12(4): 409-414. |
| [23] |
付丽, 梁江平, 白雪峰, 等. 松辽盆地北部中浅层石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(2): 23-32. Fu L, Liang J P, Bai X F, et al. The geological conditions, resource potential, and exploration direction of oil of middle-shallow layers in the northern Songliao Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(2): 23-32. |
 2022, Vol. 31
2022, Vol. 31

