2 黑土地水土资源研究省级重点实验室, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150036;
3 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 岩石圈演化国家重点实验室, 北京 100029;
4 中国科学院青海盐湖研究所, 青海 西宁 810008;
5 中国科学院古脊椎动物与古人类研究所, 北京 100044;
6 黑龙江省地质矿产局, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150036;
7 中国科学技术大学地球和空间科学学院, 安徽 合肥 230026)
更新世期间,高纬冰量[1~3]、全球海洋温度[4]、全球海平面[5]和季风系统[6]均显示了冰期-间冰期的气候旋回特征。伴随主导周期由40 ka向100 ka转变的“中更新世转型”(mid-Pleistocene Transition,简称MPT)出现,使得早更新世晚期-中更新世早期(1200~700 ka)成为古气候学界普遍关注的重要时段[2, 7]。MPT的发生常被归因于非线性的地球轨道驱动[8]、大气CO2浓度/大洋碳库的变化[9~10]或者北半球风化层的剥蚀[11]。除了主导周期转变,约900 ka以后,高纬冰量扩张[12~13]、全球海平面下降[5]、大洋碳库的变化[9, 14]和季风系统的变化[15~17]也是其较为明显的特征。
东亚季风系统位于中-低纬度,是全球气候系统的重要组成部分,与高低纬过程均密切联系,受到太阳辐射、全球冰量、海平面和大气CO2浓度等因素的综合影响[6]。在古季风的研究中,夏季风降水常被作为指示季风强度的指标[18]。在MPT过程中,东亚夏季风降水的变化响应研究有助于更深刻认识MPT的触发机制。
基于黄土和冲积平原沉积等记录,学者们开展了大量重建夏季风降水演化的工作[19~26]。然而,不同记录、不同指标重建的MPT前后东亚夏季风降水变化趋势并不一致。基于黄土的粒度[19]和孢粉记录[20]的研究显示MPT前后夏季风降水有减弱的趋势,后被来自华北冲积平原沉积的孢粉记录研究支持[21],且在机制上与全球冰量的扩张相联系[19]。而黄土的磁化率[22~23]、碳酸盐含量[24]以及矿物或化学风化指标[25~26]的研究结果表明MPT前后夏季风降水有逐渐增加的趋势。关于降水增加这一趋势,在驱动机制方面,也存在不同解释。一些学者认为青藏高原的隆升可能起到比较关键的作用[23, 27~28];另一些学者则认为可能是热带东西太平洋海表温度变化增大,拉尼娜(La Niña)现象频率增加,从而导致东亚夏季风降水增强[26]。另外,以上大部分记录并未区分是冰期,还是间冰期的夏季风降水变化,仍需更多的记录加以研究。
湖泊记录是古气候、古环境变化研究的重要载体,因其分布广泛,在全球气候变化的区域响应研究方面独具优势[29],多被应用于晚第四纪古气候环境演化研究,尤其在全新世时段取得大量成果[30~38]。
东北平原位于东亚季风区最北缘,冬季受西伯利亚高压影响,寒冷干燥,夏季受携带低纬大洋水汽的夏季风环流控制,温暖湿润,是研究季风环流对高低纬过程响应的理想区域。已有研究发现,在早-中更新世时期,东北平原存在一个面积约为50000 km2的大湖,中-晚更新世干涸[39~42],该套湖相沉积地层的年龄为1180~450 ka[42],是研究MPT期间古气候变化的良好载体。本文利用测得的该套湖相沉积的高分辨率粒度记录重建约900 ka前后冰期夏季风降水的变化趋势,并初步探讨其与全球冰量、海平面和大西洋经向翻转流(Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation,简称AMOC)变化等因素的联系。
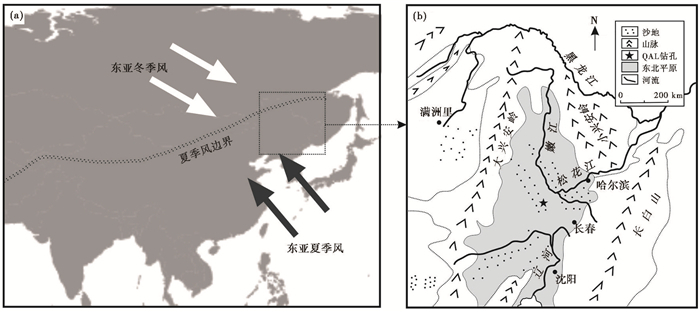
1 区域概况东北平原也称松辽平原,松辽分水岭以南为辽河平原,以北为松嫩平原,位于我国东亚季风区东北缘(图 1),西与大兴安岭接壤,北与小兴安岭紧邻,东为长白山山脉。东北平原地区沉积了巨厚的侏罗纪-白垩纪地层和420~530 m厚的古近纪-新近纪地层,以及75~200 m厚的第四纪地层[40]。
研究区处于温带和暖温带范围,属于温带大陆性季风气候,是中国湿润的东部季风区和内陆干旱区之间的过渡带。一年四季分明,夏季温热多雨,冬季寒冷干燥。7月均温21~26 ℃,1月均温-24~-9 ℃;年降水量350~700 mm,降水量的85 % ~90 %集中于暖季(5~10月)[43]。
|
图 1 QAL钻孔的地理位置(a)和东北平原放大图(b) Fig. 1 Geographic location of core QAL (a) and map of the Northeast Plain (b) |
QAL钻孔(44°49′04″N,123°48′46″E)位于吉林省乾安县城西南约50 km,地处东北平原腹地(图 1),是过去研究被认为的第四纪松嫩古大湖范围的相对中心位置[39~41]。我们于2015年采用双管单动内衬塑料套管钻探取芯技术,获得了120.54 m岩芯。本研究针对上部71 m以粉砂-粘土颗粒为主、相对较细的岩芯沉积物,开展10 cm间距的粒度研究。磁极性柱和磁化率数据引自已发表结果[42]。
粒度分析在中国地质科学院地质力学研究所第四纪环境研究室完成,所用仪器为英国Malvern公司生产的Mastersizer 2000激光粒度仪,测量范围为0.02~2000 μm,粒级分辨率为0.01,重复测试的相对误差<2 %。具体操作简述如下:取适量沉积物样品加少量30 %双氧水(H2O2),摇匀并用电热板加热至150 ℃以除去有机质,然后加入10 ml 10 %的盐酸(HCl)除去碳酸盐,静置48 h,将溶液中和后,再加入10 ml 10 %的六偏磷酸钠((NaPO3)6)分散剂,超声10 min使样品颗粒充分分散后上机测试[44]。
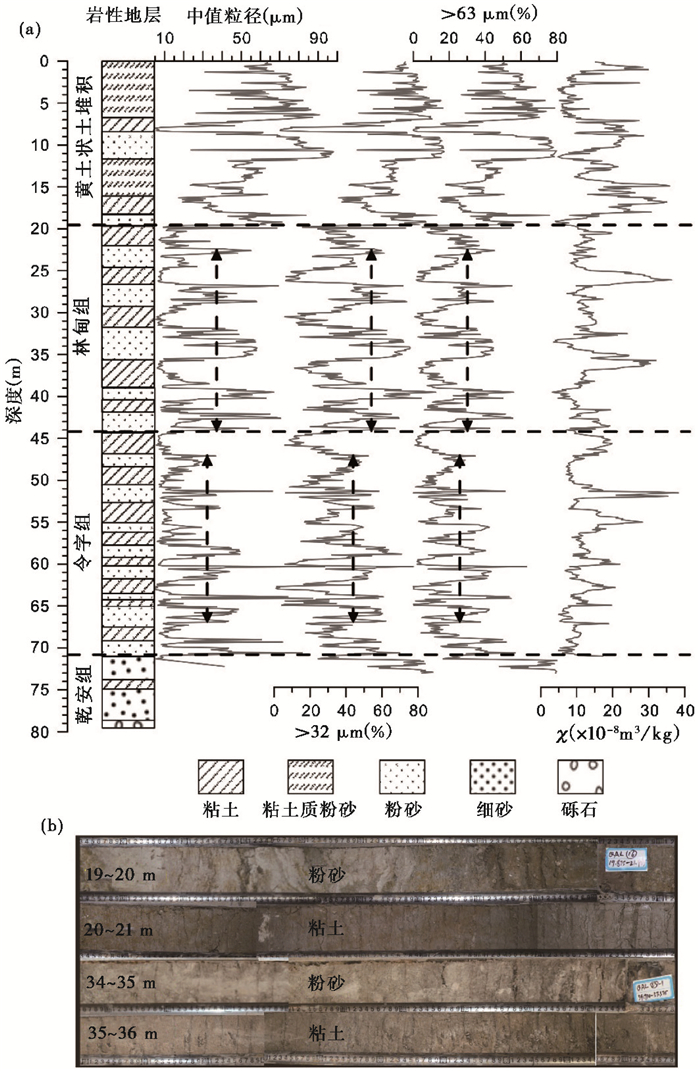
3 结果与讨论 3.1 粒度特征QAL钻孔沉积物粒度变化特征自下而上可划分为4段,并且与该孔磁化率地层也能较好对应[42],分别对应于前人划分的乾安组、令字组、林甸组和上面的黄土状土堆积阶段[40](图 2)。
|
图 2 QAL钻孔的粒度和磁化率(χ)记录(a)及特征层位岩芯照片(b) Fig. 2 The grain size and magnetic susceptibility(χ)in sediments of core QAL (a) and photos of typical layers (b) |
乾安组(80~71 m深):全钻孔最粗,上部以黄绿、棕红和灰棕色粉细砂为主,夹棕黑色粉质粘土,下部为砾石层,为河流相沉积环境。
令字组(71~44 m深)和林甸组(44~19.5 m深):为灰绿色粘土与灰白色粉砂互层,含贝壳化石,为湖泊沉积环境,为全钻孔最细,粘土含量最高。令字组和林甸组湖相沉积的粒度主要特征有两个:1)林甸组明显粗于令字组,具体表现为粉砂层中值粒径的平均值由32 μm增加至36 μm,>32 μm的百分含量由46 %增加至53 %,>63 μm的百分含量由26.7 %增加至29.7 %;2)次级波动明显,并且随岩性呈现规律性变化。
黄土状土堆积阶段(19.5~0 m深):含灰白色粉砂,棕黑色粘土层位,但较多层位出现棕黄色粘土质粉砂层,粒度急剧变粗,中值粒径变大,砂含量升高,仅次于乾安组地层;从沉积相分析该段的沉积环境表现为湖泊大面积缩小,并存在几近干涸的时期,有风成的黄土和二次搬运的黄土状土出现。
前人研究[40]显示,该区位于第四纪松嫩古大湖范围相对中心的位置,沉积物粒度的变化与湖平面的高低关系密切。面积较小湖泊沉积物的粒度可能直接受岸边降水侵蚀搬运动力的影响较大,降水越大,造成入湖碎屑颗粒越粗[45];而一般情况下,且距河口较远处,都表现为“降水少,湖平面低,湖心沉积物粒度粗”的沉积模式[44, 46~47]。对内蒙古呼伦湖(面积2338 km2)的研究显示,沉积物中值粒径大,砂含量高代表低湖面的阶段,揭示夏季风带来降水少,为冷期,反之亦然[46]。另外,在本次研究中发现,粒度粗的低湖面阶段常对应磁化率低值(图 2a),表明强/软磁性矿物含量少,弱/硬磁性矿物相对较多[42],同时,色度数据显示红度和黄度也都呈现低值(未发表数据),很可能说明此时段磁赤铁矿含量低,进而反映较弱的风化,对应干冷的冰期。综上,QAL孔的粒度能够较好地反映冰期-间冰期的变化,粒度粗对应冰期,粒度细对应间冰期。
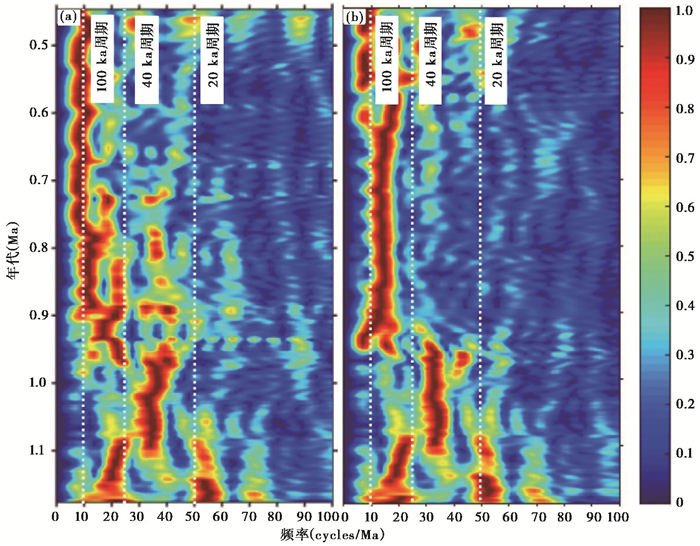
3.2 年代学之前OSL和古地磁的年代框架[42]将上部71 m地层年代定为0~1180 ka,以此为基础,建立了初步的粒度变化时间序列,并进行小波分析(图 3a)的结果显示:1)1100~920 ka期间,以约27 ka周期(对应为岁差周期)为主;2)在约980 ka时,约50 ka周期(斜率周期)出现,延续至820 ka;3)约900 ka时,约100 ka周期(应为偏心率或者冰量周期)出现。可以看出,MPT转型期间,是从约20 ka的岁差周期至约40 ka的斜率周期,再到100 ka偏心率周期的转变过程,显著的约100 ka周期为与深海氧同位素[3]对比(图 4和表 1)从而获得QAL孔更为精细的粒度时间演化序列奠定基础。年代对比后的小波分析结果显示在约900 ka出现了更为清晰的约100 ka周期(图 3b),佐证了对比年代的准确性。
|
图 3 QAL钻孔湖相沉积粒度记录的小波分析 (a)基于OSL和古地磁年代的序列;(b)与深海氧同位素对比后的序列右侧图例为能谱的色标,为无量纲,颜色越暖强度越大 Fig. 3 Wavelet power spectra for the grain size of core QAL. (a)The time series based on OSL and paleomagnetic; (b)The time series compared with benthic δ18O. The illustration on the right is the color standard of the energy spectrum, which is dimensionless. The warmer the color, the greater the intensity |
|
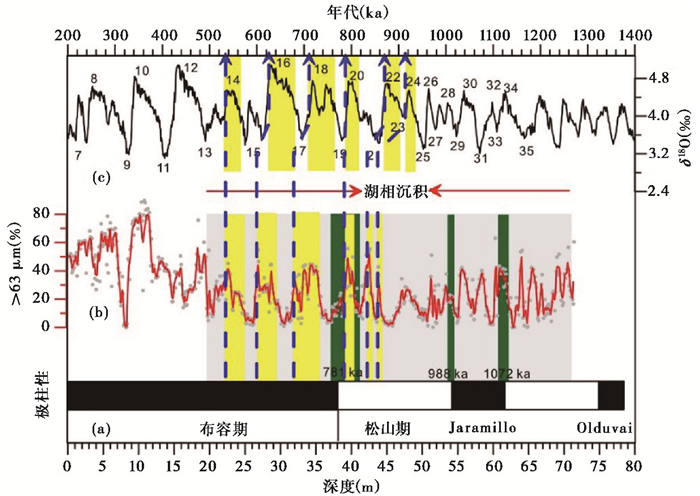
图 4
QAL钻孔湖相沉积粒度记录与海洋沉积δ18O的对比
(a)和(b)分别为QAL钻孔的磁极性柱和>63 μm百分含量;(c)海洋沉积δ18O[3] 灰色阴影表示湖相沉积层位,绿色阴影表示古地磁极性倒转界线范围,黄色阴影表示与深海氧同位素对比阶段,蓝色虚线箭头表示对比年龄控制点 Fig. 4 Comparison of grain size time series of lacustrine deposits for core QAL with benthicδ18O. (a)Polarity zonation and (b) > 63 μm percentage content of core QAL; (c)Benthic δ18O[3]. The grey interval indicates lacustrine deposits, yellow intervals indicate comparison with δ18O, green intervals show boundary range of paleomagnetic polarity reversal, and blue dotted arrows indicate controlling point of comparison age |
| 表 1 QAL钻孔湖相沉积的年龄控制点 Table 1 Age controlling points for lacustrine deposits of Core QAL |
中国黄土是季风演化研究的良好记录,在MPT以后,黄土的粒度和磁化率等指标均呈现明显的约100 ka冰量周期[18, 48]。冰期-间冰期尺度上夏季风的变化与全球冰量关系密切[24, 49],夏季风减弱对应冰期,夏季风增强对应间冰期。为此,结合以上分析,本文将QAL孔湖相沉积粒度与深海氧同位素对比(图 4),从而获得较为精确的年代序列。
QAL孔的粒度与深海氧同位素对比获得了6个年龄控制点(图 4),地磁极性倒转获得2个控制点(表 1)。对比年龄控制点的选择主要基于以下两点原则:1)控制点选择在约900 ka以后,因为此时段全球冰量出现100 ka主导周期,能够与QAL粒度记录很好对比,而约900 ka之前,基于黄土记录的夏季风演化主导周期是40 ka还是20 ka尚存在不同说法[18, 48, 50],因此无法进行明确的对比;2)控制点选择在冰期向间冰期的转变期,过渡时间较短,减小了对比误差。我们通过年龄控制点之间的线性内插获得每个样品点的年龄。
3.3 粒度重建的东亚夏季风降水演化及其驱动机制QAL钻孔湖相沉积的粒度显示,约900 ka以后,冰期的夏季风降水有明显减弱的趋势(图 5a),类似的转变也被记录在黄土高原的黄土中。尽管黄土粒度与冬季风强度关系密切[49, 51~54],但沙漠边缘黄土的砂含量也被用来指示夏季风雨带的移动[19, 55],靖边黄土剖面的砂含量约900 ka后,无论是冰期还是间冰期都变粗,指示了夏季风降水减弱[19]。朝那黄土剖面孢粉记录表明此时期从相对温湿的森林草原植被向旱生草本植物明显增加的开放型森林草原植被转变,说明气候有变干的趋势[20]。最近,华北平原钻孔孢粉揭示此时期森林向草原转变,也指示了阶段性变干的趋势,反映了夏季风降水减弱的变化[21]。
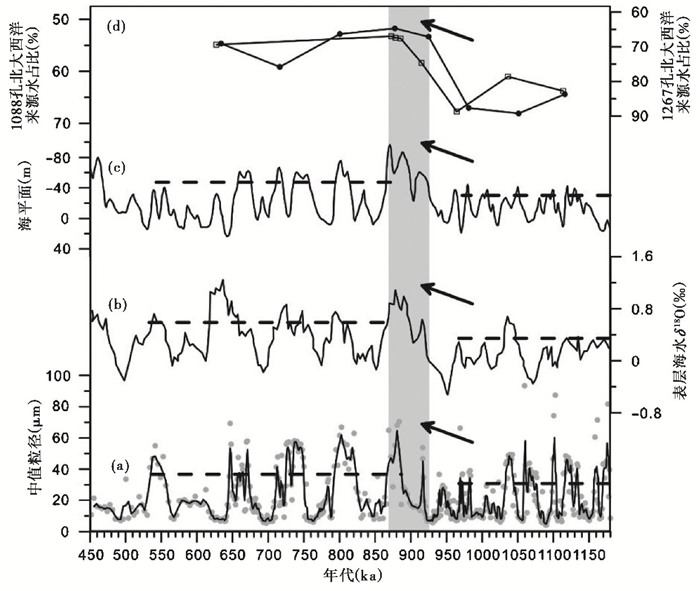
|
图 5 QAL钻孔粒度 (a)与其他记录对比(a)粒度;(b)表层海水δ18O[13];(c)海平面[5];(d)1088孔(实心圆点)和1267孔(空心方框)反映的北大西洋来源水占比[9] Fig. 5 Comparison of grain size time series of lacustrine deposits for core QAL (a) with benthic δ18O(b)[13], sea level (c)[5] and percentage of North Atlantic sourced water(NAW) (d)(solid dot 1088, hollow box 1267)[9] |
与东亚夏季风降水变化关系密切的因素主要涉及到外部因素(太阳辐射)和内部过程(全球冰量/海平面变化、AMOC的变化、大气CO2浓度和青藏高原的隆升)的相互作用。鉴于以下3点原因:1)约900 ka前后地球轨道参数并未引起北半球夏季太阳辐射明显的趋势性变化;2)青藏高原隆升对间冰期东亚夏季风具有加强作用[27~28],但冰期时高原隆升对东亚夏季风的作用尚不明确,MPT转型期间高原隆升的直接证据不足;3)大气CO2浓度通过高纬冰量影响季风,本文仅重点考虑全球冰量、海平面变化以及AMOC对东亚夏季风降水演化的影响。
全球大洋57个底栖有孔虫δ18O综合曲线反映了全球冰量的变化[3],但同时也包含大洋深水温度的信号。Ford和Raymo[13]利用底栖有孔虫Mg/Ca矫正底栖有孔虫δ18O曲线,并为了去除局域洋流和盐度的影响,综合北大西洋孔(Site 607)、北太平洋孔(Site 1028)和南太平洋孔(Site 1123)建立了表层海水δ18O曲线,从而重建了全球冰量的变化。其结果显示,约900 ka以后,全球冰量明显扩张(图 5b),但这次扩张被认为是南极冰量的变化[12~13]。
然而,南极冰量的增长会通过增强马斯克林(Mascarene)高压,进而增加跨赤道压力梯度,可能会增强印度夏季风[56]和东亚夏季风[57]。为此,全球冰量扩张的直接影响可能不是约900 ka以后东亚夏季风降水减少的主要因素。
基于地中海钻孔沉积物浮游有孔虫δ18O建立的海平面变化曲线(图 5c)也显示约900 ka后,海平面明显下降[5]。海平面下降会使黄海、东海和南海部分海域暴露成陆地[58],而我国东北地区处于东亚夏季风影响边缘区,降水会因水汽的传输距离的增加而减少。
经过海-气模式模拟,AMOC减弱会使得热带太平洋区域“热带辐合带”(Intertropical Convergence Zone,简称ITCZ)南移,在南热带太平洋区域产生厄尔尼诺(El Nio)状态,沃克环流(Walker Circulation)减弱;而在北热带太平洋区域呈现拉尼娜(La Niña)状态,沃克环流加强,ITCZ的位置沿赤道南北更加对称,进而减弱印度夏季风和东亚夏季风降水的强度[59~60]。基于北大西洋孔(Site 607)和南大西洋孔(Site 1267)冰期钕同位素比值(εNd)重建的深层水来源显示北大西洋来源水(NAW)约900 ka后明显减少(图 5d)[9],进而表明AMOC减弱,这也和南大西洋孔(Site 1090/1088)εNd和底栖有孔虫δ 13 C数据结果一致[14]。
综上,冰量扩张所造成的海平面下降和AMOC的减弱对热带太平洋区域大气环流的影响可能是造成冰期东亚夏季风降水在约900 ka以后明显减少的主要原因。
过去较长尺度东亚夏季风降水演化的重建主要是基于黄土记录的研究,然而冰期黄土粉尘大量沉积会对如磁化率以及地球化学等风化成壤指标产生影响。因此,位于东亚季风区,受季风降水影响显著的古湖沉积可能是未来长尺度季风降水演化重建的理想材料,未来应加强不同区域古湖相沉积样品的采集,实施长尺度湖泊钻探计划,弥补目前轨道尺度夏季风降水演化研究存在的不足,这将有助于对轨道尺度东亚夏季风演化动力机制的理解。
4 结论本研究以东北平原QAL孔沉积物为研究对象,在过去开展的OSL和古地磁年代,以及磁化率地层研究的基础上,重点进行粒度测试分析发现:1)湖相沉积林甸组明显较令字组颗粒粗,具体表现为粉砂层中值粒径的平均值由32 μm增加至36 μm,>32 μm的百分含量由46 %增加至53 %,>63 μm的百分含量由26.7 %增加至29.7 %,且次级波动明显,随岩性呈现规律性变化;2)中值粒径大、砂含量高,且磁化率低的层位代表低湖面的阶段,揭示夏季风带来降水少,风化弱,为冷期,反之亦然;3)基于OSL和古地磁所获得初步的粒度时间序列的小波分析结果显示约900 ka后呈现清晰的100 ka周期,为与深海氧同位素对比获得更为精细的年代序列奠定了基础;4)对比获得粒度的精细年代序列显示,约900 ka后冰期东亚夏季风降水有显著减弱的趋势。高纬冰量扩张造成的全球海平面下降导致更多陆地暴露出海平面,增加了大洋水汽的输送距离,可能是降水减弱的一个影响因素。另外,AMOC减弱会使得热带太平洋区域ITCZ南移,在南热带太平洋区域产生厄尔尼诺状态,沃克环流减弱,而在北热带太平洋区域呈现拉尼娜状态,沃克环流加强,ITCZ的位置沿赤道南北更加对称,从而减弱东亚夏季风降水的强度。
鉴于湖泊水平面变化与夏季风降水的密切联系,未来应加强东亚季风区不同区域长尺度湖泊沉积研究,弥补目前轨道尺度夏季风降水演化研究存在的不足,这将有助于对轨道尺度东亚夏季风演化动力机制的理解。
致谢: 王铠铭、王鹤、樊瑛、任明兰、李想、张晶、刘畅和刘莉莉参与样品的采集,在此一并致谢!
| [1] |
Hays J D, Imbrie J, Shackleton N J. Variations in the Earth's orbit:Pacemaker of the ice ages[J]. Science, 1976, 194(4270): 1121-1132. DOI:10.1126/science.194.4270.1121 |
| [2] |
Ruddiman W F, Raymo M E, Martinson D G, et al. Pleistocene evolution:Northern hemisphere ice sheets and North Atlantic Ocean[J]. Paleoceanography, 1989, 4(4): 353-412. DOI:10.1029/PA004i004p00353 |
| [3] |
Lisiecki L E, Raymo M E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records[J]. Paleoceanography, 2005, 20: PA1003. DOI:10.1029/2004PA001071 |
| [4] |
Herbert T D, Peterson L C, Lawrence K T, et al. Tropical ocean temperatures over the past 3.5 million years[J]. Science, 2010, 328(5985): 1530-1534. DOI:10.1126/science.1185435 |
| [5] |
Rohling E J, Foster G L, Grant K M, et al. Sea-level and deep-sea-temperature variability over the past 5.3 million years[J]. Nature, 2014, 508(7497): 477-482. DOI:10.1038/nature13230 |
| [6] |
An Z. Global monsoon dynamics and climate change[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2015, 43: 2.1-2.49. DOI:10.1146/annurev-earth-060313-054623 |
| [7] |
Raymo M E, Oppo D W, Curry W. The Mid-Pleistocene climate transition:A deep sea carbon isotopic perspective[J]. Paleoceanography, 1997, 12(4): 546-559. DOI:10.1029/97PA01019 |
| [8] |
Imbrie J, Berger A, Boyle E A, et al. On the structure and origin of major glaciation cycles 2. The 100, 000 year cycle[J]. Paleoceanography, 1993, 8(6): 699-735. DOI:10.1029/93PA02751 |
| [9] |
Farmer J R, Hönisch B, Haynes L L, et al. Deep Atlantic Ocean carbon storage and the rise of 100, 000-year glacial cycles[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2019, 12(5): 355-360. DOI:10.1038/s41561-019-0334-6 |
| [10] |
Willeit M, Ganopolski A, Calov R, et al. Mid-Pleistocene transition in glacial cycles explained by declining CO2 and regolith removal[J]. Science Advances, 2019, 5(4): eaav7337. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.aav7337 |
| [11] |
Clark P, Archer D, Pollard D, et al. The Middle Pleistocene transition:Characteristics, mechanisms, and implication for long-term changes in atmospheric pCO2[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(23): 3150-3184. |
| [12] |
Elderfield H, Ferretti P, Greaves M, et al. Evolution of ocean temperature and ice volume through the mid-Pleistocene climate transition[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6095): 704-709. DOI:10.1126/science.1221294 |
| [13] |
Ford H L, Raymo M E. Regional and global signals in seawater δ18O records across the mid-Pleistocene transition[J]. Geology, 2020, 48(2): 113-117. DOI:10.1130/G46546.1 |
| [14] |
Pena L D, Goldstein S L. Thermohaline circulation crisis and impacts during the mid-Pleistocene transition[J]. Science, 2014, 345(6194): 318-322. DOI:10.1126/science.1249770 |
| [15] |
孙有斌, 郭飞. 中国黄土记录的季风快速变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(5): 963-973. Sun Youbin, Guo Fei. Rapid monsoon changes recorded by Chinese loess deposits[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2017, 37(5): 963-973. |
| [16] |
刘瑞璇, 鹿化煜, 王珧, 等. 东阿拉伯海拉克希米盆地浊流沉积序列的粒度变化及其对中更新世气候转型的响应[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(5): 1120-1129. Liu Ruixuan, Lu Huayu, Wang Yao, et al. Grain size analysis of a depositional sequence in the Laxmi Basin(IODP Hole U1456A, Arabian Sea)reveals the Indian monsoon shift at the mid-Pleistocene Climatic Transition[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(5): 1120-1129. |
| [17] |
王海粟, 党皓文, 翦知湣. 中更新世转型时期南海北部上层水体结构演化特征——ODP1146站浮游有孔虫稳定同位素记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(2): 316-327. Wang Haisu, Dang Haowen, Jian Zhimin. Variations in the upper water structure of northern South China Sea during the mid-Pleistocene Climate Transition Period:Planktonic foraminifera oxygen isotope records of ODP site 1146[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(2): 316-327. |
| [18] |
Sun Y, Yin Q, Crucifix M, et al. Diverse manifestations of the mid-Pleistocene climate transition[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10: 352. DOI:10.1038/s41467-018-08257-9 |
| [19] |
Ding Z L, Derbyshire E, Yang S L, et al. Stepwise expansion of desert environment across Northern China in the past 3.5 Ma and implications for monsoon evolution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 237(1-2): 45-55. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.06.036 |
| [20] |
Wu F, Fang X, Ma Y, et al. Plio-Quaternary stepwise drying of Asia:Evidence from a 3-Ma pollen record from the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 257(1-2): 160-169. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.02.029 |
| [21] |
Zhou X Y, Yang J L, Wang S Q, et al. Vegetation change and evolutionary response of large mammal fauna during the mid-Pleistocene Transition in temperate northern East Asia[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2018, 505: 287-294. DOI:10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.06.007 |
| [22] |
An Z, Liu T, Lu Y, et al. The long-term paleomonsoon variation recorded by the loess-paleosol sequence in Central China[J]. Quaternary International, 1990, 7-8: 91-95. DOI:10.1016/1040-6182(90)90042-3 |
| [23] |
Zhang J, Li J, Guo B, et al. Magnetostratigraphic age and monsoonal evolution recorded by the thickest Quaternary loess deposit of the Lanzhou region, western Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2016, 139: 17-29. DOI:10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.02.025 |
| [24] |
Sun Y, An Z, Clemens S C, et al. Seven million years of wind and precipitation variability on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 297(3-4): 525-535. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2010.07.004 |
| [25] |
Chen X, Fang X, An Z, et al. An 8.1 Ma calcite record of Asian summer monsoon evolution on the Chinese central Loess Plateau[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 2007, 50(3): 392-403. DOI:10.1007/s11430-007-0016-x |
| [26] |
Meng X, Liu L, Wang X T, et al. Mineralogical evidence of reduced East Asian summer monsoon rainfall on the Chinese loess plateau during the Early Pleistocene interglacials[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2018, 486: 61-69. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2017.12.048 |
| [27] |
An Z S, Kutzbach J E, Prell W L, et al. Evolution of Asian monsoons an phased uplift of the Himalaya-Tibetan Plateau since Late Miocene times[J]. Nature, 2001, 411(6833): 62-66. DOI:10.1038/35075035 |
| [28] |
Song Y, Fang X, King J W, et al. Magnetic parameter variations in the Chaona loess/paleosol sequences in the central Chinese Loess Plateau, and their significance for the Middle Pleistocene climate transition[J]. Quaternary Research, 2014, 81(3): 433-444. DOI:10.1016/j.yqres.2013.10.002 |
| [29] |
沈吉, 薛滨, 吴敬禄, 等. 湖泊沉积与环境演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 1-473. Shen Ji, Xue Bin, Wu Jinglu, et al. Lake Sediments and Environmental Evolution[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010: 1-473. |
| [30] |
Yancheva G, Nowaczyk N R, Mingram J, et al. Influence of the intertropical convergence zone on the East Asian monsoon[J]. Nature, 2007, 445(7123): 74-77. DOI:10.1038/nature05431 |
| [31] |
An Z, Colman S M, Zhou W, et al. Interplay between the Westerlies and Asian monsoon recorded in Lake Qinghai sediments since 32 ka[J]. Scientific Reports, 2012, 2: 619. DOI:10.1038/srep00619 |
| [32] |
Xu D, Lu H, Chu G, et al. 500-year climate cycles stacking of recent centennial warming documented in an East Asian pollen record[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 3611. DOI:10.1038/srep03611 |
| [33] |
Zhou X, Sun L, Zhan T, et al. Time-transgressive onset of the Holocene Optimum in the East Asian monsoon region[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016, 456: 39-46. DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2016.09.052 |
| [34] |
Liu X, Zhan T, Zhou X, et al. Late onset of the Holocene rainfall maximum in Northeastern China inferred from a pollen record from the sediments of Tianchi Crater Lake[J]. Quaternary Research, 2019, 92(1): 1-13. DOI:10.1017/qua.2019.4 |
| [35] |
范佳伟, 肖举乐, 温锐林, 等. 内蒙古达里湖沉积记录的中晚全新世干旱事件[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(3): 701-716. Fan Jiawei, Xiao Jule, Wen Ruilin, et al. Middle to Late Holocene drought events recorded by the sediments from Dali Lake, Inner Mongolia[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(3): 701-716. |
| [36] |
崔巧玉, 赵艳. 大兴安岭阿尔山天池湖泊沉积物记录的全新世气候突变[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(6): 1346-1356. Cui Qiaoyu, Zhao Yan. Climatic abrupt events implied by lacustrine sediments of Arxan Crater Lake, in the central Great Khingan Mountains, NE China during Holocene[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(6): 1346-1356. |
| [37] |
张菀漪, 张静雅, Nusrat Nazir, 等. 青藏高原东北缘冬给错纳湖全新世湖面波动[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(4): 1018-1033. Zhang Wanyi, Zhang Jingya, Nusrat Nazir, et al. The records of Donggi Cona lake-level fluctuations since the Holocene in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(4): 1018-1033. |
| [38] |
李婷, 张虎才, 蔡萌, 等. 抚仙湖全新世自生碳酸盐及其区域气候和湖泊水位指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(3): 642-654. Li Ting, Zhang Hucai, Cai Meng, et al. The composition of carbonate matters in the sediments from Lake Fuxian and significance of paleoclimate and water level changes[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(3): 642-654. |
| [39] |
裘善文, 夏玉梅, 李凤华, 等. 松辽平原第四纪中期古地理研究[J]. 科学通报, 1984, 29(3): 172-174. Qiu Shanwen, Xia Yumei, Li Fenghua, et al. Mid-Quaternary paleogeography of Songliao Plain of China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1984, 29(3): 172-174. |
| [40] |
裘善文, 夏玉梅, 汪佩芳, 等. 松辽平原更新世地层及其沉积环境的研究[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1988, 18(4): 431-442. Qiu Shanwen, Xia Yumei, Wang Peifang, et al. Pleistocene stratigraphy and sedimentary environment in Songliao Plain of China[J]. Science in China(Series B), 1988, 18(4): 431-442. |
| [41] |
裘善文, 王锡魁, 张淑芹, 等. 松辽平原古大湖演变及其平原的形成[J]. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32(5): 1011-1021. Qiu Shanwen, Wang Xikui, Zhang Shuqin, et al. The evolution of the large paleolake in Songliao Plain and its formation[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32(5): 1011-1021. |
| [42] |
詹涛, 曾方明, 谢远云, 等. 东北平原钻孔的磁性地层定年及松嫩古湖演化[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(11): 1179-1190. Zhan Tao, Zeng Fangming, Xie Yuanyun, et al. Magnetostratigraphic dating of a drill core from the Northeast Plain of China:Implications for the evolution of Songnen paleo-lake[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(11): 1179-1190. |
| [43] |
贺伟, 布仁仓, 熊在平, 等. 1961-2005年东北地区气温和降水变化趋势[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(2): 519-531. He Wei, Bu Rencang, Xiong Zaiping, et al. Characteristics of temperature and precipitation in Northeastern China from 1961 to 2005[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(2): 519-531. |
| [44] |
张龙吴, 张虎才, 常凤琴, 等. 云南异龙湖沉积物粒度空间变化特征及其环境指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(5): 1159-1170. Zhang Longwu, Zhang Hucai, Chang Fenqin, et al. Spatial variation characteristics of sediment size and its environmental indication significance in Lake Yilong, Yunnan Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(5): 1159-1170. |
| [45] |
Yan H, Sun L, Oppo D W, et al. South China Sea hydrological changes and Pacific Walker Circulation variations over the last millennium[J]. Nature Communications, 2011, 2: 293. DOI:10.1038/ncomms1297 |
| [46] |
Xiao J, Chang Z, Wen R, et al. Holocene weak monsoon intervals indicated by low lake levels at Hulun Lake in the monsoonal margin region of northeastern Inner Mongolia, China[J]. The Holocene, 2009, 19(6): 899-908. DOI:10.1177/0959683609336574 |
| [47] |
吴铎, 周爱锋, 张家武, 等. 我国季风边缘区湖泊沉积记录的全新世亚洲夏季风衰退事件[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(3): 665-677. Wu Duo, Zhou Aifeng, Zhang Jiawu, et al. Abrupt decreasing of Holocene Asian summer monsoon recorded by lake sediments from monsoon margin[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(3): 665-677. |
| [48] |
Sun Y, Chen J, Clemens S C, et al. East Asian monsoon variability over the last seven glacial cycles recorded by a loess sequence from the northwestern Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2006, 7: Q12Q02. DOI:10.1029/2006GC001287 |
| [49] |
Hao Q, Wang L, Oldfield F, et al. Delayed build-up of Arctic ice sheets during 400, 000-year minima in insolation variability[J]. Nature, 2012, 490: 393-396. DOI:10.1038/nature11493 |
| [50] |
Ding Z, Derbyshire E, Yang S L, et al. Stacked 2.6-Ma grain size record from the Chinese loess based on five sections and correlation with the deep-sea δ18O record[J]. Paleoceanography, 2002, 17(3): 5-1-5-21. DOI:10.1029/2001PA000725 |
| [51] |
Ding Z, Liu T, Rutter N, et al. Ice-volume forcing of the East Asia winter monsoon variation in the past 800, 000 years[J]. Quaternary Research, 1995, 44(2): 149-159. |
| [52] |
杨石岭, 丁仲礼. 黄土高原黄土粒度的空间变化及其古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(5): 934-944. Yang Shiling, Ding Zhongli. Spatial changes in grain size of loess deposits in the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for palaeoenvironment[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2017, 37(5): 934-944. |
| [53] |
李涛, 李高军. 斜度驱动第四纪冰期-间冰期转换——来自中国黄土的证据[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(5): 1111-1119. Li Tao, Li Gaojun. Obliquity pacing of deglaciations in the Pleistocene:Evidence from the Chinese loess deposits[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(5): 1111-1119. |
| [54] |
郭飞, 王婷, 刘宇明, 等. 临夏黄土记录的26万年来季风快速变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(3): 557-564. Guo Fei, Wang Ting, Liu Yuming, et al. Rapid Asian monsoon changes recorded by loess depositions in Linxia since 260 ka B.P.[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(3): 557-564. |
| [55] |
Yang S, Ding Z. Advance-retreat history of the East-Asian summer monsoon rainfall belt over Northern China during the last two glacial-interglacial cycles[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 274(3): 499-510. |
| [56] |
An Z, Clemens S, Shen J, et al. Glacial-interglacial Indian summer monsoon dynamics[J]. Science, 2011, 333(6043): 719-723. DOI:10.1126/science.1203752 |
| [57] |
Koutsodendris A, Sachse D, Appel E, et al. Prolonged monsoonal moisture availability preconditioned glaciation of the Tibetan Plateau during the mid-Pleistocene transition[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(23). DOI:10.1029/2018GL079303 |
| [58] |
Nakagawa T, Okuda M, Yonenobu H, et al. Regulation of the monsoon climate by two different orbital rhythms and forcing mechanisms[J]. Geology, 2008, 36(6): 491-494. DOI:10.1130/G24586A.1 |
| [59] |
Zhang R, Delworth T L. Simulated tropical response to a substantial weakening of the Atlantic thermohaline circulation[J]. Journal of Climate, 2005, 18(12): 1853-1860. DOI:10.1175/JCLI3460.1 |
| [60] |
Sun Y, Clemens S C, Morrill C, et al. Influence of Atlantic meridional overturning circulation on the East Asian winter monsoon[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2012, 5(1): 46-49. DOI:10.1038/ngeo1326 |
2 Key Laboratory of Black Soil and Water Resources Research of Heilongjiang Province, Harbin 150036, Heilongjiang;
3 State Key Laboratory of Lithospheric Evolution, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029;
4 Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xining 810008, Qinghai;
5 Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100044;
6 Heilongjiang Bureau of Geology & Mineral Resources, Harbin 150036, Heilongjiang;
7 School of Earth and Space Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, Anhui)
Abstract
The mid-Pleistocene transition(MPT) is characterized by not only the transition of the ice cycles from 40 ka to 100 ka, but also changes in amplitude of high latitude ice sheet, global sea level and CO2/ocean carbon storage after ca. 900 ka, which exert profound influence on the evolution of the East Asian summer monsoon. However, there are different views on the trend of the East Asian summer monsoon precipitation(EASMP) during this period and its driving mechanism. Previous studies based on grain size and pollen percentages in loess indicate a decreasing trend of the EASMP after MPT, which is supported by pollen record from alluvial sediments in North China. This trend was linked to the expansion of global ice volume. On the contrary, results of magnetic susceptibility, carbonate content, minerals and chemical weathering indices of loess show that the EASMP after MPT increased gradually. The increasing trend of the EASMP was related to different forcing factors, including the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau, and the increasing of the sea surface temperature variability in the tropical East-West Pacific Ocean and the frequency of La Niña phenomenon.Upon published chronology from paleomagnetism and OSL(optically stimulated luminescence) dating, a new EASMP record was reconstructed in this paper on the basis of grain size in sediments from Core QAL(44°49'04″N, 123°48'46″E), with 120.54 m drilling depth. The grain size of the samples from 0~71 m were analysed with 10 cm intervals. The results show that:(1) There are relative fine-grained lacustrine sediments(19.5~71.0 m) during 1180~450 ka, with coarser grains, whose average value in silty sand layer is median particle size 36 μm, >32 μm percentage content 53%, >63 μm percentage content 29.7% in Lindian Formation and finer ones, whose average value in silty sand layer is median particle size 32 μm, >32 μm percentage content 46%, >63 μm percentage content 26.7% in Lingzi Formation; (2) Grain size of the sediments increased during the glacial periods, showing low lake levels and less EASMP; (3) 100-ka cycle is obvious after ca. 900 ka, corresponding well with benthic δ18O record; (4) Glacial precipitation decreased obviously after ca. 900 ka. The decreasing of the global sea level, caused by the expansion of ice sheet in high latitude, led to more land exposure and longer transport distance of ocean water vapor, might be the main cause of the EASMP reduction. In addition, the weakening of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation(AMOC) will cause the southward movement of the Intertropical Convergence Zone(ITCZ) in the tropical Pacific, which will produce El Niño conditions in the southern tropical Pacific region, and weaken Walker circulation, but put the northern tropical Pacific region under La Niña conditions, strengthening the Walker circulation. ITCZ is more symmetrical along the equator. Thus, it weakens the intensity of the EASMP.Paleolacustrine deposition can be applied to reconstruct long timescale EASMP changes. In the future, more studies on paleolacustrine deposition in different regions of the East Asian monsoon region should be carried out to reconstruct the long-term evolution of the summer monsoon, which will contribute to the understanding of the dynamic mechanisms of changes in summer monsoon on orbital timescale. 2020, Vol.40
2020, Vol.40
