2 自然资源部第一海洋研究所, 海洋地质与成矿作用重点实验室, 山东 青岛 266061;
3 青岛海洋科学与技术试点国家实验室, 海洋地质过程与环境功能实验室, 山东 青岛 266237;
4 泰国普吉 海洋生物中心, 普吉 83000;
5 泰国海洋和海岸资源研究中心, 曼谷 74000)
亚洲大陆边缘有巨量的陆源物质输入[1],对这些陆源沉积物“源-汇”过程的研究成为了近年来地学界的研究热点[2]。对亚洲大陆边缘沉积物物源的研究能够帮助我们认识陆源沉积物组成,追踪沉积物从源到汇的运移途径,从而了解亚洲大陆边缘物质交换、环境演化的规律[3~8]。
元素地球化学方法是沉积物物源研究常用的方法[9~13]。首先,氧化还原敏感元素的沉积受海洋氧化还原条件的控制,因此可以利用沉积物中氧化还原敏感元素的含量和变化特征重建古海洋沉积环境的氧化还原状态[14]。稀土元素的化学活动性较弱,在风化剥蚀、搬运、沉积过程中不易受到外界影响而发生迁移,因此能够较好地反映出沉积物的原始特征,用于物源恢复[15~16]。
泰国湾位于南海西南缘,是热带地区半封闭型陆架海。泰国湾周围分布多条大型入海河流,每年携带1亿吨以上的陆源物质入海[17~18]。泰国湾在冰期低海面时出露为陆地,其上河流广布[19~20],冰消期海平面上升以来,湾内沉积了厚度从数十厘米到三十米不等的沉积体[21~22]。这些沉积物保存了丰富的高分辨率地质记录,为研究末次冰消期以来海洋环境演化提供了优越的条件。
研究显示,泰国湾表层沉积物以粉砂为主,砂、粉砂和粘土组分分别占19 %、67 %和14 % [23]。粘土矿物中伊利石最多,平均占50 %,其次是高岭石(34 %)和绿泥石(14 %),蒙皂石含量最少(2 %)[24]。优势重矿物为菱铁矿、普通角闪石和褐铁矿,三者平均含量总和达到70.6 % [25]。常量元素中,Al2O3平均占9.71 %,主要富集于西部苏梅岛附近,而在泰国湾南部和北部含量较低,Fe2O3、MgO、K2O、Na2O、TiO2、Cr、V、Zn、Co、Ni、Cu、Pb等元素分布与Al2O3相似;CaO和Sr在北部的曼谷湾和南部的宋卡附近出现高值区,在泰国湾西部沿岸含量很低[23]。稀土元素平均总量为137.21 μg/g,在泰国湾东北沿岸和苏梅岛区域出现高值中心[26]。泰国湾现代沉积可以划分3个主要沉积区,分别为西北部的泰国沿岸海域、中部海域和靠近马来西亚的南部海域,主要物质来源分别为中南半岛、南海南部和马来半岛[23~24]。国际上对泰国湾的研究起步较晚,前人已在泰国湾沉积物物源研究上取得了一些成果,但大多数研究集中于现代沉积,对地质历史上泰国湾沉积物物源变化与沉积环境演化还不深入,缺乏高分辨率的沉积记录研究。因此,本文旨在利用采自泰国湾西部的T93沉积物柱状样品,通过元素地球化学手段来探究末次冰消期以来泰国湾沉积物来源的变迁历史。
1 研究区概况泰国湾位于中南半岛和马来半岛之间,经纬度范围从5°~13°30′N到99°~106°E,总面积约35000 km2,湾内水深平均45.5 m[27]。泰国湾受季风影响显著,夏季盛行西南季风,环流基本呈顺时针方向,冬季盛行东北季风,北部环流转变为逆时针方向(图 1)。泰国湾周边有多条较大的入海河流(表 1),其中最北部流入曼谷湾的昭披耶河(Chao Phraya River)、湄干河(Mae Klong River)、塔钦河(Ta Chin River)和邦巴功河(Bang Pakong River)是泰国湾北部及西北部沿岸陆源物质的主要贡献者[25],南部的吉兰丹河(Kelantan River)和彭亨河(Pahang River)位于马来半岛,是泰国湾南部陆源物质的主要贡献者[28]。此外,还有西部沿岸的他彼河(Tapi River)、北大年河(Pattani River),越南南部的湄公河(Mekong River)等。

|
图 1 泰国湾地理概况(a)与现代沉积物输运趋势(b) 环流资料引自Buranapratheprat和Bunpapong[29],现代沉积物输运趋势引自张杨硕等[30] Fig. 1 Geographical situation (a) and the moving trend of bottom sediments (b) of the Gulf of Thailand. Mean surface current is modified from Buranapratheprat and Bunpapong[29], the moving trend of bottom sediments are from Zhang, et al.[30] |
泰国湾沉积物主要陆源区中,中南半岛受到古特提斯洋壳俯冲影响,构造和岩性较复杂,包括陆源弧安山岩、洋岛玄武岩、花岗岩等[31~33],而马来半岛吉兰丹河流域主要是三叠纪海相沉积岩、第四纪沉积物[34]。末次冰期,泰国湾海平面比现代低100 m以上,泰国湾乃至整个巽他陆架出露成陆地,中南半岛和马来半岛相连[35~36]。冰消期之前,陆架上发育古湄南-柔佛河、古巽他河等大河流系,存在深达40 m的下切河谷[37],陆源物质丰富。约14300 cal.a B.P.,海平面开始快速上升,巽他陆架东部开始发生海水入侵,12700 cal.a B.P.前后泰国湾南部、中部和西北部局部地区被海水淹没,到10800 cal.a B.P.泰国湾大部分区域都已成为海洋环境[22]。约4000~6000 cal.a B.P.,海平面上升至最高点,高出现代海平面2.5 m以上,在此之后,海平面稍有下降,至1000 cal.a B.P.左右趋近于现代水平[22, 38],形成高位沉积体系。
2 材料与方法 2.1 研究材料T93重力柱状样采自泰国湾西部的苏梅岛附近,经纬度为9.9261°N,100.6442°E(图 1),样品于2012年5月22日由泰国科考船SEAFDEC采集,全长381 cm,采样水深59 m。从环流角度来看(图 1),泰国湾环流大致可分为西部沿岸流、北部曼谷湾区域环流、泰国湾中部主体环流3个部分,而苏梅岛恰好处在这3个环流范围交接的海域。在冬季泰国湾南部洋流北上至此处分为东西两支流,曼谷湾内洋流南下至此处;夏季泰国湾南部洋流北上至苏梅岛以南,围绕苏梅岛形成一个逆时针的局部环流,而曼谷湾内海水很难到达这里。另外泰国湾中部大范围的底质沉积物都有向苏梅岛聚集的趋势,北部曼谷湾内少量物质可以经由曼谷湾东北部,从泰国湾东侧运移至此[30]。T93柱状样品位置优越,与泰国湾整体和各个局部联系紧密,在地质历史时期随气候变化,其对于物源变化的响应较为敏感。
T93柱状样的年代、粒度、颜色反射率测试已由张杨硕[39]完成。将AMS 14C测试结果校正并换算成日历年,建立T93重力柱状样的年代框架(图 2),柱样平均沉积速率为26.9 cm/ka。柱样底部(14640 cal.a B.P.)到243 cm(7885 cal.a B.P.)的沉积速率仅20.4 cm/ka,之后沉积速率突增,163~243 cm(5660~7885 cal.a B.P.)高达36 cm/ka;接下来的81~163 cm岩段(2500~5660 cal.a B.P.)沉积速率在24.2~28.3 cm/ka之间,21~81 cm(783~2500 cal.a B.P.)大幅提升为34.9 cm/ka,柱样顶部0~21 cm(0~783 cal.a B.P.)沉积速率约为26.8 cm/ka。根据每一段的平均沉积速率,插值获得每个层位沉积物的年代(图 2),其中341 cm以下部分为外插。得到T93柱状样的底层年龄约为距今14640 a,样品取样平均年代间隔约为375 a。
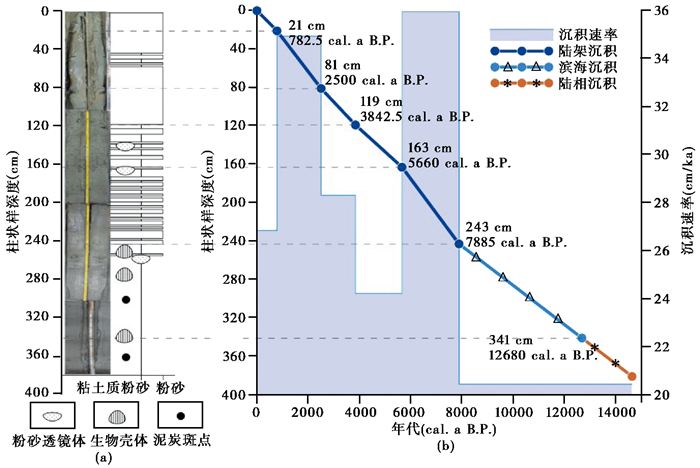
|
图 2 T93柱状样沉积概况(根据张杨硕[39]数据绘制) (a)沉积柱状图;(b)沉积速率及沉积相 Fig. 2 The sedimentation of T93 core(modified from Zhang[39]). (a)Sedimentary column; (b)Sedimentary rate and sedimentary facies |
T93柱状沉积物平均粒径6.96 ϕ,以粉砂和粘土为主,砂组分 < 1 %。380~341 cm段沉积物为褐黑色粘土质粉砂,总体为陆相沉积;341~243 cm段沉积物为粘土质粉砂,褐黑色变淡,总体为滨海沉积;243~81 cm段沉积物包括灰绿色粉砂和粘土质粉砂,属陆架沉积;81~0 cm段为较均一的灰绿色粉砂,属陆架沉积[39]。
2.2 实验步骤按照10 cm间隔取样,每份样品厚2 cm,共取得38个样品进行了元素地球化学测试。样品冻干后,用干筛法筛分,取 < 0.1 mm部分并研磨至200目。在超净化学实验室内称取粉末样品约0.5 g,加入2 ml浓度为0.25 N的盐酸,振荡并放置24 h以除去样品中的碳酸盐。使用超纯蒸馏水洗去残留的盐酸,烘干。称取干样50 mg,用超纯水润湿后,加入1.5 ml浓硝酸和1.5 ml氢氟酸,在190 ℃下密闭加热溶样。溶样完毕后蒸干,加入浓硝酸和Rh内标溶液(500 μg/kg),密闭置于150 ℃烘箱内12 h。冷却后用2 %的硝酸定容,摇匀。常量元素及部分微量元素(Ba、Cu、Sr、V、Zn、Zr)由ICP- OES测试,其他微量元素含量由ICP-MS测试,共测试9种常量元素和42种微量元素含量,包括14种稀土元素。每10个样品加测一个重复样,并使用标准样品GSD9-1监控测试质量,测试的相对误差 < 6 %。样品的分样和元素分析测试工作均在自然资源部第一海洋研究所海洋地质与成矿作用重点实验室完成。
3 结果 3.1 常微量元素含量变化沉积物常量元素除SiO2之外,Al2O3含量最高,平均14.23 %;其次为Fe2O3,平均4.55 %,Al2O3和Fe2O3平均占沉积物总量的18 % (图 3)。其余常量元素平均含量按从多到少的顺序为MgO(1.95 %)、K2O(1.87 %)、TiO2 (0.84 %)、Na2O(0.50 %)、CaO(0.26 %)、P2O5 (0.05 %)和MnO(0.04 %)。微量元素中含量最高的是Zr,平均达到267.74 μg/g,其次是Ba,平均为258.67 μg/g,其他含量较高的元素有Rb(168.13 μg/g)、V(77.42 μg/g)、Cr(75.12 μg/g)、Li(70.58 μg/g)、Zn(60.72 μg/g)、Sr(51.77 μg/g)等。利用化学风化指数(CIA)可以评估沉积物受化学风化的程度[40~41],公式为CIA=[Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO*+Na2O+K2O)]×100,其中CaO*代表硅酸盐中的CaO含量[42]。由于在样品处理过程中已经去除了碳酸钙,因此测试结果中的CaO含量可以直接用于计算CIA。样品CIA平均约84.22,代表沉积物受到了强烈的化学风化[43]。U/Th比值平均为0.19,表明样品始终沉积于强烈的氧化环境中[44]。
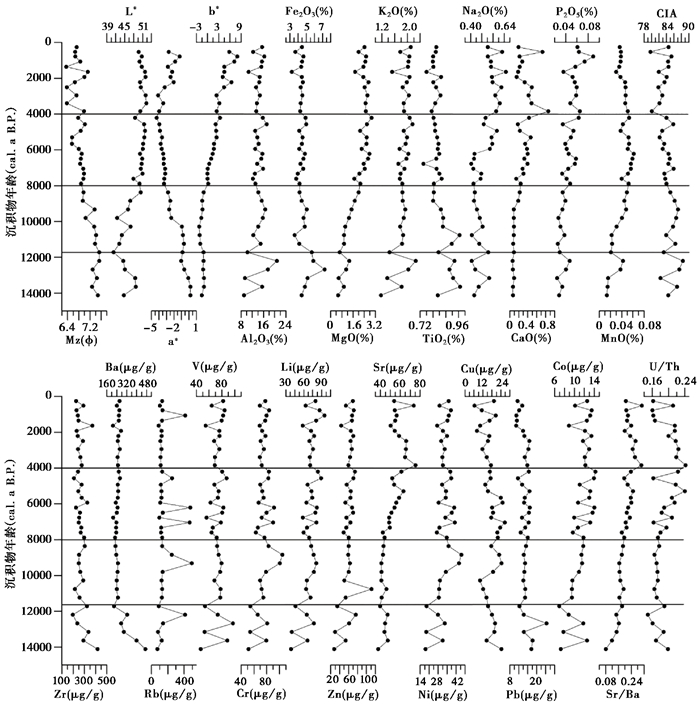
|
图 3 常微量元素垂向分布特征粒径和颜色反射率数据引自张杨硕[39] Fig. 3 Distribution characteristics of major and trace elements(grain size and color reflectance of sediment are from Zhang[39]) |
沉积物的稀土元素总量(ΣREE)在112.86 μg/g到178.49 μg/g之间,平均149.76 μg/g。轻稀土元素总量(ΣLREE)在102.07 μg/g到160.00 μg/g之间,平均为134.88 μg/g,重稀土元素总量(ΣHREE)在10. 79 μg/g到18. 49 μg/g之间,平均为14. 89 μg/g。ΣLREE/ΣHREE平均为9. 09,沉积物富集轻稀土,这通常被认为是陆源碎屑的标志[45]。以球粒陨石数据进行标准化[46],(La/Yb)n平均为8. 97,(La/Sm)n和(Gd/Yb)n平均值分别为4.43和1.32。δEu在0.56到0.65之间,平均为0.60,沉积物具有较明显的铕异常;δCe值在0.92到0.99之间,平均为0.96,铈异常不明显(图 4)。
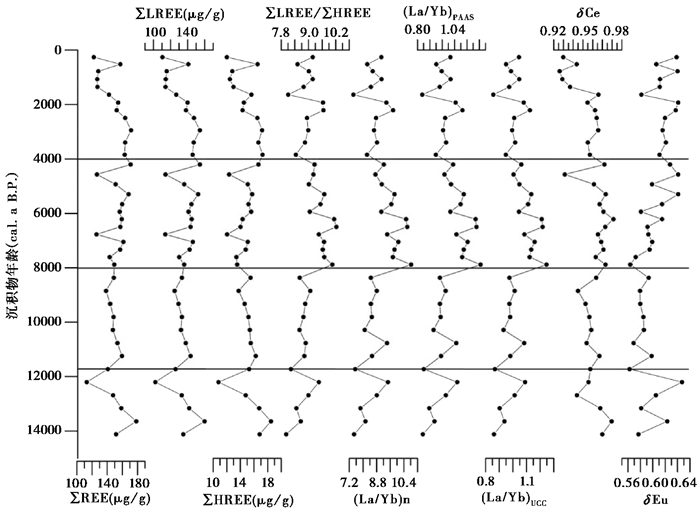
|
图 4 稀土元素垂向分布特征球粒陨石标准引自Masuda[46] ,澳大利亚后太古宙页岩标准值和上陆壳平均值引自Taylor和McLennan[47] Fig. 4 Distribution characteristics of rare earth elements(chondrite values are from Masuda[46], PAAS and UCC values are from Taylor and McLennan[47]) |
根据沉积物Al、Fe、Mg、Na、Ti、Zr、Sr、Cu、Co等常微量元素、稀土元素结果以及张杨硕[39]的粒度和颜色反射率中亮度参数(L *)、红绿参数(a *)、黄蓝参数(b *)的时间序列变化,可以将T93柱状样的沉积划分为4个阶段(表 2),年代分别为14640~11700 cal.a B.P.、11700~8000 cal.a B.P.、8000~4000 cal.a B.P.和4000 cal.a B.P.至今。
| 表 2 T93柱状样各阶段沉积物参数变化范围及平均值 Table 2 Range and average value of characteristics in each part of T93 core |
(1) 14640~11700 cal.a B.P.,沉积物粒径最细,呈较暗的褐黑色;本阶段多数元素含量波动较大,MgO、K2O、CaO、MnO、Li、Co等元素处在最低值,Fe2O3、TiO2、Zr、Ba处在最高值,其中Zr和Ba从最高值减少约30 %;CIA较高,平均为85.46。稀土元素总量平均为148.44 μg/g,波动剧烈,ΣLREE/ΣHREE约8.64。
(2) 11700~8000 cal.a B.P.,平均粒径迅速增大,沉积物亮度增强,颜色偏黄绿;MgO含量从0.6 %大幅增至2.1 %,MnO含量也增加一倍左右,TiO2、Na2O有所减少;CIA增至85.60。稀土元素含量略有升高,ΣREE平均148.72 μg/g,ΣLREE/ΣHREE小幅上升,平均为8.96。
(3) 8000~4000 cal.a B.P.,沉积物颗粒变粗,颜色偏向黄绿色;Na2O含量增至前一阶段的1.5倍,CaO和Sr含量也有所升高,其余常量和微量元素含量相对保持稳定;CIA稍有下降,平均83.71。稀土元素含量增多,ΣREE达到153.54 μg/g,而ΣLREE/ΣHREE则在8000 cal.a B.P.突增约10 %后波动下降,至本段末期仍然较前一段稍高,平均为9.51。
(4) 从4000 cal.a B.P.至今,粒径和多数元素含量与上一段末期相比变化不大,只有CaO和Sr有一定减少趋势,沉积物绿色减弱,略微偏向黄褐色。稀土总量明显减少,ΣREE值平均为147.79 μg/g,而ΣLREE/ΣHREE值也有回落,基本保持在8.94左右。
4 讨论 4.1 泰国湾物源识别指标——稀土元素稀土元素由于其不相容性,在岩浆过程中倾向于富集在岩浆后期产物中,并且在表生地质作用中不易迁移,一般被认为主要来自陆源[48]。为了进一步确认稀土元素来源,以球粒陨石数据[46]对T93沉积物稀土元素的配分模式进行标准化[47, 49](图 5)。T93柱状样4个沉积阶段的稀土元素配分模式都很相似,配分曲线总体呈负斜率,相对富集轻稀土,有较明显的Eu负异常,没有明显Ce异常,标准化曲线呈近似“V”字形。曲线与上地壳接近一致,而与原始地幔、洋中脊玄武岩等非陆源岩石有很大差异,说明沉积物中的稀土元素主要受沉积物的陆地源区控制。另外,从沉积物稀土元素指标与CIA和常量元素的相关性分析来看(表 3),稀土元素与沉积物经受的化学风化程度相关性不高,在长距离搬运过程中化学风化等表生地质作用对稀土元素的影响不明显。因此,沉积物稀土元素适合作为物源判别的指标。δEu、La/Yb、La/Sm、Gd/Yb等稀土元素比值往往与源岩岩性有关,是物源研究的可靠指标,已被成功地运用在亚洲大陆边缘沉积物的物源研究中[50~53]。前人也曾在南海使用稀土元素指标进行过物源研究,结果表明稀土元素指标在本区域物源指示上有一定参考价值[54]。本文选取δEu值和(La/Yb)PAAS值对T93柱状样进行物源示踪,通过(La/Yb)PAAS-δEu图解探讨不同源区对各个沉积阶段沉积物来源的贡献。对δEu和(La/Yb)PAAS与平均粒径的相关关系进行分析(图 6),发现两种稀土元素指标与沉积物粒径之间并没有表现出明显的相关性,说明沉积物δEu和(La/Yb)PAAS基本不受粒度效应的控制。

|
图 5 稀土元素配分模式 上陆壳数据引自Taylor和McLennan[47];原始地幔和洋中脊玄武岩数据引自Sun和McDonough[49];所有数据使用球粒陨石数据进行标准化[46] Fig. 5 Standardized REE patterns. Data of UCC are from Taylor and McLennan[47]; Data of primitive mantle and MORB are from Sun and McDonough[49]; All the data are standardized by chondrite values from Masuda[46] |
| 表 3 稀土元素指标与部分常量元素相关性分析 Table 3 Correlation analysis of REE indicators and some major elements |
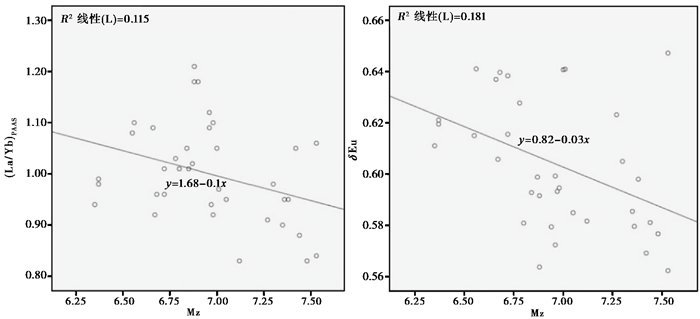
|
图 6 稀土元素指标与粒径相关性 Fig. 6 Correlation between REE proxy and grain size of sediment |
前人研究显示,泰国湾西部主要存在3个物源区,分别为中南半岛、马来半岛和南海[23~24]。我们以曼谷湾口表层沉积物参数作为中南半岛陆源物质的代用指标,以吉兰丹河河口表层沉积物参数作为马来半岛陆源物质的代用指标[26],以南海西南海盆表层沉积物参数作为南海物质的代用指标[54]。南海物质的(La/Yb)PAAS值在0.55到0.87之间,δEu值在0.48到0.60之间,整体位于(La/Yb)PAAS-δEu图解的左下角,以较低的(La/Yb)PAAS值、δEu值为特征;中南半岛物质的(La/Yb)PAAS值约在0.98到1.22之间(图 7a),δEu值为0.47到0.76,整体位于(La/Yb)PAAS-δEu图解的顶部,以(La/Yb)PAAS值最高为特征;马来半岛端元处于中南半岛和南海端元中间,(La/Yb)PAAS值从0.79到1.00,δEu值为0.57到0.71。与泰国湾内沉积物相比,南海物质整体具有较小的δEu和(La/Yb)PAAS值;在泰国湾内,北部中南半岛的沉积物具有相对更高的(La/Yb)PAAS值(图 7a)。
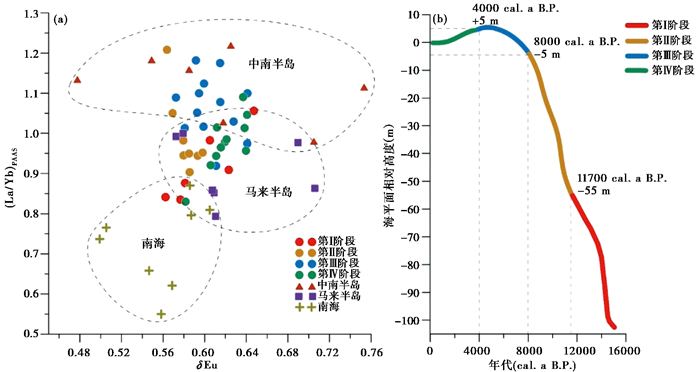
|
图 7 沉积物物源变迁和海平面变化 南海数据引自Wei等[54];泰国湾数据引自Liu等[26];海平面变化由Hanebuth等[22]修改而来(a)沉积物物源变迁;(b)泰国湾海平面变化 Fig. 7 Comparison of sediment provenance and sea-level change near the Gulf of Thailand(data of South China Sea from Wei, et al.[54]; data of Gulf of Thailand from Liu, et al.[26]; sea-level change is modified from Hanebuth, et al.[22]). (a)Provenance change of sediments; (b)Sea-level change in Gulf of Thailand |
沉积物为陆相褐黑色粘土质粉砂,颜色反射率中红绿指标a *相对较高[39],这是由于沉积物含有较多Fe2O3成分,整体相对偏红,说明其氧化程度较高。这一阶段U/Th比值处于低值期,平均为0.18(图 3),同样表明沉积环境氧化性相对较强。一般认为CIA达到80即为强烈风化[42],而这一阶段T93柱状样沉积物CIA平均达到了85.46,表明元素组成中较活跃的Ca、Na和K流失严重,特别是CaO几乎流失殆尽,而TiO2、Zr、Ba含量很高(图 3)。本阶段基本与东亚末次冰消期增温时期一致[55],泰国湾海平面低,沉积物整体呈现出风化后期产物的特点。沉积物δEu在0.56到0.65之间,平均0.60,(La/Yb)PAAS在0.83到1.06之间,平均0.92,在(La/Yb)PAAS-δEu图解上主要分布在南海和马来半岛端元区内(图 7a)。
泰国湾在冰期出露为陆地,进入冰消期后,随着海平面上升(图 7b),海水开始自南海侵入外陆架,至12.7 cal.a B.P.泰国湾南部、北部和西北部部分区域已经被海水淹没[22]。在这期间一定有大量来自泰国湾外的海水自南方侵入泰国湾,这些海水可能将少量来自南海的物质携带至泰国湾西部。在本阶段T93总体沉积为陆相,并且样品300 cm以下部分偶见泥炭层(图 2),表明样品此时很可能处于湖泊环境或者河流沉积环境,因此靠近研究区的马来半岛物质有可能在此沉积。此外,我们认为冰期由巽他陆架上的大河流系携带的北部陆源物质也是不可忽视的部分(图 2)。因此,这期间沉积物以泰国湾南部马来半岛陆源物质为主,同时也受南海和中南半岛物质的影响。由于沉积物沉积环境不稳定,且混杂了多种来源的物质,本阶段各元素含量及指标波动幅度较大,在(La/Yb)PAAS-δEu图解上的点位较分散。
4.2.2 早全新世海平面快速上升期的滨海沉积(11700~8000 cal.a B.P.)沉积物整体为滨海相的褐黑色粘土质粉砂,但逐渐向陆架相灰绿色过渡。粒径明显增大,表明此时水动力条件可能有所增强。元素中MgO、MnO含量明显增多,Fe2O3和TiO2含量大幅降低(图 3),河流输入比例可能有所下降。本阶段沉积物U/Th值平均为0.17,处于较低水平。末次冰消期后,海平面更加迅速上升(图 7b),泰国湾西部主体部分由滨海环境迅速向陆架环境转变,水动力变强,因此沉积界面总体氧化性随水深增大不降反升,至9.5 cal.a B.P.泰国湾大部分区域都成为海洋环境[22]。沉积物δEu在0.56到0.60之间,平均为0.58,(La/Yb)PAAS在0.90到1.21之间,平均为0.99。这一阶段沉积物在(La/Yb)PAAS-δEu图解上的点位相对集中(图 7a),表明沉积物来源相对单一,基本位于泰国湾南部端元区。因此,沉积物主要为马来半岛陆源物质。
4.2.3 高海平面时期的陆架沉积(8000~4000 cal.a B.P.)沉积物主要为灰绿色粉砂,颗粒继续粗化,CIA先降低后稍有升高,总体呈下降趋势,平均83.71。MgO、Na2O、CaO、Sr含量均较明显增加,其中Na2O含量在本阶段中从0.4 %大幅增至0.6 %;稀土元素含量达到最高值(图 3)。沉积物δEu处于0.56到0.64之间,平均0.60,(La/Yb)PAAS在0.92到1.18之间,平均为1.08,在(La/Yb)PAAS-δEu图解上大部分落在中南半岛端元区(图 7a)。
沉积物U/Th比值平均为0.20,处于最高值阶段。本阶段初期至5000 cal.a B.P.,U/Th持续升高,表明沉积环境氧化性稍有减弱;约4500 cal.a B.P.有一次较强烈的波动,但4000~5000 cal.a B.P.期间沉积环境氧化性总体达到最弱。从氧化还原指标的变化来看,沉积环境含氧量与前一阶段相比有所降低,这可能与水深持续增大有关。这一阶段泰国湾海平面普遍高于现代,有研究显示,曼谷粘土的最大年龄约为8000年[21],也就是说在本阶段初期海侵范围已达到今天的曼谷附近。到达高海平面时期后,由于海侵范围广,泰国湾沉积速率也有所上升。8000~6000 cal.a B.P.时期柱状样沉积速率变得非常高(图 2),而沉积物特征接近中南半岛物质,说明在海面上升过程中来自中南半岛的物质增量非常多,有大量中南半岛物质被向南运输至泰国湾西部,其对泰国湾西部沉积物的影响力达到了顶峰(图 7a)。本阶段沉积物主要来自中南半岛,是中南半岛物质对泰国湾西部沉积物影响最大的阶段。
4.2.4 海平面略有下降的稳定陆架沉积(4000 cal.a B.P.至今)该阶段沉积物以灰绿色粉砂为主,但与前一阶段相比偏红、偏黄。CIA平均82.90,下降至末次冰消期以来的最低水平,但仍属于强烈风化。沉积物元素组分中只有CaO,Sr和Pb的含量有所下降,其余元素虽然偶有波动,但总体保持稳定或没有明显变化趋势(图 3)。U/Th比值经过了前一阶段的增大后明显回落,平均值仍为0.20。大约在4000 cal.a B.P.,泰国湾海平面上升至最高点后开始下降(图 7b),U/Th比值的变化也表明了这一点。2000 cal.a B.P.前后柱状样沉积速率再次突增,这次沉积速率突增事件可与8000~6000 cal.a B.P.的沉积速率突增事件一起讨论。根据Tanabe等[56]对昭披耶河三角洲的沉积演化研究,约7000~3000 cal.a B.P.时期在昭披耶河河口处发育有一片泥滩,在河口区域形成了一个小型内湾(the Sananivate Mud Shoal),与泰国湾主体分隔开来。在此期间,可能有大量河流携带的沉积物充填在内湾中,而进入泰国湾的部分相对减少。3000~2000 cal.a B.P.内湾被河口沉积物完全充填,河流携带的沉积物得以越过三角洲进入泰国湾内,三角洲进积作用也开始加速。小型内湾的形成与消失可能是泰国湾在到达高海平面时期之后的6000~2000 cal.a B.P.低沉积速率和2000 cal.a B.P.沉积速率突增的原因之一。δEu分布在0.58到0.64之间,平均0.62,(La/Yb)PAAS分布在0.83到1.01之间,平均约0.97。沉积物在(La/Yb)PAAS-δEu图解上的点位呈条带状右倾分布,横跨过南海、泰国湾南部和泰国湾北部3个分区,但总体落在马来半岛和中南半岛端元区,表明沉积物物源以马来半岛为主,以中南半岛为辅,这与泰国湾西部表层沉积物的物源组成相符[23~24]。沉积物物源组成的变化表明随着海平面轻微下降,中南半岛陆源物质对泰国湾西部沉积物的影响力被大大削弱。前人对泰国湾表层沉积物进行的地球化学研究表明,现代曼谷湾的沉积体系相对独立,曼谷湾内沉积物对泰国湾主体部分影响力有限[57],因此距今4000年前中南半岛物质对泰国湾影响力的下降可能意味着泰国湾现代沉积体系基本形成。
5 结论T93柱状样品基本保存了末次冰消期以来泰国湾沉积环境和物源变迁的沉积记录。对样品进行常微量元素测试,结合已有的柱状样年代、粒度、颜色反射率、沉积相等信息,泰国湾物源变迁过程可以从底到顶划分为4个阶段:
(1) 第Ⅰ阶段(14640~11700 cal.a B.P.):沉积物为褐黑色的粘土质粉砂,平均粒径为7.42 ϕ,为陆相沉积。CaO含量极少,TiO2、Zr、Ba含量高,元素含量大幅波动。U/Th比值处于低值期,平均为0.18,沉积物氧化性相对较强,化学风化严重。沉积物δEu在0.56到0.65之间,平均0.60,(La/Yb)PAAS在0.83到1.06之间,平均0.92。在这一阶段沉积环境不稳定,物质来源也较复杂。沉积物以来自泰国湾南部的马来半岛为主,少量来自中南半岛和南海物质。
(2) 第Ⅱ阶段(11700~8000 cal.a B.P.):海平面迅速上升,沉积物较上一阶段变细,平均粒径为7.17 ϕ,褐黑色减淡,主要为滨海相沉积。MgO、MnO含量明显增多,Fe2O3和TiO2减少。沉积物δEu在0.56到0.60之间,平均为0.58,(La/Yb)PAAS在0.90到1.21之间,平均为0.99,在(La/Yb)PAAS-δEu图解上的点位相对集中,与前一阶段相比沉积物来源相对单一,主要为马来半岛物质。
(3) 第Ⅲ阶段(8000~4000 cal.a B.P.):沉积物为灰绿色粉砂和粘土质粉砂,平均粒径为6.85 ϕ。随着海平面上升至最高值阶段,沉积环境的氧化性也达到了最弱的阶段,U/Th比值增至平均0.20。MgO、Na2O、CaO、Sr含量均有增多,稀土元素总量达到最高值。沉积物δEu处于0.56到0.64之间,平均0.60,(La/Yb)PAAS在0.92到1.18之间,平均为1.08,主要来自泰国湾北部的中南半岛。
(4) 第Ⅳ阶段(4000 cal.a B.P.至今):沉积物为灰绿色粉砂,平均粒径达到6.71 ϕ的最低值。海平面从最高位略微下降,沉积物U/Th比值也有降低趋势,平均仍为0.20。元素特征总体保持稳定,只有CaO、Sr和Pb含量有较明显的降低,δEu分布在0.58到0.64之间,平均0.62,(La/Yb)PAAS分布在0.83到1.01之间,平均约0.97。沉积物物源组成与现代趋于一致,主要来自马来半岛,其次为中南半岛。泰国湾现代沉积体系已基本形成。
致谢: 自然资源部第一海洋研究所朱爱美、张辉、杨晓晨协助进行了实验,泰国东南亚渔业发展研究中心“M V SEAFDEC”调查船全体船员提供了海上调查后勤支持,感谢他们的帮助和支持。
| [1] |
Milliman J D, Meade R H. World-wide delivery of river sediment to the oceans[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1983, 91(1): 1-21. |
| [2] |
李铁刚, 曹奇原, 李安春, 等. 从源到汇:大陆边缘的沉积作用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2003, 18(5): 713-721. Li Tiegang, Cao Qiyuan, Li Anchun, et al. Source to sink:Sedimentation in the continental margins[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2003, 18(5): 713-721. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2003.05.011 |
| [3] |
Xu F, Hu B, Dou Y, et al. Sediment provenance and paleoenvironmental changes in the northwestern shelf mud area of the South China Sea since the mid-Holocene[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2017, 144: 21-30. DOI:10.1016/j.csr.2017.06.013 |
| [4] |
Awasthi N, Ray J S, Singh A K, et al. Provenance of the Late Quaternary sediments in the Andaman Sea:Implications for monsoon variability and ocean circulation[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2014, 15(10): 3890-3906. DOI:10.1002/2014GC005462 |
| [5] |
Wang K S, Shi X F, Zou J J, et al. Sediment provenance variations in the southern Okhotsk Sea over the last 180 ka:Evidence from light and heavy minerals[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2017, 479: 61-70. DOI:10.1016/j.palaeo.2017.04.017 |
| [6] |
Um I K, Choi M S, Bahk J J, et al. Discrimination of sediment provenance using rare earth elements in the Ulleung Basin, East/Japan Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2013, 346(6): 208-219. |
| [7] |
Fagel N, Not C, Gueibe J, et al. Late Quaternary evolution of sediment provenances in the Central Arctic Ocean:Mineral assemblage, trace element composition and Nd and Pb isotope fingerprints of detrital fraction from the Northern Mendeleev Ridge[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2014, 92(4): 140-154. |
| [8] |
褚征, 胡宁静, 刘季花, 等. 西菲律宾海表层沉积物稀土元素地球化学特征及物源指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(5): 53-62. Chu Zheng, Hu Ningjing, Liu Jihua, et al. Rare earth elements in sediments of west Philippine Sea and their implications for sediment provenance[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(5): 53-62. |
| [9] |
Hoskin P W O, Ireland T R. Rare earth element chemistry of zircon and its use as a provenance indicator[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(7): 627. DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<627:REECOZ>2.0.CO;2 |
| [10] |
Marx S K, Kamber B S. Trace-element systematics of sediments in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia:Sediment provenance and palaeoclimate implications of fine scale chemical heterogeneity[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2010, 25(8): 1221-1237. DOI:10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.05.007 |
| [11] |
Xu F J, Li A C, Li T G, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry in the inner shelf of the East China Sea and its implication to sediment provenances[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2011, 29(7): 702-709. DOI:10.1016/S1002-0721(10)60526-1 |
| [12] |
黄雨振, 陈秀玲, 程良清, 等. 准噶尔盆地表层沉积物的稀土元素特征与物源指示[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(6): 1325-1335. Huang Yuzhen, Chen Xiuling, Cheng Liangqing, et al. REE characteristics and its provenance implication of surface sediments in the Junggar Basin[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(6): 1325-1335. |
| [13] |
黄颖, 朱丽东, 张晓, 等. 庐山北麓JL红土剖面粉砂粒级元素地球化学特征及其物源意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(5): 1092-1102. Huang Ying, Zhu Lidong, Zhang Xiao, et al. Geochemical characteristics and their provenance implications of the silt fraction from JL red earth section in Lushan region, Jiujiang, South China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(5): 1092-1102. |
| [14] |
常华进, 储雪蕾, 冯连君, 等. 氧化还原敏感微量元素对古海洋沉积环境的指示意义[J]. 地质论评, 2009, 55(1): 91-99. Chang Huajin, Chu Xuelei, Feng Lianjun, et al. Redox sensitive trace elements as paleoenvironments proxies[J]. Geological Review, 2009, 55(1): 91-99. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2009.01.011 |
| [15] |
杨守业, 李从先. REE示踪沉积物物源研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 1999, 14(2): 164-167. Yang Shouye, Li Congxian. Research progress in REE tracer for sediment source[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 1999, 14(2): 164-167. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1999.02.010 |
| [16] |
杨守业, 韦刚健, 夏小平, 等. 长江口晚新生代沉积物的物源研究:REE和Nd同位素制约[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(3): 37-44. Yang Shouye, Wei Gangjian, Xia Xiaoping, et al. Provenance study of the Late Cenozoic sediments in the Changjaing delta:REE and Nd isotopic constraints[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(3): 37-44. |
| [17] |
Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L, Albertin C S. Flux and fate of fluvial sediments leaving large islands in the East Indies[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 1999, 41(1-2): 97-107. DOI:10.1016/S1385-1101(98)00040-9 |
| [18] |
Milliman J D, Farnsworth K L. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean:A Global Synthesis[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2013: 1-384.
|
| [19] |
Hanebuth T J J, Stattegger K, Schimanski A, et al. Late Pleistocene forced-regressive deposits on the Sunda Shelf (Southeast Asia)[J]. Marine Geology, 2003, 199(1-2): 139-157. DOI:10.1016/S0025-3227(03)00129-4 |
| [20] |
Alqahtani F A, Johnson H D, Jackson C A L, et al. Nature, origin and evolution of a Late Pleistocene incised valley-fill, Sunda Shelf, Southeast Asia[J]. Sedimentology, 2015, 62(4): 1198-1232. DOI:10.1111/sed.12185 |
| [21] |
Somboon J R P, Thiramongkol N. Holocene highstand shoreline of the Chao Phraya delta, Thailand[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1992, 7(1): 53-60. DOI:10.1016/0743-9547(92)90014-3 |
| [22] |
Hanebuth T J, Voris H K, Yokoyama Y, et al. Formation and fate of sedimentary depocentres on Southeast Asia's Sunda Shelf over the past sea-level cycle and biogeographic implications[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2011, 104(1-3): 92-110. DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.09.006 |
| [23] |
Liu S F, Shi X F, Yang G, et al. Distribution of major and trace elements in surface sediments of the western Gulf of Thailand:Implications to modern sedimentation[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 2016, 117: 81-91. DOI:10.1016/j.csr.2016.02.002 |
| [24] |
Shi X F, Liu S F, Fang X S, et al. Distribution of clay minerals in surface sediments of the western Gulf of Thailand:Sources and transport patterns[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 105: 390-398. DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.02.005 |
| [25] |
王昆山, 石学法, 刘升发, 等. 泰国湾西部表层沉积物重矿物分布特征:对物质来源和沉积环境的指示[J]. 第四纪研究, 2014, 24(3): 183-194. Wang Kunshan, Shi Xuefa, Liu Shengfa, et al. Spatial distribution of heavy minerals in the surface sediments from the western Gulf of Thailand:Implications for sediment provenance and sedimentary environment[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 24(3): 183-194. |
| [26] |
Liu S F, Zhang H, Zhu A M, et al. Distribution of rare earth elements in surface sediments of the western Gulf of Thailand:Constraints from sedimentology and mineralogy[J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 527: 52-63. DOI:10.1016/j.quaint.2018.08.010 |
| [27] |
Tomczak M, Godfrey J S. Regional Oceanography:An Introduction[M]. Oxford: Elsevier, 2005: 1-382.
|
| [28] |
Sathiamurthy E. River discharge characteristics of major east coast rivers of Peninsular Malaysia into South China Sea[C]//1st International Workshop on the Fluvial Sediment Supply to the South China Sea. Shanghai, 2008: 27-28.
|
| [29] |
Buranapratheprat A, Bunpapong M. A two dimensional hydrodynamic model for the Gulf of Thailand[C]//Proceedings of The IOC/WESTPAC Fourth International Scientific Symposium. Okinawa, 1998, 469: 478.
|
| [30] |
张杨硕, 乔淑卿, 石学法, 等. 泰国湾底质沉积物输运趋势[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2017, 37(1): 86-92. Zhang Yangshuo, Qiao Shuqing, Shi Xuefa, et al. Moving trend of bottom sediments in Gulf of Thailand[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2017, 37(1): 86-92. |
| [31] |
沈上越, 冯庆来, 杨文强, 等. 泰国北部清莱-南邦带弧火山岩特征研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2011, 31(1): 22-26. Shen Shangyue, Feng Qinglai, Yang Wenqiang, et al. Study on arc-volcanic rocks from the Chiang Rai-Lamping Belt in Northern Thailand[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2011, 31(1): 22-26. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2011.01.004 |
| [32] |
Kittipongvises S, Chavalparit O, Sutthirat C. Greenhouse gases and energy intensity of granite rock mining operations in Thailand:A case of industrial rock-construction[J]. Nephron Clinical Practice, 2016, 18(1): 64-75. |
| [33] |
Marwick B. Stone Artefacts and Human Ecology at Two Rockshelters in Northwest Thailand[D]. Canberra: The Doctoral's Dissertation of Australian National University, 2008: 124-125.
|
| [34] |
Tate R B, Tan D N K, Ng T F. Geological Map of Peninsular Malaysia(Scale 1!1000000)[Z]. Geological Society of Malaysia and University Malaya, 2008.
|
| [35] |
Oppo D W, Sun Y. Amplitude and timing of sea-surface temperature change in the northern South China Sea:Dynamic link to the East Asian monsoon[J]. Geology, 2005, 33(10): 785-788. DOI:10.1130/G21867.1 |
| [36] |
Hanebuth T, Stattegger K, Grootes P M. Rapid flooding of the Sunda Shelf:A late-glacial sea-level record[J]. Science, 2000, 288(5468): 1033-1035. DOI:10.1126/science.288.5468.1033 |
| [37] |
汪品先. 巽他陆架——淹没的亚马逊河盆地?[J]. 地球科学进展, 2017, 32(11): 5-11. Wang Pinxian. The Sunda Shelf-A submerged Amazon Basin?[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2017, 32(11): 5-11. |
| [38] |
Tjia H D. Sea-level changes in the tectonically stable Malay-Thai Peninsula[J]. Quaternary International, 1996, 31: 95-101. DOI:10.1016/1040-6182(95)00025-E |
| [39] |
张杨硕.泰国湾T93孔沉积特征: 晚更新世以来古温度及东亚冬季风演化记录[D].青岛: 自然资源部第一海洋研究所硕士论文, 2017: 11-42. Zhang Yangshuo. Sediment Characteristics and Change of East Asia Winter Monsoon of Core T93 from Gulf of Thailand[D]. Qingdao: The Master's Thesis of First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, 2017: 11-42. |
| [40] |
琚琛琪, 牛东风, 李保生, 等. 广东西樵山MIS 5a网纹红土常量元素分布及其气候意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(5): 1083-1091. Ju Chenqi, Niu Dongfeng, Li Baosheng, et al. Reticulate laterite constant element distribution and its significance in MIS 5a, Xiqiaoshan, Guangdong Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(5): 1083-1091. |
| [41] |
张伊琳, 董艳, 吴超, 等. 江苏南通黄泥山黄土漫反射光谱特征及古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(2): 529-536. Zhang Yilin, Dong Yan, Wu Chao, et al. Diffuse reflectance spectrum characteristics of the Huangnishan loess in Nantong, Jiangsu Province and their paleoenvironmental significances[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(2): 529-536. |
| [42] |
Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature, 1982, 299(5885): 715-717. DOI:10.1038/299715a0 |
| [43] |
王浩, 刘志飞, Sathiamurthy E, 等. 马来半岛和婆罗洲北部的化学风化作用:来自河流表层沉积物的粘土矿物和元素地球化学记录[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2011, 41(2): 205-215. Wang Hao, Liu Zhifei, Sathiamurthy E, et al. Chemical weathering in Malay Peninsula and North Borneo:Clay mineralogy and element geochemistry of river surface sediments[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(2): 205-215. |
| [44] |
Jones B, Manning D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1-4): 111-129. DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X |
| [45] |
Henderson P. General geochemical properties and abundances of the rare earth elements[J]. Developments in Geochemistry, 1984, 2: 1-32. DOI:10.1016/B978-0-444-42148-7.50006-X |
| [46] |
Masuda A. Abundances of monoisotopic REE, consistent with the Leedey chondrite values[J]. Geochemical Journal, 1975, 9(3): 183-184. DOI:10.2343/geochemj.9.183 |
| [47] |
Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985: 1-312.
|
| [48] |
刘英俊. 元素地球化学导论[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1987: 75-78. Liu Yingjun. Introduction to Elemental Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1987: 75-78. |
| [49] |
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19 |
| [50] |
Li C S, Shi X F, Kao S J, et al. Rare earth elements in fine-grained sediments of major rivers from the high-standing island of Taiwan[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 2013(69): 39-47. |
| [51] |
Xu Z, Lim D, Choi J, et al. Rare earth elements in bottom sediments of major rivers around the Yellow Sea:Implications for sediment provenance[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2009, 29(5): 291-300. DOI:10.1007/s00367-009-0142-x |
| [52] |
窦衍光, 李军, 李炎. 北部湾东部海域表层沉积物稀土元素组成及物源指示意义[J]. 地球化学, 2012, 41(2): 147-158. Dou Yanguang, Li Jun, Li Yan. REE compositions and provenance implication of surface sediments in Beibu Gulf[J]. Geochimica, 2012, 41(2): 147-158. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2012.02.006 |
| [53] |
杨守业, 李超, 王中波, 等. 现代长江沉积物地球化学组成的不均一性与物源示踪[J]. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33(4): 645-655. Yang Shouye, Li Chao, Wang Zhongbo, et al. Heterogeneity of geochemical compositions of the Changjiang River sediments and provenance indication[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(4): 645-655. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.04.03 |
| [54] |
Wei G J, Liu Y, Ma J L, et al. Nd, Sr isotopes and elemental geochemistry of surface sediments from the South China Sea:Implications for Provenance Tracing[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 319-322: 21-34. DOI:10.1016/j.margeo.2012.05.007 |
| [55] |
Xu D, Lu H, Wu N, et al. Asynchronous marine-terrestrial signals of the last deglacial warming in East Asia associated with low-and high-latitude climate changes[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2013, 110(24): 9657-9662. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1300025110 |
| [56] |
Tanabe S, Saito Y, Sato Y, et al. Stratigraphy and Holocene evolution of the mud-dominated Chao Phraya delta, Thailand[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003, 22(8-9): 789-807. DOI:10.1016/S0277-3791(02)00242-1 |
| [57] |
Windom H L, Silpipat S, Chanpongsang A, et al. Trace metal composition of and accumulation rates of sediments in the upper Gulf of Thailand[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 1984, 19(2): 133-142. DOI:10.1016/0272-7714(84)90060-X |
2 Key Laboratory of Marine Geology and Metallogeny, First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, Qingdao 266061, Shandong;
3 Laboratory for Marine Geology, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology(Qingdao), Qingdao 266237, Shandong;
4 Phuket Marine Biological Center, Phuket 83000, Thailand;
5 Department of Marine and Coastal Resources, Marine and Coastal Resources Research Center, Bangkok 74000, Thailand)
Abstract
A 381-centimeter long gravity core T93 located at 9.9261°N, 100.6442°E was collected from the western Gulf of Thailand(5°~13°30'N, 99°~106°E) by SEAFDEC in May 2012, with a sampling water depth of 59 m. A total of 38 samples were collected at intervals of 10 cm, and the bottom age is about 14640 a B.P., so the sampling interval is about 375 a. Major and trace element content of < 0.1 mm part of the samples were measured, and the evolution of sediments provenance and sedimentary environment since the Last Deglacial is discussed on the basis of AMS 14C dating, grain-size, color reflectance and element content data. The results show that the process of sedimentation can be divided into four stages: (1)From 14640 cal.a B. P. to 11700 cal.a B. P., the sea level is basically low and the sediments composed of clayey silt is deposited in a terrestrial environment. The content of alkaline elements such as Na, K, Ca and Mg is extremely low, while the content of Fe, Ti and Ba is high, showing a strong chemical weathering intensity. The average δEu is 0.60 and(La/Yb)PAAS is 0.92, respectively, indicating that the sediments are mainly from the Malay Peninsula and partly the Indo-China Peninsula and the South China Sea. (2)From 11700 cal.a B. P. to 8000 cal.a B. P., the sea level rises rapidly and the western Gulf of Thailand is in a coastal environment. The content of silt and active elements show a slight increase. By contrast, the content of Fe, Ti, and Ba decrease. The average δEu is 0.58 and(La/Yb)PAAS is 0.99, indicating the sediments are mainly from the Malay Peninsula. (3)From 8000 cal.a B. P. to 4000 cal.a B. P., the sea level reaches the maximum. The western Gulf of Thailand become a shelf environment and the sediments consist of silt and clayey silt. The content of Na increases by 50% while the other elements change little, and the chemical weathering intensity becomes weaker. The average δEu and(La/Yb)PAAS value is 0.60 and 1.08 respectively, indicating that the sediments mainly derive from the Indo-China Peninsula. (4)The last 4000 years, the elemental and grain-size composition of the sediments remain steady as the sea level slightly decreases. The average δEu is 0.62 and(La/Yb)PAAS is 0.97, hence the sediments are mainly influenced by material from the Malay Peninsula, and partly affected by sediments from the Indo-China Peninsula. 2020, Vol.40
2020, Vol.40

