2 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 中国科学院新生代地质与环境重点实验室, 北京 100029;
3 中国科学院青藏高原地球科学卓越创新中心, 北京 100101;
4 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049;
5 郑州市文物考古研究院, 河南 郑州 450052;
6 中国科学院地球科学研究院, 北京 100029;
7 福建师范大学地理科学学院, 福建 福州 350007;
8 河南师范大学历史文化学院, 河南 新乡 453007)
农业起源与发展是人类历史上的重要变革,不仅深刻改变了人类的生计方式,而且为社会演进与文明形成奠定了根基[1~2]。在中国起源的北方旱作和南方稻作两套农业系统,共同孕育出了中华农耕文明,对后世影响深远。全新世中期(新石器时代中晚期)(6000~3000 cal. B. C.)是我国谷物由野生向驯化发展、生业经济由采集向农业转变的关键阶段[3~5],同时也是气候发生明显波动的时期[6~7]。研究全新世中期农业的时空演变过程及其与气候环境的关系,将有助于深入认识中国古代文明起源的过程和机制[8~9]。以豫中西为腹心,包括晋南、关中、豫北冀南,外及黄河中游和淮河上中游大部分在内的中原文化区[10],是我国古代农业起源,发展和传播的关键地区之一,也是华夏文明兴起的摇篮[11~19],因此是研究上述问题的理想区域。
中原地区已开展的系统植物考古工作集中于关中盆地[20]、伊洛河流域[21]、颍河上游区域[22]、洛阳盆地[23]等区域以及舞阳贾湖[24]、邓州八里岗[25]、三门峡南交口[26]、灵宝西坡[15]、西安鱼化寨[27]等大型遗址,获得了全新世中期即裴李岗文化和仰韶文化时期大量的植物遗存证据,并对农作物种类、结构及其演变过程进行了探讨。与以上区域相比,同属中原腹地的郑州地区却较少引人关注。郑州地区北临黄河,西依嵩山,具有多样的地貌及土壤类型,同时拥有丰富的文化遗址[28~31],被认为是旱作农业起源和稻作农业早期传播的重点地区之一[11~13]。然而,由于区域性系统植物考古研究的缺乏,尤其是发现裴李岗文化时期植物大遗存的遗址相对较少[21, 32~34],学术界对郑州地区全新世中期农业的时空演变过程及其影响因素仍不甚清晰。郑州地区早期农作物结构如何演变?旱作、稻作以及稻-旱混作在地理上如何分布?其时空演变与气候、地貌、水文等自然要素以及社会文化因素有何联系?都是亟待解决的问题。
目前,炭化植物遗存分析、淀粉粒分析和植硅体分析是研究古代农业的主要方法。其中,植硅体作为一种二氧化硅矿物,具有耐高温、抗风化的特点,可在考古堆积中长久保存[35],而且随着植硅体形态学研究的深入,植硅体分析在粟、黍、稻、麦等农作物的鉴定上可明确区分到种,是确切的农业活动证据,所以被越来越多地应用于农业起源和传播的研究中[36]。除此之外,区域性的植物考古研究也已成为全面认识农业发展时空格局的重要途径[21, 23, 37]。本文以郑州地区为研究区域进行系统植物考古调查,选择位于不同地貌部位、不同等级规模的13处裴李岗文化和仰韶文化遗址进行采样,通过植硅体分析和AMS 14 C测定,尝试揭示全新世中期郑州地区古代农业的时空变化特征及其影响因素。
1 研究区概况郑州地区位于黄河中游的河南省西部,地处黄土高原与华北平原的过渡地带,总地势为西高东低(图 1)。区域内地貌主要包含构造山地、低山丘陵、冲积平原、黄土地貌与风成沙丘沙地,以嵩山为中心呈环状分布[38]。嵩山、箕山等山系属构造中、低山,海拔高度700~1500 m;再向外为山前丘陵,海拔200~500 m;东部郑州市区一带属于黄河冲积平原,海拔100 m左右。黄土地貌主要分布在宽阔的河流谷地,主要有黄土塬、黄土丘陵和黄土阶地[39]。该区河流众多,黄河流经本区北部,嵩山东麓的贾鲁河和南麓的颍河属淮河水系。此外,一些较小的河流如双洎河、索须河、溱洧河等在区域早期文化的发展中也起到非常重要的作用[29, 40]。
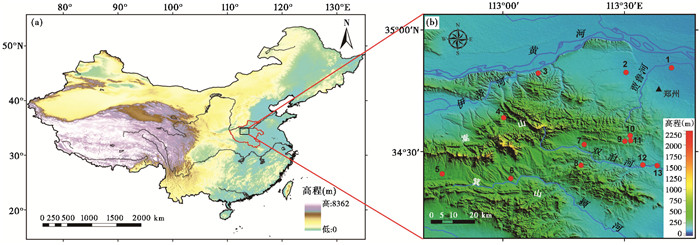
|
图 1 研究区地理位置(a)和采样遗址点分布图(b) 1.大河村(Dahecun);2.朱寨(Zhuzhai);3.庄岭(Zhuangling);4.坞罗西坡(Wuluoxipo);5.颍阳(Yingyang);6.袁村(Yuancun);7.马鞍河(Maanhe);8.菜园沟(Caiyuangou);9.马沟(Magou);10.李家沟(Lijiagou);11.沙石嘴(Shashizui);12.王嘴(Wangzui);13.北李庄(Beilizhuang) Fig. 1 Location of the study area (a) and distribution of the sampled sites (b) |
郑州地处暖温带,属于大陆性季风气候,年平均气温14 ℃,年均降水量640 mm,植被属暖温带落叶阔叶林亚地带[41]。区域内土壤多为风积、洪积黄土母质以及第四纪红土,广泛形成黄土、白面土、红粘土等土壤类型,以黄土为主。河流冲积平原的土壤母质为河流冲积物,土壤有沙土、沙壤土和淤土。目前,该区山间盆地和丘陵台地、坡地绝大多数已被开辟为农田,种有小麦、玉米、甘薯、谷子、豆类和棉花等农作物。
郑州地区最早的古人类文化可追溯至10万年前后的旧石器时代中期[42],随后在旧石器时代晚期(约距今5~2万年)经历了一个古人类发展的繁荣时期,共发现有300多处旧石器及动物化石地点,成为中国与东亚旧石器文化及现代人起源研究的关键区域[43]。进入全新世,该区先后出现了李家沟文化、裴李岗文化、仰韶文化、龙山文化、二里头文化、二里岗文化。李家沟文化填补了郑州乃至中原地区从旧石器晚期细石器文化到新石器中期裴李岗文化之间的空白[44]。裴李岗文化遗址较少,采用广谱生计策略,兼有农作物种植;仰韶文化遗址大量增加,出现等级分化,农业成为经济主体;龙山文化聚落等级分化扩大,出现城址聚落,小麦、大豆加入农业生产,农作物布局开始趋向复杂化;二里头-二里岗文化时期,都邑性质的大型中心聚落形成,粟、黍、稻、小麦、大豆五谷齐全,为早期国家和华夏文明的形成提供了坚实的经济基础[3]。
2 材料与方法本文在郑州地区选取裴李岗文化和仰韶文化时期的遗址13处。这些遗址分布于嵩山周围的河流附近,其中位于冲积平原区的有2处,位于浅山丘陵区黄土台塬沟谷地带的有11处(图 1和表 1)。根据遗址面积划分规模等级,裴李岗文化遗址中一级大型聚落2处,二级中小型聚落3处,一共5处;仰韶文化遗址中一级聚落5处,二级聚落2处,三级聚落3处,一共10处(表 1),其中庄岭和朱寨遗址中既有裴李岗文化堆积又有仰韶文化堆积。我们对这13处遗址的58个遗迹单位进行了考察(图 2和表 1),对于一些具有多层堆积的房址、灰坑和文化层等遗迹,按照不同的位置、深度和背景分别采取土样,共采集了225份植硅体分析样品。
| 表 1 采样遗址地理信息及植硅体样品采集统计表 Table 1 Summary of geographic information and samples collected for phytolith analysis from the thirteen sites in Zhengzhou area |
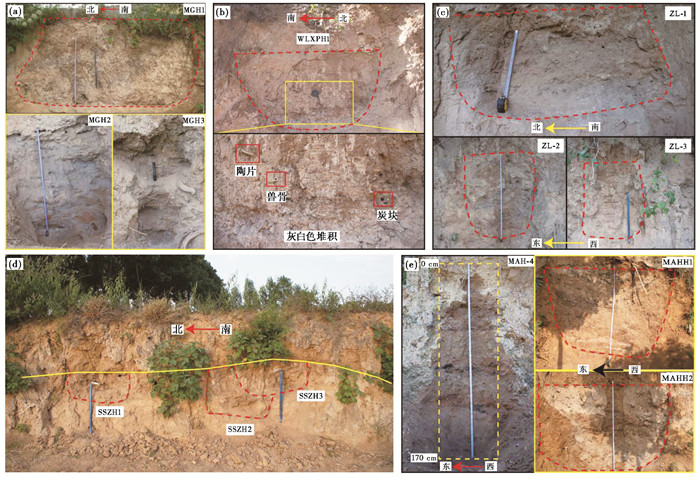
|
图 2 本文部分研究遗址的采样遗迹 (a)马沟(Magou);(b)坞罗西坡(Wuluoxipo);(c)庄岭(Zhuangling);(d)沙石嘴(Shashizui);(e)马鞍河(Maanhe) Fig. 2 Photos of sampled contexts from some investigated sites in the paper |
所有考古样品的植硅体提取采用湿式灰化法,具体步骤如下:1)样品描述与称重。分析样品重量为2 g;2)将样品放入试管,加30 %双氧水,使其充分反应以去除有机质,然后加蒸馏水离心清洗3次;3)加入10 %盐酸及石松孢子片(27637粒/片),放入沸水中加热15分钟以去除钙质,然后加蒸馏水离心清洗3次;4)加比重为2.35的溴化锌重液进行浮选;5)将浮选出的样品用蒸馏水和无水乙醇洗净,然后用中性树胶制成固定玻片待用。
植硅体的统计和鉴定是在400倍徕卡DM750光学显微镜下进行的。大部分样品统计400粒以上,对于植硅体含量少的样品则至少统计200粒,并同时计数石松孢子。植硅体鉴定参照王永吉和吕厚远[45]的分类标准,粟、黍植硅体鉴定依据Lu等[46]的区分标准,水稻植硅体鉴定依据王永吉和吕厚远[45]及Lu等[47]的分类标准。然后计算每个植硅体类型的百分含量(单个类型数与总统计数的比值×100 %)。每个样品植硅体浓度通过公式:植硅体浓度(粒/克)=(鉴定的植硅体数量×外加石松孢子数)/(鉴定的石松孢子数×样品取样重量)计算得出。对同一时期所有发现农作物的样品,将统计到的谷物植硅体数量相加求取总数,然后计算每个农作物植硅体的相对百分含量(单个农作物植硅体数与谷物植硅体总数的比值×100 %)。水稻三种特征植硅体类型在此计算中进行数量上的合并,共同代表水稻与其他农作物进行对比。植硅体出土概率借鉴了植物大遗存出土概率分析方法,根据发现有某种植物种类植硅体的样品在总样品数中所占的比例计算得出。
我们选择了30份测年样品进行AMS 14 C定年。所用植硅体测年材料按照Zuo等[48]改进后的流程提纯,通过光学显微镜、扫描电镜和能谱分析的共同检查,已确认植硅体中无粘土和炭屑等杂质[48]。14 C年代通过OxCal 4.2.3程序[49]和IntCal13校正曲线[50]校正为日历年龄。
3 结果 3.1 测年结果在14 C测年结果中(表 2),除李家沟遗址剖面LJG1、朱寨遗址灰坑H218和H214这3个样品的结果与文化属性不符外(本文未采用),其余27个年代数据分布在6417~2628 cal. B. C.之间(95.4 %置信区间),与裴李岗文化和仰韶文化的年代相吻合。根据所采遗迹的测年数据和考古地层年代,在本文研究范围内,坞罗西坡、王嘴、李家沟为裴李岗文化遗址;庄岭、朱寨为裴李岗文化和仰韶文化晚期遗址;颍阳、袁村、马鞍河为仰韶文化中晚期遗址;马沟、沙石嘴、菜园沟、大河村、北李庄为仰韶文化晚期遗址。
| 表 2 本文研究遗址的AMS 14C测年数据 Table 2 AMS 14C radiocarbon dating results from the analyzed sites |
13处考古遗址225份植硅体样品中,共鉴定出24个植硅体类型,统计103927粒个体。样品植硅体含量不一,但总体上较为丰富,平均浓度可达313×104粒/ g。在171个样品中发现了农作物植硅体,百分含量在0.2 % ~33.0 %之间,可鉴定的种类有黍、粟和稻。黍、粟植硅体来自种子的稃壳(黍η型:图 3-1、2和3;粟Ω型:图 3-5、6和7),水稻植硅体主要是来自稃壳的双峰型(图 3-8、9和10),少量来自茎叶组织的并排哑铃型和扇型(图 3-4和11)。其他常见植硅体类型有哑铃型(图 3-13)、短鞍型(图 3-12)、扇型、方型(图 3-16)、棒型、尖型、帽型(图 3-14)以及齿型(图 3-15)等。下文将按照时代顺序,重点介绍农作物植硅体的鉴定结果。

|
图 3 郑州地区考古遗址常见植硅体形态 1,2,3—黍稃壳η型(η type from husks of common millet);4—水稻并排哑铃型(parallel bilobe from rice);5,6,7—粟稃壳Ω型(Ω type from husks of foxtail millet);8,9,10—水稻双峰型(double-peaked from rice);11—水稻扇型(bulliform from rice);12—短鞍型(short saddle);13—哑铃型(bilobate);14—帽型(rondel);15—齿型(trapeziform sinuate);16—方型(square) Fig. 3 Shapes of common phytoliths from archaeological sites in Zhengzhou area |
除王嘴遗址外,其他4处裴李岗文化遗址均发现了农作物植硅体(表 3)。
在坞罗西坡遗址,WLXPH1灰坑(图 2b)9个样品中仅底部的3个样品发现了农作物植硅体,其中黍植硅体数量(7粒)略多于粟植硅体(4粒),而在百分含量上黍植硅体(0.24 % ~0.70 %)所占的比例也要大于粟植硅体(0~0.69 %)。为了确定两种农作物的相对比例,对这3个样品进行第二次观察,仅鉴定和统计黍、粟植硅体。其中一个样品黍、粟植硅体含量极少,统计一张玻片只发现了9粒黍植硅体,其他两个样品均统计了200粒之上。共鉴定出黍植硅体268粒,粟植硅体148粒,黍约是粟的1.8倍,与第一次观察的黍、粟相对比例一致。
在李家沟遗址,南区LJG1文化层剖面和北区剖面LJG2样品中仅各发现1粒黍植硅体,百分含量分别为0.38 %和0.28 %。对LJG2样品再观察一张玻片后,又发现了3粒黍植硅体,没有发现其他农作物。
在庄岭遗址,3个灰坑24份样品全部发现农作物植硅体,每个样品中黍植硅体数量均多于粟植硅体,共计发现黍植硅体376粒,粟植硅体63粒,百分含量范围分别为0.63 % ~13.94 %和0~1.60 %。
在朱寨遗址,12个裴李岗文化灰坑中有9个发现了农作物植硅体,共统计黍植硅体448粒,粟植硅体4粒,水稻双峰型植硅体29粒和水稻扇型植硅体3粒。在百分含量上黍植硅体最高可达40 %,粟植硅体比例很少,最高仅0.57 %,水稻植硅体含量最高是5 %。
3.2.2 仰韶文化中晚期在10处仰韶文化中晚期遗址中,马沟、庄岭、沙石嘴和北李庄4处遗址仅发现了黍和粟,其他6处遗址则黍、粟、稻均有发现。从发现数量来看(表 3),多数遗址中黍植硅体最多,在样品中的百分含量最高可达28 % (朱寨遗址),但在北李庄遗址,粟植硅体的数量(28粒)和百分含量(0.36 % ~1.74 %)均高于黍(14粒;0~0.96 %)。在黍、粟、稻同出的6处遗址中,水稻植硅体的数量一般最少,但在颍阳和菜园沟遗址,水稻植硅体的数量超过了粟(表 3)。稻壳双峰型植硅体(共622粒)占所发现水稻植硅体的95 %,水稻扇型和并排哑铃植硅体的数量极少,这一比例说明当时稻属植物的收获可能采用割穗的方式,将稻穗和少量茎叶一同带回遗址[51]。此外,在谷物加工过程中,因为脱穗的副产品主要是产生扇型和并排哑铃型植硅体的稻叶或细小的茎秆,而脱壳的副产品主要是产生双峰型植硅体的稻壳[52],所以这些样品中以双峰型植硅体为主的组合,除了可能表明收割方式是割穗外,还有一种可能性就是样品沉积物由脱壳的副产品而非脱穗的副产品构成。如果采集的样品来自脱穗的副产品,那么就可能发现大量的水稻扇型和哑铃型植硅体了。
| 表 3 郑州地区考古样品中农作物植硅体数量统计 Table 3 Quantitative statistics of crop phytoliths from archaeological samples in Zhengzhou area |
本文植硅体分析结果表明,郑州地区裴李岗文化时期的农作物包含黍、粟、稻3种,整体上属稻-旱混作农业模式。
为了进一步分析裴李岗时期的整体农作物结构,我们将发现的农作物植硅体单独进行分析,计算各农作物的相对百分含量。由于坞罗西坡和李家沟遗址仅发现少量农作物植硅体(表 3),所以其在整体农作物结构分析中的统计意义略显不足。分析结果显示,黍在整个农作物结构中所占比例最高(88.88 %),其次为粟(7.67 %),而稻的比例最低(3.46 %)。此外,我们还采用两种统计方法计算各农作物的出土概率,一种以65个总样品量(包括王嘴遗址样品)为分析单位,一种以5个总遗址数(包括王嘴遗址)为分析单位,计算出土各农作物的样品/遗址在总数中所占的比例。结果表明,按第一种方法,黍、粟、稻的出土概率依次为53.9 %、35.4 %和9.2 %;按第二种方法,黍、粟、稻的出土概率依次为80 %、60 %和20 %。综合植硅体相对百分比和出土概率的分析结果,郑州地区裴李岗时期的农作物结构中,黍的比重最大,其产量远超粟和稻,是当时人类的主要粮食作物,粟占次要地位,而稻虽有种植,但就其产量而言可能只是农业生产中的补充作物。
遗址间因自然条件和规模等级的不同,其农作物种类和结构也可能存在差异[23]。我们据此将本文研究遗址以及唐户遗址[53]分为2组。坞罗西坡、李家沟和庄岭遗址为一组,它们面积较小,均为中小聚落,地处浅山丘陵区的黄土台塬沟谷地带;朱寨和唐户遗址为一组,其面积较大,为大型聚落,地处河流冲积平原(表 1)。利用每个遗址的植硅体数据计算各农作物的相对百分含量。结果显示(图 4),台塬沟谷地带3处遗址的农作物只有黍和粟两种,黍占主导地位(63 % ~100 %),而李家沟遗址只发现黍这种唯一的农作物;平原区2处遗址除粟、黍外,还发现稻,而且稻的比例(7 % ~12 %)超过粟,仅次于黍(88 % ~92 %)。
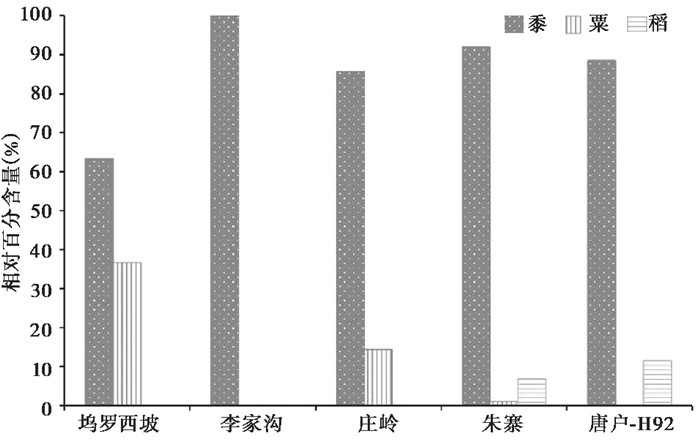
|
图 4 裴李岗文化遗址黍、粟、稻植硅体相对百分含量 唐户遗址数据来自文献[53] Fig. 4 Relative percentage of phytolith from common millet, foxtail millet, and rice at different Peiligang culture sites.The H92 data of the Tanghu site are adapted from reference[53] |
综合而言,郑州地区裴李岗时期是以黍占主导的黍、粟、稻混作农业;不同地貌单元的遗址具有不同的农业格局,在平原地带为稻-旱混作,在台塬沟谷为黍粟旱作农业。
3.3.2 郑州地区仰韶文化中晚期的农业特征植硅体分析结果表明,郑州地区仰韶文化中晚期的农作物依然包含黍、粟、稻这3种,整体延续了裴李岗文化时期形成的稻-旱混作模式。
我们计算了10个仰韶文化中晚期遗址各农作物植硅体的相对百分含量,以考察整体农作物结构。结果显示,黍在整个农作物结构中所占比例仍然最高(60.85 %),粟占其次(27.16 %),而稻的比例依然最低(11.99 %)。此外,我们继续采用两种统计方法计算各农作物的出土概率,一种以160个总样品量为分析单位,一种以10个总遗址数为分析单位,计算出土各农作物的样品/遗址在总数中所占的比例。结果表明,按第一种方法,黍、粟和稻的出土概率依次为80.6 %、67.5 %和43.8 %,按第二种方法,黍和粟的出土概率均为100 %,稻的出土概率为60 %。综合植硅体相对百分比和出土概率的分析结果,郑州地区仰韶中晚期的农作物结构中,黍的产量最大,仍然是先民主要的粮食作物,粟的产量还是没有超过黍,而稻在农业生产中的比重依然很小。
按照地貌部位,朱寨和大河村遗址位于冲积平原,其他8处遗址位于台塬沟谷;按照聚落规模,朱寨、大河村、颍阳、马鞍河和袁村遗址属一级大型聚落,马沟、沙石嘴、庄岭、菜园沟和北李庄遗址属于二、三级中小型聚落(表 1)。从图 5可以看出,此时稻不仅种植在冲积平原,而且种植在台塬沟谷的部分遗址,其中颍阳和菜园沟遗址稻的比例甚至接近或超过了冲积平原区朱寨和大河村遗址的比例。将大型聚落和中小型聚落的农作物加以对比,发现在5处大型聚落中均有水稻植硅体发现,但在5处中小型聚落中,仅菜园沟遗址发现了水稻植硅体。这说明郑州地区仰韶中晚期的稻作主要集中在大型遗址中,中小遗址大部分仍从事黍粟旱作农业。
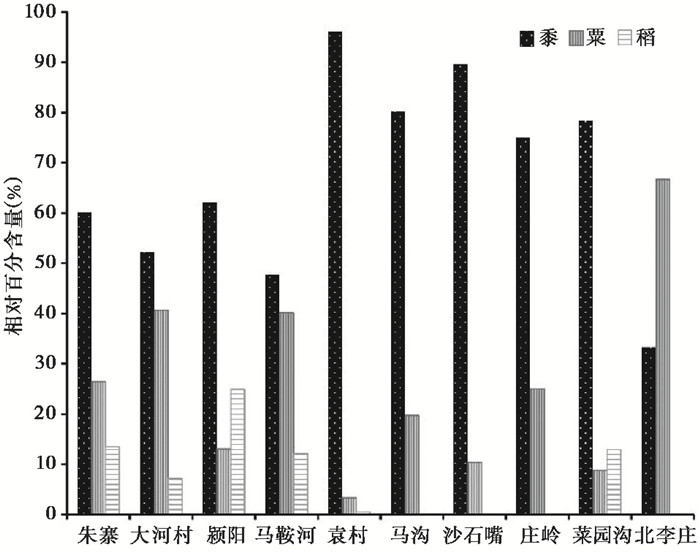
|
图 5 仰韶文化中晚期遗址黍、粟、稻植硅体相对百分含量 Fig. 5 Relative percentage of phytolith from common millet, foxtail millet, and rice at different middle-late Yangshao culture sites |
以上分析揭示了在裴李岗文化和仰韶文化中晚期,郑州地区是以黍、粟、稻为主要粮食作物的混作农业模式,而不单纯是旱作模式;旱作农业以黍为主,而不是粟,仰韶文化中晚期并未发生粟黍比例更替;稻在裴李岗文化时期就已经出现在郑州地区,但一直都不是主要作物,黍粟的核心地位始终没有受到稻作的冲击。虽然仰韶中晚期以黍为主的大格局不变,但相较于裴李岗时期,粟和稻的比例均显著提高(图 6),稻作不再局限于冲积平原区和大型聚落,在台塬沟谷区和中小聚落也有分布,标志着仰韶文化中晚期农作物多样化程度的加深以及农作物种植结构的优化。
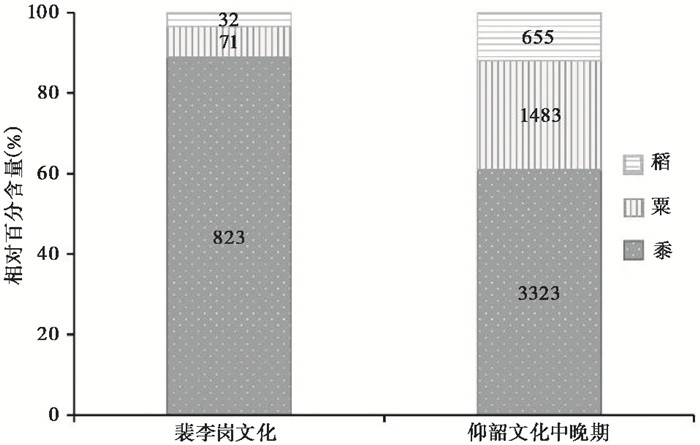
|
图 6 郑州地区全新世中期农作物植硅体的相对百分含量变化 Fig. 6 Relative percentage of crop phytoliths during mid-Holocene in Zhengzhou area |
裴李岗文化是中原古代农业形成过程的关键阶段,素来被视为北方旱作农业的代表之一[3, 54~55],但在郑州地区裴李岗文化时期的炭化农作物遗存一直十分稀少[21, 23, 56~58],而遗址中普遍存在的粟类淀粉粒并未明确是粟还是黍或是二者兼有[59~60]。最近,唐户[53, 61]和朱寨[32~33]遗址的植物考古工作发现了大量裴李岗时期黍、粟、稻的炭化种子、植硅体以及淀粉粒,结合本文裴李岗文化遗址的植硅体分析结果,表明郑州地区裴李岗文化时期不仅具有旱作农业,同时也形成了稻-旱混作的农业模式。
距今8000年前后,北方地区整体进入以黍为主的旱作农业体系,各地分别出现发展水平相似的旱作经济文化,而稻属作物向北扩展[4, 62~63]。此时在黄河流域的朱寨、唐户、月庄[64]和西河[65]遗址均出现了稻和黍粟被共同利用的现象,表明郑州地区和山东西部的旱作农业者最早开发了北扩的稻属资源,发展出稻-旱混作农业。在北方旱作区,相对于黍粟,稻的生长需要更多的水热资源,那么这时稻作北扩以及稻-旱混作的形成应该与全新世适宜期的到来密不可分。
全新世适宜期时,全球平均温度比现在(1961~1990年)高约1 ℃[6],而在中国可能要高出2~4 ℃[66~69],与此同时,东亚季风快速增强带来更多的降水[7, 70],夏季风雨带向北推移[71],东部季风区变得温暖湿润,这种适宜的气候条件很可能促使野生稻资源的分布范围覆盖到长江以北,甚至黄河中下游地区[4, 72~73],从而被当地先民利用和栽培,进而发展出稻作农业。当然,适宜期暖湿气候促动的人群流动和文化传播也可能带来稻作的北传。有学者认为,在全新世适宜期来临之际,随着暖温带和亚热带的持续北移,来自长江中游地区的文化及人群逐渐北进到淮汉地区,然后向北迅速扩展到黄河流域,与北方新石器文化相遇发展为裴李岗、老官台和后李文化,南方的稻属资源和稻作技术便传入北方[74~75]。无论是稻属资源的自然北扩,还是文化北进的稻作传入,都能说明黄河流域距今8000前后稻-旱混作的出现是在适宜期稳定暖湿的气候背景下发展起来的,农业的扩展伴随着文化的融合。
根据本文分析结果,结合莪沟、裴李岗、沙窝李、岗时、寨根、班沟、府店、石固、唐户等9处遗址的植物考古数据[34],揭示出郑州地区裴李岗时期,浅山丘陵区遗址的先民从事旱作农业,稻-旱混作农业只分布在冲积平原区。在相同的气候条件下,不同遗址农业模式的选择主要受地貌和水文条件影响[34]。这种空间格局也反映了人类对不同自然环境的适应性生存策略。
浅山丘陵区的遗址主要分布在河流沟谷两岸的黄土台地上,所处位置相对较高,不仅远离水源,而且适于耕作的平坦土地面积较小,不能满足稻作的需求。粟类作物,尤其是黍,对水分的需求较低,可在年均降雨量为350~550 mm的条件下良好生长于黄土沉积之上[76~77],因此更加适合浅山丘陵区的自然环境。另外,该区域遗址很可能是小村落甚至是流动人群的季节性营地[3],当地先民不太可能投入时间和精力从事劳动量巨大的稻作农业,而粟类作物生长期较短,通常80~120天即可成熟,加之旱作方法并不需要太多田间管理[77],黍粟农业因而成为当地居民的首选。
冲积平原区的遗址通常位于两河交汇处的台地上,所处位置相对较低。该区域广阔平坦,水源充足,土地肥沃,适合稻作。区域内遗址面积较大,具有更高的定居程度和更多的人口数量[3],为先民在旱作耕种之外持续种植和管理稻属植物提供了必要条件,从而促成当地稻-旱混作农业的形成。
与郑州地区遗址不同的是,位于淮河流域冲积平原区的贾湖遗址发现了大量裴李岗时期的水稻,却未出现任何同时期的粟黍类遗存[51, 62]。该遗址毗邻贾湖以及沙河、北汝河,大量的水生动植物资源如莲藕、菱角、鱼骨、蚌壳等与水稻同出[3, 62],而且遗址古土壤中发现有较多水生和沼生植物的孢粉和植硅体[78],这表明当时贾湖遗址周围是沼泽湖塘遍布的湿地环境。因为黍、粟生长需要排水性良好的土壤,所以这一环境并不适合旱作耕种。由此可知,在不同河流的冲积平原地区,局地水文生态环境是影响先民农作物选择的重要因素。
仰韶文化中晚期被认为处于北方旱作农业形成过程的完成阶段[27]。以耕种粟和黍为主的旱作农业已经成为中国北方地区仰韶文化分布范围内的经济主体,而稻作农业则少量存在[4]。本文分析结果表明,郑州地区此时也出现了类似的以黍粟为主要农作物,稻属作物含量较少的农业种植格局。在仰韶时代(约距今7000~5000年期间),我国北方处于全新世适宜期,降水量达到全新世的最高值,气候温暖湿润[7, 79],为粟的广泛栽培提供了合适的气候条件,郑州地区粟的比例也迅速上升(图 6),但这没有从根本上改变该区以黍为主的种植结构,可见此时气候并不是影响旱作农业粟、黍种植比例的关键因素。
如前文所述,郑州地区仰韶文化中晚期粟和稻的种植比例均显著提高,而且稻作已经分布到了台塬沟谷地带以及中小遗址当中,裴李岗时期稻属植物无法种植在黄土台塬的困难似乎已经被突破。这说明仰韶中晚期的农耕技术得到改进,优化了农作物结构,而稻-旱混作在更多遗址得到普及,这些进展使得农业取代采集活动成为先民生业经济的首选方式,最终促进了仰韶文化中晚期农业社会的建立[27]。
最新的研究表明,谷芽酒酿造以及宴饮活动是黄河中游仰韶文化人群的一个重要的共同文化特征[80~84]。残留物分析则显示,黍和稻是仰韶谷芽酒的主要谷物原料,但尚未发现粟的痕迹[80~84]。因此,以黍和稻为主要原料的谷芽酒酿造与饮酒活动的流行,既可能是仰韶时期农业生产以黍为主要作物的社会动力,也很可能是稻作向更多遗址传播的社会背景。此外,仰韶时期的统治阶层很可能将组织酿酒和宴饮活动集中在大型遗址,以作为获取与维护权力的重要手段[80, 83],与此同时,稻作农业也集中在大型聚落中。因此,稻很可能作为一种“贵食”被大城市里的显贵们享用。水稻在仰韶时期的这种分布状况及其重要性,可能促进了郑州地区乃至黄河下游地区聚落功能分化以及社会复杂化进程的出现。
综上所述,郑州地区是稻-旱混作最早出现的地区之一,在其黍粟旱作农业形成之际,便接受了稻作农业。但在裴李岗时期更偏重于黍,稻作仅局限于平原地带,经过仰韶文化中晚期的发展,粟、稻比例明显增加,稻作在空间上更加普及,混作体系的结构和分布日趋合理。黍、粟、稻3种农作物的混合耕作,形成于全新世适宜期暖湿的气候环境,伴随着南北方人口和生产技术的交流,使早期农业既稳定发展又不断调整和革新,成为郑州地区文化发展源源不断的动力,为该区向文明阶段的连续演进提供了必要的物质条件。
5 结论通过13个考古遗址的225个植硅体样品的分析,本文认为:1)郑州地区在裴李岗文化时期和仰韶文化中晚期均属于以黍为主的黍、粟、稻混作的农业格局;2)距今8000年前后,在全新世适宜期气候转暖变湿的背景下,稻作北传至黄河中游旱作区,形成了该地区最早的稻-旱混作模式;3)裴李岗时期农业的空间格局是,在冲积平原地带为稻-旱混作,在台塬沟谷地带为黍粟旱作,不同遗址农业的选择主要受地貌和水文因素影响;仰韶中晚期,粟和稻的比例显著提高,稻作进一步分布于台塬沟谷和中小聚落,标志着农耕技术的进步和作物结构的优化,而仰韶时期以黍-稻为原料的酿酒及宴饮活动的普及应是黍占主导和稻作传播的社会动力,这意味着农业生产开始打破自然条件限制,为郑州地区农业社会的建立和文明化进程奠定了基础。
致谢: 感谢审稿专家和编辑部杨美芳老师对本文提出的建设性意见和帮助。
| [1] |
Bellwood P. First Farmers:The Origins of Agricultural Societies[M]. London: Blackwell Publishing, 2005: 1-384.
|
| [2] |
陈胜前. 史前的现代化——中国农业起源过程的文化生态考察[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013: 1-359. Chen Shengqian. Modernization in Prehistory:Cultural Ecological Investigation on the Process of Agricultural Origin in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013: 1-359. |
| [3] |
Liu L, Chen X C. The Archaeology of China:From the Late Paleolithic to the Early Bronze Age[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012: 1-475.
|
| [4] |
秦岭.中国农业起源的植物考古研究与展望[C]//北京大学考古文博学院, 北京大学中国考古学研究中心.考古学研究(九).北京: 文物出版社, 2012: 260-315. Qin Ling. Archaeobotanical research and expectations on Chinese agriculture origin[C]//School of Archaeology and Museology of Peking University, Center of the Study of Chinese Archaeology of Peking University. Archaeological Research (9). Beijing: Cultural Relics Publishing House, 2012: 260-315. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KGXY201200017.htm |
| [5] |
赵志军. 中国古代农业的形成过程——浮选出土植物遗存证据[J]. 第四纪研究, 2014, 34(1): 73-84. Zhao Zhijun. The process of origin of agriculture in China:Archaeological evidence from flotation results[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34(1): 73-84. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.01.10 |
| [6] |
Marcott S A, Shakun J D, Clark P U, et al. A reconstruction of regional and global temperature for the past 11, 300 years[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6124): 1198-1201. DOI:10.1126/science.1228026 |
| [7] |
Chen F, Xu Q, Chen J, et al. East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5: 11186. DOI:10.1038/srep11186 |
| [8] |
Lu H Y. New methods and progress in research on the origins and evolution of prehistoric agriculture in China[J]. Science China:Earth Sciences, 2017, 60(12): 2141-2159. DOI:10.1007/s11430-017-9145-2 |
| [9] |
An C, Feng Z, Tang L. Environmental change and cultural response between 8000 and 4000 cal. yr BP in the western Loess Plateau, Northwest China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2004, 19(6): 529-535. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1417 |
| [10] |
韩建业. 论新石器时代中原文化的历史地位[J]. 江汉考古, 2004(1): 59-64. Han Jianye. Historical position of Central Plain cultures in Neolithic China[J]. Jianghan Archaeology, 2004(1): 59-64. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-0327.2004.01.009 |
| [11] |
夏正楷. 环境考古学——理论与实践[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2012: 1-352. Xia Zhengkai. Environmental Archaeology:Principles and Practice[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press, 2012: 1-352. |
| [12] |
王星光. 气候变化与黄河中下游地区的早期稻作农业[J]. 中国农史, 2011, 30(3): 3-12. Wang Xingguang. The climatic change and the early rice cultivation in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Agricultural History of China, 2011, 30(3): 3-12. |
| [13] |
王星光. 李家沟遗址与中原农业的起源[J]. 中国农史, 2013, 32(6): 13-20. Wang Xingguang. Lijiagou site and agricultural origin in the Central Plain[J]. Agricultural History of China, 2013, 32(6): 13-20. |
| [14] |
王星光, 徐栩. 新石器时代粟稻混作区初探[J]. 中国农史, 2003, 22(3): 3-9. Wang Xingguang, Xu Xu. A discussion on the rice-millet blended zone in the Neolithic Age[J]. Agricultural History of China, 2003, 22(3): 3-9. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-4459.2003.03.001 |
| [15] |
赵志军.中华文明形成时期的农业经济特点[M]//中国社会科学院考古研究所科技考古中心.科技考古(第3辑).北京: 科学出版社, 2011: 1-35. Zhao Zhijun. The characteristics of agriculture during the formation of Chinese civilization[M]//The Center for Scientific Archaeology, Institute of Archaeology, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. Science for Archaeology(Vol.3). Beijing: Science Press, 2011: 1-35. |
| [16] |
袁靖. 中华文明探源工程十年回顾:中华文明起源与早期发展过程中的技术与生业研究[J]. 南方文物, 2012(4): 5-12. Yuan Jing. Review of the project aimed at tracing the origins of Chinese civilization during the last ten years:Research on the technology and subsistence in the origin and early development of Chinese civilization[J]. Cultural Relics in Southern China, 2012(4): 5-12. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-6275.2012.04.002 |
| [17] |
庞小霞, 高江涛. 中原地区文明化进程中农业经济考察[J]. 农业考古, 2006(4): 1-13. Pang Xiaoxia, Gao Jiangtao. An investigation of agricultural economy in the process of civilization in the Central Plain[J]. Agricultural Archaeology, 2006(4): 1-13. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-2335.2006.04.001 |
| [18] |
赵志军.公元前2500-公元前1500年中原地区农业经济研究[M]//中国社会科学院考古研究所科技考古中心.科技考古(第2辑).北京: 科学出版社, 2007: 1-11. Zhao Zhijun. Research on the agriculture of the Central Plain during the period from 2500 BC to 1500 BC[M]//The Center for Scientific Archaeology, Institute of Archaeology, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. Science for Archaeology(Vol. 2). Beijing: Science Press, 2007: 1-11. |
| [19] |
韩建业. 中原和江汉地区文明化进程比较[J]. 江汉考古, 2016(6): 39-44. Han Jianye. A comparison of civilized course between the Central Plain and Jianghan area[J]. Jianghan Archaeology, 2016(6): 39-44. |
| [20] |
张健平, 吕厚远, 吴乃琴, 等. 关中盆地6000-2100 cal. a B.P.期间黍、粟农业的植硅体证据[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(2): 287-297. Zhang Jianping, Lü Houyuan, Wu Naiqin, et al. Phytolith evidence of millet agriculture during about 6000-2100 a B.P. in the Guanzhong Basin, China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2010, 30(2): 287-297. |
| [21] |
Lee G-A, Crawford G W, Liu L, et al. Plants and people from the early Neolithic to Shang periods in North China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2007, 104(3): 1087-1092. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0609763104 |
| [22] |
傅稻镰, 张海, 方燕明.颍河中上游谷地植物考古调查的初步报告[M]//北京大学考古文博学院, 河南省文物考古研究所.登封王城岗考古发现与研究(2002-2005).郑州: 大象出版社, 2007: 916-958. Fuller D Q, Zhang Hai, Fang Yanming. A preliminary report of the survey archaeobotany of the upper Ying Valley(Henan Province)[M]//School of Archaeology and Museology of Peking University, Henan Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology. Archaeological Discovery and Research at the Wangchenggang Site in Dengfeng(2002-2005). Zhengzhou: Great Elephant Publisher, 2007: 916-958. |
| [23] |
张俊娜, 夏正楷, 张小虎. 洛阳盆地新石器-青铜时期的炭化植物遗存[J]. 科学通报, 2014, 59(34): 3388-3397. Zhang Junna, Xia Zhengkai, Zhang Xiaohu. Research on charred plant remains from the Neolithic to the Bronze Age in Luoyang Basin[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(34): 3388-3397. |
| [24] |
赵志军, 张居中. 贾湖遗址2001年度浮选结果报告[J]. 考古, 2009(8): 84-93. Zhao Zhijun, Zhang Juzhong. Flotation results of 2001 excavation season from Jiahu site[J]. Archaeology, 2009(8): 84-93. |
| [25] |
Deng Z H, Qin L, Gao Y, et al. From early domesticated rice of the middle Yangtze basin to millet, rice and wheat agriculture:Archaeobotanical macro-remains from Baligang, Nanyang Basin, Central China[J]. PLoS ONE, 2015, 10: e0139885. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0139885 |
| [26] |
秦岭.南交口遗址2007年出土仰韶文化早、中期植物遗存及相关问题探讨[M]//河南省文物考古研究所.三门峡南交口.北京: 科学出版社, 2009: 427-435. Qin Ling. The 2007 Nanjiaokou site excavated Early to Mid Yangshao plant remains[M]//Henan Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology. Nanjiaokou Site in Sanmenxia. Beijing: Science Press, 2009: 427-435. |
| [27] |
赵志军. 仰韶文化时期农耕生产的发展和农业社会的建立——鱼化寨遗址浮选结果的分析[J]. 江汉考古, 2017(6): 98-108. Zhao Zhijun. The development of agriculture in the time of Yangshao Culture and the establishment of agricultural society:An analysis on the flotation result of Yuhuazhai site[J]. Jianghan Archaeology, 2017(6): 98-108. |
| [28] |
张松林.郑州文物考古工作回顾与思考[M]//张松林.郑州文物考古与研究(一)(上).北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 3-28. Zhang Songlin. Reviewing and thinking of archaeological work in Zhengzhou[M]//Zhang Songlin. Archaeological Research in Zhengzhou(Vol. 2, Part A). Beijing: Science Press, 2003: 3-28. |
| [29] |
周昆叔, 张松林, 张震宇, 等. 论嵩山文化圈[J]. 中原文物, 2005(1): 12-20. Zhou Kunshu, Zhang Songlin, Zhang Zhenyu, et al. Research on the Mountain Song culture circle[J]. Cultural Relics of Central China, 2005(1): 12-20. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-1731.2005.01.002 |
| [30] |
刘彦锋, 鲍颖建.郑州朱寨遗址考古发掘与收获[N].中国文物报, 2012年7月13日第8版. Liu Yanfeng, Bao Yingjian. Excavation and discovery of the Zhuzhai site in Zhengzhou City[N]. China Cultural Relics News, 13th July, 2012, 8th Page. |
| [31] |
河南师范大学历史文化学院, 郑州市文物考古研究院. 郑州市朱寨遗址裴李岗文化遗存[J]. 考古, 2017(5): 14-24. The School of History and Culture, Henan Normal University, Zhengzhou Municipal Institute of Archaeology. The remains of the Peiligang Culture in the Zhuzhai site, Zhengzhou City[J]. Archaeology, 2017(5): 14-24. |
| [32] |
Bestel S, Bao Y, Zhong H, et al. Wild plant use and multi-cropping at the early Neolithic Zhuzhai site in the middle Yellow River region, China[J]. The Holocene, 2018, 28(2): 195-207. DOI:10.1177/0959683617721328 |
| [33] |
Wang C, Lu H, Gu W, et al. Temporal changes of mixed millet and rice agriculture in Neolithic-Bronze Age Central Plain, China:Archaeobotanical evidence from the Zhuzhai site[J]. The Holocene, 2018, 28(5): 738-754. DOI:10.1177/0959683617744269 |
| [34] |
Wang C, Lu H, Gu W, et al. The spatial pattern of farming and factors influencing it during the Peiligang Culture period in the middle Yellow River valley, China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2017, 62(23): 1565-1568. |
| [35] |
Piperno D R. Phytoliths:A Comprehensive Guide for Archaeologists and Paleoecologists[M]. New York: AltaMira Press, 2006: 1-238.
|
| [36] |
Ball T, Chandler-Ezell K, Dickau R, et al. Phytoliths as a tool for investigations of agricultural origins and dispersals around the world[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2016, 68: 32-45. DOI:10.1016/j.jas.2015.08.010 |
| [37] |
Pearsall D M. Paleoethnobotany:A Hand Book of Procedure(Third edition)[M]. Walnut Creek: Left Coast Press, 2015: 1-600.
|
| [38] |
邱士可, 鲁鹏. 河南伊洛河流域更新世地貌演变及驱动评述[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 2013, 29(3): 96-100. Qiu Shike, Lu Peng. Pleistocene landform evolution and its drive review of the Yiluo River basin in Henan Province[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 2013, 29(3): 96-100. |
| [39] |
鲁鹏, 田燕, 陈盼盼, 等. 环嵩山地区9000-3000 a BP聚落分布与区域构造的关系[J]. 地理学报, 2014, 69(6): 738-746. Lu Peng, Tian Yan, Chen Panpan, et al. The relationship between settlements distribution and regionaltectonics around the Songshan Mountain during 9000-3000 a BP[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2014, 69(6): 738-746. |
| [40] |
张震宇, 周昆叔, 杨瑞霞, 等. 双洎河流域环境考古[J]. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27(3): 453-460. Zhang Zhenyu, Zhou Kunshu, Yang Ruixia, et al. Environmental archaeology in the Shuangji River basin[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27(3): 453-460. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.03.018 |
| [41] |
王文楷, 毛继周, 陈代光. 河南地理志[M]. 郑州: 河南人民出版社, 1990: 1-465. Wang Wenkai, Mao Jizhou, Chen Daiguang. Geography in Henan[M]. Zhengzhou: Henan People's Publishing House, 1990: 1-465. |
| [42] |
王幼平.织机洞的石器工业与古人类活动[C]//北京大学考古文博学院, 北京大学中国考古学研究中心.考古学研究(七).北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 136-148. Wang Youping. Paleolithic industry and human activities in Zhijidong site[C]//School of Archaeology and Museology of Peking University, Center of the Study of Chinese Archaeology of Peking University. Archaeological Research (7). Beijing: Cultural Relics Press, 2008: 136-148. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KGXY200800014.htm |
| [43] |
王幼平, 汪松枝. MIS 3阶段嵩山东麓旧石器发现与问题[J]. 人类学学报, 2014, 33(3): 304-314. Wang Youping, Wang Songzhi. New achievements and perspectives on Paleolithic archaeology during the MIS 3 along the eastern foot of Songshan Mountain, Henan Province[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 2014, 33(3): 304-314. |
| [44] |
王幼平. 新密李家沟遗址研究进展及相关问题[J]. 中原文物, 2014(1): 20-24. Wang Youping. Research progress and related issues on the Lijiagou site, Xinmi County[J]. Cultural Relics of Central China, 2014(1): 20-24. |
| [45] |
王永吉, 吕厚远. 植物硅酸体研究及应用[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993: 1-228. Wang Yongji, Lü Houyuan. The Study of Phytolith and Its Application[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1993: 1-228. |
| [46] |
Lu H, Zhang J, Wu N, et al. Phytoliths analysis for the discrimination of foxtail millet(Setaria italica)and common millet(Panicum miliaceum)[J]. PLoS ONE, 2009, 4(2): e4448. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0004448 |
| [47] |
Lu H, Wu N, Liu B. Recognition of rice phytoliths[C]//Pinilla A, Juan-Tresserras J, Machado M J. Monografias del Centro de Ciencias Medioambientales 4. Madrid, 1997: 159-174.
|
| [48] |
Zuo X, Lu H, Zhang J, et al. Radiocarbon dating of prehistoric phytoliths:A preliminary study of archaeological sites in China[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 26769. DOI:10.1038/srep26769 |
| [49] |
Bronk Ramsey C. Bayesian analysis of radiocarbon dates[J]. Radiocarbon, 2009, 51(1): 337-360. DOI:10.1017/S0033822200033865 |
| [50] |
Reimer P J, Bard E, Bayliss A, et al. IntCal13 and marine13 radiocarbon age calibration curves 0-50, 000 years cal BP[J]. Radiocarbon, 2013, 55(4): 1869-1887. DOI:10.2458/azu_js_rc.55.16947 |
| [51] |
张居中, 程至杰, 蓝万里, 等. 河南舞阳贾湖遗址植物考古研究的新进展[J]. 考古, 2018(4): 100-110. Zhang Juzhong, Cheng Zhijie, Lan Wanli, et al. New archaeobotanical progress of Jiahu site, Wuyang County, Henan Province[J]. Archaeology, 2018(4): 100-110. |
| [52] |
Harvey E L, Fuller D Q. Investigating crop processing using phytolith analysis:The example of rice and millets[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2005, 32(5): 739-752. DOI:10.1016/j.jas.2004.12.010 |
| [53] |
Zhang J, Lu H, Gu W, et al. Early mixed farming of millet and rice 7800 years ago in the middle Yellow River region, China[J]. PLoS ONE, 2012, 7(12): e52146. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0052146 |
| [54] |
Lu T L D. The transition from foraging to farming in China[J]. Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association, 1999, 18: 77-80. |
| [55] |
李友谋. 裴李岗文化[M]. 北京: 文物出版社, 2003: 1-211. Li Youmou. Peiligang Culture[M]. Beijing: Cultural Relics Publishing House, 2003: 1-211. |
| [56] |
王吉怀. 新郑沙窝李遗址发现碳化粟粒[J]. 农业考古, 1984(2): 276. Wang Jihuai. Carbonized foxtail millets were found in the Shawoli site, Xinzheng[J]. Agricultural Archaeology, 1984(2): 276. |
| [57] |
许天申. 论裴李岗文化时期的原始农业——河南古代农业研究之一[J]. 中原文物, 1998(3): 12-23. Xu Tianshen. Discussion of original agriculture of the Peiligang period:One of the ancient agricultural research sites in Henan Province[J]. Cultural Relics of Central China, 1998(3): 12-23. |
| [58] |
孔昭宸, 刘长江, 张居中. 渑池班村新石器遗址植物遗存及其在人类环境学上的意义[J]. 人类学学报, 1999, 18(4): 290-295. Kong Zhaochen, Liu Changjiang, Zhang Juzhong. Discovery of plant remains in the Neolithic site at the Bancun site, Mianchi County, Henan Province and their significance in human environment[J]. Acta Anthropologica Sinica, 1999, 18(4): 290-295. |
| [59] |
张永辉, 翁屹, 姚凌, 等. 裴李岗遗址出土石磨盘表面淀粉粒的鉴定与分析[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31(5): 891-899. Zhang Yonghui, Weng Yi, Yao Ling, et al. Identification and analysis of starch granules on the surface of the slabs from Peiligang site[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2011, 31(5): 891-899. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.05.14 |
| [60] |
张永辉.裴李岗文化植物类食物加工工具表面淀粉粒研究[D].合肥: 中国科学技术大学硕士学位论文, 2011: 1-63. Zhang Yonghui. Research of Starch Granules on the Surface of the Tools of Botanic Food of the Peiligang Culture[D]. Hefei: The Master's Thesis of University of Science and Technology of China, 2011: 1-63. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D142067 |
| [61] |
杨玉璋, 李为亚, 姚凌, 等. 淀粉粒分析揭示的河南唐户遗址裴李岗文化古人类植物性食物资源利用[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(1): 229-239. Yang Yuzhang, Li Weiya, Yao Ling, et al. Plant resources utilization at the Tanghu siteduring the Peiligang Culture period based on starch grain analysis, Henan Province[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(1): 229-239. |
| [62] |
Zhao Z. New archaeobotanic data for the study of the origins of agriculture in China[J]. Current Anthropology, 2011, 52(S4): S295-S306. DOI:10.1086/659308 |
| [63] |
刘长江, 靳桂云, 孔昭宸. 植物考古:种子和果实研究[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 1-273. Liu Changjiang, Jin Guiyun, Kong Zhaochen. Archaeobotany:Research on Seeds and Fruits[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 1-273. |
| [64] |
Crawford G W, Chen X X, Luan F S, et al. People and plant interaction at the Houli Culture Yuezhuang site in Shandong Province, China[J]. The Holocene, 2016, 26(10): 1594-1604. DOI:10.1177/0959683616650269 |
| [65] |
Jin G Y, Wu W W, Zhang K S, et al. 8000-year old rice remains from the north edge of the Shandong Highlands, East China[J]. Journal of Archaeological Science, 2014, 51: 34-42. DOI:10.1016/j.jas.2013.01.007 |
| [66] |
Zheng Z, Yuan B, Petit-Maire N. Paleoenvironments in China during the Last Glacial Maximum and the Holocene Optimum[J]. Episodes, 1998, 21(3): 152-158. |
| [67] |
Wang S, Gong D. Climate in China during the four special periods in Holocene[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2000, 10(4): 325-332. |
| [68] |
Ge Q, Wang S, Wen X, et al. Temperature and precipitation changes in China during the Holocene[J]. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 2007, 24(6): 1024-1036. DOI:10.1007/s00376-007-1024-7 |
| [69] |
方修琦, 侯光良. 中国全新世气温序列的集成重建[J]. 地理科学, 2011, 31(4): 385-393. Fang Xiuqi, Hou Guangliang. Synthetically reconstructed Holocene temperature change in China[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2011, 31(4): 385-393. |
| [70] |
Xiao J, Xu Q, Nakamura T, et al. Holocene vegetation variation in the Daihai Lake region of North-Central China:A direct indication of the Asian monsoon climatic history[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2004, 23(14-15): 1669-1679. DOI:10.1016/j.quascirev.2004.01.005 |
| [71] |
Yang S, Ding Z, Li Y, et al. Warming-induced northwestward migration of the East Asian monsoon rain belt from the Last Glacial Maximum to the mid-Holocene[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(43): 13178-13183. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1504688112 |
| [72] |
Fuller D, Sato Y, Castillo C, et al. Consilience of genetics and archaeobotany in the entangled history of rice[J]. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2010, 2(2): 115-131. DOI:10.1007/s12520-010-0035-y |
| [73] |
d'Alpoim Guedes J, Jin G, Bocinsky R K. The impact of climate on the spread of rice to North-Eastern China:A new look at the data from Shandong Province[J]. PLoS ONE, 2015, 10(6): e0130430. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0130430 |
| [74] |
张弛. 论贾湖一期文化遗存[J]. 文物, 2011(3): 46-53. Zhang Chi. On the cultural remains of Jiahu 1 Phase[J]. Cultural Relics, 2011(3): 46-53. |
| [75] |
Zhang C, Hsiao-Chun H. Jiahu 1:Earliest farmers beyond the Yangtze River[J]. Antiquity, 2013, 87(335): 46-63. DOI:10.1017/S0003598X00048614 |
| [76] |
Lu H, Zhang J, Liu K B, et al. Earliest domestication of common millet(Panicum miliaceum)in East Asia extended to 10, 000 years ago[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2009, 106(18): 7367-7372. DOI:10.1073/pnas.0900158106 |
| [77] |
Weber S, Lehman H, Barela T, et al. Rice or millets:Early farming strategies in prehistoric Central Thailand[J]. Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, 2010, 2(2): 79-88. DOI:10.1007/s12520-010-0030-3 |
| [78] |
陈报章. 河南贾湖遗址植硅石组合及其在环境考古学上的意义[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2001, 18(2): 211-216. Chen Baozhang. Phytolith assemblages of the Neolithic site at Jiahu, Henan Province and its significance in environmental archaeology[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2001, 18(2): 211-216. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2001.02.010 |
| [79] |
An C B, Feng Z D, Barton L. Dry or humid?Mid-Holocene humidity changes in arid and semi-arid China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2006, 25(3): 351-361. |
| [80] |
刘莉, 王佳静, 陈星灿, 等. 仰韶文化大房子与宴饮传统:河南偃师灰嘴遗址F1地面和陶器残留物分析[J]. 中原文物, 2018(1): 32-43. Liu Li, Wang Jiajing, Chen Xingcan, et al. Large houses and feasting tradition of the Yangshao culture:Starch and phytolith analyses of the residues from pottery vessels and floors of house No.1 at Huizui in Yanshi, Henan[J]. Cultural Relics of Central China, 2018(1): 32-43. |
| [81] |
刘莉, 王佳静, 赵昊, 等. 陕西蓝田新街遗址仰韶文化晚期陶器残留物分析:酿造谷芽酒的新证据[J]. 农业考古, 2018(1): 7-15. Liu Li, Wang Jiajing, Zhao Hao, et al. Residue analyses on pottery from the late Yangshao Culture site of Xinjie in Lantian, Shanxi:New evidence of beer brewing[J]. Agricultural Archaeology, 2018(1): 7-15. |
| [82] |
刘莉. 早期陶器、煮粥、酿酒与社会复杂化的发展[J]. 中原文物, 2017(2): 24-34. Liu Li. Early pottery, cooking porridge, beer brewing and the development of social complexity[J]. Cultural Relics of Central China, 2017(2): 24-34. |
| [83] |
刘莉, 王佳静, 赵雅楠, 等. 仰韶文化的谷芽酒:解密杨官寨遗址的陶器功能[J]. 农业考古, 2017, 6: 26-32. Liu Li, Wang Jiajing, Zhao Yanan, et al. The beer of Yangshao culture:Revealing the function of pottery from the Yangguanzhai site in Shanxi[J]. Agricultural Archaeology, 2017, 6(6): 26-32. |
| [84] |
Wang J J, Liu L, Ball T, et al. Revealing a 5, 000-y-old beer recipe in China[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(23): 6444-6448. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1601465113 |
2 Key Laboratory of Cenozoic and Environment, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029;
3 CAS Center for Excellence in Tibetan Plateau Earth Science, Beijing 100101;
4 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049;
5 Zhengzhou Municipal Institute of Archaeology, Zhengzhou 450052, Henan;
6 Institutions of Earth Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029;
7 School of Geographical Sciences, Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou 350007, Fujian;
8 The School of History and Culture, Henan Normal University, Xinxiang 453007, Henan)
Abstract
The origin and development of agriculture is an important transformation in human subsistence and is also economic base for the rise of civilizations. The Zhengzhou area is acknowledged as a home to the millet agriculture in North China and one of the major regions for the northward spread of rice agriculture from South China, where the Huaxia civilization rise. However, the spatial-temporal evolution of its agriculture during the mid-Holocene is still unclear, mainly due to the limited regional archaeobotanical research.In this paper, a total of 13 Peiligang-Yangshao culture sites such as Zhuangling(34°49'19"N, 113°8'46"E), Yingyang(34°24'29"N, 112°45'4"E), Yuancun(34°23'21"N, 113°1'57"E), Caiyuangou(34°26'34"N, 113°19'18"E), Maanhe(34°31'44"N, 113°20'6"E), Magou(34°32'31"N, 113°30'7"E), Shashizui(34°32'42"N, 113°31'34"E), Beilizhuang(34°26'32"N, 113°38'5"E), Dahecun(34°50'38"N, 113°41'38"E), Zhuzhai(34°49'31"N, 113°30'19"E), Wuluoxipo(34°38'20"N, 113°0'14"E), Lijiagou(34°33'54"N, 113°31'26"E), and Wangzui(34°26'54"N, 113°34'33"E) in Zhengzhou area, which located on different landforms and had different sizes, were selected to do systematic sampling. A total of 225 and 30 samples were collected from ash pits and cultural layers for phytolith analysis and AMS radiocarbon dating, respectively. We then extracted phytoliths from these samples by wet oxidation method, and phytolith counting and identification were performed using Leica DM750 optical microscope at 400 magnification. In most samples, more than 400 phytoliths were counted. The radiocarbon dating was conducted at Beta Analytic Radiocarbon Dating Laboratory.Except for three abnormal dates from LJG1 in Lijiagou site and H218 and H214 in Zhuzhai site, the dates are in line with the cultural ages. The available dates cover the time interval 6417~2628 cal.B.C.(95.4% range), which falls within the age of the Peiligang culture and Yangshao culture. 24 phytolith types were identified from all 225 samples, including η type from husks of common millet(Panicum miliaceum), Ω type from husks of foxtail millet(Setaria italica), and double-peaked, bulliform, and parallel-bilobe types from rice(Oryza sativa). Quantitative analysis of these crop phytoliths indicated that mixed millet and rice agriculture formed in the Zhengzhou area about 8000 years ago, which was benefitted from the warm-wet conditions during the Holocene Climatic Optimum. Common millet was the principal crop in the Peiligang and middle-late Yangshao periods. During the Peiligang period, the spatial pattern of farming was millet farming in the hilly lands, while mixed farming was conducted in the alluvial plains. In the same climate background, the agricultural mode selection in different sites was mainly influenced by landform and hydrology. During the middle-late Yangshao period, the proportion of foxtail millet and rice was significantly higher than that in Peiligang culture, and rice cultivation was no longer confined to large sites situated in the lowlands and began to spread into the hilly lands and small sites, suggesting the deepening of crop diversity and the optimization of agriculture planting structure. This pattern of crop production may have been mainly influenced by social background and artificial selection, which overcame the limitation of environmental factors, facilitating the establishment of an agricultural society and the civilizing process in Zhengzhou area. 2019, Vol.39
2019, Vol.39
