2 吉林大学边疆考古研究中心, 吉林 长春 130024;
3 黑龙江省文物考古研究所, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150008;
4 齐齐哈尔第十六中学, 黑龙江 齐齐哈尔 161006;
5 苏州新区实验小学, 江苏 苏州 215011)
嫩江流域是东北地区古代先民遗存分布比较密集的地区。20世纪30年代,梁思永[1]首次对黑龙江省齐齐哈尔市附近的昂昂溪遗址进行了调查和发掘,揭开了嫩江流域考古的序幕。自此,众多学者在嫩江流域发现了大量自新石器时代以来的遗址[2]。以压琢细石器为特征的昂昂溪文化是嫩江流域典型的新石器时代的文化,是中国北方“渔猎文化”的代表[3],也是嫩江流域文明起源过程中具有里程碑意义的界标[4]。嫩江流域青铜时代以来的考古文化依据年代早晚顺序分别是小拉哈文化(夏至早商时期)[5]、白金宝文化(西周至春秋时期)和汉书二期文化(战国至西汉时期)[6]。
我国考古遗址众多,在不同的地区形成了各具特色、体系和连续的文化序列,如黄河上游的齐家文化-寺洼文化-辛店文化[7];长江下游的马家浜文化-崧泽文化-良渚文化-马桥文化[8];西拉木伦河流域的赵宝沟文化-红山文化-小河沿文化-夏家店下层文化[9]。而不同的文化形式及发展很大程度上会受到自然环境变化的影响,尤其与全新世的气候密切相关。早全新世是新石器文化的发展期,中全新世温暖期是新石器文化的高潮期,一般在气候相对稳定的时期,文化得以发展并推进文明进程,全新世后期,气候相对变凉干,在气候发生突变的不稳定期,可能导致文化的衰落或转型[10]。叶玮等[11]从自然环境演变的角度探讨了良渚文化发展与消亡的过程,提出文化的发生与发展受自然环境的制约;莫多闻等[12]对甘肃葫芦河流域的考古学文化和古环境进行了调查和研究后提出,气候变化带来的植被变化是葫芦河流域文化变迁的一个主要原因;夏正楷等[13]对内蒙西拉木伦河流域的考古学文化演变的地貌背景进行了分析,发现人类活动和地貌等自然环境因素之间有明显的相互关系。嫩江流域与中原地区及东北南部相比,环境背景存在一定的差异,孕育的史前文化也具有鲜明的地域特色。从出土的相关材料来看,嫩江流域的新石器文化以“渔猎文化”为主要类型,这与在黄河、长江及东北南部地区发现的“种植农业型新石器文化”存在着较大的区别[1]。而目前鲜有对嫩江流域新石器时代以来文化演变的环境背景研究,并且考古学界对嫩江流域昂昂溪文化衰亡的原因及昂昂溪先民的去向问题存在着一定的争议[14]。
植硅体以其保存性好、原地沉积的特点,被广泛地应用于研究古植被、古环境的变化[15~16]以及环境考古研究[17~19]。王淑云等[17]通过对浙江余姚田螺山遗址植硅体和硅藻等化石的研究,分析了史前先民活动的环境背景;萧家仪等[18]通过对南京郭家山遗址进行植硅体分析,探讨了湖熟文化的环境背景;邹胜利等[19]对湖北省金罗家考古遗址进行了多环芳烃的分布和植硅体分析探讨了人类活动和古环境之间的关系。而利用粒度分析测得沉积物的粒度参数能够敏感地反映沉积物质来源,是恢复沉积物沉积过程的重要替代指标[20~24]。烧失量可以结合其他古环境记录重建古气候和古环境[25~28]。昂昂溪新石器时代遗址多位于适合渔猎的河湖附近的沙丘或台地上,在嫩江流域广泛分布,以嫩江沿岸最为密集,多达百余处[29]。生产工具主要是压制石器和骨器。而洪河遗址遗存丰富,与昂昂溪遗址有相近的出土器物特征和年代跨度1) 1)由吉林大学边疆考古研究中心汤卓炜老师提供的数据,目前尚未发表,是嫩江中游地区昂昂溪文化的代表遗址之一,为研究嫩江流域古代人类活动的环境背景提供了载体。本文通过对洪河遗址附近的自然沉积剖面进行植硅体、粒度及烧失量的多指标分析,结合考古学和相关学科的研究,初步探讨了嫩江流域的新石器时代以来文化演变的环境背景;并结合其他考古文献资料,尝试从环境变化的角度解释昂昂溪文化衰亡的原因及史前先民的去向问题。
1 研究区概况嫩江流域(44°02′~50°36′N,119°12′~127°54′E)位于大兴安岭以东,中国东北平原的西北部,地跨黑龙江、吉林、内蒙古三省区。海拔约150~200 m。嫩江流域属于寒温带半湿润大陆性气候,冬季漫长而寒冷,夏季短促而多雨,年均气温2~4 ℃。土壤类型主要有草甸土、暗棕壤、黑钙土、风沙土、沼泽土等。本区植被类型主要为草甸草原,同时也有沼生植被、盐生植被和沙生植被分布[30]。
洪河遗址位于黑龙江省齐齐哈尔市富拉尔基区杜尔门沁达斡尔乡洪河村东南约1 km处的嫩江中游右岸。与梁思永先生1930年发掘确立的昂昂溪文化的五福遗址直线距离约12 km[1]。洪河遗址呈细窄条带状沿嫩江分布,东西宽百余米,南北长达十余千米,地表高出现有江面近10 m。遗址发掘面积约750 m2,文化层深度达3.2 m,发现了包含有新石器时代和青铜时代两个阶段的文化遗存1)。发掘过程中发现了环壕和房址,属于大型聚落遗址,出土器物主要包括陶器(陶罐、陶壶、陶杯)、石器(拇指盖型刮削器、石镞、石钻、石刃)、骨器(骨锥、骨鱼镖、骨镞)和蚌器(蚌刀、穿孔饰件)等,文化遗存较为丰富。遗址周围分布的现代植物主要是蒿属(Artemisia)、藜科(Chenopodiaceae)、禾本科(Poaceae)、菊科(Asteraceae)、十字花科(Brassicaceae)等[31]。
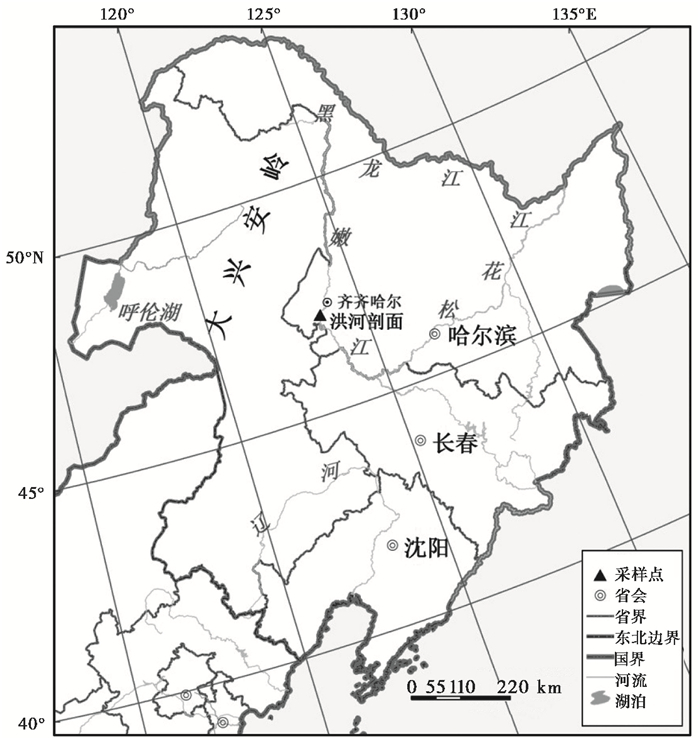
2 剖面采样与研究方法 2.1 剖面采样及年代测定洪河剖面(47°07′50″N,123°37′08″E)选自洪河遗址附近西北方向的自然沉积地层(图 1),剖面深3 m,由下至上间隔10 cm采样,共采得30个样品,分别编号为QH1~QH30。根据Shepard[32]对沉积岩性的分类原则以及剖面沉积物特征的变化,自下而上沉积物分为4层,分别为灰色砂层(300~290 cm)、粉砂质砂(290~200 cm)、含粉砂的砂(200~70 cm)和砂(70~0 cm)。为了确定采样剖面的年代,实验采集了4个沉积物样品,分别在台湾大学地球科学系和广州地球化学研究所进行了AMS 14C年龄测试(表 1),对所获得的年龄数据采用Calib Rev 7.0.1程序[33]校正至日历年龄后,通过线性内插确定剖面的年龄为7024 cal. a B. P.以来。
|
图 1 嫩江中游洪河剖面位置示意图 Fig. 1 The location of Honghe profile in the middle reaches of Nenjiang River |
| 表 1 洪河剖面沉积物样品的AMS 14C年代测定结果 Table 1 Results of AMS 14C dating of soil samples from Honghe profile |
对剖面样品进行植硅体提取、鉴定和统计,同时测定沉积物样品的粒度特征和烧失量。
(1) 植硅体分析:实验采取湿式灰化法处理样品[34],样品烘干后,称取5 g样品置于离心管中,加浓度为10%的稀盐酸溶液除碳酸盐,用蒸馏水清洗盐酸后加入浓HNO3溶液反应至有机质完全氧化,再用蒸馏水清洗硝酸后加入重液浮选植硅体,清洗重液后加入孢子并清洗至中性,用树胶制作永久薄片并在Motic生物显微镜下观察统计植硅体,每个样品统计植硅体300粒以上。植硅体组合分布可以指示植被与气候环境的变化,结合不同指数研究可以半定量研究环境的冷暖、干湿变化。如气候指数(Ic=早熟禾亚科植硅体/(早熟禾亚科植硅体+虎尾草亚科植硅体+黍亚科植硅体)和干旱指数(Iph=虎尾草亚科植硅体/(虎尾草亚科植硅体+黍亚科植硅体),均可用于研究环境的变化[35~37],其中虎尾草亚科植硅体为短鞍型,产于C4旱生草本植物;哑铃型和十字型则为黍亚科植硅体,产于C4非旱生草本;帽型和齿型为早熟禾亚科植硅体,产于C3草本植物。
(2) 粒度分析:将样品烘干后置于离心管中,先后加入浓度为10%的稀盐酸溶液和浓度为30%的H2O2溶液,去除样品种的碳酸盐和有机质,蒸馏水清洗至中性后向样品中加入六偏磷酸钠((NaPO3)6)溶液,并置于超声波振荡器中振荡7 min,用Microtrac S3500激光粒度仪进行粒度测试,得到各样品的粒度参数数据。
(3) 烧失量分析:将样品烘干后称重,置于马弗炉中500 ℃加热4 h后取出称重,计算前后重量差即为烧失量变化。有研究表明,沉积物中有机碳含量与烧失量呈现一致的变化关系[25]。因此,烧失量变化可以反映沉积物中有机碳含量变化,进而可以反映出沉积物中有机质的含量变化。
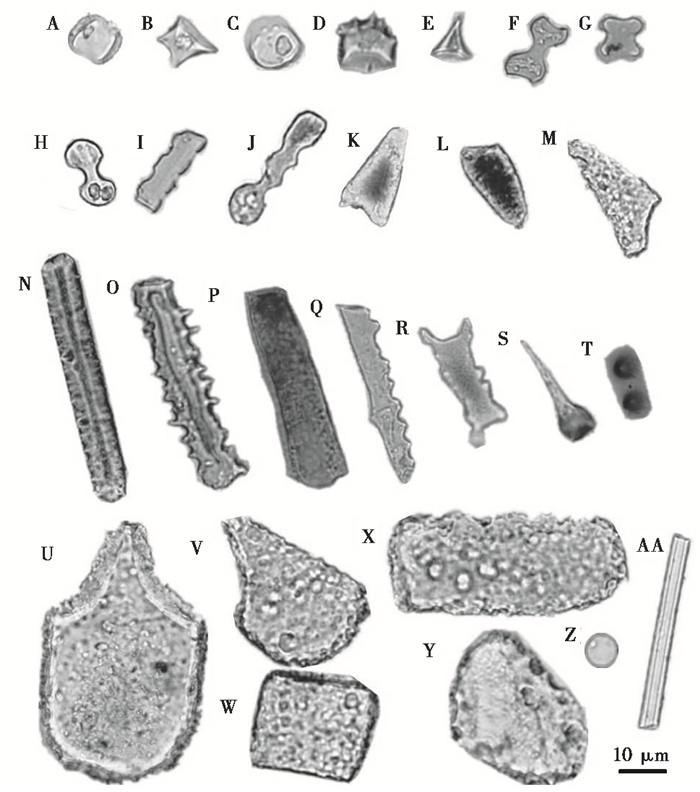
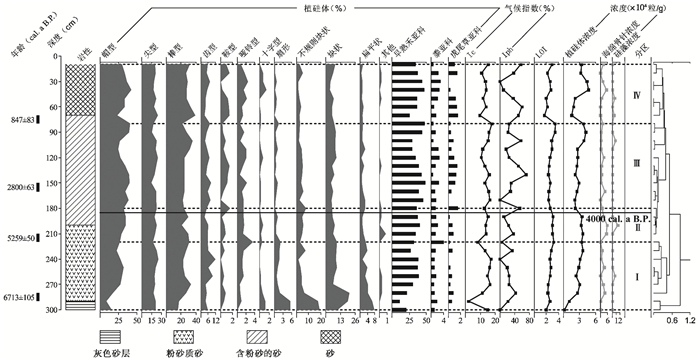
3 结果分析 3.1 植硅体分析和粒度分析结果通过对洪河剖面的30个样品进行镜下鉴定,共统计了9986粒植硅体,类型分别有:鞍型、帽型、哑铃型、十字型、齿型、尖型、棒型、扇型、块状、毛发状等,同时剖面中还发现了少量的海绵骨针和硅藻(图 2)。综合分析植硅体组合的变化特征,结合聚类分析结果,洪河剖面植硅体变化自下而上可分为4个组合带(图 3)。
|
图 2 洪河剖面代表性植硅体形态 A~B:鞍型(saddle);C~E:帽型(rondel);F:哑铃型(bilobate);G:十字型(cross);H~J:齿型(trapeziform);K~M:尖型(lanceolate);N~R:棒型(elongate);S:毛发状(hair);T:硅质突起(conical epidermal);U~V扇型(cuneiform);W~Y:块状(blocky);Z:硅藻(diatom);AA:海绵骨针(sponge spicules) Fig. 2 Microphotographs of phytoliths in Honghe profile |
|
图 3 洪河剖面植硅体百分含量、植硅体指数、植硅体浓度及烧失量变化图谱 Fig. 3 The percentage, the index and the concentration of phytolith and LOI for Honghe profile |
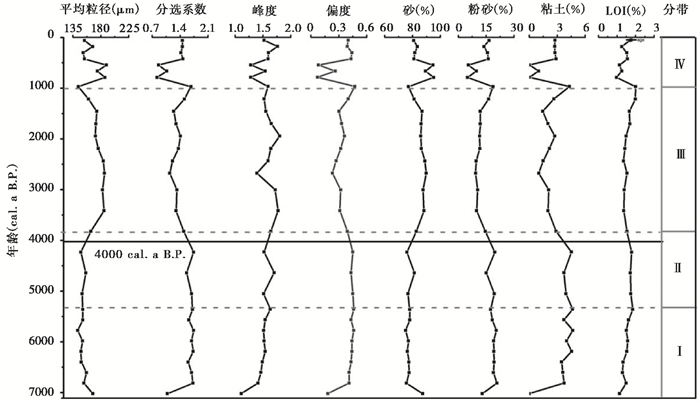
根据洪河遗址剖面各粒级百分比、粒度参数特征(平均粒径(Mz)、标准差(Sd)、分选系数(σI)、偏度(SkI)和峰度(KG))(图 4)、频率分布曲线和概率累积曲线(图 5)可知:剖面岩性总体较粗,沉积物颗粒分布在0~700 μm之间,平均粒径大部分在143.7~188.9 μm之间,均以砂(平均含量82.7%)为主,粉砂次之(平均含量14.6%),分选系数(σI)介于0.9~1.7之间,整体分选中等;偏度(SkI)大多集中在0.4~0.5之间,多为极正偏;峰度(KG)多在1.1~1.5之间,属于较尖窄的沉积物形态。频率分布曲线呈现不对称双峰曲线,主峰的众数值在105~400 μm之间。概率累积曲线呈三段式。鉴于洪河遗址濒临嫩江,位于高河漫滩的沙丘之上,附近沙地广泛分布,沙源丰富,并受到冬季风的影响,冬春季节风力作用较强,形成动力条件较稳定,风积作用应是剖面形成的主要动力。裘善文等[38]对松嫩沙地黑龙江他拉哈镇的剖面沉积物研究发现,沉积物平均粒径在100~250 μm之间,把他拉哈沙地风成沙的粒度特征和嫩江冲积沙进行对比,发现两者的平均粒径相差不大;李取生[39]通过对松嫩沙地黑龙江齐齐哈尔卧牛吐剖面的浅黄色细沙层进行粒度、重矿物和石英砂表面扫描电镜分析,发现细砂既有风成特点,又保留了些冲积特征。因此,推测洪河剖面沉积物来自于嫩江冲积沙经风力吹扬、搬运、堆积而成。
|
图 4 洪河剖面粒度参数变化曲线 Fig. 4 Variation of grain size parameters of Honghe profile |

|
图 5 洪河剖面样品的粒径频率分布曲线和概率累积曲线 Fig. 5 Grain size frequency distribution curves andcumulative frequency distribution curves for Honghe profile |
根据植硅体聚类分析的特征,对洪河剖面植硅体分析、粒度分析和烧失量测定的结果进行综合描述,自下而上分为4个组合带谱(图 3和4)。
带Ⅰ:(300~220 cm):7024~5360 cal. a B. P.
本带帽型、尖型、棒型和块状植硅体含量较多,早熟禾亚科植硅体含量逐渐增加,扇型植硅体含量较多,达到剖面中的最高值。黍亚科和虎尾草亚科植硅体含量较少。干旱指数较低,海绵骨针浓度相对较高,烧失量和植硅体浓度呈上升趋势。平均粒径多集中于142.7~167.2 μm之间,砂的含量最高(74.92%~87.16%),粉砂次之,粘土含量波动较大。
带Ⅱ:(220~180 cm):5360~3820 cal. a B. P.
本带帽型植硅体含量较带Ⅰ增加,尖型、棒型植硅体百分含量较大,块状植硅体含量比带Ⅰ减少。早熟禾亚科植硅体含量较带Ⅰ减少。Ic指数较带Ⅰ有所降低,植硅体浓度和烧失量含量略有增加,而海绵骨针和硅藻的浓度增加并达到了剖面的最大值。平均粒径介于147.6~163.8 μm之间,分选系数介于1.5~1.8之间,砂的百分含量较带Ⅰ增加,粉砂和粘土的含量减少。
带Ⅲ:(180~80 cm):3820~1000 cal. a B. P.
本带帽型植硅体含量增加后减少,尖型、棒型和齿型植硅体含量仍然较大,早熟禾亚科植硅体所占百分比也呈先增加后减少的趋势,黍亚科和虎尾草亚科植硅体含量增加。Ic指数逐渐减小,Iph指数增大后减小,并达到了剖面的最大值,海绵骨针和硅藻浓度较带Ⅱ减小;烧失量和植硅体浓度较带Ⅱ明显降低。平均粒径介于171.3~185.9 μm之间,沉积物较带Ⅱ明显变粗,分选系数介于1.14~1.41之间,较带Ⅱ减小,分选变好,砂的百分含量较带Ⅱ明显增加(平均含量87.7%)。
带Ⅳ:(80~0 cm):1000 cal. a B. P.至今
本带帽型植硅体呈增多的趋势,哑铃型和十字型植硅体含量增加,早熟禾亚科植硅体百分比波动较大,Ic和Iph百分含量随时间波动较大。在800~500 cal. a B. P.左右,Iph达到了一个峰值,Ic指数较小,烧失量和植硅体浓度明显变小。且该阶段平均粒径剧增,砂的含量明显增多,粉砂和粘土含量增加,分选较好。
4 讨论 4.1 嫩江流域的环境背景植硅体分析结果显示洪河遗址的植硅体主要来自于禾本科植物,其中以早熟禾亚科(C3植物)为主(20.88%~47.77%),黍亚科和虎尾草亚科植物较少,偶见莎草科植物。植硅体分析研究结果表明在7020~3820 cal. a B. P.期间,气候整体较为温暖湿润。植硅体浓度和烧失量结果显示植被状况在7024~4200 cal. a B. P.期间较好,早熟禾亚科植物含量逐渐增加。刘嘉丽等[40]对大兴安岭四方山天池的研究发现陆生C3植物在7200~4500 cal. a B. P.期间对沉积物有机质的贡献比例逐渐增大,气候湿润;裘善文等[38]发现松嫩沙地在7500~4000 a B. P.左右,正处于全新世中期大暖期时期,沙丘固定,古土壤发育,是气候的最适宜期且植被状况较好;自4000 cal. a B. P.之后,植硅体结果和粒度结果显示,各参数均发生明显变化,气候逐渐变冷干;Stebich等[41]通过对四海龙湾的玛珥湖岩芯的孢粉分析发现4000 cal. a B. P.左右降水呈现减少的趋势。3824~1000 cal. a B. P.之后,温度降低,降水减少,受气候的影响,植硅体浓度和烧失量含量较低,有机质含量减少,植被覆盖减少;Chen等[42]通过对镜泊湖的孢粉分析发现,3600~2100 cal. a B. P.期间,草本花粉含量增加,指示气候冷干;崔美玲等[43]对哈尼湖的花粉研究也发现在3784~1380 a B. P.期间,针叶类乔木占优势,湿生及水生的草本消失,气候变凉干。自1000 cal. a B. P.之后,各指标波动较大,气候较为不稳定,且在1000~500 cal. a B. P.期间,气候较干,C3植物含量减少,有机质减少,植被状况明显变差,沉积物粒径明显变粗;裘善文和李取生[39, 44]认为近1000年以来,松嫩沙地气候趋于变干,加上人类的过度开垦、放牧、樵采等经济活动,土地沙漠化日趋严重,导致区域环境恶化,植被覆盖减少;Li等[45]通过对镜泊湖沉积物的孢粉分析发现在1000~680 cal. a B. P.期间,松属和栎属花粉含量减少,蒿属、唇形科和玄参科等草本植物的花粉含量增加,指示人类活动对植被的较大的影响。
4.2 嫩江流域昂昂溪文化衰亡的原因考古发现昂昂溪文化兴盛于6000~4000 a B. P.之间;4000 a B. P.之后,嫩江中游的昂昂溪文化逐渐消亡,嫩江下游小拉哈文化和白金宝文化兴起[46]。而目前在考古学中关于新石器时代昂昂溪文化衰亡的原因一直存在疑问[14]。大量考古学证据表明,全新世中晚期大约4000 a B. P.前后是中国新石器文化向青铜文化发展过程中的一个里程碑式的质变点,主要标志之一是中原周围地区的新石器文化发生衰落[47~48],而文化衰落往往和严重的环境变化事件,特别是灾难性的或者快速的气候变化事件相联系[49]。吴文祥和刘东生[50]认为4000 a B. P.左右的降温事件是导致中国中原周围地区五大新石器文化迅速衰落的主要因素;方修琦和孙宁[51]认为分布于燕北内蒙古岱海地区的老虎山文化在4300 a B. P.左右发生中断的原因也可能与当时的强降温事件有关;田广金和唐晓[52]认为考古学文化的演替和发展受环境的制约主要表现为在暖湿气候条件下,中原文化北上,东部文化西进;在冷湿、冷干气候条件下,文化南下和东进。因此,气候由湿润向干旱过渡时,会引起植被带迁移等环境的变化,史前人类可能会随着植被带南迁,离开原来的生活区域。
嫩江流域新石器时代的昂昂溪文化在6000~4000 cal. a B. P.进入繁盛期,“渔猎文化”得到了长足的发展,出土了大量的压制石器和渔猎工具。在洪河遗址的新石器时代遗存中发现了环壕和房址,出土了陶器、石器、骨器和蚌器等。洪河遗址的环壕内聚落规模是比较大的,而环壕是生产力和社会组织完备及资源竞争加剧的标识,修筑如此规模的环壕聚落,表明洪河遗址先民的生产力已经比较发达并过着一种定居式的以渔猎经济为主的生业模式1)。有研究表明,7200~5000 a B. P.是全新世气候的最适宜期,中纬度地区的年平均温度比现在高3~4 ℃,降水量增加,暖温带落叶阔叶林带北推约了3个纬度[53],燕山以北直到大兴安岭南段地区在当时都是属于暖温带气候,在这样的自然环境条件下,原始的自然条件才能够维持相当数量人口的定居生活[54],因而昂昂溪文化得以发展。本研究表明,4000 cal. a B. P.左右,植硅体浓度和烧失量呈现下降的趋势,植被状况变差;适应寒冷气候的C3植物植硅体含量增加,Iph变大,Ic减小,说明气候相对于之前有变冷干的趋势。沉积物平均粒径增大,砂含量增多,粉砂和粘土含量减少,分选性变好,风沙活动增强。Li等[55]对嫩江下游黑龙江省泰来县代克剖面的植硅体研究结果显示,在4440~3850 cal. a B. P.左右,植硅体以尖型和棒型为主,植硅体浓度大幅度下降,干旱指数增加,气候变冷干。李取生[39]认为4500~3500 a B. P.之间是松嫩沙地的扩张期,受冬季风影响较强,风沙活动较为频繁。在4000~1700 cal. a B. P.期间,气候持续冷干,同时嫩江流域的昂昂溪文化逐渐衰落。另外,研究发现洪河遗址该时期的房屋结构较为特别,未见柱洞和门道;出土的陶器,多见鬲和罐,多已破碎,难以成形,还有少量的陶支座、刮削器、骨锥、铜锥等器物,表明聚落范围缩小1)。
1) 由吉林大学边疆考古研究中心汤卓炜老师提供的数据,目前尚未发表
1) 由吉林大学边疆考古研究中心汤卓炜老师提供的数据,目前尚未发表
内蒙古的西拉木伦河流域在6000~4000 a B. P.左右也是人类活动十分活跃的地区[56],夏正楷等[13]通过该地区的调查研究发现,西拉木伦河流域的红山文化和小河沿文化在4000 a B. P.后逐渐衰落,并且把红山文化的突然中断归结于气候的恶化和科尔沁沙地的扩张,而4000 cal. a B. P.之后的降温过程在嫩江中游洪河剖面的分析结果中也有所体现。嫩江下游的小拉哈文化和白金宝文化在3800~2500 a B. P.期间兴起[57],朱永刚[58]认为昂昂溪文化-小拉哈文化-白金宝文化的遗存之间存在不同程度的递进与演变的联系;拉哈二期遗存的陶器以大口深腹筒形罐为主,沿袭了东北地区新石器文化的传统,可能是昂昂溪文化的继承者;白金宝一期遗存与拉哈二期遗存的文化面貌很接近,陶器特征也有很多共性,同时发现了陶鬲,是进入青铜时代的标志物。通过对嫩江流域目前发现的青铜时期的遗址点梳理发现遗址多靠近嫩江,证明青铜时代先民的生产生活与嫩江的关系仍然密切。嫩江流域史前考古学文化在空间上的分布和时间上的演替,不可否认会受到社会、经济、战争及周边文化的影响,但是在环境考古研究中,长时间的气候变化趋势与文化变迁的关系也是可以观察到的[49]。在本研究区,全新世中期相对温暖湿润的条件是昂昂溪文化发展的气候背景,4000 cal. a B. P.之后持续的冷干气候导致嫩江流域温度下降,降水减少,植被带南移,昂昂溪文化逐渐衰落,嫩江中下游的小拉哈和白金宝文化逐渐兴起。因而推测环境变化是导致部分居民离开昂昂溪地区沿嫩江逐渐向更加温暖的下游迁移、寻找更为适宜的栖息地生存繁衍的部分原因。嫩江中游的昂昂溪文化逐渐消亡,被更为先进和广泛分布的小拉哈文化和白金宝文化取而代之。洪河遗址中发现的上层遗存1)是白金宝文化在嫩江流域最靠北的发掘地点,说明4000 cal. a B. P.之后,洪河地区虽然也发现了白金宝文化,但只是白金宝文化影响的边缘区,从另一方面也证明嫩江流域人类文化中心的南迁。
5 结论本文通过对洪河剖面的植硅体分析、粒度分析和烧失量测定重建了新石器时代以来洪河剖面的植被环境、沉积环境和气候环境。洪河剖面植硅体类型主要包括帽型、棒型、尖型和齿型,主要来自于禾本科植物,并以早熟禾亚科(C3植物)为主。洪河剖面沉积物的平均粒径大部分在143.7~188.9 μm之间,均以砂为主,分选较好,主要由嫩江冲积沙经风力吹扬、搬运、堆积而成。在7024~3820 cal. a B. P.期间,气候环境总体温暖湿润,适宜人类在嫩江流域地区生存繁衍,并孕育了典型的昂昂溪“渔猎文化”。3820~1000 cal. a B. P.期间,气候较为冷干,昂昂溪文化逐渐衰落。1000 cal. a B. P.以来,由于人类活动的过度影响,土地沙漠化日趋严重,导致区域环境恶化。嫩江流域史前文化在空间上的分布和时间上的演替,不仅受社会、经济、战争及周边文化的影响,也与环境变化有密切的关系。综合多指标分析结果表明,在4000 cal. a B. P.左右,气候呈现逐渐变冷干的趋势,植被带南移,嫩江中游以渔猎为生的先民的生产活动受到了限制,因而推测环境变化是导致部分居民离开昂昂溪地区沿嫩江逐渐向更加温暖的下游迁移,以寻找更为适宜的栖息地生存繁衍的部分原因,嫩江中游的昂昂溪文化随之消亡,被更为先进和广泛分布的小拉哈文化白金宝文化取而代之。
致谢: 感谢东北师范大学地理科学学院杨秀云同学、段天南同学和熊志飞同学在实验工作中给予的帮助;感谢审稿专家和编辑部杨美芳老师建议性的修改意见。
| [1] |
梁思永. 昂昂溪史前遗址[C]//梁思永. 梁思永考古论文集. 北京: 科学出版社, 1959: 1-162. Liang Siyong. Ang'angxi prehistoric site[C]//Liang Siyong. Archaeological Collection. Beijing: Science Press, 1959: 1-162. |
| [2] |
赵宾福. 嫩江流域新石器时代生业方式研究[J]. 考古, 2007(11): 55-61. Zhao Binfu. Neolithic subsistence practice of Nenjiang River Valley[J]. Archaeology, 2007(11): 55-61. |
| [3] |
张泰湘. 嫩江流域原始文化初论[J]. 北方文物, 1985(2): 11-15. Zhang Taixiang. The original culture of Nenjiang River Basin[J]. Northern Cultural Relics, 1985(2): 11-15. |
| [4] |
黄任远. 黑龙江流域文明研究[M]. 哈尔滨: 黑龙江人民出版社, 2006: 25-28. Huang Renyuan. Researches in Heilongjiang Basin Civilization[M]. Harbin: Heilongjiang People's Publishing House, 2006: 25-28. |
| [5] |
赵宾福, 张伟. 论小拉哈文化[J]. 北方文物, 2008(2): 9-16. Zhao Binfu, Zhang Wei. A preliminary study on the Xiaolaha Culture[J]. Northern Cultural Relics, 2008(2): 9-16. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-0483.2008.02.002 |
| [6] |
张伟. 嫩江流域夏至东汉时期的五支考古学文化[J]. 北方文物, 2010(2): 29-37. Zhang Wei. Five archaeological cultures in the Nenjiang River Basin during Xia Dynasty to Eastern Han Dynasty[J]. Northern Cultural Relics, 2010(2): 29-37. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-0483.2010.02.008 |
| [7] |
中国科学院考古研究所甘肃工作队. 甘肃永靖秦魏家齐家文化墓地[J]. 考古学报, 1975(2): 57-96. Gansu Working Team, Institute of Archaeology, Chinese Academy Sciences. The Qijia cemetery at the site of Qinweijia in Yongjing, Gansu[J]. Acta Archaeologica Sinica, 1975(2): 57-96. |
| [8] |
张勄. 崧泽文化三题[J]. 东南文化, 2015(1): 49-56. Zhang Min. Three issues of the Songze Culture[J]. Southeast Culture, 2015(1): 49-56. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-179X.2015.01.006 |
| [9] |
杨虎. 辽西地区新石器-铜石并用时代考古文化序列与分期[J]. 文物, 1994(5): 37-52. Yang Hu. Neolithic-Copper stone and series and stages of archaeological culture in the western of Liaoning Province[J]. Cultural Relics, 1994(5): 37-52. |
| [10] |
吴文祥, 刘东生. 4000 a B.P.前后东亚季风变迁与中原周围地区新石器文化的衰落[J]. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24(3): 278-284. Wu Wenxiang, Liu Tungsheng. Variations in East Asia monsoon around 4000 a B.P. and the collapse of Neolithic cultures around Central Plain[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24(3): 278-284. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2004.03.006 |
| [11] |
叶玮, 李凤全, 沈叶琴, 等. 良渚文化期自然环境变化与人类文明发展的耦合[J]. 浙江师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 29(4): 455-460. Ye Wei, Li Fengquan, Shen Yeqin, et al. Coupling relation between the environmental changes and human civilization development during Liangzhu Culture period[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Normal University(Natural Sciences), 2006, 29(4): 455-460. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5051.2006.04.021 |
| [12] |
莫多闻, 李非, 李水城, 等. 甘肃葫芦河流域中全新世环境演化及其对人类活动的影响[J]. 地理学报, 1996, 51(1): 59-69. Mo Duowen, Li Fei, Li Shuicheng, et al. A preliminary study on the paleoenvironment of the Middle Holocene in the Hulu River area in Gansu Province and its effects on human activity[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1996, 51(1): 59-69. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1996.01.008 |
| [13] |
夏正楷, 邓辉, 武弘麟. 内蒙西拉木伦河流域考古文化演变的地貌背景分析[J]. 地理学报, 2000, 55(3): 329-336. Xia Zhengkai, Deng Hui, Wu Honglin. Geomorphologic background of the prehistoric cultural evolution in the Xar Moron Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2000, 55(3): 329-336. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2000.03.009 |
| [14] |
赵宾福. 松嫩平原早期青铜文化的发现与认识[J]. 边疆考古研究, 2002(1): 181-193. Zhao Binfu. Discoveries and understanding of the Early Bronze cultures in the Plain of Songhua River & Nen River[J]. Research of China's Frontier Archaeology, 2002(1): 181-193. |
| [15] |
王永吉, 吕厚远. 植物硅酸体研究及应用[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1993: 1-228. Wang Yongji, Lü Houyuan. Phytolith Study and Its Application[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1993: 1-228. |
| [16] |
覃军干, 张新荣, 张强, 等. 近1000年以来气候波动在广西桂北地区沉积物中的记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(2): 268-277. Qin Jungan, Zhang Xinrong, Zhang Qiang, et al. Climate oscillations recorded in the sediment from north Guilin, Guangxi during the past 1000 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(2): 268-277. |
| [17] |
王淑云, 莫多闻, 孙国平, 等. 浙江余姚田螺山遗址古人类活动的环境背景分析——植硅体、硅藻等化石证据[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(2): 326-334. Wang Shuyun, Mo Duowen, Sun Guoping, et al. Environmental context of ancient human activity in Tianluoshan site, Yuyao City, Zhejiang Province:Fossil evidence of phytolith and diatom[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2010, 30(2): 326-334. |
| [18] |
萧家仪, 徐时强, 肖霞云, 等. 南京郭家山遗址植硅体分析与湖熟文化环境背景[J]. 古生物学报, 2011, 50(2): 268-274. Xiao Jiayi, Xu Shiqiang, Xiao Xiayun, et al. Phytoliths and environment of the Hu-Shu Culture of Guojiashan archaeological. site, Nanjing[J]. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 2011, 50(2): 268-274. |
| [19] |
邹胜利, 谢树成, 李勇, 等. 湖北省金罗家考古遗址土壤中多环芳烃的分布和植硅体的分析及其意义[J]. 生态环境学报, 2011, 20(10): 1461-1469. Zou Shengli, Xie Shucheng, Li Yong, et al. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phytolith analysis of archaeological. soil of Jinluojia site in Hubei Province[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011, 20(10): 1461-1469. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2011.10.013 |
| [20] |
成都地质学院陕北队编. 沉积岩(物)粒度分析及其应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1978: 1-147. The Shanbei Group of Chengdu College of Geology. Grain Size Analysis of Sedimentary Rock(Sediment)and Application[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1978: 1-147. |
| [21] |
贾飞飞, 鲁瑞洁, 高尚玉. 毛乌素沙漠东南缘湖沼相沉积物粒度特征记录的12.2 cal.ka B.P.以来的区域环境变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(5): 1211-1220. Jia Feifei, Lu Ruijie, Gao Shangyu, et al. Environmental changes recorded from grain-size characteristics of the lacustrine-peat sediments from southeastern margin of Mu Us Desert since 12.2 cal.ka B.P.[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(5): 1211-1220. |
| [22] |
李楠楠, 介冬梅, 阳金秀, 等. 长白山西麓泥炭灰分粒度特征及其环境意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2014, 32(5): 873-883. Li Nannan, Jie Dongmei, Yang Jinxiu, et al. Grain-size characteristics and environmental significance of peat ash in the west foothill of Changbai Mountain[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2014, 32(5): 873-883. |
| [23] |
聂军胜, 李曼. 柴达木盆地晚中新世河湖相沉积物粒度组成及其古环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(5): 1017-1026. Nie Junsheng, Li Man. A grain size study on Late Miocene Huaitoutala section, NE Qaidam Basin, and its implications for Asian monsoon evolution[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2017, 37(5): 1017-1026. |
| [24] |
郭超, 马玉贞, 刘杰瑞, 等. 过去2000年来西藏羊卓雍错沉积物粒度记录的气候变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(2): 405-419. Guo Chao, Ma Yuzhen, Liu Jierui, et al. climatic change recorded by grain size in the past about 2000 years from Yanzhog Yumco Lake, Tibet[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(2): 405-419. |
| [25] |
张佳华, 孔昭宸, 杜乃秋. 烧失量数值波动对北京地区过去气候和环境的特征响应[J]. 生态学报, 1998, 18(4): 343-347. Zhang Jiahua, Kong Zhaochen, Du Naiqiu. The respondence of loss-on ignition range to past climate and environment in Beijing[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 1998, 18(4): 343-347. |
| [26] |
李泽涛, 李冰, 李月丛, 等. 泥河湾盆地油房剖面旧石器时代中期到晚期文化过渡的环境背景[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(3): 463-473. Li Zetao, Li Bing, Li Yuecong, et al. The climate-environment background of Youfang site in Nihewan Basin during the transitional period from mid to late Paleolithic period[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2017, 37(3): 463-473. |
| [27] |
韩鹏, 刘兴起. 内蒙古中东部查干淖尔湖流域7000年以来的气候演变[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(6): 1381-1390. Han Peng, Liu Xingqi. The climate evolution inferred from Chagan-Nuur in middle-east part of Inner Mongolia since the last 7000 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2017, 37(6): 1381-1390. |
| [28] |
王庆锋, 金会军, 吴青柏, 等. 距今约6000年以来青藏高原东北部黄河源区冻结泥炭沉积记录的气候演化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(2): 402-415. Wang Qingfeng, Jin Huijun, Wu Qingbai, et al. Climatic evolution since 6 cal.ka B.P. recorded by frozen peat deposits in the source area of the Yellow River, northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2017, 37(2): 402-415. |
| [29] |
赵善桐, 杨虎. 昂昂溪新石器时代遗址的调查[J]. 考古, 1974(2): 99-108. Zhao Shantong, Yang Hu. Investigation of the Angangxi Neolithic site[J]. Archaeology, 1974(2): 99-108. |
| [30] |
宋长春, 何岩, 邓伟, 等. 松嫩平原盐渍土壤生态地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 1-206. Song Changchun, He Yan, Deng Wei, et al. Ecological Geochemistry of Salinization Soil in Songnen Plain[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2003: 1-206. |
| [31] |
李德晖, 介冬梅, 高桂在, 等. 松嫩草原典型群落对应表土植硅体组合特征[J]. 第四纪研究, 2018, 38(4): 1035-1049. Li Dehui, Jie Dongmei, Gao Guizai, et al. Characteristics of phytolith assemblages of topsoil in typical communities of Songnen Grassland[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(4): 1035-1049. |
| [32] |
Shepard F P. Nomenclature based on sand-silt-clay ratios[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Geology, 1954, 24(3): 151-158. |
| [33] |
Stuiver M, Reimer P J. Extended 14C database and revised Calib radiocarbon calibration program[J]. Radiocarbon, 1993, 35: 215-230. DOI:10.1017/S0033822200013904 |
| [34] |
伦子健, 顾延生, 刘红叶, 等. 神农架大九湖湿地表土植硅体记录及其环境意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(3): 656-665. Lun Zijian, Gu Yansheng, Liu Hongye, et al. Phytolith records in the surface soils of Dajiuhu wetland and their environmental significance, Shennongjia Mountains[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(3): 656-665. |
| [35] |
Twiss P C, Suess E, Smith R M. Morphological classification of grass phytoliths[J]. Soil Science of America Proceedings, 1969, 33(33): 109-115. |
| [36] |
Tieszen L, Senyimba M, Imbamba S, et al. The distribution of C3 and C4 grasses and carbon isotope discrimination along an altitudinal and moisture gradient in Kenya[J]. Oecologia, 1979, 37(3): 337-350. DOI:10.1007/BF00347910 |
| [37] |
Kondo R, Childs C W, Atkinson I A E, et al. Opal Phytoliths of New Zealand[M]. Lincoln: Manaaki Whenua Press, 1994: 85-86.
|
| [38] |
裘善文, 王其存, 陈国双, 等. 松嫩沙地沙漠化及防治研究——以杜尔伯特蒙古族自治县他拉哈镇为例[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(2): 331-338. Qiu Shanwen, Wang Qicun, Chen Guoshuang, et al. Study on desertification and its controlling techniques in Songnen Sandy Land, China:A case study in the Talaha Town, Duerbote Mongolian Autonomous County of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2011, 31(2): 331-338. |
| [39] |
李取生. 松嫩沙地历史演变的初步研究[J]. 科学通报, 1990, 35(11): 854-856. Li Qusheng. A primary study on the historical. change of Songnen Sandy Land[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1990, 35(11): 854-856. |
| [40] |
刘嘉丽, 刘强, 储国强, 等. 大兴安岭四方山天池15.4 kaB.P.以来湖泊沉积记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(4): 901-912. Liu Jiali, Liu Qiang, Chu Guoqiang, et al. Sediment record at Lake Sifangshan in the central-northern part of the Great Xing'an Range, Northeast China since 15.4 ka B. P[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(4): 901-912. |
| [41] |
Stebich M, Rehfeld K, Schlütz F, et al. Holocene vegetation and climate dynamics of NE China based on the pollen record from Sihailongwan Maar Lake[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2015, 124: 275-289. DOI:10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.07.021 |
| [42] |
Chen R, Shen J, Li C, et al. Mid-to Late-Holocene East Asian summer monsoon variability recorded in lacustrine sediments from Jingpo Lake, Northeastern China[J]. The Holocene, 2014, 146(3): 454-468. |
| [43] |
崔美玲, 罗运利, 孙湘君. 吉林哈尼湖钻孔5000年以来的古植被气候变化指示[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2006, 26(5): 117-122. Cui Meiling, Luo Yunli, Sun Xiangjun. Paleovegetational and paleoclimatic changes in Hani Lake, Jilin since 5 ka B.P[J]. Marine Geilogy & Quaternary Geology, 2006, 26(5): 117-122. |
| [44] |
裘善文, 李取生. 东北平原西部沙地古土壤与全新世环境变迁[J]. 第四纪研究, 1992(3): 224-232. Qiu Shanwen, Li Qusheng. Paleosols of sandy lands and environmental changes in the western plain of Northeast China during Holocene[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1992(3): 224-232. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1992.03.004 |
| [45] |
Li C H, Wu Y, Hou X H. Holocene vegetation and climate in Northeast China revealed from Jingbo Lake sediment[J]. Quaternary International, 2011, 229(1): 67-73. |
| [46] |
朱永刚. 松嫩平原先白金宝文化遗存的发现与研究[J]. 北方文物, 1998(1): 19-28. Zhu Yonggang. Discovery and research on the preservation of the pre-Baijinbao Culture in the Songnen Plain[J]. Northern Cultural Relics, 1998(1): 19-28. |
| [47] |
安成邦, 冯兆东, 唐领余, 等. 甘肃中部4000年前环境变化与古文化变迁[J]. 地理学报, 2003, 58(5): 743-748. An Chengbang, Feng Zhaodong, Tang Lingyu, et al. Environmental changes and cultural transition at 4 cal.ka B.P. in Central Gansu[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2003, 58(5): 743-748. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2003.05.013 |
| [48] |
段天璟. 胶东半岛和辽东半岛岳石文化的相关问题[J]. 边疆考古研究, 2003(0): 131-151. Duan Tianjing. Some problems of Yueshi Culture in Jiaodong Peninsula and Liaodong Peninsula[J]. Research of China's Frontier Archaeology, 2003(0): 131-151. |
| [49] |
安成邦, 王琳, 吉笃学, 等. 甘青文化区新石器文化的时空变化和可能的环境动力[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(6): 923-927. An Chengbang, Wang Lin, Ji Duxue, et al. The temporal and spatial change of Neolithic cultures in Gansu-Qinghai region and possible environmental forcing[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(6): 923-927. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2006.06.006 |
| [50] |
吴文祥, 刘东生. 4000 a B.P.前后降温事件与中华文明的诞生[J]. 第四纪研究, 2001, 21(5): 443-451. Wu Wenxiang, Liu Tungsheng. 4000 a B.P. event and its implications for the origin of ancient Chinese civilization[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2001, 21(5): 443-451. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.05.008 |
| [51] |
方修琦, 孙宁. 降温事件:4.3 ka BP岱海老虎山文化中断的可能原因[J]. 人文地理, 1998, 13(1): 75-80. Fang Xiuqi, Sun Ning. Cold event:A possible cause of the interruption of the Laohushan Culture[J]. Human Geography, 1998, 13(1): 75-80. |
| [52] |
田广金, 唐晓峰. 岱海地区距今7000-2000年间人地关系研究[J]. 中国历史地理论丛, 2001, 3(4): 111-121. Tian Guangjin, Tang Xiaofeng. A study on the man-environment relation in the Daihai area of Inner-Mongolia[J]. Collections of Essays On Chinese Historical Geography, 2001, 3(4): 111-121. |
| [53] |
施雅风, 孔昭宸, 王苏民, 等. 中国全新世大暖期的气候波动与重要事件[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1992, 22(12): 1300-1308. Shi Yafeng, Kong Zhaochen, Wang Sumin, et al. The climatic fluctuations and important events of Holocene Megathemal in China[J]. Science in China(Series B), 1992, 22(12): 1300-1308. |
| [54] |
邓辉. 全新世大暖期燕北地区人地关系的演变[J]. 地理学报, 1997, 52(1): 63-71. Deng Hui. The change of the man-land relationship in the northern Yanshan Mountain region during Megathermal[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1997, 52(1): 63-71. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1997.01.009 |
| [55] |
Li N N, Sack D, Gao G Z, et al. Holocene Artemisia-Chenopodiaceae-dominated grassland in North China:Real or imaginary?[J]. The Holocene, 2017, 28(5): 834-841. |
| [56] |
莫多闻, 杨晓燕, 王辉, 等. 红山文化牛河梁遗址形成的环境背景与人地关系研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2002, 22(2): 174-181. Mo Duowen, Yang Xiaoyan, Wang Hui, et al. Study on the environmental background of Niuheliang site, Hongshan Culture, and the relationship between ancient man and environment[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2002, 22(2): 174-181. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2002.02.011 |
| [57] |
朱永刚. 肇源白金宝遗址第三次发掘与松嫩平原汉代以前古文化遗存的年代序列[J]. 吉林大学社会科学学报, 1998(2): 75-80. Zhu Yonggang. The third dig of the historic site of Zhao Yuan Platinum Treasures[J]. Jilin University Journal Social Sciences Edition, 1998(2): 75-80. |
| [58] |
朱永刚. 从肇源白金宝遗址看松嫩平原的青铜时代[J]. 吉林大学社会科学学报, 2008, 48(1): 96-101. Zhu Yonggang. The Bronze Age of Songnen plain seen from Baijinbao site, Zhaoyuan[J]. Jilin University Journal Social Sciences Edition, 2008, 48(1): 96-101. |
2 Research Center for Chinese Frontier Archaeology of Jilin University, Changchun 130024, Jilin;
3 Heilongjiang Provincial Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology, Harbin 150008, Heilongjiang;
4 The No. 16 Middle School of Qiqihar, Qiqihar 161006, Heilongjiang;
5 Suzhou New District Experimental Primary School, Suzhou 215011, Jiangsu)
Abstract
The Nenjiang River Basin(44°02'~50°36'N, 119°12'~127°54'E) located in the eastern of Daxing'anling Mountains, northwest of the Northeast Plain, China. Many cultural sites since the Neolithic in the Nenjiang River Basin provide plenty materials for studying environmental change and ancient human activities in the region. The Angangxi Culture in the Nenjiang River Basin is the representative culture of "Fishing and Hunting culture" in northern China.Honghe Neolithic site lies on the right bank of the middle reaches of Nenjiang River, Tsitsihar City, Heilongjiang Province, in Northeast China. It is a representative site of Angangxi Culture. The studied natural sediment profile(47°07'50"N, 123°37'08"E) is located to the northwest of the Honghe Neolithic site. We sampled a 3 m sequence and thirty samples were collected at 10-cm intervals from the bottom to the top, numbered sequentially from QH1~QH30. The profile was divided into four layers based on sediment color and deposition characteristics. Detailed information about the sediment composition of the profile is given in Fig.3. The chronological sequence was determined by AMS 14C dating. The vegetation at the site consists mainly of Artemisia, Chenopodiaceae, Poaceae, Asteraceae, Ulmus, Salix and Brassicaceae. We conducted phytolith analysis, grain size analysis and LOI measurement, combined with archaeological articles, to explore the environmental background of human activities in the Nenjiang River Basin since Neolithic Age and find the reasons for the decline of Angangxi "fishing and hunting Neolithic culture".The results of phytolith analysis showed that the phytoliths in the Honghe profile were mainly rondel, elongate, lanceolate and trapeziform and the vegetation was dominated by Pooideae(C3 plants). The results of grain size analysis showed that the sediments of the Honghe profile are mainly composed of the alluvial sands from Nenjiang River, which were transported by wind. During 7024~3820 cal.a B.P., the climate was warm and wet. It was suitable for humans to survive and the Angangxi Culture was flourished. During 3820~1000 cal.a B.P., integrated the multi-proxy results show that the climate was gradually becoming cold and dry, while the Angangxi culture was gradually declining at around 4000 cal.a B.P. The archaeological data proved that there are progressive and evolutionary relationship between the remains of the Angangxi Culture and the Baijinbao Culture in Nenjiang River Basin. It is undeniably that the spatial distribution and temporal succession of different cultures in the Nenjiang River Basin were influenced by economy, war and surrounding culture. Therefore, it is speculated that the continuous cold and dry climate prompted the residents leaved the Angangxi region and migrated to the downstream of the Nenjiang River, looking for a warmer and more suitable habitat to survive. The Angangxi Culture in the middle reaches of the Nenjiang River gradually disappeared, replaced by Xiaolaha Culture and Baijinbao Culture. Since 1000 cal.a B.P., The environment was dry and the land desertification became increasingly serious due to the excessive influence of human activities. 2019, Vol.39
2019, Vol.39

