② 青岛海洋地质研究所, 青岛 266071;
③ 山东理工大学资源与环境工程学院, 淄博 255049)
北黄海为一半封闭陆架浅海,平均水深38m,陆架坡度相对平缓[1, 2],末次冰盛期裸露成陆,之后随着海平面的阶梯式上升[3, 4],海水逐步侵入北黄海陆架区,沉积环境由河流作用为主逐渐转变为受海洋动力环境(波浪、 潮流、 沿岸流等)控制[5, 6],在陆架区形成特征的沉积地层,这些地层蕴含了丰富的地质和古环境信息,是研究陆架区晚第四纪以来海平面变化与沉积环境演化的良好载体。
近年来国内外学者采用沉积物粒度[7-9]、 矿物学[10-17]、 地球化学[18-21]、 古生物学[6, 22-26]及浅地层剖面[27]或与岩芯相结合[4, 5, 27-30]等方法,在北黄海陆架陆续开展了沉积地层、 物源、 事件沉积、 晚第四纪沉积演化等方面的研究,取得了大量的研究成果,然而这些研究多集中在山东半岛北部近岸及北黄海中部海域,针对北黄海辽东半岛东南近岸晚第四纪以来沉积环境的研究较少涉及,研究成果多局限于表层沉积物,仅Chen等[21]依据高分辨率浅地层剖面资料,探讨了全新世中期以来辽东半岛东南近岸泥质沉积的物源及其形成机制。
本文以辽东半岛东南近岸泥质区4个柱状岩芯为研究对象,通过详细的岩性与微体古生物分析,结合AMS 14 C 测年资料,揭示了末次冰消期以来研究区的沉积环境演化及其对海平面变化的响应。
1 研究区水文环境特征北黄海大部分海域属于正规半日潮,仅成山头以东至朝鲜半岛大青岛一带为不规则半日潮。北黄海潮差分布西岸明显小于东岸,辽东半岛东南近岸最大潮差不足3m,东岸最大潮差普遍大于4~5m[31]。北黄海潮流流速近岸海域较大,辽东半岛东南近岸流速为60~100cm/s,西朝鲜湾海域可达120cm/s[32]。
北黄海流系复杂[33],主要包括黄海暖流、 鲁北沿岸流、 辽南沿岸流和朝鲜沿岸流( 图 1)。黄海暖流流向终年向北,冬强夏弱,流速一般为5~10cm/s[34]。冬季,黄海暖流北上进入北黄海,在北黄海向东、 西各有一条分支分别与朝鲜沿岸流和鲁北沿岸流汇合,后逐渐偏西,其延伸部分可进入渤海[35]; 夏季,由于南黄海冷水南向入侵,黄海暖流受阻向北仅至 35°N附近。鲁北沿岸流终年沿山东半岛北部东流,绕过成山头后沿40~50m等深线南下,冬强夏弱,流速冬季最大为44cm/s,夏季最大为20cm/s[34]。由鸭绿江冲淡水组成的辽南沿岸流,沿辽东半岛东南沿岸流向渤海海峡,流向终年稳定,夏季由于鸭绿江径流量的影响,流速超过10cm/s,冬季在东北风的影响下,长山列岛附近的流速接近10cm/s[36]。

|
图 1 研究区水文环境[33]及岩芯位置图圈色线代表辽东半岛东南近岸泥质沉积等厚线[21](单位: m) Fig. 1 The regional hydrography[33] of study area and the cores locations. The circle lines denote isopaches of the mud deposit in the southeast coastal area of the Liaodong Peninsula[21] and thickness is in meters |
本研究所分析的4个柱状岩芯( 表 1和 图 1)是由青岛海洋地质研究所“业治铮轮”于2013年8月利用振动取样器采集。在室内对岩芯进行了详细描述和精细分样,大致4cm间隔取样,共采集不同层位的岩芯样品233个用于微体古生物鉴定。
| 表 1 研究区4个岩芯概况 Table 1 Information of four cores in the study area |
微体古生物鉴定在山东理工大学完成,样品充分浸泡后过250目(0.063mm)的标准筛冲洗并烘干,鉴定时过120目(0.125mm)标准筛,显微镜下对粗样( >0.125mm)中的有孔虫和介形虫进行统计,对于微体化石丰度较大的样品采用二分法鉴定1/2、 1/4……的样品,每样统计底栖有孔虫不少于100枚、 介形类不少于50枚,丰度较低的样品则统计全样。由于4个岩芯中介形虫含量较低,仅在个别层位出现,个数过少而不具有统计意义,因此,本研究仅对底栖有孔虫的数据资料进行了分析。有孔虫、 介形虫的鉴定主要依据何炎等[37]、 汪品先等[38, 39]、 赵泉鸿等[40, 41]、 李淑鸾[42]等文献。
选取4个岩芯中的泥炭层与混合底栖有孔虫样品共计8个于美国Beta Analytic Inc.AMS 14 C 实验室完成年代测试,本文原始测年数据采用CALIB6.0.2软件进行日历年校正,采用的海洋碳储库差值ΔR=-127±2a,依据CALIB6.0.2提供的渤海西部(Map No.415)、 南黄海西部(Map No.416)[43]与南黄海东部(Map No.417)[44] 3个海洋库存年龄的加权平均获得。本文所用的日历年龄均从公元1950年向前推算,以cal. a B .P. 标识。数据结果见 表 2。
| 表 2 研究区4个岩芯的AMS 14 C 年代数据 Table 2 AMS 14 C data of four cores in the study area |
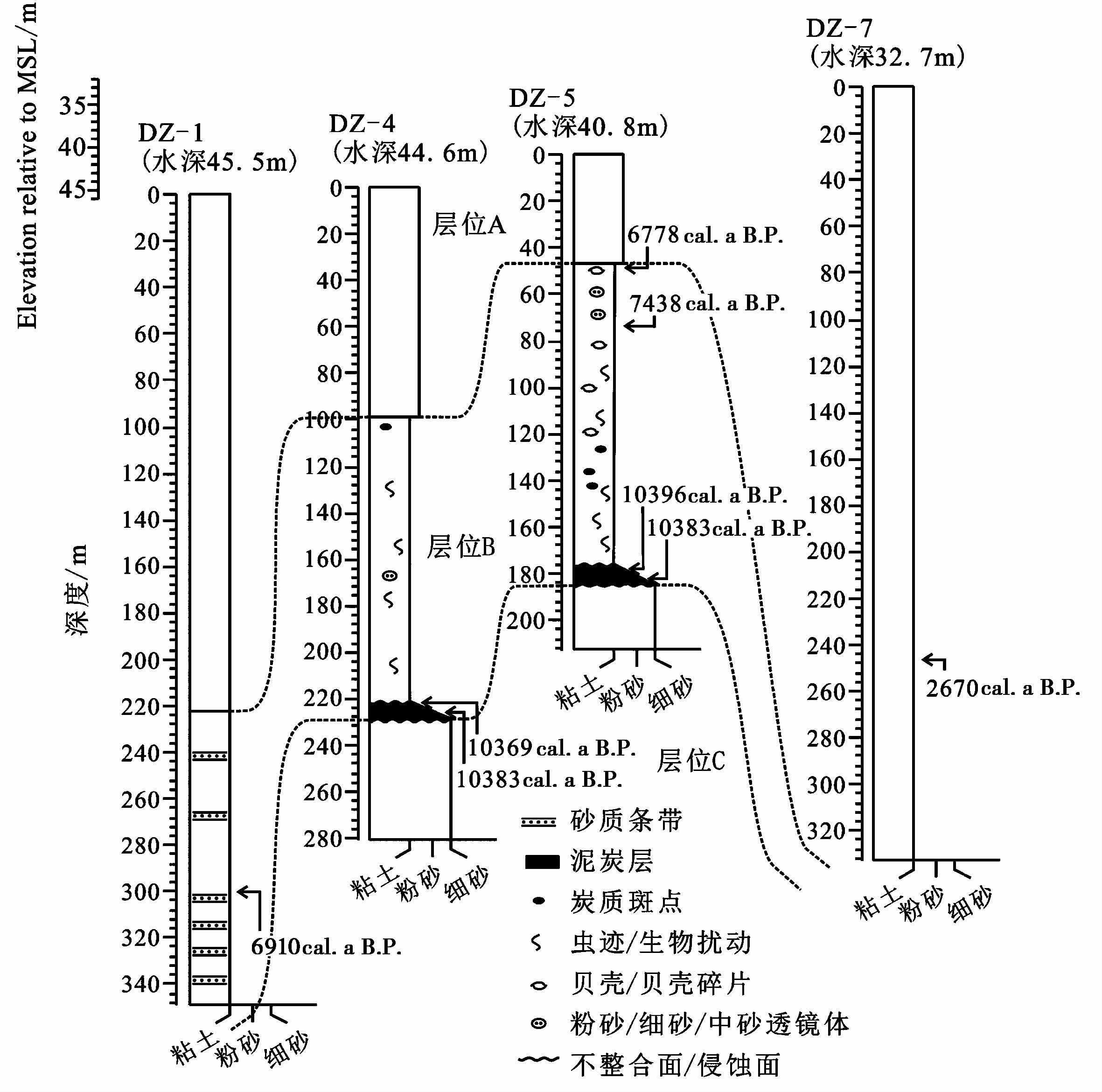
年代数据表明( 表 2),辽东半岛东南近岸泥质区4个岩芯的沉积地层记录了末次冰消期以来的沉积历史。依据岩芯沉积物的颜色、 岩性、 沉积构造等特征的分析,结合测年数据,可以将研究区末次冰消期以来的沉积地层自下而上划分C、 B、 A共3个层位,分别对应约10396cal .a B .P. 之前、 10396~6778cal .a B .P. 期间与约6778cal .a B .P. 高海面以来的3个沉积阶段。
层位C(约10396cal .a B .P. 之前),分别出现于岩芯DZ-4和DZ-5最底部的231~281cm段与185~213cm段,且未揭示该层位的底界( 图 2),其他两岩芯均未到达此深度。该段地层岩性均一,主要为黄褐色细砂,与上覆地层为侵蚀不整合接触,该段地层为全新世海侵开始之前的河流相沉积。
|
图 2 研究区DZ-1、 DZ-4、 DZ-5和DZ-7岩芯的岩性地层划分 Fig. 2 Lithological stratigraphy of cores DZ-1,DZ-4,DZ-5 and DZ-7 in the study area |
层位B(约10396~6778cal .a B .P. 期间),该层位分别出现于3个岩芯DZ-1、 DZ-4和DZ-5的349~223cm段、 231~99cm段和185~47cm段的地层中,其中DZ-1柱状岩芯未揭示该层位的底界。该段地层底部有一厚为9cm的泥炭层,分别对应DZ-4和DZ-5岩芯的231~222cm段和185~176cm段( 图 2); 其上岩性主要为粘土,自下而上颜色由黄褐色逐渐转变为灰褐色,下部见大量生物扰动及炭质斑点,块状构造发育,上部粉砂透镜体或薄层增多,其中DZ-5柱状岩芯该层位上部见大量贝壳碎片。该段地层与上覆地层为渐变接触,岩性特征及测年结果显示,该层位记录了研究区全新世海侵开始至高海面期间的滨海相沉积。
层位A(约6778cal .a B .P. 高海面以来),该层位在研究区4个岩芯中均有出现,分别对应DZ-1、 DZ-4、 DZ-5和DZ-7岩芯的223~0cm段、 99~0cm段、 47~0cm段和333~0cm段,其中DZ-7柱状岩芯未揭示该层位的底界( 图 2)。该段地层岩性均一,主要为深灰色粉砂质粘土(DZ-4和DZ-5岩芯)与粘土(DZ-1和DZ-7岩芯),含水量较下部地层明显增加,该段地层记录了研究区全新世高海面以来的浅海相沉积。
| 表 3 研究区4个岩芯沉积物的底栖有孔虫鉴定结果 Table 3 The results of benthic foraminifera from sediments of the four cores in the study area |
辽东半岛东南近岸泥质区4个岩芯沉积物的底栖有孔虫鉴定结果显示(表 3),研究区末次冰消期以来的底栖有孔虫主要出现的种属为 Buccella frigida、 Protelphidium turberculatum、 Ammonia becarii var. 、 Cribrononion subincertum、 Ammonia dominicana、 Elphidium advenum、 Elphidium magellanicum、 Rosalina floridana、 Nonion anamalinoidea、 Ammonia compressiuscula、 Ammonia ketienziensis等,以滨岸及浅海相属种为主,各岩芯沉积物底栖有孔虫组合特征见 表 3。已有研究表明,中国东部陆架海区底栖有孔虫的分布主要受水深、 温度及盐度等因素的控制[37-39, 42]。本文根据各属种的水深分布及其温度、 盐度因素,将研究区的底栖有孔虫划分为3大类。
类型Ⅰ: 半咸水类,主要包括近岸低盐属种Rosalina floridana与Nonion anamalinoidea( 图 3),这两个种属广见于河口等少盐至中盐受陆源淡水影响的半咸水环境[45, 46]。
类型Ⅱ: 滨岸广盐类,主要分布在水深20m以浅的滨岸浅水环境,主要包括广温广盐Ammonia becarii var. 与Cribrononion subincertum( 图 3),这两个属种是我国东部陆架海区最常见的滨岸浅水种,广见于潮上带、 潮间带、 潟湖与河口湾等半咸水及正常盐度的滨岸浅海[6, 24, 25, 39, 47-49],其中Ammonia becarii var. 生存的温度与盐度范围更大,分别为10~35℃与3 ‰ ~50 ‰ 。

|
图 3 研究区4个柱状岩芯常见的底栖有孔虫 半咸水类: 1~2. Rosalina floridana,3~4. Nonion anamalinoidea; 滨岸广盐类: 5~6. Ammonia becarii var.,7~8. Cribrononion subincertum; 浅海类: 9. Protelphidium turberculatum,10~11. Buccella frigida,12. Elphidium magellanicum,13~14. Ammonia compressiuscula, 15~16. Ammonia ketienziensis (图版中标尺为200μm) Fig. 3 Common benthic foraminiferal species of four cores in the study area |
类型Ⅲ: 浅海类,主要分布在水深20m以深的陆架浅海环境,涉及的属种较多,主要为冷水种(Protelphidium turberculatum与 Buccella frigida)、 沿岸流分布区的低温低盐属种Elphidium magellanicum以及生存于较深水环境的Ammonia compressiuscula与Ammonia ketienziensis( 图 3)。Protelphidium turberculatum和Buccella frigida是我国渤、 黄、 东海常见的低温低盐环境代表种,主要集中在沿岸流影响区以及冷水团控制的范围以内,显示出明显的水温效应[24, 25, 38, 39, 47-49]; Elphidium magellanicum代表低潮坪的浅海环境,常见于沿岸流分布区[39, 50]; Ammonia compressiuscula与Ammonia ketienziensis在我国东部陆架区广泛分布,与水深之间的对应关系明显,分别对应水深20~50m与50m以深的区域[1, 38, 49]。
依据研究区4个岩芯沉积物中底栖有孔虫的垂向变化规律,可以将工作区末次冰消期以来的生物地层自下而上由老至新划分为3个层段,与岩性地层相对应。
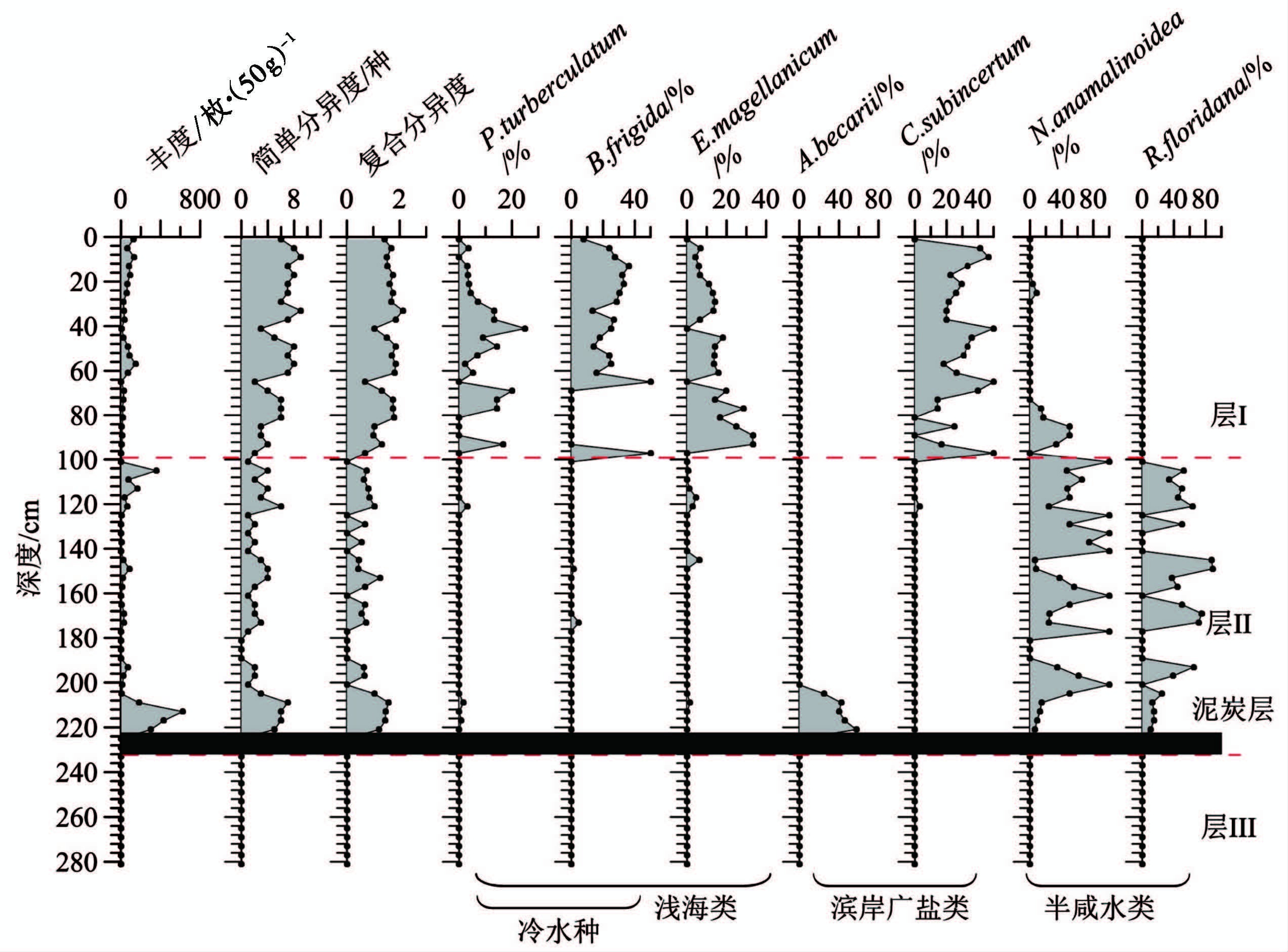
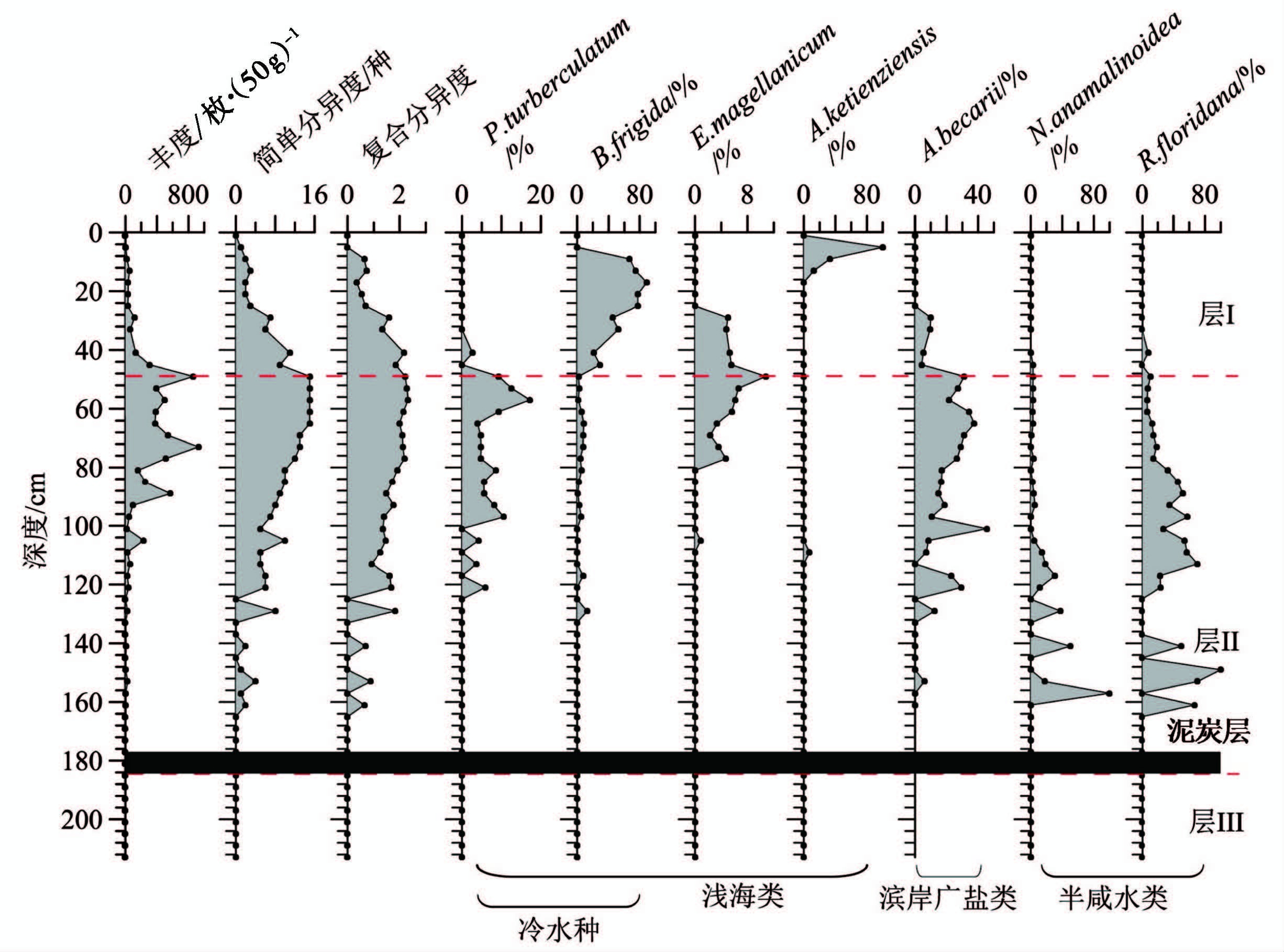
层Ⅲ(与层位C相对应,约10396cal .a B .P. 之前)。该层的划分主要基于DZ-4和DZ-5岩芯底部沉积物中底栖有孔虫的变化( 图 4和5)。该层位两岩芯中均未发现任何微体古生物化石,上覆的泥炭层及其测年结果显示,该段地层为全新世海侵开始之前海水尚未侵入的陆相沉积。
|
图 4 DZ-4岩芯底栖有孔虫垂向分布 Fig. 4 Downcore distribution of benthic foraminifera in core DZ-4 |
|
图 5 DZ-5岩芯底栖有孔虫垂向分布 Fig. 5 Downcore distribution of benthic foraminifera in core DZ-5 |
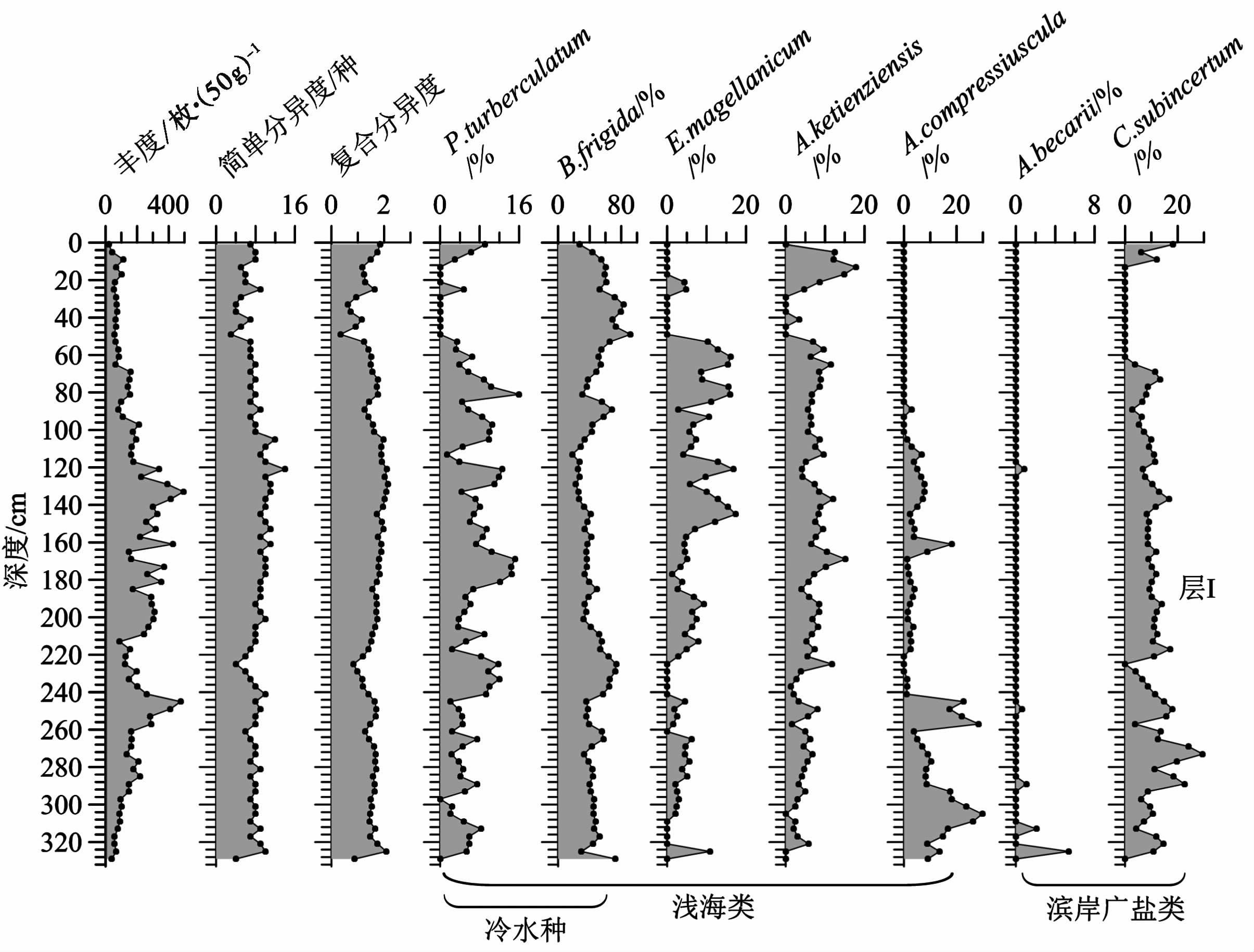
层Ⅱ(与层位B相对应,约10396~6778cal .a B .P. 期间)。 该层划分主要依据岩芯DZ-1(349~223cm段)、 DZ-4(231~99cm段)和DZ-5(185~47cm段)沉积物中有孔虫的变化( 图 4~6)。

|
图 6 DZ-1岩芯底栖有孔虫垂向分布 Fig. 6 Downcore distribution of benthic foraminifera in core DZ-1 |
DZ-1岩芯349~223cm段沉积物中有孔虫丰度高,变化幅度大,平均丰度843.0枚/50g,简单分异度与复合分异度的平均值分别为12.2种和1.88。该段有孔虫优势种主要包括浅海类属种Ammonia compressiuscula (平均含量32.31 % )、 广盐性滨岸浅水种Cribrononion subincertum (平均含量15.17 % )与Ammonia becarii var.(平均含量10.09 % )、 半咸水种Rosalina floridana(平均含量7.93 % ),且下部层位广盐性滨岸浅水种Ammonia becarii var. 与半咸水种Rosalina floridana占主导,至上部层位浅海类属种Ammonia compressiuscula优势地位趋于明显。300~302cm段混合底栖有孔虫AMS 14 C 测年日历年龄为6910cal .a B .P . ,总体显示了该阶段对应全新世中期海平面逐渐上升至最高海平面的过程。
DZ-4岩芯的层Ⅱ段始于有孔虫含量极低的泥炭层,该层段有孔虫丰度明显低于DZ-1岩芯,平均丰度84.0枚/50g,简单分异度与复合分异度较低,平均值分别为2.6种和0.59。有孔虫优势种以半咸水种Nonion anamalinoidea (46.88 % )和Rosalina floridana(30.08 % )为主,波动幅度较大,且下部泥炭层之上的层位广盐性滨岸浅水种Ammonia becarii var. 占一定比例(某些层位含量可达57.69 % ),反映了潮坪沉积环境。
DZ-5岩芯层Ⅱ段与DZ-4岩芯相似,同样始于有孔虫含量极低的泥炭层,该层段有孔虫丰度变化大,平均丰度190.1枚/50g,且自下而上有孔虫丰度逐渐增大,简单分异度和复合分异度呈现出相同的变化特征。段内有孔虫优势种主要包括半咸水种Rosalina floridana(平均含量26.83 % )和Nonion anamalinoidea (平均含量9.83 % )、 广盐性滨岸浅水种Ammonia becarii var.(平均含量14.02 % )。自下而上优势种由半咸水种Rosalina floridana和Nonion anamalinoidea逐渐过渡至广盐性滨岸浅水种Ammonia becarii var.,且下部多个层位有孔虫缺失,上部层位浅海类种Protelphidium turberculatum和Elphidium magellanicum含量明显增加,该层段对应海水由岸线附近上升至最高海平面期间的沉积过程。
3个岩芯该段地层中有孔虫丰度、 简单分异度及复合分异度垂向波动为末次冰消期以来最大,显示了复杂多变的沉积环境。优势种自下而上由广盐性滨岸浅水种或半咸水种逐渐过渡至浅海类种,反应了全新世早中期海水由岸线附近逐渐上升至最高海平面的过程。
层Ⅰ(与层位A相对应,约6778cal .a B .P. 高海面以来)。 该层的分析主要基于岩芯DZ-1(223~0cm段)、 DZ-4(99~0cm段)、 DZ-5(47~0cm段)和DZ-7沉积物中有孔虫的变化( 图 4~7)。
|
图 7 DZ-7岩芯底栖有孔虫垂向分布 Fig. 7 Downcore distribution of benthic foraminifera in core DZ-7 |
DZ-1岩芯223~0cm段中有孔虫丰度较高,平均值为386.4枚/50g,简单分异度与复合分异度平均值分别为9.5种和1.70。该岩芯层Ⅰ段有孔虫优势种主要包括近岸低盐浅水属种Cribrononion subincertum(平均含量37.18 % )、 浅海类冷水种Buccella frigida(平均含量19.76 % )、 Protelphidium turberculatum(平均含量8.56 % )与沿岸流分布区的低温低盐属种Elphidium magellanicum(平均含量6.46 % ),显示了冷水环境对DZ-1岩芯该阶段的控制作用。
DZ-4岩芯层Ⅰ段有孔虫丰度明显低于DZ-1,平均值仅为50.0枚/50g,简单分异度与复合分异度平均值分别为5.9种和1.52。该岩芯层Ⅰ段有孔虫优势种以浅海类冷水种(Buccella frigida 与Protelphidium turberculatum(平均含量26.67 % )与沿岸流分布区的低温低盐属种Elphidium magellanicum(平均含量13.16 % )为主,同时近岸低盐浅水属种Cribrononion subincertum含量较高,平均含量24.36 % ,总体反映了DZ-4岩芯该阶段明显受到沿岸冷水环境的主要作用。
DZ-5岩芯47~0cm段有孔虫丰度较低,平均值为71.6枚/50g,且自下而上逐渐减少,简单分异度与复合分异度呈现相同的变化趋势。该岩芯层Ⅰ段有孔虫优势种主要包括浅海类冷水种Buccella frigida (平均含量48.52 % )、 较深水环境种Ammonia ketienziensis(平均含量13.26 % )和沿岸流分布区的低温低盐属种Elphidium magellanicum(平均含量9.60 % ),总体显示DZ-5岩芯该阶段水深较大且明显受到冷水环境的影响。
DZ-7岩芯有孔虫丰度平均值为180.5枚/50g,简单分异度与复合分异度平均值分别为8.0种和1.56。该岩芯有孔虫的优势种以浅海类冷水种Buccella frigida(平均含量46.68 % )和沿岸流分布区的低温低盐属种Elphidium magellanicum(平均含量14.52 % )为主,反映了沿岸冷水环境对DZ-7岩芯该阶段的主控作用。
4个岩芯层Ⅰ段沉积物中底栖有孔虫变化特征基本吻合,优势种以浅海类冷水种与沿岸流分布区的低温低盐属种为主,总体显示全新世高海面以来沿岸冷水环境对研究区层Ⅰ段地层的主控作用。
4 讨论 4.1 研究区泥炭层对海平面变化的响应泥炭层是淡水沼泽或盐沼环境中的植物被快速埋藏下来而形成的有机碳含量高的暗褐色-黑色沉积物,常被作为 14 C年代测定的理想材料[2, 4, 5, 26, 28, 51, 52],同时也是沉积环境与海平面变化的重要标志[53-55]。
前人研究发现,北黄海泥炭层在北黄海西部尤其渤海海峡入口水深50~54m附近的岩芯剖面中广泛发育( 图 8),如岩芯剖面A-O29(38°45.4′N,121°58.5′E) 与B-I35(38°28.1′N,121°59.7′E)[26]、 NYS-3(38°50.0′N,122°0.0′E)[28]、 NYS-101(37°42.2′N,122°48.2′E) [5]( 图 1),其形成与寒冷而湿润的气候相对应,形成时代介于12320~11346cal .a B .P . ,可作为末次冰消期气候回冷事件——Younger Dryas事件(12.9~11.6ka期间)在北黄海响应的重要证据[5, 26, 28]; 而Younger Dryas事件期间,北黄海另一重要标志层沉积——硬质粘土层(12602~10357cal .a B .P. 期间)在北黄海中部水深53m附近岩芯剖面DLC70-2(38°27.02′N,122°24.2′E) 的沉积记录中得以发现[56],有关这一时期的硬质粘土层在岩芯剖面A-O29的两泥炭层之间同样存在[26]( 图 8)。
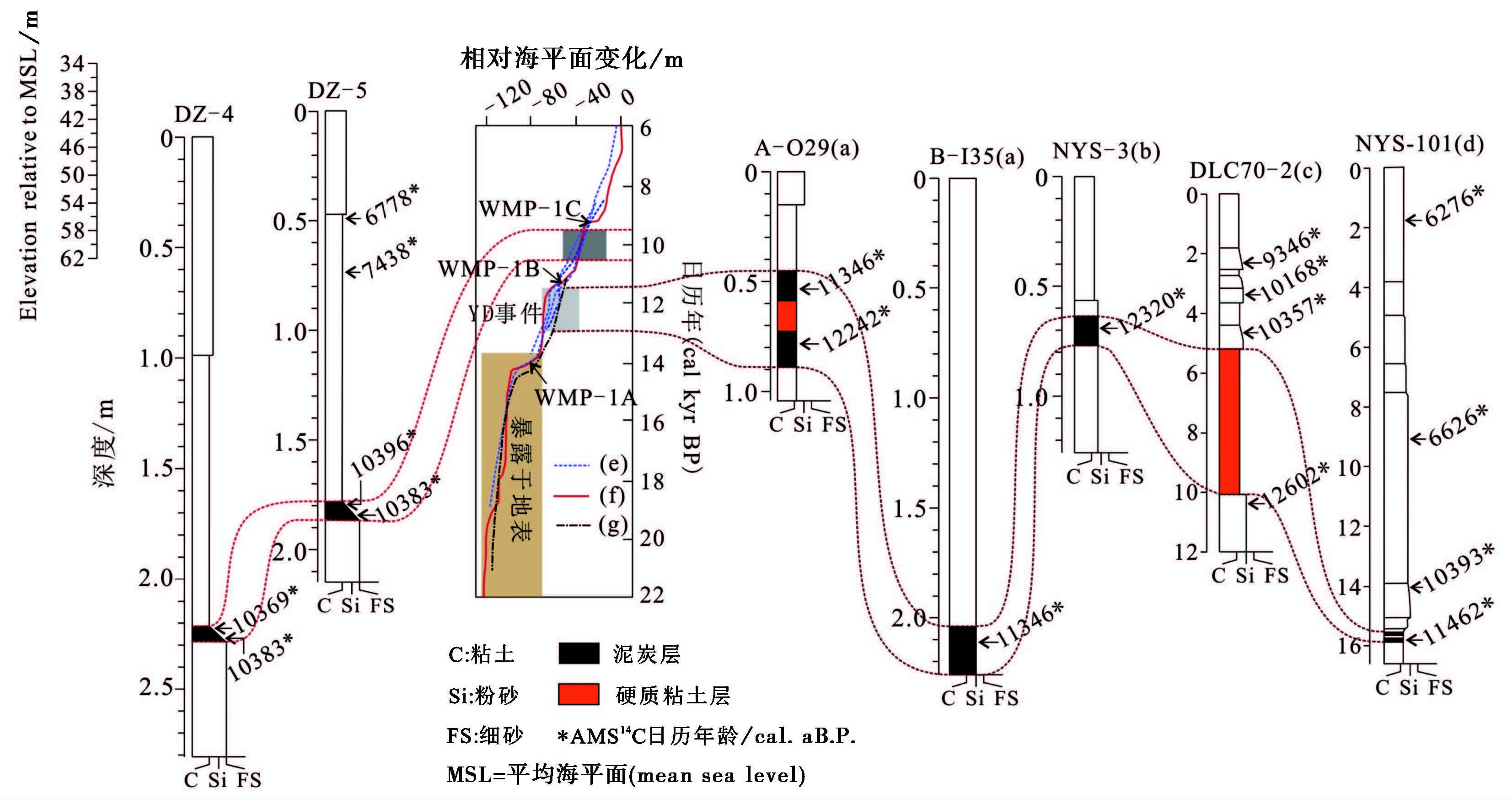
|
图 8 北黄海泥炭层及硬质粘土层(DZ-4与DZ-5(本研究),a[26],b[28],c[56],d[5])与海平面变化(e[3],f[4],g[57])对比(岩芯位置见 图 1) Fig. 8 Correlations of peat layers and hard clay(DZ-4 and DZ-5 from this study,a[26],b[28],c[56] and d[5])and relative sea-level changes(e[3],f[4] and g[57])in North Yellow Sea(see core locations in Fig. 1) |
本研究中出现泥炭层的2个岩芯DZ-4和DZ-5的水深分别为44.6m和40.8m,泥炭层厚度均为9cm,2个岩芯剖面泥炭层的底部埋深分别为46.91m和42.65m。泥炭层中顶、 底4个层位AMS 14 C 测年的日历年龄介于10396~10369cal .a B .P . ,其形成时代与Younger Dryas事件在北黄海的响应沉积——50~54m水深左右的泥炭层[26]及硬质粘土层[56]相差近2000年。Younger Dryas事件期间,北黄海海平面在现今海平面以下50~60m徘徊[4, 26],此时,DZ-4与DZ-5岩芯泥炭层位明显暴露于地表,发育层C的河流相沉积。2次融水脉冲事件WMP-1B(11.6~11.3cal .a B .P.)与WMP-1C(9.9~9.0cal .a B .P.)使海平面发生快速上升,上升范围分别为-58~-45m和-36~-16m[58, 59],而2次融水脉冲事件之间发生的1000多年期间,海平面曾一度停滞或徘徊[4, 58],此时DZ-4和DZ-5剖面泥炭层的埋深与当时海平面相当,即当时研究区的水深变化介于-43至-47m,且北黄海这一时期的植被以针叶林为主,林下生长着大量的蕨类植物,气候寒冷而湿润[60],具备泥炭沼泽的形成和发育的良好地理环境和气候条件。因而,研究区岩芯剖面出现的泥炭层与2次融水脉冲事件(MWP-1B与MWP-1C)期间海平面相对停滞的过程密切相关。然而,这一海平面变化过程沉积的响应并未如Younger Dryas事件一样在全球沉积地层中广泛分布,在西太平洋边缘海的浅海陆架区,能提供这一海平面变化过程有力证据的沉积记录较少。
4.2 研究区末次冰消期以来的沉积环境演化本文4个岩芯剖面保存了末次冰消期以来的沉积记录,这一时期研究区的海平面呈现出明显的阶梯式上升的特征[3, 4],导致沉积环境发生相应的变化。本论文依据辽东半岛东南近岸泥质区内4个岩芯的岩性地层与生物地层的划分,结合海平面变化曲线,揭示了研究区末次冰消期以来3个阶段的沉积环境演化: 约10396cal .a B .P. 之前的河流相沉积、 约10396~6778cal .a B .P. 期间潮坪-滨海相沉积、 约6778cal .a B .P. 高海面以来浅海相沉积。
阶段Ⅲ. 末次冰消期以来至约10396cal .a B .P. 期间
末次冰盛期(30.0~19.0cal .a B .P.)至MWP-1B融水脉冲事件(11.6~11.3cal .a B .P.)期间,北黄海海平面由位于现今海平面120m以下[61, 62]阶梯式上升至-45m附近[3, 4, 58, 59],这一时期辽东半岛东南近岸泥质区仍暴露于地表,岩性以均一的黄褐色细砂为主,未发现微体古生物化石,广泛发育河流相沉积,期间经历的MWP-1A融水脉冲事件与Younger Dryas变冷事件在研究剖面中未能识别,这也印证了李铁刚等[26]提出的Younger Dryas变冷事件期间北黄海海平面位于约50m的认识。
阶段Ⅱ. 约10396~6778cal .a B .P. 期间
融水脉冲事件MWP-1B和MWP-1C之间为一海平面缓慢上升或徘徊时期,这一时期海平面上升幅度不超过4m[4, 58],这一时期在研究区的响应沉积为辽东半岛东南近岸泥质区约10396~10369cal .a B .P. 发育的泥炭层。约10369~6778cal .a B .P. 全新世高海面期间,随着海平面的上升,海水开始侵入研究区,形成的地层岩性主要为黄褐色粘土,且生物扰动及炭质斑点发育; 沉积物中底栖有孔虫优势种以半咸水种Rosalina floridana和Nonion anamalinoidea为主,同时广盐性滨岸浅水种Ammonia becarii var. 占一定比例,对应潮坪相沉积。随着水深的进一步增加,潮流作用增强,形成地层的岩性过渡至灰褐色粘土,且粉砂透镜体与粉砂薄层发育,见贝壳碎片; 沉积物中底栖有孔虫浅海类种如Ammonia compressiuscula的优势地位趋于明显,而半咸水种Rosalina floridana、 Nonion anamalinoidea及广盐性滨岸浅水种Ammonia becarii var. 含量逐渐减少。该阶段总体反映了全新世早中期海水由岸线附近逐渐上升至最高海平面的过程,受控于潮流作用,对应潮坪相-滨海相的过渡沉积。
阶段Ⅰ. 约6778cal .a B .P. 高海面以来
至约6778cal .a B .P. 研究区海平面达到最大,黄海暖流形成,北黄海现代环流格局建立,这与前人研究结果相一致[6, 63, 64]。形成的地层岩性总体为均一的深灰色粘土或粉砂质粘土,含水量较高; 沉积物中底栖有孔虫优势种主要包括浅海类冷水种Buccella frigida和Protelphidium turberculatum、 沿岸流分布区的低温低盐属种Elphidium magellanicum,显示了该阶段冷水团及沿岸流对研究区的主控作用,代表了与目前相似的冷涡边缘的冷水环境,主要为鸭绿江&大洋河等辽东半岛东南近岸中小河流入海细颗粒物质在辽南沿岸流的携带下,沿岸搬运至研究区,受黄海暖流的顶托作用在研究区沿岸沉积[21],该阶段对应全新世约6778cal .a B .P. 高海面以来的浅海相沉积。这一时期源自黄河入海物质的浅海相沉积——山东半岛近岸泥质沉积与北黄海中部泥质沉积也被认为是鲁北沿岸流与黄海暖流的共同作用下的产物[5, 29]。因而,北黄海约6778cal .a B .P. 高海面以来的沉积格局主要受控于沿岸流、 黄海暖流为主的环流体系。
值得注意的是,研究区岩芯剖面约6778cal .a B .P. 高海面以来的底栖有孔虫丰度普遍低于约10396~6778cal .a B .P. 期间,这种现象明显异于其他海区。其中辽东半岛东南近岸泥质区东南边缘的2个岩芯DZ-4和DZ-5在约6778cal .a B .P. 高海面以来的沉积物明显变粗,显示该区域这一时期水动力强化显著[8],从而导致底栖有孔虫丰度减少; 而DZ-1和DZ-7两岩芯高海面以来丰度的减少,推测由物源的转换与沉积速率的增加所引起,高海面以前,物源主要黄河远端的入海物质,沉积速率相对较低,约6778cal .a B .P. 高海面以来,北黄海环流格局形成,鸭绿江和大洋河入海物质在辽南沿岸流与黄海暖流的作用下在研究区堆积,沉积速率相对较高[21]。
5 结论本文通过对取自辽东半岛东南近岸泥质区4个岩芯的岩性、 微体古生物以及AMS 14 C 年代学的分析,揭示了研究区末次冰消期以来的沉积环境演化,并探讨了事件沉积对海平面变化的响应。结论如下:
辽东半岛东南近岸泥质区岩芯沉积物记录了末次冰消期以来的沉积环境演化信息。研究表明,这种演化与海平面变化存在良好的对应关系,且具有明显的阶段性特征。
低海面沉积阶段(末次冰消期至约10396cal .a B .P. 期间): 该阶段岩性均一,主要为黄褐色细砂,与上覆地层为侵蚀接触,岩芯沉积物种未发现任何微体古生物化石,对应海水尚未到达研究区的河流沉积环境。
全新世海侵阶段(10396~6778cal .a B .P. 期间): 该阶段始于有孔虫含量极低的泥炭层(约10396~10369cal .a B .P. 期间),对应代表陆海沉积发生转换的盐沼沉积环境; 随着海平面的逐渐上升,形成了约10369~6778cal .a B .P. 期间的沉积地层,该段地层岩性自下而上由黄褐色粘土变为灰褐色粘土,与上覆地层为渐变接触,下部层位底栖有孔虫优势种以半咸水种Rosalina floridana、 Nonion anamalinoidea以及广盐性滨岸浅水种Ammonia becarii var. 为主,至上部层位浅海类种如Ammonia compressiuscula的优势地位趋于明显,对应海平面上升过程中潮流作用下的潮坪-滨海沉积环境。
全新世高海面沉积阶段(约6778cal .a B .P. 以来): 该阶段岩性均一,主要为深灰色粉砂质粘土与粘土,岩芯沉积物中底栖有孔虫优势种以浅海类 冷水种Buccella frigida和Protelphidium turberculatum、 沿岸流分布区的低温低盐属种Elphidium magellanicum为主,显示了该阶段冷水团及沿岸流的主控作用,对应高海面以来沿岸流与黄海暖流为主的环流体系影响下的浅海沉积环境。
研究区泥炭层的AMS 14 C 日历年龄介于约10396~10369cal .a B .P. 之间,与Younger Dryas事件在北黄海响应的泥炭层或硬质粘土层为不同时期的沉积,与发生在末次冰消期以来两次融水脉冲事件MWP-1B(11.6~11.3cal .a B .P.)与MWP-1C(9.9~9.0cal .a B .P.)之间海平面缓慢上升期相吻合,表明北黄海这一时期泥炭层的形成可能与两次融水脉冲事件期间的海平面变化过程密切相关,可作为这一海平面事件在北黄海陆架响应的一个重要证据。而研究区泥炭层的出现表明这一海平面缓慢上升过程中存在停滞阶段。
| 1 |
刘敏厚, 吴世迎, 王永吉.
黄海晚第四纪沉积 . 北京: 海洋出版社, 1987 .
Liu Minhou, Wu Shiying, Wang Yongji. Late Quaternary Deposition in the Yellow Sea. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1987 . (  0) 0)
|
| 2 |
秦蕴珊, 赵一阳, 陈丽蓉.
黄海地质 . 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989 .
Qin Yunshan, Zhao Yiyang, Chen Lirong. The Geology of the Yellow Sea. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1989 . (  0) 0)
|
| 3 |
Bard E, Hamelin B, Arnold M, et al. Deglacial sea-level record from Tahiti corals and the timing of global meltwater discharge.
Nature,1996, 382 : 241~244.
doi:10.1038/382241a0 ( 0) 0)
|
| 4 |
Liu J Paul, Milliman John D, Gao Shu, et al. Holocene development of the Yellow River's subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea.
Marine Geology,2004, 209 (1-4) : 45~67.
doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2004.06.009 ( 0) 0)
|
| 5 |
Liu Jian, Saito Y, Wang Hong, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea.
Marine Geology,2007, 236 (3/4) : 165~187.
( 0) 0)
|
| 6 |
陈晓辉, 李日辉, 蓝先洪, 等. MIS 3中期以来北黄海中部陆架古环境演化.
沉积学报,2016, 34 (1) : 102~110.
Chen Xiaohui, Li Rihui, Lan Xianhong, et al. Paleo-environmental evolution in the central shelf of the North Yellow Sea since mid-MIS 3. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2016, 34 (1) : 102~110. (  0) 0)
|
| 7 |
程鹏, 高抒. 北黄海西部海底沉积物的粒度特征和净输运趋势.
海洋与湖沼,2000, 31 (6) : 604~615.
Cheng Peng, Gao Shu. Net sediment transport patterns over the northwestern Yellow Sea, based upon grain size trend analysis. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica,2000, 31 (6) : 604~615. (  0) 0)
|
| 8 |
王伟, 李安春, 徐方建, 等. 北黄海表层沉积物粒度分布特征及其沉积环境分析.
海洋与湖沼,2009, 40 (5) : 525~531.
Wang Wei, Li Anchun, Xu Fangjian, et al. Distribution of surface sediments and sedimentary environment in the north Yellow Sea. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica,2009, 40 (5) : 525~531. (  0) 0)
|
| 9 |
涂路遥, 周鑫, 刘毅, 等. 近海泥质沉积物敏感粒径作为冬季风强度指标的再研究:与器测数据的对比.
第四纪研究,2015, 35 (6) : 1393~1400.
Tu Luyao, Zhou Xin, Liu Yi, et al. Re-analysis of sensitive grain size of coastal muddy sediments as proxy of winter monsoon strength:Comparison with instrumental data. Quaternary Sciences,2015, 35 (6) : 1393~1400. (  0) 0)
|
| 10 |
陈丽蓉. 渤海、黄海、东海沉积物中矿物组合的研究.
海洋科学,1989, 6 (2) : 1~8.
Chen Lirong. A study on mineral assemblages in sediments of the Bohai Sea, the Huanghai Sea and the East China Sea. Marine Sciences,1989, 6 (2) : 1~8. (  0) 0)
|
| 11 |
Liu Jian, Saito Y, Kong Xianghuai, et al. Geochemical characteristics of sediment as indicators of post-glacial environmental changes off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea.
Continental Shelf Research,2009, 29 (7) : 846~855.
doi:10.1016/j.csr.2009.01.002 ( 0) 0)
|
| 12 |
李艳, 李安春, 万世明, 等. 大连湾近海表层沉积物矿物组合分布特征及其物源环境.
海洋地质与第四纪地质,2009, 29 (4) : 115~121.
Li Yan, Li Anchun, Wan Shiming, et al. Distribution of mineral assemblages in offshore surface sediments of Dalian Bay in the northwestern North Yellow Sea and their provenance and environmental implications. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2009, 29 (4) : 115~121. (  0) 0)
|
| 13 |
程岩, 刘月, 李富祥, 等. 鸭绿江口及邻近浅海碎屑矿物特征与物源辨识.
地理研究,2010, 29 (11) : 1950~1959.
Cheng Yan, Liu Yue, Li Fuxiang, et al. Detrital mineral characteristics and material source identification in surface sediments of Yalu River estuary and adjacent waters. Geographical Research,2010, 29 (11) : 1950~1959. (  0) 0)
|
| 14 |
李艳, 李安春, 黄朋. 大连湾近海表层沉积物重矿物组合分布特征及其物源环境指示.
海洋地质与第四纪地质,2011, 31 (6) : 13~20.
Li Yan, Li Anchun, Huang Peng. Distribution of heavy mineral assemblages in subsurface sediments of Dalian Bay and their implications for provenance and environment. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2011, 31 (6) : 13~20. (  0) 0)
|
| 15 |
Huang Peng, Li Tiegang, Li Anchun, et al. Distribution, enrichment and sources of heavy metals in surface sediments of the North Yellow Sea.
Continental Shelf Research,2014, 73 : 1~13.
doi:10.1016/j.csr.2013.11.014 ( 0) 0)
|
| 16 |
Li Yan, Li Anchun, Huang Peng, et al. Clay minerals in surface sediment of the North Yellow Sea and their implication to provenance and transportation.
Continental Shelf Research,2014, 90 : 33~40.
doi:10.1016/j.csr.2014.01.020 ( 0) 0)
|
| 17 |
秦亚超, 李日辉, 姜学钧. 黄海中北部和渤海东部表层沉积物轻矿物特征及其指示意义.
第四纪研究,2014, 34 (3) : 611~622.
Qin Yachao, Li Rihui, Jiang Xuejun. Characteristics of light minerals in the surficial sediments and their implications in the north central Yellow and eastern Bohai Seas. Quaternary Sciences,2014, 34 (3) : 611~622. (  0) 0)
|
| 18 |
Kim G, Yang H S, Church T M. Geochemistry of alkaline earth elements(Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba)in the surface sediments of the Yellow Sea.
Chemical Geology,1999, 153 (1-4) : 1~10.
doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00149-1 ( 0) 0)
|
| 19 |
齐君, 李凤业, 宋金明, 等. 北黄海沉积速率及其沉积通量.
海洋地质与第四纪地质,2004, 24 (2) : 9~14.
Qi Jun, Li Fengye, Song Jinming, et al. Sedimentation rate and flux of the North Yellow Sea. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2004, 24 (2) : 9~14. (  0) 0)
|
| 20 |
严杰, 高建华, 李军, 等. 鸭绿江河口及近岸地区稀土元素的物源指示意义.
海洋地质与第四纪地质,2010, 30 (4) : 95~103.
Yan Jie, Gao Jianhua, Li Jun, et al. Implications of REE for provenance in the Yalu estuary and its adjacent sea area. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2010, 30 (4) : 95~103. (  0) 0)
|
| 21 |
Chen Xiaohui, Li Tiegang, Zhang Xunhua, et al. A Holocene Yalu River-derived fine-grained deposit in the southeast coastal area of Liaodong Peninsula.
Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology,2013, 31 (3) : 636~647.
doi:10.1007/s00343-013-2087-1 ( 0) 0)
|
| 22 |
Kim J M, Kucera M. Benthic foraminifer record of environmental changes in the Yellow Sea(Hwanghae)during the last 15000 years.
Quaternary Science Reviews,2000, 19 (11) : 1067~1085.
doi:10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00086-4 ( 0) 0)
|
| 23 |
Zhang S W, Wang Q Y, Lu Y, et al. Observation of the seasonal evolution of the Yellow Sea Cold Water Mass in 1996-1998.
Continental Shelf Research,2008, 28 (3) : 442~457.
doi:10.1016/j.csr.2007.10.002 ( 0) 0)
|
| 24 |
孙荣涛, 李铁刚, 常凤鸣. 北黄海表层沉积物中的底栖有孔虫分布与海洋环境.
海洋地质与第四纪地质,2009, 29 (4) : 21~28.
Sun Rongtao, Li Tiegang, Chang Fengming. Distribution of benthic foraminifera and its bearing on marine environmental factors in the North Yellow Sea surface sediments. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2009, 29 (4) : 21~28. (  0) 0)
|
| 25 |
孙荣涛, 李铁刚, 常凤鸣. 全新世北黄海泥质区环境演化的底栖有孔虫记录.
海洋地质与第四纪地质,2010, 30 (5) : 83~90.
Sun Rongtao, Li Tiegang, Chang Fengming. Environmental evolution of the northern Yellow Sea muddy area during Holocene based on benthic foraminifera records. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2010, 30 (5) : 83~90. (  0) 0)
|
| 26 |
李铁刚, 常凤鸣, 于心科. Younger Dryas事件与北黄海泥炭层的形成.
地学前缘,2010, 17 (1) : 322~329.
Li Tiegang, Chang Fengming, Yu Xinke. Younger Dryas Event and formation of peat layers in the northern Yellow Sea. Earth Science Frontiers,2010, 17 (1) : 322~329. (  0) 0)
|
| 27 |
程鹏, 高抒, 刘敬圃, 等. 北黄海西部全新统分布的初步认识.
第四纪研究,2001, 21 (4) : 37.
Cheng Peng, Gao Shu, Liu Jingpu, et al. Preliminary analysis of the distribution of Holocene deposits in the west of the North Yellow Sea. Quaternary Sciences,2001, 21 (4) : 37. (  0) 0)
|
| 28 |
Liu J P, Milliman J D, Gao S. The Shandong mud wedge and post-glacial sediment accumulation in the Yellow Sea.
Geo-Marine Letters,2002, 21 (4) : 212~218.
( 0) 0)
|
| 29 |
Yang Z S, Liu J P. A unique Yellow River-derived distal subaqueous delta in the Yellow Sea.
Marine Geology,2007, 240 (1-4) : 169~176.
doi:10.1016/j.margeo.2007.02.008 ( 0) 0)
|
| 30 |
陈晓辉, 李日辉, 徐晓达. 北黄海浅层声学地层.
海洋地质与第四纪地质,2011, 31 (3) : 17~22.
Chen Xiaohui, Li Rihui, Xu Xiaoda. Shallow seismic records and Late Pleistocene stratigraphy of the North Yellow Sea. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2011, 31 (3) : 17~22. (  0) 0)
|
| 31 |
Choi B H, Eum H M, Woo S B. Modeling of coupled tide-wave-surge process in the Yellow Sea.
Ocean Engineering,2003, 30 : 739~759.
doi:10.1016/S0029-8018(02)00064-1 ( 0) 0)
|
| 32 |
刘爱菊, 尹逊福, 卢铭. 黄海潮汐特征(Ⅱ).
黄渤海海洋,1984, 2 (2) : 24~27.
Liu Aijun, Yin Xunfu, Lu Ming. The tidal characteristics in the Huanghai Sea(Ⅱ). Journal of Oceanography of Huanghai & Bohai Seas,1984, 2 (2) : 24~27. (  0) 0)
|
| 33 |
苏育嵩. 黄东海地理环境概况、环流系统与中心渔场.
山东海洋学院学报,1986, 16 (1) : 12~28.
Su Yusong. A survey of geographic environment, circulation system and the central fishing grounds in the Huanghai Sea and East China Sea. Journal of Shandong College of Oceanology,1986, 16 (1) : 12~28. (  0) 0)
|
| 34 |
李乃胜, 赵松龄, 鲍·瓦西里耶夫.
西北太平洋边缘海地质 . 哈尔滨: 黑龙江教育出版社, 2001 .
Li Naisheng, Zhao Songling, Wasiliev Boris. Geology of Marginal Sea in the Northwest Pacific. Harbin: Heilongjiang Educational Press, 2001 . (  0) 0)
|
| 35 |
Liu Zhenxia, Xia Dongxing, Berné S, et al. Tidal deposition systems of China's continental shelf, with special reference to the eastern Bohai Sea.
Marine Geology,1998, 145 (3/4) : 225~153.
( 0) 0)
|
| 36 |
李培英, 杜军, 刘乐军, 等.
中国海岸带灾害地质特征及评价 . 北京: 海洋出版社, 2007 .
Li Peiying, Du Jun, Liu Lejun, et al. Characteristics and Evaluation of Hazard Geology in Coastal Zone of China. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2007 . (  0) 0)
|
| 37 |
何炎, 胡兰英, 王克良. 江苏东部第四纪有孔虫.
中国科学院地质古生物研究所集刊,1965 (4) : 51~162.
He Yan, Hu Lanying, Wang Keliang. Quaternary foraminifera in the east region of Jiangsu Province. Memoirs of the Institute of Geology and Palaeontology, Chinese Academy of Science,1965 (4) : 51~162. (  0) 0)
|
| 38 |
汪品先, 闵秋宝, 卞云华. 黄海有孔虫、介形虫组合的初步研究. 见:汪品先等著. 海洋微体古生物论文集. 北京:海洋出版社, 1980. 84~100
Wang Pinxian, Min Qiubao, Bian Yunhua. A preliminary study of foraminiferal and ostracoda assemblages of the Yellow Sea. In:Wang Pinxian et al. Papers on Marine Micropaleontology. Beijing:China Ocean Press, 1980. 84~100 (  0) 0)
|
| 39 |
汪品先, 章纪军, 赵泉鸿, 等.
东海底质中的有孔虫和介形虫 . 北京: 海洋出版社, 1988 .
Wang Pinxian, Zhang Jijun, Zhao Quanhong, et al. Foraminifera and Ostracoda in Surface Sediments of the East China Sea. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 1988 . (  0) 0)
|
| 40 |
赵泉鸿, 汪品先. 中国浅海现代介形虫的数量与属种分布.
海洋与湖沼,1988, 19 (6) : 553~561.
Zhao Quanhong, Wang Pinxian. Modern ostracoda in sediments of shelf seas of China:Quantitative and qualitative distributions. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica,1988, 19 (6) : 553~561. (  0) 0)
|
| 41 |
赵泉鸿, 李小艳, 梅西, 等. 黄、渤海中、晚更新世的冷水介形类.
微体古生物学报,2014, 31 (4) : 373~386.
Zhao Quanhong, Li Xiaoyan, Mei Xi, et al. Middle-Late Pleistocene cold-water Ostracoda of the Yellow Sea and Bohai Gulf. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica,2014, 31 (4) : 373~386. (  0) 0)
|
| 42 |
李淑鸾. 辽东湾表层沉积物中有孔虫介形虫研究.
北京大学学报(自然科学版),1994, 30 (2) : 181~193.
Li Shuluan. A preliminary study of foraminifera and ostracod assemblages in the Liaodong Bay. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,1994, 30 (2) : 181~193. (  0) 0)
|
| 43 |
Southon J, Kashgarian M, Fontugne M, et al. Marine reservoir corrections for the Indian Ocean and Southeast Asia.
Radiocarbon,2002, 44 (1) : 167~180.
doi:10.1017/S0033822200064778 ( 0) 0)
|
| 44 |
Kong G S, Lee C W. Marine reservoir corrections(ΔR)for southern coastal waters of Korea.
The Sea, Journal of the Korean Society of Oceanography,2005, 10 (2) : 124~128.
( 0) 0)
|
| 45 |
Boltovskoy E, Lena H. The foraminifera(except Family Allogromiidae)which dwell in fresh water.
Journal of Foraminiferal Research,1971, 1 : 71~76.
doi:10.2113/gsjfr.1.2.71 ( 0) 0)
|
| 46 |
石油化学工业部石油勘探开发规划研究院.
渤海沿岸地区新生代有孔虫 . 北京: 科学出版社, 1978 .
Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration & Development Ministry of Petroleum Industry. The Cenozoic Foraminifera from the Coastal Region of Bohai. Beijing: Science Press, 1978 . (  0) 0)
|
| 47 |
王飞飞, 丁璇, 刘健. 南黄海西部陆架氧同位素3期以来的古沉积环境演化.
微体古生物学报,2012, 29 (3) : 235~252.
Wang Feifei, Ding Xuan, Liu Jian. Paleoenvironmental evolution in the western shelf of the southern Yellow Sea since the Marine Isotope Stage 3. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica,2012, 29 (3) : 235~252. (  0) 0)
|
| 48 |
董艺辛, 刘春莲, 陈木宏, 等. 珠江三角洲中部大鳌平原晚第四纪古生物记录及环境演化.
第四纪研究,2012, 32 (6) : 1183~1198.
Dong Yixin, Liu Chunlian, Chen Muhong, et al. Late Quaternary paleontology and environmental changes in Da'ao Plain, middle Pearl River delta, Southern China. Quaternary Sciences,2012, 32 (6) : 1183~1198. (  0) 0)
|
| 49 |
李日辉, 孙荣涛, 徐兆凯, 等. 黄海与渤海交界区附近表层沉积物中的底栖有孔虫分布与环境因素制约.
海洋地质与第四纪地质,2014, 34 (3) : 93~103.
Li Rihui, Sun Rongtao, Xu Zhaokai, et al. Distribution of benthic foraminifera in surface sediments in the junction of Bohai Sea and Yellow Sea and environmental constraints. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,2014, 34 (3) : 93~103. (  0) 0)
|
| 50 |
Murry J W. Ecology and Palaeoecology of Benthic Foraminifera.
Harlow:Longman,1991 : 1~397.
( 0) 0)
|
| 51 |
彭环环, 郑卓, 郑艳伟, 等. 肇庆高要泥炭沉积揭示的全新世植被演变及人类活动历史.
第四纪研究,2015, 35 (3) : 742~754.
Peng Huanhuan, Zheng Zhuo, Zheng Yanwei, et al. Holocene vegetation changes and human activities revealed by a peat sediment core in Gaoyao, Zhaoqing. Quaternary Sciences,2015, 35 (3) : 742~754. (  0) 0)
|
| 52 |
黄庭, 程胜高, 肖河, 等. 东北哈尼泥炭记录的早全新世长白山火山喷发及其古气候意义.
第四纪研究,2015, 35 (6) : 1500~1508.
Huang Ting, Cheng Shenggao, Xiao He, et al. Early Holocene volcanic eruption discovered in Hani peat bog of NE China and its paleoclimate implication. Quaternary Sciences,2015, 35 (6) : 1500~1508. (  0) 0)
|
| 53 |
Jordan J W, Mason O K. A 5000 year record of intertidal peat stratigraphy and sea-level change from northwest Alaska.
Quaternary International,1999, 60 : 37~47.
doi:10.1016/S1040-6182(99)00005-1 ( 0) 0)
|
| 54 |
Barber K E, Langdon P G. What drives the peat-based palaeoclimate record?A critical test using multi~proxy climate records from northern Britain.
Quaternary Science Reviews,2007, 26 : 3318~3327.
doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.09.011 ( 0) 0)
|
| 55 |
Charman D J, Barber K E, Blaauw M, et al. Climate drivers for peatland palaeoclimate records.
Quaternary Science Reviews,2009, 28 : 1811~1819.
doi:10.1016/j.quascirev.2009.05.013 ( 0) 0)
|
| 56 |
陈晓辉, 李日辉, 蓝先洪, 等. 晚更新世末北黄海中部硬质粘土层的形成及其古环境意义.
第四纪研究,2014, 34 (3) : 570~578.
Chen Xiaohui, Li Rihui, Lan Xianhong, et al. Formation and paleo-environmental implications of hard clay in the central North Yellow Sea during the late period of Pleistocene. Quaternary Sciences,2014, 34 (3) : 570~578. (  0) 0)
|
| 57 |
Hanebuth T, Statteffer K, Grootes P M. Rapid flooding of the Sunda Shelf:A late-Glacial sea-level record.
Science,2000, 228 (5468) : 1033~1035.
( 0) 0)
|
| 58 |
Fairbanks R G. A 17000-year glacio-eustatic sea level record:Influence of glacial melting rates on the Younger Dryas event and deep ocean circulation.
Nature,1989, 342 : 637~642.
doi:10.1038/342637a0 ( 0) 0)
|
| 59 |
Bard E, Hamelin B, Fairbanks R G. U-Th ages obtained by mass spectrometry in corals from Barbados:Sea level during the past 130000 years.
Nature,1990, 346 : 456~458.
doi:10.1038/346456a0 ( 0) 0)
|
| 60 |
陈金霞. 末次冰消期以来东亚季风演化:来自东海和北黄海沉积孢粉记录. 青岛:中国科学院海洋研究所博士学位论文, 2008. 1~119
Chen Jinxia. Evolution of the East Asian Monsoon Since the Last Deglaciation:Sporopollen Records in the East China Sea and the North Yellow Sea. Qingdao:The Doctor Thesis of Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008. 1~119 http://epub.cnki.net/kns/detail/detail.aspx?QueryID=2&CurRec=1&recid=&FileName=2009053344.nh&DbName=CDFD0911&DbCode=CDFD&pr= (  0) 0)
|
| 61 |
Chappell J, Omura A, Esat T, et al. Reconciliaion of Late Quaternary sea levels derived from coral terraces at Huon Peninsula with deep sea oxygen isotope records.
Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1996, 141 (1-4) : 227~236.
doi:10.1016/0012-821X(96)00062-3 ( 0) 0)
|
| 62 |
Lea D W, Martin P A, Pak D K, et al. Reconstructing a 350 ky history of sea level using planktonic Mg/Ca and oxygen isotope records from a Cocos Ridge core.
Quaternary Sciences Reviews,2002, 21 : 283~293.
doi:10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00081-6 ( 0) 0)
|
| 63 |
刘健, 李绍全, 王圣洁, 等. 末次冰消期以来黄海海平面变化与黄海暖流的形成.
海洋地质与第四纪地质,1999, 19 (1) : 13~24.
Liu Jian, Li Shaoquan, Wang Shengjie, et al. Sea level changes of the Yellow Sea and formation of the Yellow Sea Warm Current since the Last Deglaciation. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology,1999, 19 (1) : 13~24. (  0) 0)
|
| 64 |
李铁刚, 江波, 孙荣涛, 等. 末次冰消期以来东黄海暖流系统的演化.
第四纪研究,2007, 27 (6) : 945~954.
Li Tiegang, Jiang Bo, Sun Rongtao, et al. Evolution pattern of warm current system of the east China sea and the yellow sea since the Last Deglaciation. Quaternary Sciences,2007, 27 (6) : 945~954. (  0) 0)
|
② Qingdao Institute of Marine Geology, Qingdao 266071;
③ School of Resources & Environment Engineering, Shandong University of Technology, Zibo 255049)
Abstract
The southeast coastal mud area off Liaodong Peninsula was considered as one of depositional centers during the Holocene.During and since the Last Deglaciation (LD),some specific deposits related to the sea level step-rise were deposited in this area,which carries abundant information on the sedimentary environmental evolution and geological events.Four piston cores (DZ-1:38°50.65'N,121°57.02'E;DZ-4:38°54.61'N,122°08.51'E;DZ-5:38°58.40'N,122°16.76'E;DZ-7:39°04.40'N,122°24.22'E) drilled in the southeast coastal mud area off Liaodong Peninsula were split and described in detail before sampling.In order to reveal the paleo-environmental evolution in the study area since LD,233 sediment samples at about 4cm intervals in the four cores were collected for microfossils analysis and 8 samples (including 4 benthic foraminifera samples and 4 peat layer samples) for AMS 14C dating.The results suggest that the study area has experienced multistage sedimentary environmental changes (Stage Ⅲ,Stage Ⅱ and Stage Ⅰ) in response to different sea-level regimes since LD.Stage Ⅲ(during the sea-level lowstand period from the LD to ca.10396cal.a B.P.),mainly characterized by yellowish brown fine sand with no microfossils,corresponds to fluvial environment without the influence of the sea.The seawater arrived at the study area since ca.10396cal.a B.P.,and two stages (Stage Ⅱ and Stage Ⅰ) of Holocene deposits were formed from then on.Stage Ⅱ(during the sea-level rise period from ca.10396cal.a B.P.to 6778cal.a B.P.),started as a peat layer (during the period from ca.10396cal.a B.P.to ca.10369cal.a B.P.) with almost absent microfossils,corresponding to salt marsh environment showing a transition from a continental facies to a marine one,and followed by the deposits composed of yellowish brown clay to gray-brown clay from the bottom up.The benthic foraminiferal assemblages in the later section are dominated in the lower part by brackish water species including Rosalina floridana and Nonion anamalinoidea,with secondary littoral species Ammonia becarii var.,and in the upper part by shelf species,such as Ammonia compressiuscula.The Stage Ⅱ section after ca.10369cal.a B.P.is interpreted to represent the tidal-flat and littoral environments under the tidal current,related to the sea-level rise during the period from ca.10369cal.a B.P.to ca.6778cal.a B.P.Stage Ⅰ(since the highest sea level around 6778cal.a B.P.) is generally characterized by dark gray silty clay and clay.The benthic foraminiferal assemblages in this stage are dominated by cold water species including Buccella frigida and Protelphidium turberculatum,and shelf species Elphidium magellanicum associated with coastal currents,which suggests this stage corresponds to neritic environment with significant ocean circulation influence including coastal currents and the Yellow Sea Warm Current.The AMS 14C ages of peat layer are in the range between ca.10396cal.a B.P.and 10369cal.a B.P.in the study area,differing from the peat layer or the hard clay in response to Younger Dryas Event in North Yellow Sea,which are highly coincident with the age between the two Melt-Water Pulse events MWP-1B (11.6~11.3cal.a B.P.) and MWP-1C (9.9~9.0cal.a B.P.) since the Last Deglaciation.This coincidence indicates that the formation of peat layer in this paper may be closely correlated with the sea-level change between these two Melt-Water Pulse events and can be regard as an evidence of the response of the northern Yellow Sea area to it.Meanwhile,the appearance of peat layer implies that a few stagnated periods existed during the period between the two Melt-Water Pulse events MWP-1B and MWP-1C.However,the sedimentary records like the peat layer during the sea-level stagnated process in the study area are still less in other east China Seas,and need to be further studied. 2016, Vol.36
2016, Vol.36

