2020-07-31 BDS-3系统的正式开通标志着我国卫星导航系统的发展进入新阶段[1]。随着BDS-3系统的建成和国家“十四五”政策的引领,针对BDS-3的应用研究逐渐成为热点[2-7]。观测环境开阔无遮挡是实现BDS-3高精度定位的条件之一,但在实际应用中,并非所有北斗监测站点都能处于开阔环境中。
许多学者针对多路径误差的定量分析、定位影响和削弱算法等展开研究[8-14],但这些研究大多围绕BDS-2应用和BDS-3实验展开,针对实际工程应用中BDS-3多路径误差与变形监测精度相关性的研究较少。基于此,本文选取2022年doy221~348共128 d的某水利工程变形监测数据,研究各站点BDS-3观测值多路径误差及监测精度的变化规律,并分析二者的相关性。本文结果有助于“北斗+”高精度变形监测应用的推广。
1 分析方法为定量分析BDS-3观测值多路径误差对变形监测精度的影响,本文从多路径误差计算、变形监测精度计算及多路径误差和监测精度的相关性分析三方面展开研究。
1.1 多路径误差计算多路径误差反映的是观测信号在对应频率上受多路径效应的影响,多路径误差值越小,接收机抗多路径效应的能力越强。多路径误差计算公式如下[15]:
| $ \mathrm{MP}_i=P_i-\left(1+\frac{2}{\alpha-1}\right) \varphi_i+\left(\frac{2}{\alpha-1}\right) \varphi_j $ | (1) |
式中,Pi为第i频率上的伪距观测值;φi、φj分别为第i和第j频率上的相位观测值;α为第i和第j频率fi、fj之比的平方,即α=(fi/fj)2。
1.2 变形监测精度计算在得到BDS-3变形监测序列(N, E, U)t后,利用多项式对原始变形序列进行拟合,得到趋势项序列
| $ \left[\begin{array}{l} \Delta N \\ \Delta E \\ \Delta U \end{array}\right]_t=\left[\begin{array}{c} N-\hat{N} \\ E-\hat{E} \\ U-\hat{U} \end{array}\right]_t $ | (2) |
| $ \sigma=\sqrt{\frac{\sum \Delta y^2}{n}} $ | (3) |
式中,Δy为N、E、U某一方向的残差,n为观测值样本数。
1.3 相关性分析多路径误差与变形监测精度的相关系数r计算公式如下:
| $ r=\frac{\sum\left[\left(\sigma_i-\bar{\sigma}\right) \times\left(\mathrm{MP}_i-\overline{\mathrm{MP}}\right)\right]}{\sqrt{\sum\left(\sigma_i-\bar{\sigma}\right)^2 \times \sum\left(\mathrm{MP}_i-\overline{\mathrm{MP}}\right)^2}} $ | (4) |
式中,
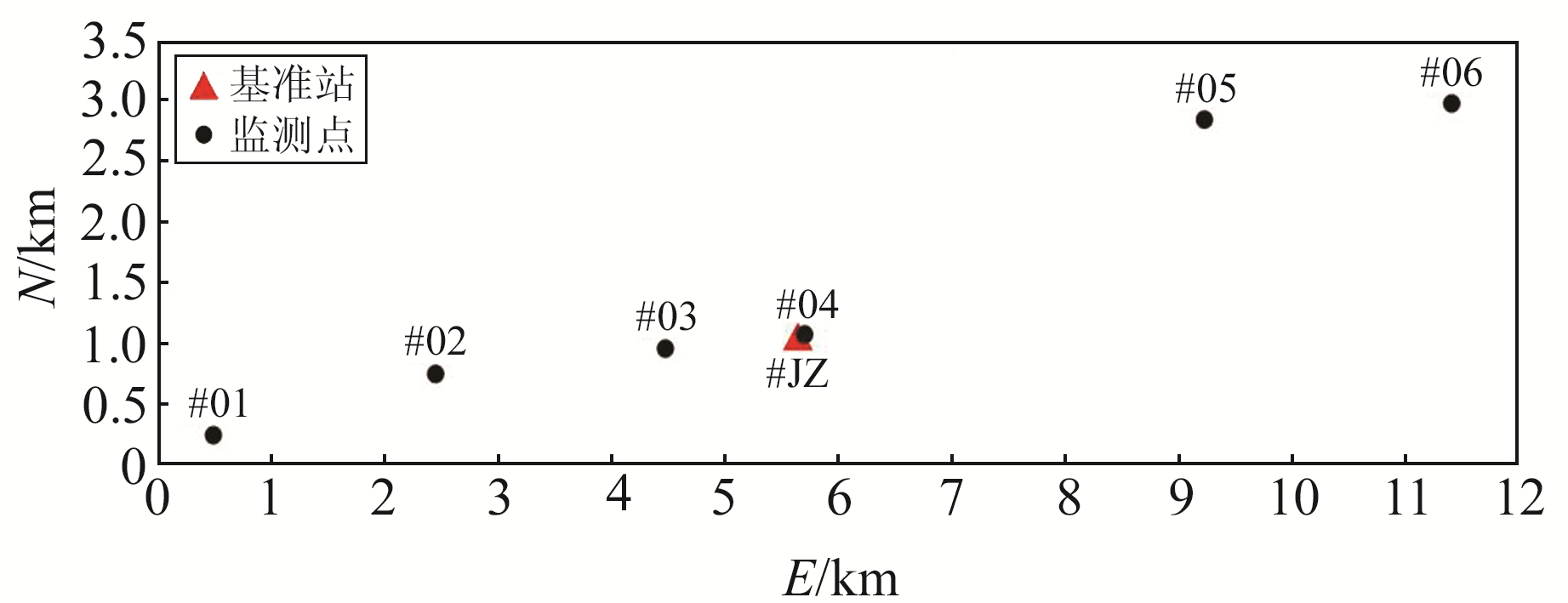
为探究多路径误差对BDS-3变形监测精度的影响,选择某水利工程变形监测应用采集的BDS-3观测数据进行分析。该监测应用共布设1个基准站(#JZ)和6个监测点(#01~#06),最远的监测点(#06)距离基准站约6 km,具体点位分布如图 1所示。
|
图 1 BDS-3变形监测站点点位分布 Fig. 1 Distribution of BDS-3 deformation monitoring station |
硬件方面,基准站采用的天线为华信HX-CGX601A带扼流圈天线,6个监测站点的天线为华信HXCGPS1000,所有接收机均支持BDS/GPS/GLONASS/GALILEO全频点信号。本文选择BDS-3 B1I和B3I观测值计算变形量,选择2022年doy221~348共128 d数据进行研究。
2.2 多路径误差分析本文基准站周围多路径误差分析分为2个阶段:监测前半段(doy221~284,共64 d)周围的树枝越长越茂盛,如图 2(a)所示;在doy284对树枝进行裁剪,如图 2(b)所示。

|
图 2 基准站周围树枝裁剪前后现场图 Fig. 2 Field images of branches around reference station before and after cutting |
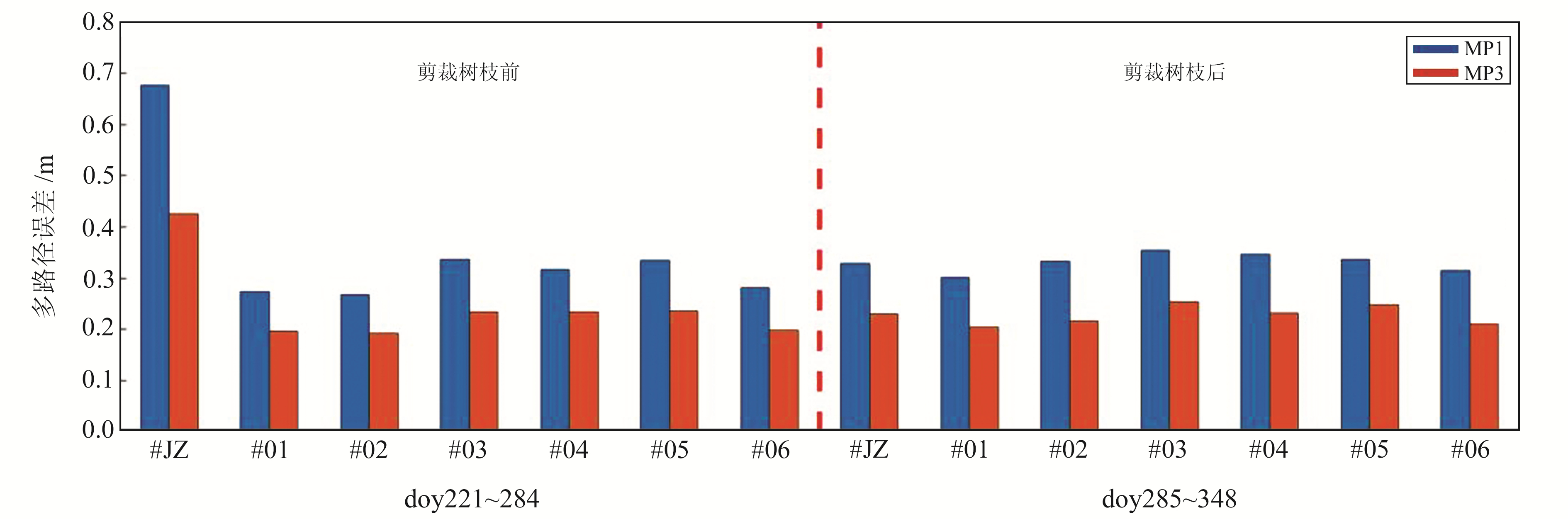
图 3为基准站监测期间BDS-3 B1I和B3I观测值多路径误差序列。由图可见,裁剪树枝前基准站B1I和B3I观测值的多路径误差分别约为0.4 m和0.7 m;裁剪树枝后B1I和B3I观测值的多路径误差明显降低,约为0.2 m和0.3 m,较之前减少50%。图 4为7个站点的平均多路径误差,由图可见,周边树木的变化对基准站的多路径误差有显著影响;由于其他6个监测点周围的观测环境没有改变,因此多路径误差无明显变化。

|
图 3 基准站北斗B1I和B3I观测值的多路径误差序列 Fig. 3 Multipath errorsequence of Beidou B1I and B3I observations |
|
图 4 所有站点多路径误差 Fig. 4 Multipath errors at all sites |
本文分别采用BDS-3 B1I和B3I单频观测值解算的监测模式,获取6个监测点N、E、U方向的变形序列。以监测点#04的B1I观测值结果为例,图 5为变形量时间序列,由图可见:1)在doy284裁剪树枝前所有监测点的变形序列波动较大;2)doy284裁剪树枝后所有监测点各方向的变形序列曲线趋于平稳。

|
图 5 使用北斗B1I观测值的变形监测原始序列 Fig. 5 The original sequence of deformation monitoring using Beidou B1I observations |
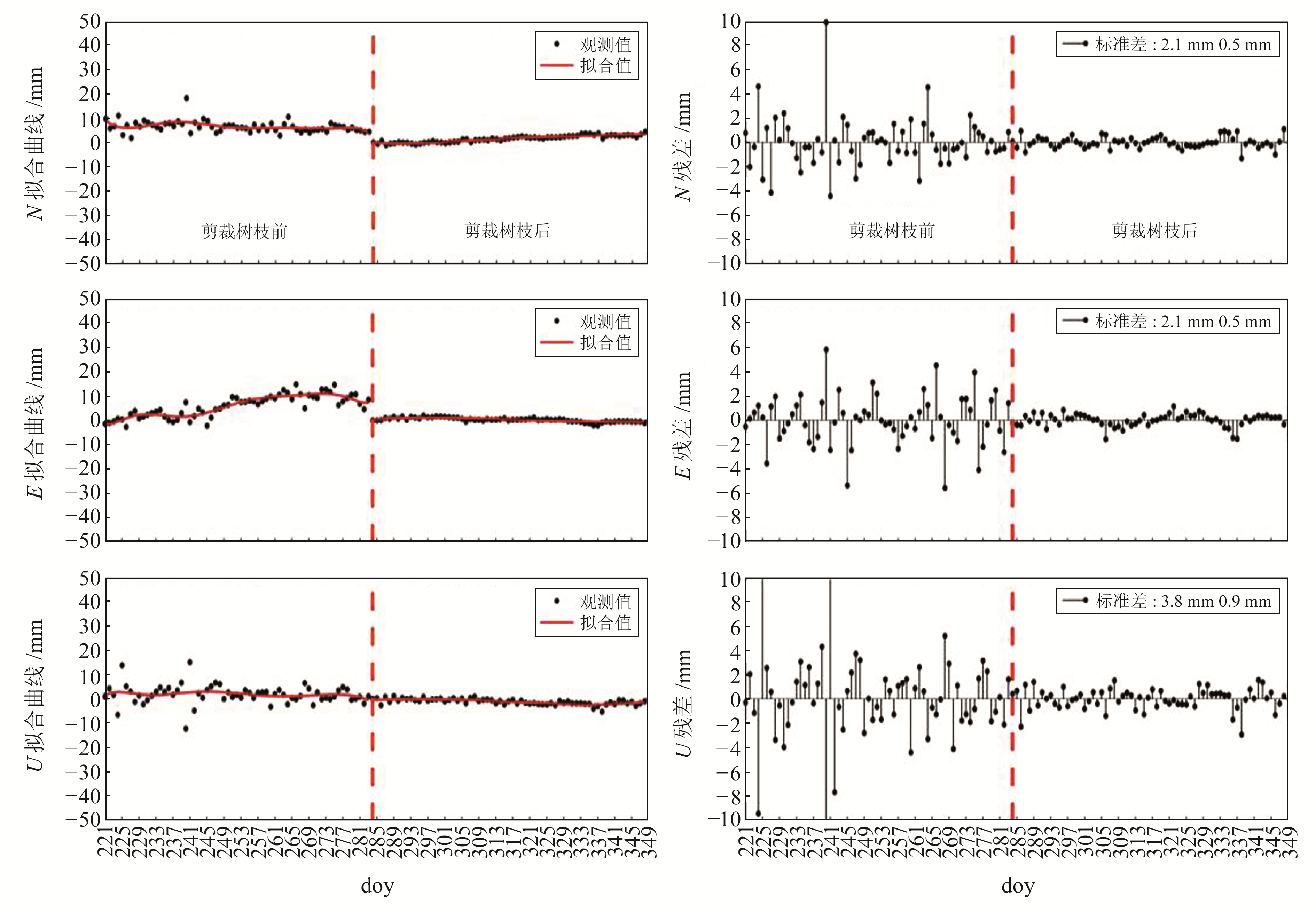
针对图 5的变形监测序列,选用4阶多项式拟合获取趋势项,用原始监测序列减去拟合曲线得到监测残差序列,结果如图 6所示。由图可见:1)doy284前各方向的残差波动较大,多在±6.0 mm范围内波动;doy284后残差波动变小,在±2.0 mm范围内波动;2)裁剪树枝前B1I观测值在N、E、U方向的监测精度分别为2.1 mm、2.1 mm、3.8 mm,裁剪树枝后监测精度分别为0.5 mm、0.5 mm、0.9 mm。
|
图 6 使用北斗B1I观测值的变形监测拟合序列和残差序列 Fig. 6 Deformation monitoring fitting sequence and residual sequence using Beidou B1I observations |
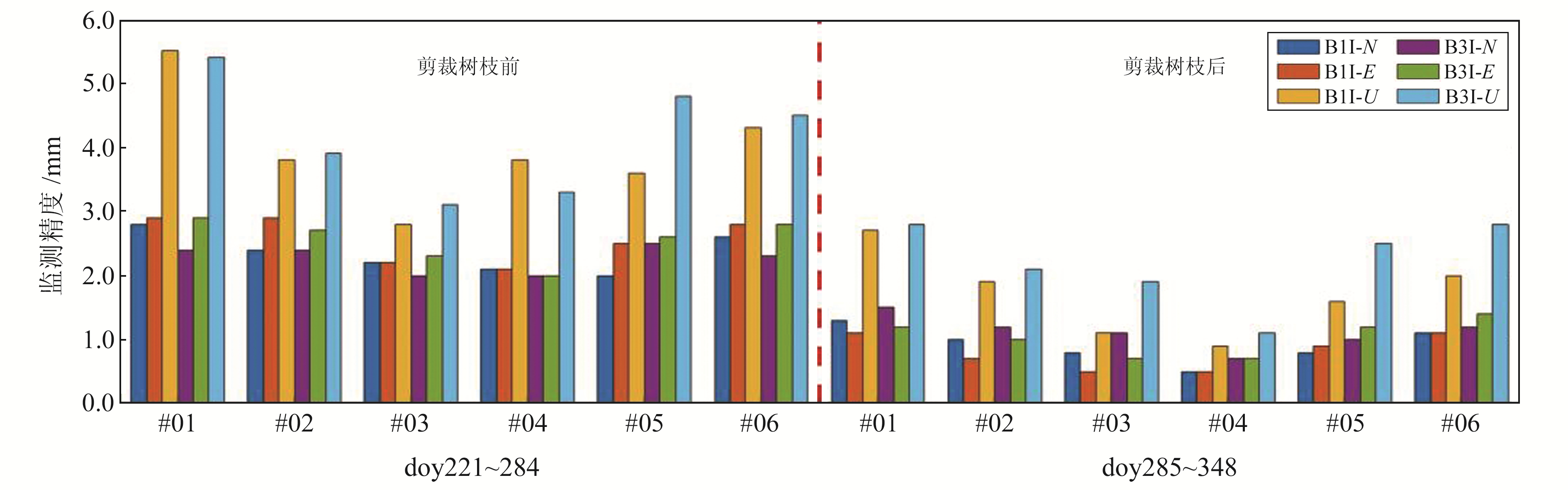
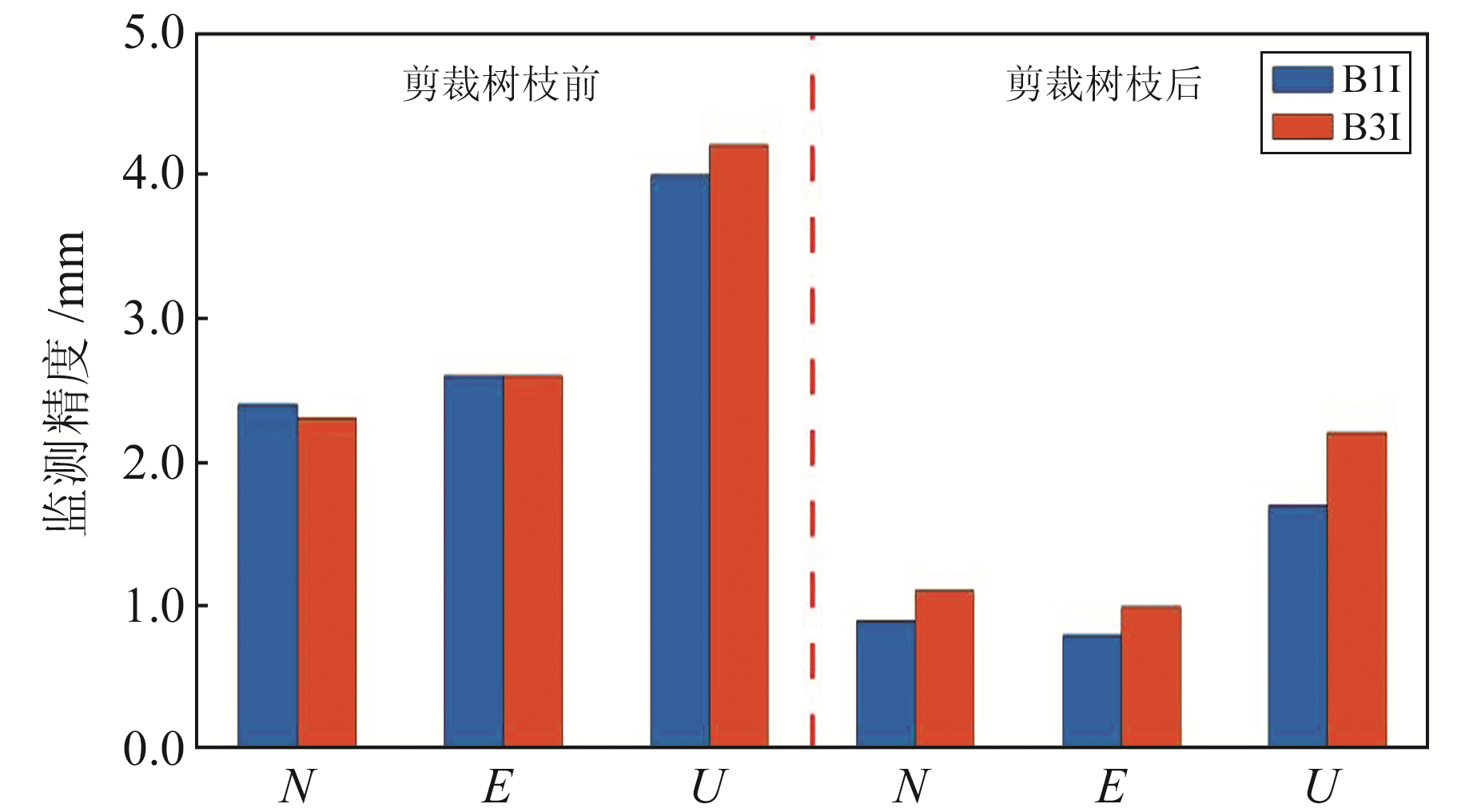
图 7为所有6个监测点使用B1I和B3I观测值在N、E、U方向的监测精度,图 8为平均监测精度。由图可见:
|
图 7 裁剪树枝前后N、E、U方向所有监测点的监测精度比较 Fig. 7 Comparison of monitoring accuracy of all monitoring points in N, E and U direction before and after pruning branches |
|
图 8 裁剪树枝前后的N、E、U方向平均监测精度比较 Fig. 8 Comparison of average monitoring accuracy in N, E and U direction before and after pruning branches |
1) 裁剪树枝前基准站多路径误差较大。N、E方向6个监测点使用B1I和B3I观测值的监测精度为2.0~3.0 mm,平均监测精度为2.4 mm、2.6 mm(B1I)和2.3 mm、2.6 mm(B3I);U方向使用B1I和B3I观测值监测精度为3.0~6.0 mm,平均监测精度分别为4.0 mm和4.2 mm。裁剪树枝后,基准站多路径误差大幅降低:N、E方向使用B1I和B3I观测值的监测精度均优于2.0 mm,平均监测精度分别提高至0.9 mm、0.8 mm(B1I)和1.1 mm、1.0 mm(B3I);U方向使用B1I和B3I观测值的监测精度均优于3.0 mm,平均精度分别提高至1.7 mm和2.2 mm。
2) 裁剪树枝前使用B1I和B3I观测值的监测精度相当,但裁剪树枝后多路径误差的影响被极大削弱,监测精度的规律更加明显。监测点距离基准站越近、监测精度越高,且B1I观测值的监测精度优于B3I观测值。该结论与中国卫星导航系统管理办公室公布的北斗B1I、B3I定位服务测试评价一致[16]。
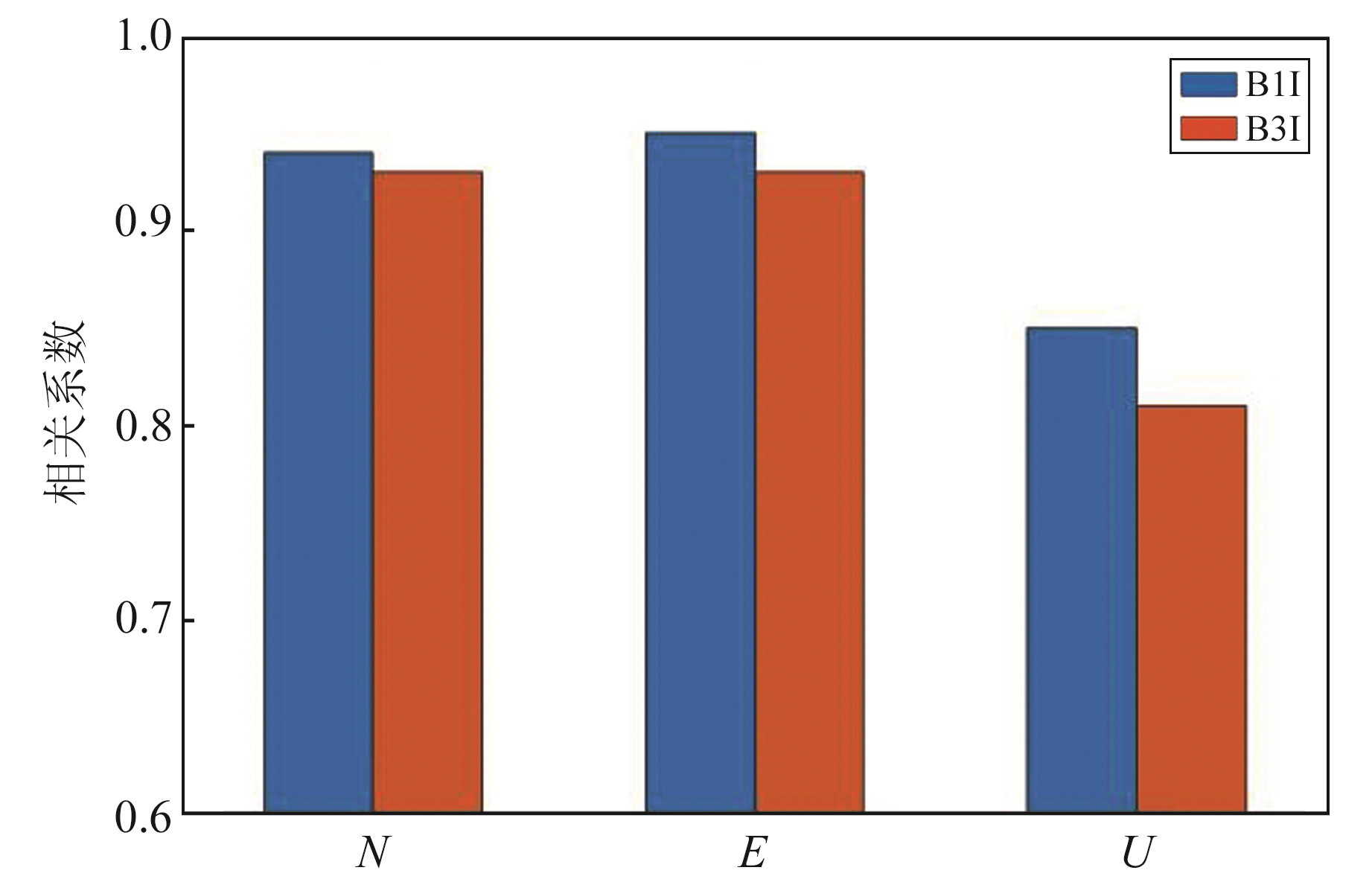
2.4 相关性分析按照式(4)对B1I和B3I观测值的多路径误差与对应的BDS-3监测精度进行相关性分析,得到的相关系数统计见表 1和图 9。可以看出:1)对于同类型观测值,水平和高程的监测精度与多路径误差存在强相关性,相关系数分别高达0.93和0.81。与高程监测精度相比,水平监测精度与多路径误差的相关系数更高;2)对于不同类型观测值,使用B1I观测值的监测精度与多路径误差的相关系数大于使用B3I观测值。
|
|
表 1 BDS-3 B1I/B3I观测值多路径误差与监测精度的相关系数统计 Tab. 1 Statistics of correlation coefficient between multipath error and monitoring accuracy of B1I/B3I observation of BDS-3 |
|
图 9 不同类型观测值的多路径误差与监测精度相关系数比较 Fig. 9 Comparison of correlation coefficients between multipath errors and monitoring accuracy of different types of observations |
1) 监测站点周围树木遮挡导致的多路径误差和BDS-3水平/高程监测精度的相关系数分别高达0.93和0.81,说明多路径误差与BDS-3变形监测精度之间存在强相关性。
2) 裁剪树枝前,使用B1I和B3I观测值在N、E、U方向的平均监测精度分别为2.4 mm、2.6 mm、4.0 mm和2.3 mm、2.6 mm、4.2 mm;裁剪树枝后,使用B1I和B3I观测值在N、E、U方向的平均监测精度分别为0.9 mm、0.8 mm、1.7 mm和1.1 mm、1.0 mm、2.2 mm。各方向的总体精度分别提高63%、69%、58%(B1I)和52%、61%、48%(B3I)。
3) 通过改变周围观测环境削弱多路径误差对变形监测结果的影响后,B1I观测值的监测结果要优于B3I观测值。因此,在短基线变形监测应用中推荐使用B1I观测值。
| [1] |
Yang Y X, Liu L, Li J L, et al. Featured Services and Performance of BDS-3[J]. Science Bulletin, 2021, 66(20): 2 135-2 143 DOI:10.1016/j.scib.2021.06.013
(  0) 0) |
| [2] |
肖健, 史俊波, 欧阳晨皓, 等. 2019~2020年北斗三号广播星历长期性能分析[C]. 第十二届中国卫星导航年会, 南昌, 2021 (Xiao Jian, Shi Junbo, Ouyang Chenhao, et al. Long-Term Performance Assessment of BDS-3 Broadcast Ephemeris in 2019 to 2020[C]. The 12th Annual China Satellite Navigation Conference, Nanchang, 2021)
(  0) 0) |
| [3] |
Shi J B, Ouyang C H, Huang Y S, et al. Assessment of BDS-3 Global Positioning Service: Ephemeris, SPP, PPP, RTK, and New Signal[J]. GPS Solutions, 2020, 24(3): 81 DOI:10.1007/s10291-020-00995-y
(  0) 0) |
| [4] |
宋伟伟, 赵新科, 楼益栋, 等. 北斗三号PPP-B2b服务性能评估[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2023, 48(3): 408-415 (Song Weiwei, Zhao Xinke, Lou Yidong, et al. Performance Evaluation of PPP-B2b Service of BDS-3[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2023, 48(3): 408-415)
(  0) 0) |
| [5] |
Lin C, Wu G Y, Feng X M, et al. Application of Multi-System Combination Precise Point Positioning in Landslide Monitoring[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(18): 8 378 DOI:10.3390/app11188378
(  0) 0) |
| [6] |
史俊波, 欧阳晨皓, 岳金广, 等. 三家北斗地基增强系统的高精度定位服务性能对比分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2022, 42(7): 712-715 (Shi Junbo, Ouyang Chenhao, Yue Jinguang, et al. High-Precision Positioning Service Performance Analysis of Three BDS Ground-Based Augmentation Systems[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2022, 42(7): 712-715)
(  0) 0) |
| [7] |
彭松, 刘建坤, 张云龙, 等. 基于北斗三号远程监测系统的公路岩质边坡开挖变形分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(33): 14 898-14 906 (Peng Song, Liu Jiankun, Zhang Yunlong, et al. Analysis of Excavation Deformation of Highway Rock Slope Based on Beidou3 Remote Monitoring System[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(33): 14 898-14 906)
(  0) 0) |
| [8] |
王西龙, 许小龙, 赵齐乐. 北斗三号系统信号质量分析及轨道精度验证[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2023, 48(4): 611-619 (Wang Xilong, Xu Xiaolong, Zhao Qile, et al. Signal Quality Analysis and Orbit Accuracy Verification of BDS-3[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2023, 48(4): 611-619)
(  0) 0) |
| [9] |
岳帆, 黄观文, 解世超, 等. 北斗三号B1C/B2a新频点信号数据质量和精密单点定位性能评估[J]. 测绘地理信息, 2023, 48(6): 20-25 (Yue Fan, Huang Guanwen, Xie Shichao, et al. Evaluation of Data Quality and Precise Point Positioning Performance of BDS-3 B1C/B2a New Signals[J]. Journal of Geomatics, 2023, 48(6): 20-25)
(  0) 0) |
| [10] |
石强, 戴吾蛟, 曾凡河, 等. BDS多路径效应特征及其对静态基线解精度的影响[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2016, 36(10): 874-878 (Shi Qiang, Dai Wujiao, Zeng Fanhe, et al. The Characteristics of BDS Carrier Phase Multipath and Its Effects on Static Baseline Solution[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2016, 36(10): 874-878)
(  0) 0) |
| [11] |
Shi J B, Huang Y S, Ouyang C H, et al. Beidou/GPS Relative Kinematic Positioning in Challenging Environments Including Poor Satellite Visibility and High Receiver Velocity[J]. Survey Review, 2020, 52(371): 172-182 DOI:10.1080/00396265.2018.1537227
(  0) 0) |
| [12] |
刘健. 滑坡环境GNSS多路径误差分析与处理技术研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2022 (Liu Jian. Research on GNSS Multipath Error Analysis and Processing Technology in Landslide Environment[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2022)
(  0) 0) |
| [13] |
易清根, 刘心龙, 刘万科. 基于EMD和小波的GPS/BDS变形监测中的多路径误差削弱方法[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2017, 37(5): 462-466 (Yi Qinggen, Liu Xinlong, Liu Wanke. Multipath Mitigation Method by Combined EMD and Wavelet in GPS/BDS Deformation Monitoring[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2017, 37(5): 462-466)
(  0) 0) |
| [14] |
刘太宗, 何秀凤, 贾东振, 等. 观测值域恒星日滤波方法在高铁路基变形监测中的应用[J]. 导航定位学报, 2023, 11(1): 39-47 (Liu Taizong, He Xiufeng, Jia Dongzhen, et al. Application of Sidereal Day Filtering Method in Observation Range in Deformation Monitoring of High-Speed Railway Subgrade[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2023, 11(1): 39-47)
(  0) 0) |
| [15] |
陈明, 郭际明, 龚晓鹏, 等. 基于国家基准站的北斗数据质量分析[J]. 测绘科学, 2017, 42(7): 29-35 (Chen Ming, Guo Jiming, Gong Xiaopeng, et al. Data Quality Analysis of BDS Observation Data Based on the National GNSS Reference Stations[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, 42(7): 29-35)
(  0) 0) |
| [16] |
中国卫星导航系统管理办公室测试评估研究中心. 中阿联合北斗测试评价结果[EB/OL]. http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201904/P020190412511925861044.pdf (Test and Assessment Research Center of China Satellite Navigation Office. Results of Beidou Testing and Evaluation Joint Project between China and Arab States[EB/OL]. http://www.beidou.gov.cn/xt/gfxz/201904/P020190412-511925861044.pdf)
(  0) 0) |
 2024, Vol. 44
2024, Vol. 44


