2. 云南经济管理学院工程学院,云南省安宁市麒麟路17号,650106
周跳是影响GPS监测数据可靠性的因素之一,高精度的监测成果必须保证载波相位观测值中无周跳存在[1-2]。周跳探测方法主要有相位多次求差法[3]、电离层残差法[4-6]、非差法[7-8]、双频码相组合法[9]、拟合法[10-11]和TurboEdit方法[12-14]等。上述方法在实际应用中均存在一定局限性,如相位多次求差法对小周跳探测不敏感; 双频码相组合法与电离层残差法不能确定周跳发生的频率位置及多值问题,并且对特殊组合周跳失效; 拟合法对数据个数及拟合阶数要求较高,同时也会产生拟合误差和舍入误差; TurboEdit方法中MW组合观测值易受伪距观测值噪声的影响,部分周跳容易被噪声湮没。针对上述问题,本文组建相位方程ΔΦ=ΔN1-(λ2/λ1)ΔN2,考虑到周跳在ΔΦ、ΔN1、ΔN2序列上表现为异常值的特点,利用Grubbs准则探测ΔN1、ΔN2异常值,通过约束ΔN1、ΔN2的范围来探测不同组合周跳。
1 双频周跳探测模型在双频条件下,设L1和L2上周跳大小分别为ΔN1、ΔN2,根据相位和伪距观测值可得:
| $ \left\{\begin{array}{l} \Delta \mathit{\Phi}=\Delta N_{1}-\frac{\lambda_{2}}{\lambda_{1}} \Delta N_{2}+\left[\Delta_{\text {ion }}(t+1)-\Delta_{\text {ion }}(t)\right] \\ \Delta N_{1}=\Delta \mathit{\Phi}_{1}-\frac{\Delta P_{1}}{\lambda_{1}}+\Delta \varepsilon_{1} \\ \Delta N_{2}=\Delta \mathit{\Phi}_{2}-\frac{\Delta P_{2}}{\lambda_{2}}+\Delta \varepsilon_{2} \end{array}\right. $ | (1) |
式中,ΔΦ为电离层残差在历元间的变化值; λ为波长; Δion(t)为某时刻的电离层残差; Δε为总误差项,主要受电离层和多路径影响。
若采样间隔较小,电离层在历元间的变化Δion(t)很小,则式(1)可简化为:
| $ \left\{\begin{array}{l} \Delta \mathit{\Phi}=\Delta N_{1}-\frac{77}{60} \Delta N_{2} \\ \Delta N_{1}=\Delta \mathit{\Phi}_{1}-\frac{\Delta P_{1}}{\lambda_{1}} \\ \Delta N_{2}=\Delta \mathit{\Phi}_{2}-\frac{\Delta P_{2}}{\lambda_{2}} \end{array}\right. $ | (2) |
从式(2)可以看出,针对2个未知数ΔN1、ΔN2,1个方程无法解算出周跳值,因此可通过计算附有限制条件ΔΦ=ΔN1-(λ2/λ1)ΔN2来确定ΔN1、ΔN2的取值区间。
2 双频周跳特征分析假设ΔΦ服从正态
设存在观测序列Y=(Y1, Y2, …, Yn),构建Grubbs检验统计量:
| $ G = \frac{{\mathop {\max }\limits_{i = 1, 2, \cdots , n} \left| {{Y_i} - \bar Y} \right|}}{S} $ | (3) |
式中,
Grubbs检验统计量为样本标准偏差单位与样本均值的最大绝对偏差。在显著性水平α下,若
| $ G>\frac{n-1}{\sqrt{n}} \sqrt{\frac{t_{\alpha /(2 n), n-2}^{2}}{n-2+t_{\alpha /(2 n), n-2}^{2}}} $ | (4) |
表明存在异常值,即存在周跳。式中,tα/(2n), n-2表示具有(n-2)自由度和显著性水平α/(2n)的T分布临界值。
4 区间搜索法周跳探测流程对于式(2),由于周跳ΔN1、ΔN2的整数特性,若能限制ΔN1、ΔN2范围,则可利用
1) 组建观测序列ΔΦ、ΔN1、ΔN2。
2) 判断序列ΔΦ是否超出范围[-0.07, 0.07]。若是,则ΔΦ存在普通周跳,记录ΔΦ对应的位置ti、ΔΦ(ti),并执行3);若否,则ΔΦ无普通周跳,执行4)。
3) 剔除ti位置对应的ΔN1(ti)、ΔN2(ti),将余下序列组成新序列ΔYN1、ΔYN2,利用Grubbs准则分别探测新序列ΔYN1、ΔYN2是否存在奇异值; 若是,分别探测ΔYN1、ΔYN2奇异值的位置及t1i、ΔYN1(t1i)、t2i、ΔYN2(t2i)大小,并计算剔除ΔYN1、ΔYN2中奇异值后的序列中误差m1、m2,然后执行5);若否,则无特殊周跳。
4) 利用Grubbs准则分别探测序列ΔN1、ΔN2是否存在奇异值; 若是,分别探测ΔN1、ΔN2奇异值的位置及t1i、ΔN1(t1i)、t2i、ΔN2(t2i)大小,并计算剔除ΔN1、ΔN2奇异值后的序列中误差m1、m2,然后执行5);若否,则无特殊周跳。
5) 判断t1i、t2i是否存在相同值t12i; 若是,则存在特殊周跳,计算剔除ti、t1i、t2i位置ΔΦ后的中误差m,分别执行6)~8)以探测普通周跳、(9, 7)型特殊周跳和(77, 60)型特殊周跳; 若否,则无特殊周跳。
6) 计算普通周跳:
| $ \left\{\begin{array}{l} \left|\Delta N_{1}-\frac{77}{60} \Delta N_{2}-\Delta {\Phi}(t i)\right|<k m, k=3 \\ \Delta N_{1} \in \mathrm{INT} \\ {\left[\Delta N_{1}(t i)-3 m_{1} \quad \Delta N_{1}(t i)+3 m_{1}\right]} \\ \Delta N_{2} \in \mathrm{INT} \\ {\left[\Delta N_{2}(t i)-3 m_{2} \quad \Delta N_{2}(t i)+3 m_{2}\right]} \end{array}\right. $ | (5) |
7) 计算(9, 7)型特殊周跳:
| $ \left\{\begin{array}{l} \left|\Delta N_{1}-\frac{77}{60} \Delta N_{2}\right|<0.07 \\ \Delta N_{1} \in \mathrm{INT} \\ {\left[\Delta N_{1}(t 12 i)-3 m_{1} \quad \Delta N_{1}(t 12 i)+3 m_{1}\right]} \\ \Delta N_{2} \in \mathrm{INT} \\ {\left[\Delta N_{2}(t 12 i)-3 m_{2} \quad \Delta N_{2}(t 12 i)+3 m_{2}\right]} \end{array}\right. $ | (6) |
8) 计算(77, 60)型特殊周跳:
| $ \left\{\begin{array}{l} |\Delta N_{1}-\frac{77}{60} \Delta N_{2}|=0 \\ \Delta N_{1} \in \mathrm{INT} \\ [\Delta N_{1}(t 12 i)-3 m_{1} & \Delta N_{1}(t 12 i)+3 m_{1} ] \\ \Delta N_{2} \in \mathrm{INT} \\ [\Delta N_{2}(t 12 i)-3 m_{2} & \Delta N_{2}(t 12 i)+3 m_{2}] \end{array}\right. $ | (7) |
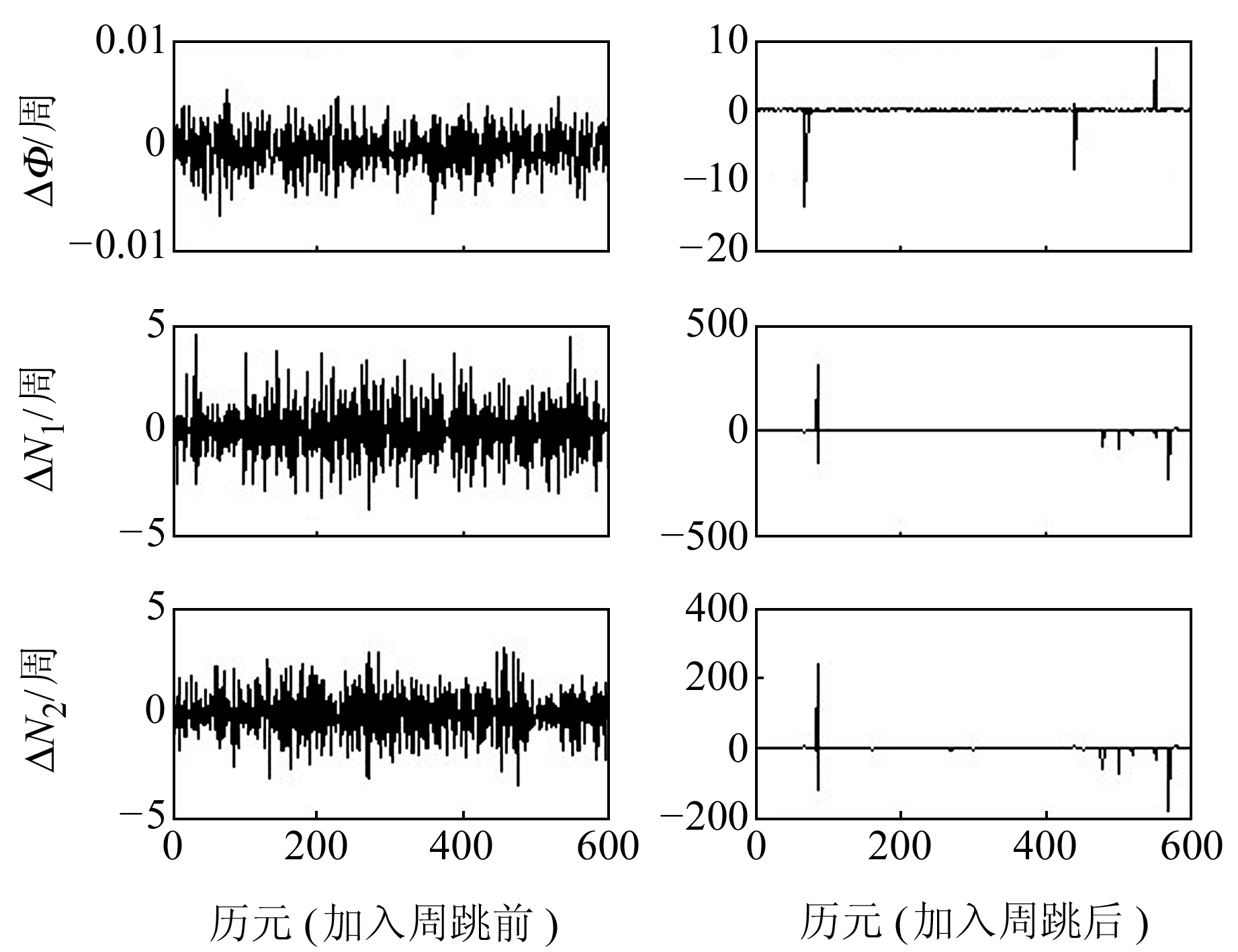
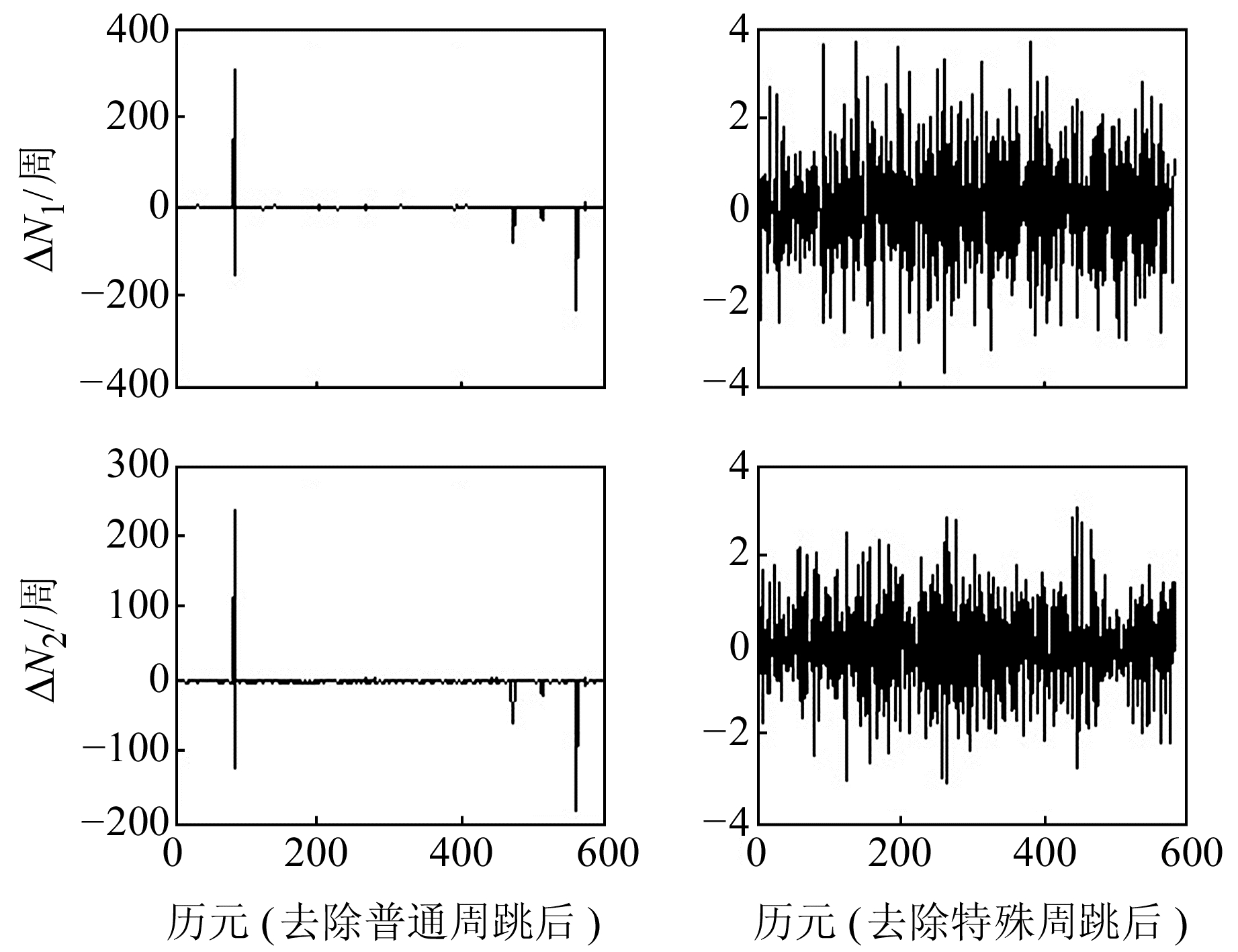
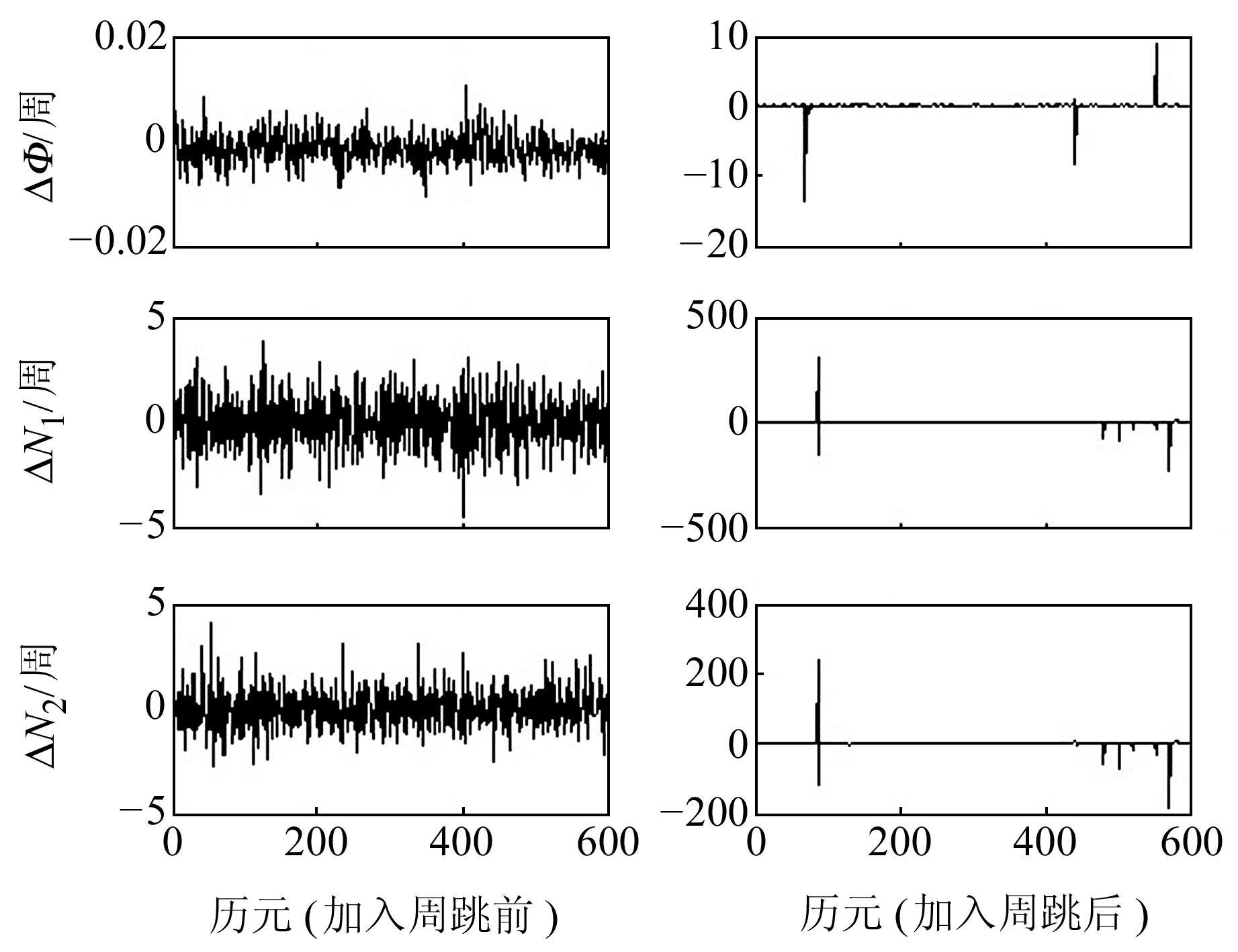
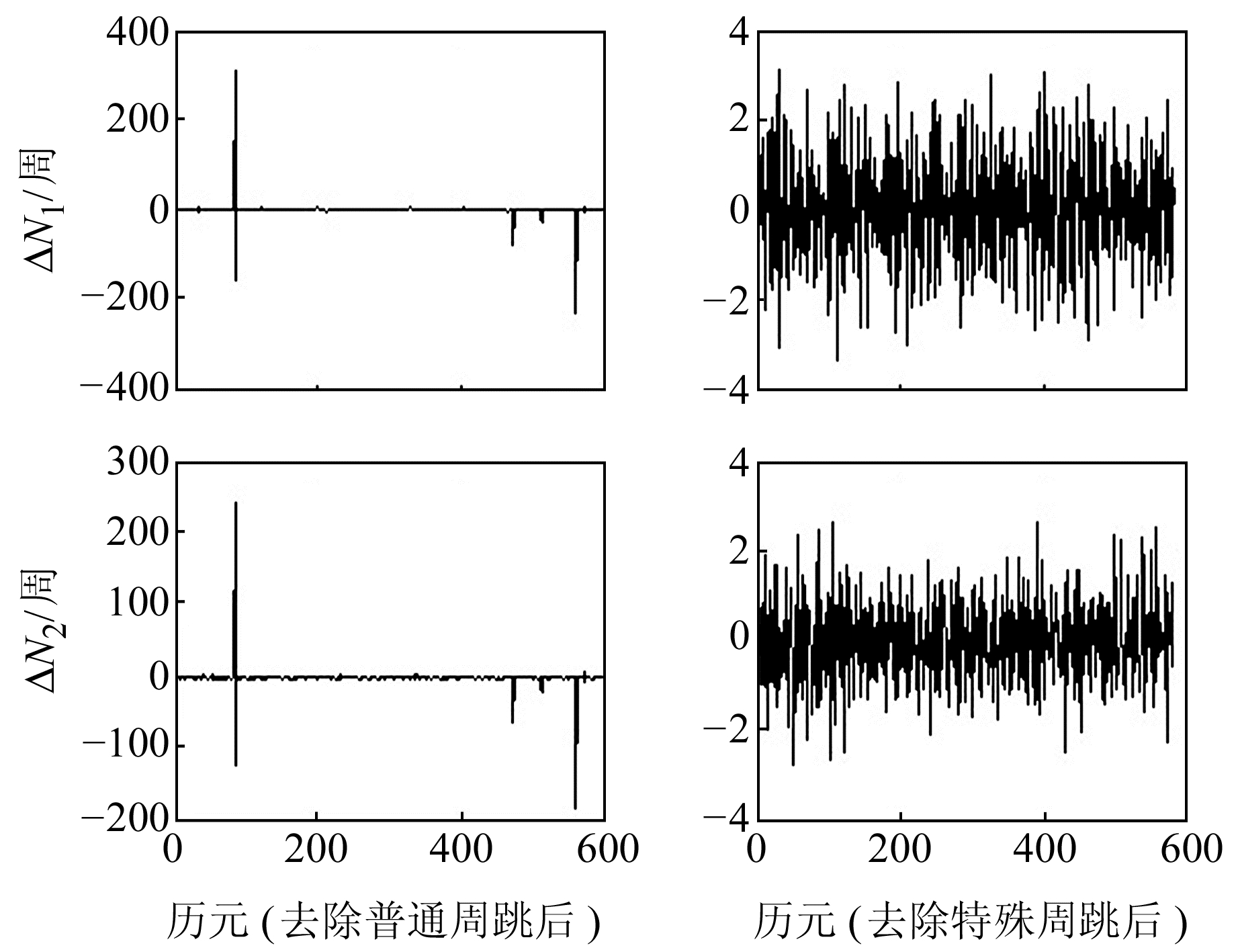
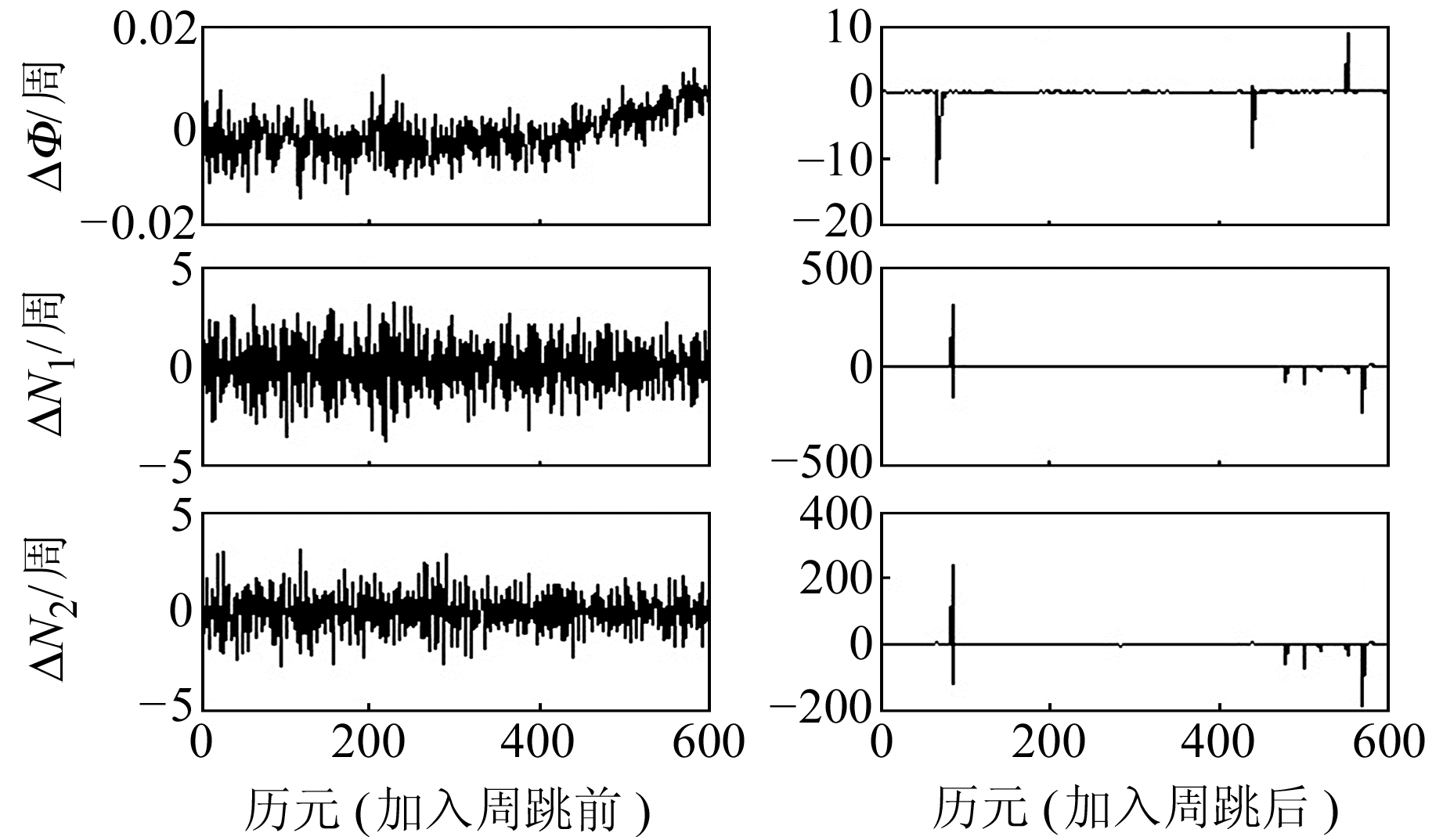
本文对提出的基于Grubbs准则和区间搜索的周跳探测方法进行验证,实验数据采样率为1 s。在原采样率1 s数据基础上,提取采样率为5 s、15 s的双频观测数据进行分析。实验时人为加入连续或非连续的不同组合周跳(ΔN1、ΔN2),图 1~6为加入周跳前后ΔΦ、ΔN1、ΔN2序列对比,探测结果与直接取整法[15]对比见表 1~3(单位周)。
|
图 1 采样率为1 s时加入周跳前后结果对比 Fig. 1 Comparison of 1 s sampling before and after adding cycle slip |
|
图 2 剔除不同组合周跳后结果(1 s采样) Fig. 2 Results of 1 s sampling after excluding different combinations of cycle slip |
|
图 3 采样率为5 s时加入周跳前后结果对比 Fig. 3 Comparison of 5 s sampling before and after adding cycle slip |
|
图 4 剔除不同组合周跳后结果(5 s采样) Fig. 4 Results of 5 s sampling after excluding different combinations of cycle slip |
|
图 5 采样率为15 s时加入周跳前后结果对比 Fig. 5 Comparison of 15 s sampling before and after adding cycle slip |

|
图 6 剔除不同组合周跳后结果(15 s采样) Fig. 6 Results of 15 s sampling after excluding different combinations of cycle slip |
|
|
表 1 采样率为1 s时周跳探测及对比 Tab. 1 Cycle detection and comparison of 1 s sampling |
|
|
表 2 采样率为5 s时周跳探测及对比 Tab. 2 Cycle detection and comparison of 5 s sampling |
|
|
表 3 采样率为15 s时周跳探测及对比 Tab. 3 Cycle detection and comparison of 15 s sampling |
从图 1、图 3和图 5可以看出,加入周跳前后序列波动发生明显变化,周跳大小对序列ΔΦ、ΔN1、ΔN2均有影响; 从图 2、图 4和图 6可以看出,本文方法能准确剔除普通周跳和特殊型周跳。
从表 1~3可以看出,本文方法探测的周跳与人为加入的周跳完全一致; 而取整法能探测出位置,但准确性较低。随着采样间隔的增加,ΔΦ、ΔN1、ΔN2剔除周跳后中误差m、m1、m2均增大,但本文方法仍能准确探测周跳,取整法在双频上会产生约1~2周误差,为原噪声湮没所致。
6 结语本文基于Grubbs准则和区间搜索进行双频GPS周跳探测,得出以下结论:
1) 以ΔΦ=ΔN1-(λ2/λ1)ΔN2为主方程,同时利用周跳的整数特性,通过解附有限制条件方程可确定唯一周跳值,避免多值问题。
2) 通过Grubbs准则判断ΔN1、ΔN2异常值,剔除异常值后计算序列中误差,利用3倍中误差理论约束双频周跳的搜索范围,可避免噪声湮没问题。
3) 本文方法能准确探测出周跳发生的历元、各频率上周跳大小,同时能准确探测普通型周跳和(9, 7)型、(77, 60)型特殊周跳,以及连续周跳和非连续周跳。
4) 实验数据分析表明,对于采样率为15 s以内的数据,本文方法探测准确率高,计算成功率为100%。
| [1] |
Miao Y, Sun Z W, Wu S N. Error Analysis and Cycle-Slip Detection Research on Satellite-Borne GPS Observation[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 2011, 24(1): 95-101 DOI:10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0000056
(  0) 0) |
| [2] |
Feng S J, Ochieng W, Moore T, et al. Carrier Phase-Based Integrity Monitoring for High-Accuracy Positioning[J]. GPS Solutions, 2009, 13(1): 13-22 DOI:10.1007/s10291-008-0093-0
(  0) 0) |
| [3] |
严新生, 王一强, 白征东, 等. 联合使用高次差法和TurboEdit法自动探测、修复周跳[J]. 测绘通报, 2007(9): 5-9 (Yan Xinsheng, Wang Yiqiang, Bai Zhengdong, et al. Automatically Detect and Repair Cycle Slips Using Alliance of High Difference and TurboEdit[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, 2007(9): 5-9)
(  0) 0) |
| [4] |
Schwarz K P, Cannon M E, Wong R V C. A Comparison of GPS Kinematic Models for the Determination of Position and Velocity along a Trajectory[J]. Manuscripta Geodaetica, 1989, l4(5): 345-353
(  0) 0) |
| [5] |
张亮, 岳东杰. 相位减伪距法与电离层残差法探测和修复周跳[J]. 测绘工程, 2014, 23(2): 36-38 (Zhang Liang, Yue Dongjie. Research on Detection and Reparation for Cycle Slips Using Phase Reduce False Distance Law and Ionized Layer Remnant Method of Difference[J]. Engineering of Surveying and Mapping, 2014, 23(2): 36-38)
(  0) 0) |
| [6] |
陈品馨, 章传银, 黄昆学. 用相位减伪距法和电离层残差法探测和修复周跳[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2010, 30(2): 120-124 (Chen Pinxin, Zhang Chuanyin, Huang Kunxue. Cycle Slips Detecting and Repairing by Use of Phase Reduce Pseudorange Law and Ionized Layer Remnant Method of Difference[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2010, 30(2): 120-124)
(  0) 0) |
| [7] |
邹正标, 何秀凤, 唐旭. GPS非差数据周跳探测的TECR-MW综合法[J]. 河海大学学报: 自然科学版, 2014, 42(2): 155-158 (Zou Zhengbiao, He Xiufeng, Tang Xu. Cycle Slip Detection Using TECR and MW Combined Method for Un-Differenced GPS Data[J]. Journal of Hohai University: Natural Sciences, 2014, 42(2): 155-158)
(  0) 0) |
| [8] |
张顺, 姚宜斌, 陈鹏, 等. GPS非差数据周跳探测方法研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2012, 32(1): 101-104 (Zhang Shun, Yao Yibin, Chen Peng, et al. Research on Cycle Slip Detection Methods for Un-Differenced GPS Data[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2012, 32(1): 101-104)
(  0) 0) |
| [9] |
阳仁贵, 欧吉坤, 袁运斌. 一种GPS相位周跳分段平均组合的自动修复方法[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2009, 29(5): 76-80 (Yang Rengui, Ou Jikun, Yuan Yunbin. An Approach of Sub-Average Joint Computation for Auto Restoring GPS Phase Cycle Slip[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2009, 29(5): 76-80)
(  0) 0) |
| [10] |
李明, 高星伟, 徐爱功. 一种改进的周跳多项式拟合方法[J]. 测绘科学, 2008, 33(4): 82-83 (Li Ming, Gao Xingwei, Xu Aigong. A Modified Polynomial Fitting of Cycle-Slip Processing[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2008, 33(4): 82-83)
(  0) 0) |
| [11] |
刘宁, 熊永良, 徐韶光. 利用改进的TurboEdit算法与Chebyshev多项式探测与修复周跳[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2011, 36(12): 1 500-1 503 (Liu Ning, Xiong Yongliang, Xu Shaoguang. Detection and Repair of Cycle Slips Using Improved TurboEdit Algorithm and Chebyshev Polynomial Method[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2011, 36(12): 1 500-1 503)
(  0) 0) |
| [12] |
Blewitt G. An Automatic Editing Algorithm for GPS Data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 1990, 17(3): 199-202 DOI:10.1029/GL017i003p00199
(  0) 0) |
| [13] |
王振杰, 聂志喜, 欧吉坤. 一种基于TurboEdit改进的GPS双频观测值周跳探测方法[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2014, 39(9): 1 017-1 021 (Wang Zhenjie, Nie Zhixi, Ou Jikun. An Improved Cycle Slip Detection Based on TurboEdit Method for Dual-Frequency GPS Receiver[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(9): 1 017-1 021)
(  0) 0) |
| [14] |
吴继忠, 施闯, 方荣新. TurboEdit单站GPS数据周跳探测方法的改进[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2011, 36(1): 29-33 (Wu Jizhong, Shi Chuang, Fang Rongxin. Improving the Single Station Data Cycle Slip Detection Approach TurboEdit[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2011, 36(1): 29-33)
(  0) 0) |
| [15] |
郭翔, 鲁铁定, 裴东东. 一种双频载波相位周跳探测与修复方法[J]. 测绘科学, 2017, 42(9): 15-19 (Guo Xiang, Lu Tieding, Pei Dongdong. A Method to Cycle-Slip Detection and Repair of Dual-Frequency Carrier Phase[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 2017, 42(9): 15-19)
(  0) 0) |
2. College of Engineering, Yunnan University of Business Management, 17 Qilin Road, Anning 650106, China
 2021, Vol. 41
2021, Vol. 41

