2. 新疆工程学院数理学院,乌鲁木齐市艾丁湖路1350号,830023
中国地震局在“十五”期间建设了大规模的数字地震观测网络,钻孔应变仪作为观测地壳应变微小连续变化的前兆观测仪器,从2007年下半年开始在全国许多台站投入使用[1]。体应变观测除能清晰记录到固体潮、地震波、震前异常等重要信息外,还能记录到气压、地下水位的变化及抽水、降雨等对地应变场的干扰,加深对干扰规律的认识,是进行数据分析和准确识别震前异常的前提和基础[2]。
研究表明,作用于地表的气压波动会产生10-9量级的地壳应变[3],产生的数据响应在现代地壳形变观测资料分析中不容忽视[4]。国内有学者推导出钻孔体应变的气压影响系数计算方程式[5],建立了钻孔体应变的理论气压干扰模型[6],并对山东省数字化钻孔体应变观测中的干扰进行了分析[7-8];国外也有学者根据意大利Friuli地区的观测资料,详细分析了气压、降雨量及温度对地倾斜和地应变的影响[9-10]。本文利用温泉台体应变、辅助观测和气象三要素等观测数据,分析体应变观测在不同周期的影响因素及特征。
1 观测台站及观测系统介绍温泉台(81.01°E、44.96°N)位于北天山地震带西段,台基为华力西期花岗岩,台站周边主要断裂带有阿拉套断裂带、科古琴断裂带、喀什河断裂带、库松木契克断裂带及博阿断裂带等,地质构造上处于准噶尔盆地西侧、博罗科努山北麓及博尔塔拉断凹西部。博尔塔拉深大断裂(东西向)的南盘是上升盘,地表可见岩石破碎并形成陡壁,物探资料显示存在南北次生断裂。
温泉台体应变观测仪架设于2008年,井终孔的孔径为130 mm,井深80 m。从井的剖面上看,上覆地层为约15 m厚的砾石沙土冲积层,15~80 m深度为花岗片麻岩。在钻井及洗井的过程中发现,钻孔74 m深度以上的岩层较破碎,74~80 m深处相对完整,底部2 m为钻井施工岩屑沉积物。在洗井过程中不断有岩芯取出,有些岩芯甚至长约60 cm,说明该区域地下岩层结构复杂,井孔条件相对较差。体应变探头安装在75 m深度处,探头头部以上回填约2 m厚的水泥,水位埋深约为29 m,水位探头置于井下37 m深度处[11]。2009年探头与岩石的耦合状态达到稳定,体应变观测数据的年变规律清晰,观测资料的精度及稳定性均较高。
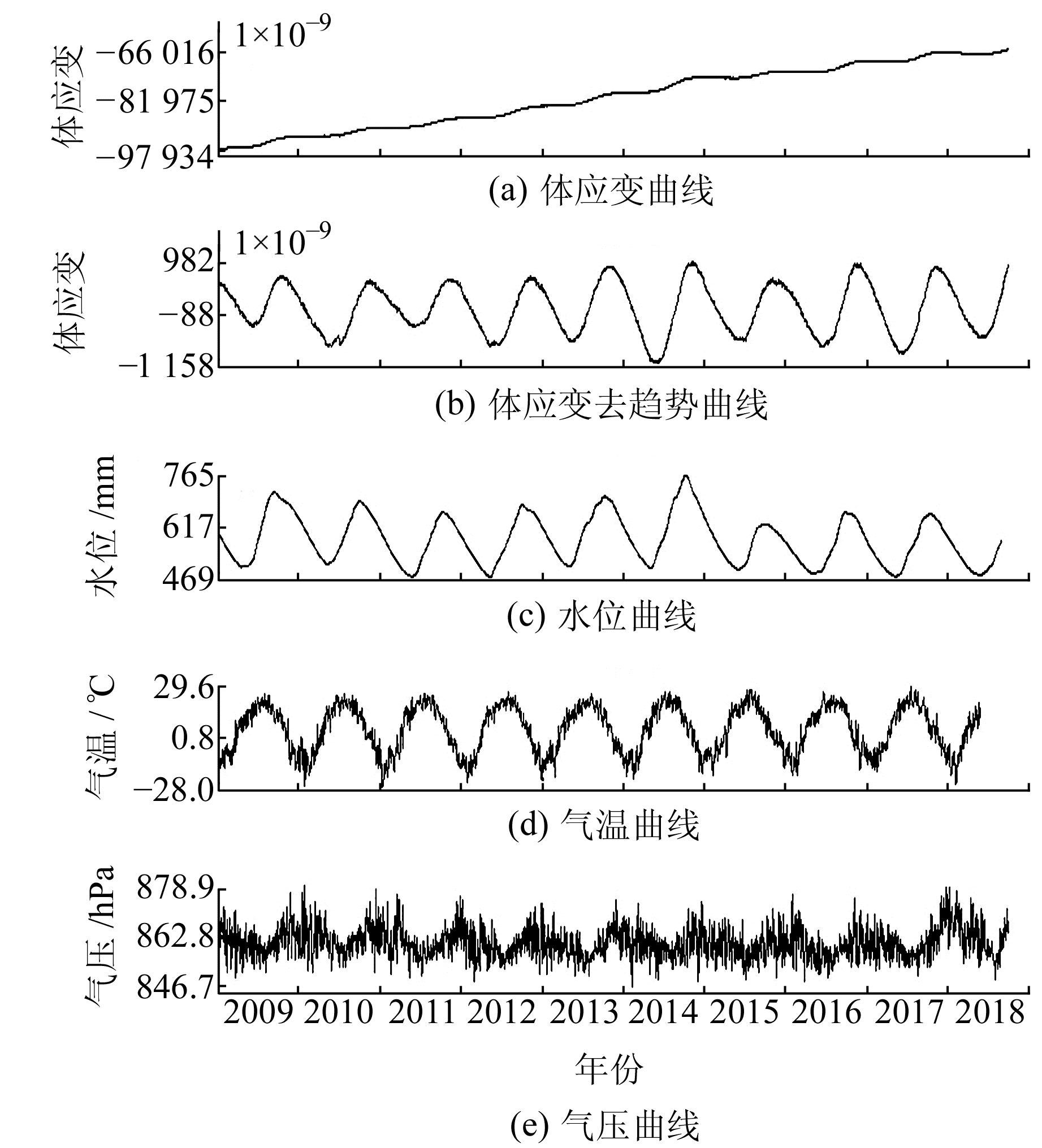
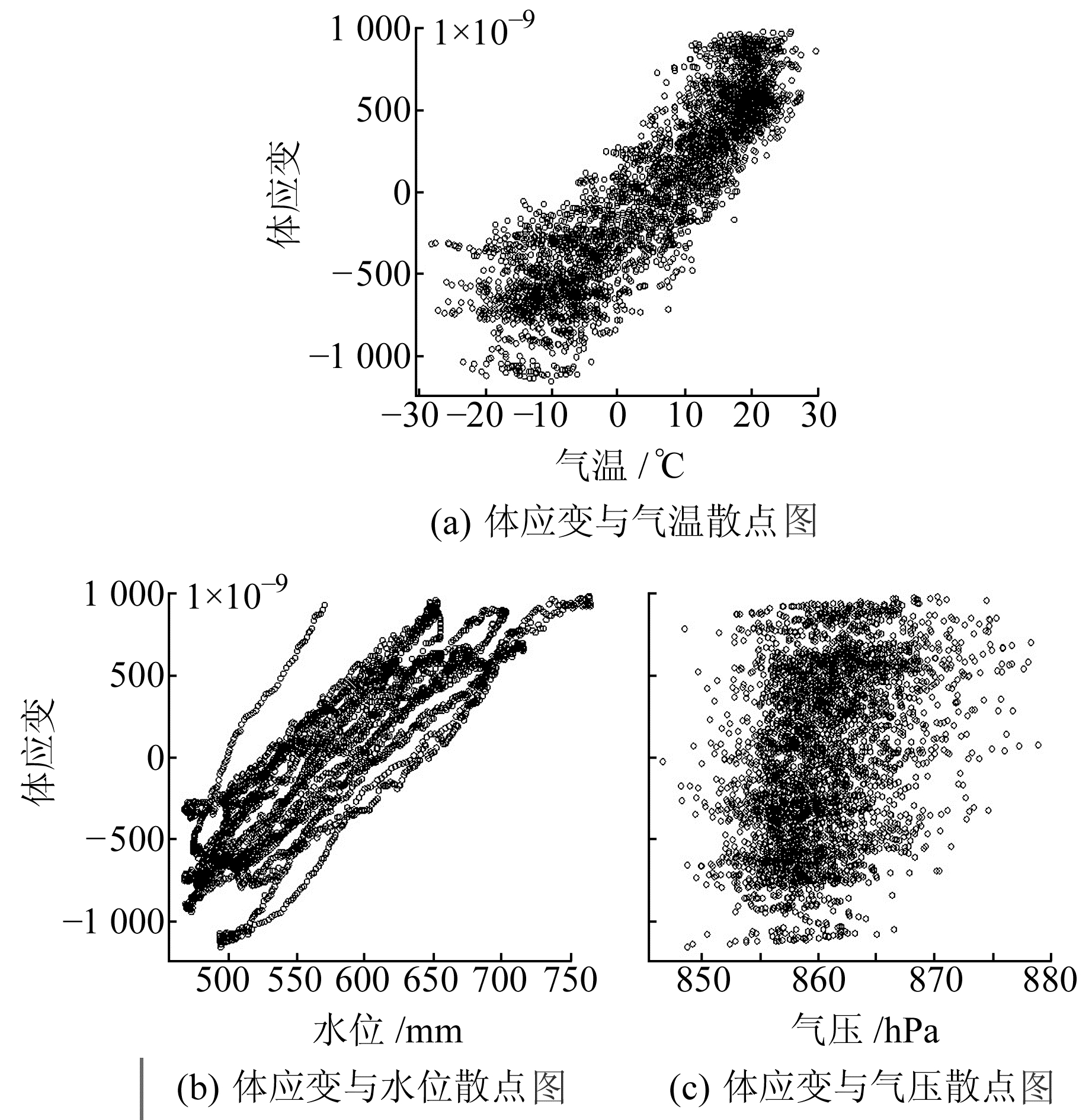
2 数据分析选取2009至2018年温泉台体应变观测资料的日均值数据,具体见图 1。由图可知,温泉台体应变既有年变特征,又有趋势变化,而水位、气压、气温等均无趋势变化。根据干扰成因的相关性[12]推断,体应变趋势性变化与气温、水位等无关。为剔除体应变的趋势性变化,按年去趋势进行计算后发现,温泉台体应变数据相位滞后气温变化125 d,两者的相关系数为0.888 8;滞后水位变化约31 d,两者的相关系数为0.861 5,分别绘制体应变与气温、水位及气压的散点图,结果见图 2。
|
图 1 温泉台体应变、水位、气温、气压曲线 Fig. 1 Curves of body strain, water level, temperature and pressure in Wenquan station |
|
图 2 温泉台体应变与气温、水位、气压等散点图 Fig. 2 Scatter plot of body strain with temperature, water level and pressure in Wenquan station |
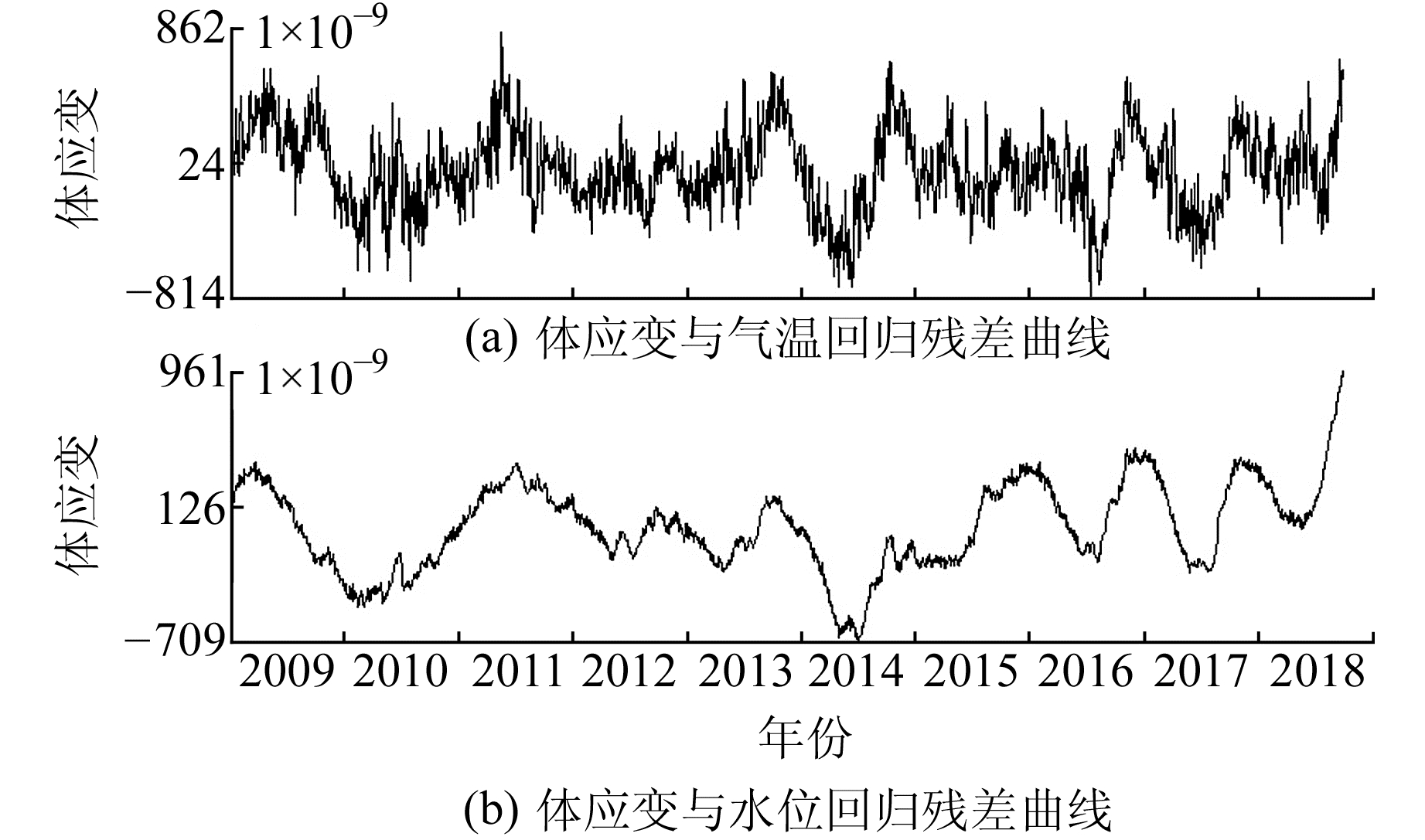
根据相关系数及图 2可知,气温和水位与温泉台体应变均具有较高的线性相关性,可利用公式y=35.977x-170.837拟合并剔除气温的影响,利用公式y=6.41x-369 3拟合并剔除水位的影响,得到等残差曲线(图 3)。
|
图 3 温泉台体应变与气温、水位回归残差曲线 Fig. 3 Regression residual curve between body strain and air temperature and water level in Wenquan station |
由图 3可知,温泉台体应变的年周期变化与气温及水位均有较大的相关性,但由于气温与水位之间也具有较高的线性相关性,相关系数为0.844,故无法确定温泉台体应变的年周期变化是受气温还是水位的影响。选取2012年以来温泉台体应变、水位、气压及气温的整点值数据,首先利用别尔采夫滤波滤除日波及半日波,再利用一般多项式分段曲线拟合法将周期在1~2个月内的月波滤除,并分别计算相关系数,结果见表 1。
|
|
表 1 温泉台体应变与气温、水位、气压各周期的相关系数 Tab. 1 Correlation coefficient of body strain with air temperature, water level and air pressure in Wenquan station |
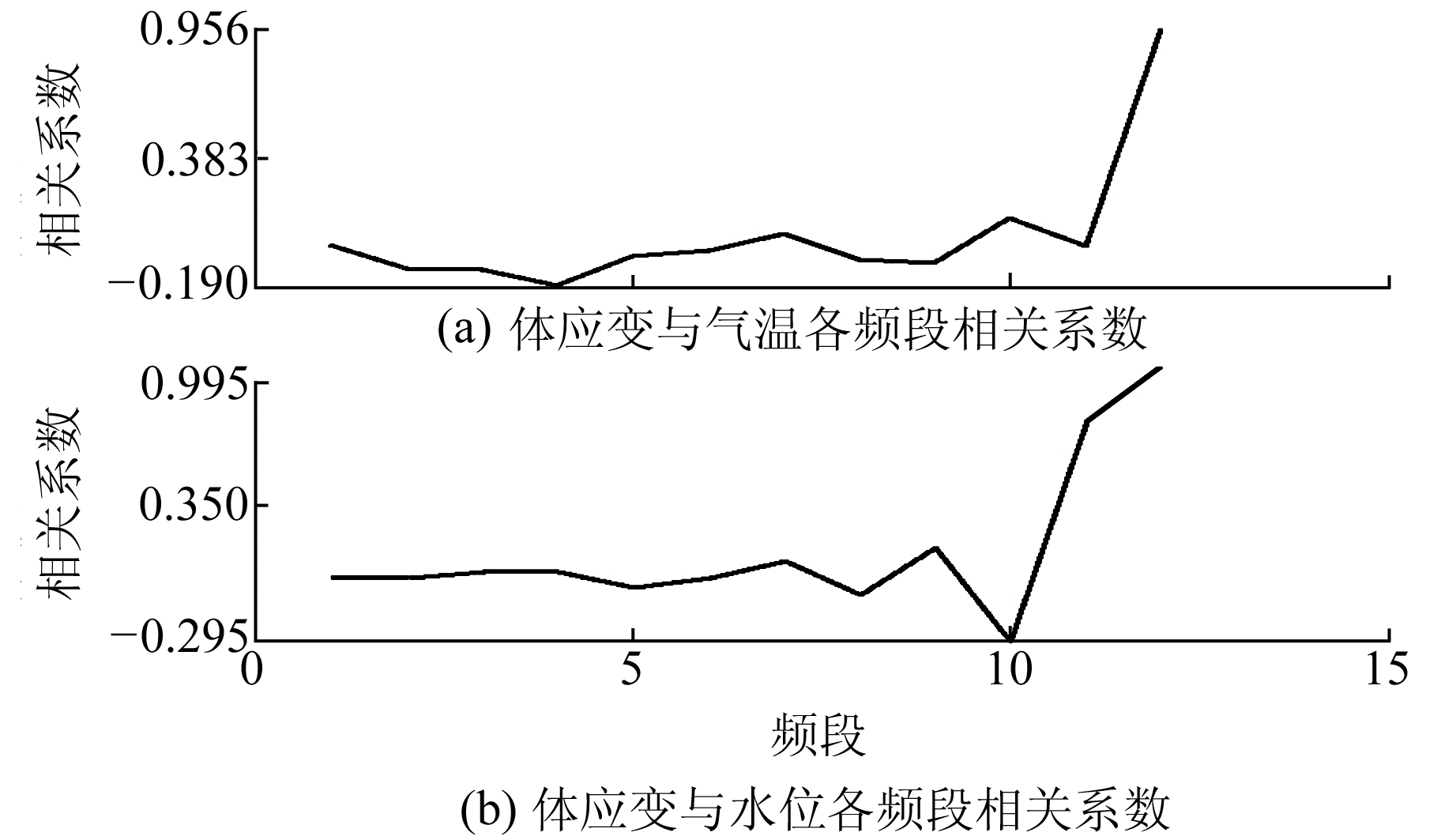
由表 1可知,温泉台体应变的日波、半日波及月波与气温、水位基本无相关性,在去除日波、半日波及月波后温泉台体应变与气温、水位均具有较高的线性相关性。进一步对2012年以来温泉台体应变、气温、水位的整点值数据进行小波分析,并划分为12个频段(2~4 h、4~8 h、8~16 h、…,以此类推),将同一频段的体应变分别与气温、水位作相关性分析,得到各频段的相关系数r,结果见图 4。
|
图 4 温泉台体应变与气温、水位各频段相关系数 Fig. 4 Correlation coefficient of body strain with temperature and water level in each frequency band in Wenquan station |
由图 4可知,温泉台体应变与气温在第12频段的相关系数为0.956,与水位在第11频段的相关系数为0.738,在第12频段的相关系数为0.994。结合图 1可知,2014年温泉台体应变及水位等年变幅度均出现增大的现象,但气温却无类似的变化,根据干扰异常成因的相关性[12]认为,水位可能是影响温泉台体应变年周期变化的主要因素。
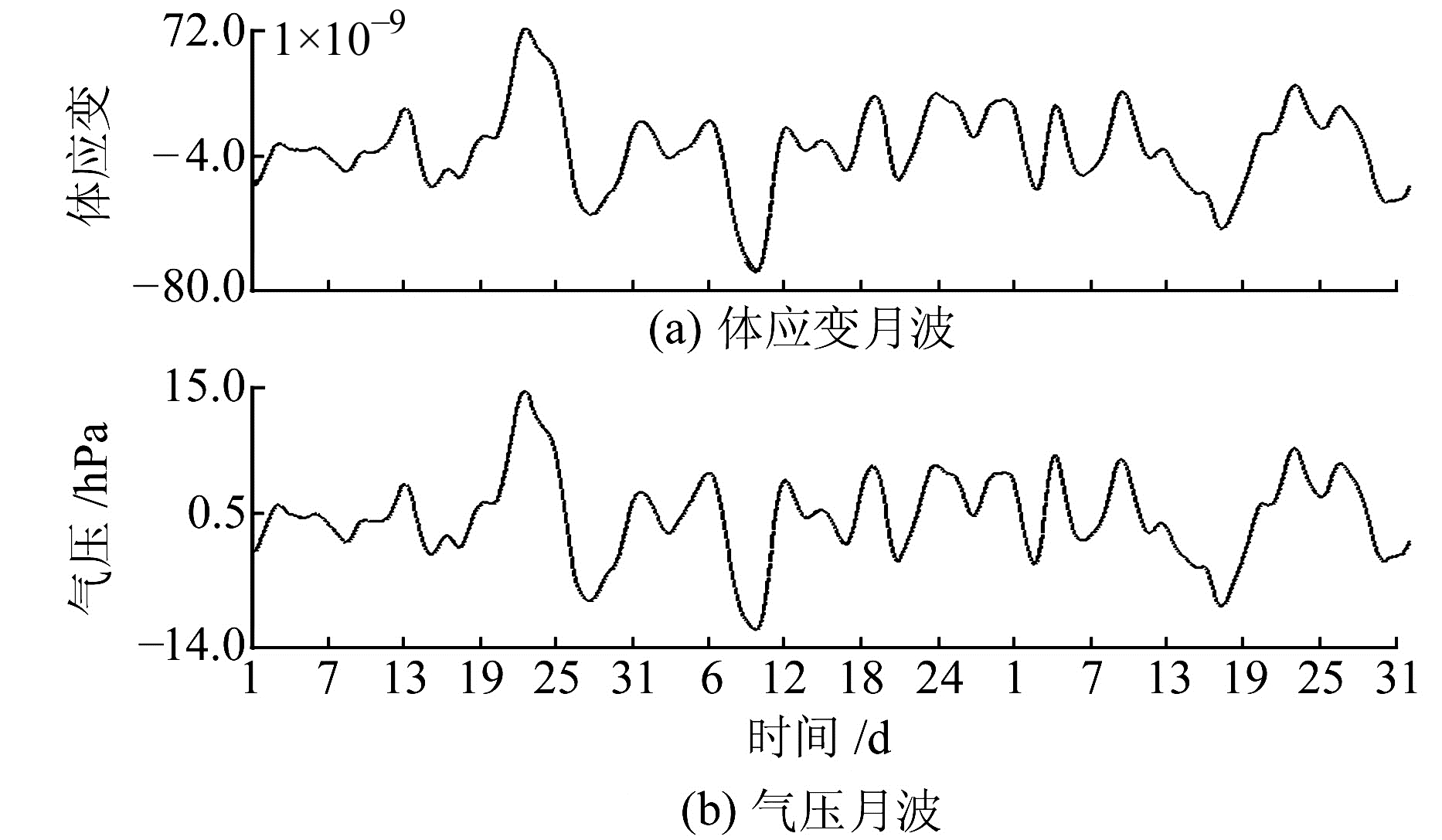
选取2016-01-01~2016-03-31温泉台体应变及气压的整点值数据,并绘制月波曲线,结果见图 5。
|
图 5 温泉台体应变、气压月波曲线 Fig. 5 Monthly wave curve of body strain and pressure in Wenquan station |
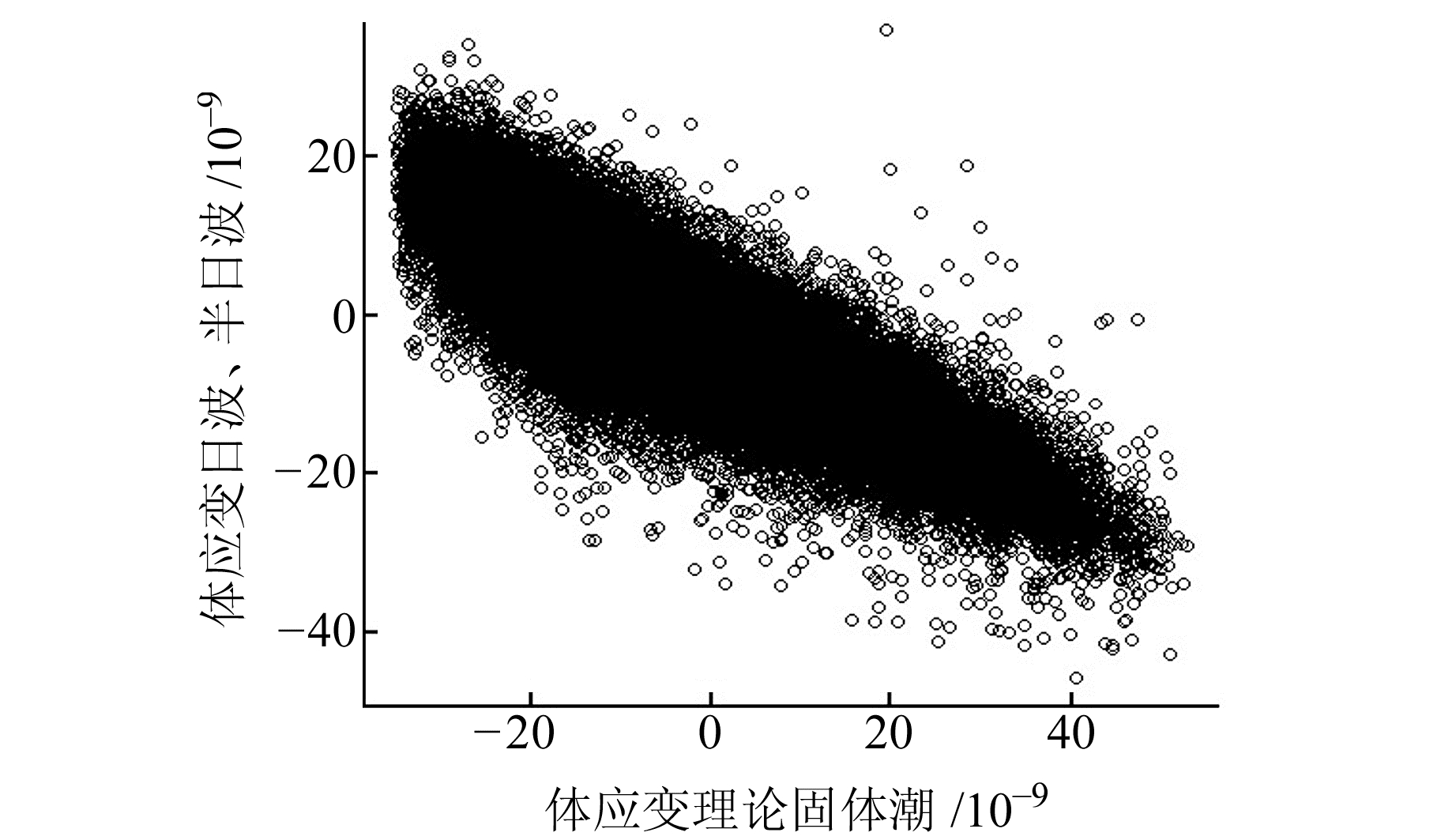
结合表 1和图 5可知,温泉台体应变与气压月波的相关系数为0.773,具有较高的线性相关性,气压对温泉台体应变的影响主要为月波。计算得到2012-01-01~2018-10-18理论固体潮与利用别尔采夫滤波得到的日波、半日波的相关系数为-0.849,并绘制散点图,结果见图 6。由图可知,温泉台体应变的日波、半日波的主要影响因素为固体潮汐,且日波及半日波均与固体潮汐有较强的线性相关性。
|
图 6 温泉台体应变日波、半日波与理论固体潮散点图 Fig. 6 Scatter plot of body strain daily wave, semi-daily wave and theoretical solid tide in Wenquan station |
形变台站设计观测的目标值是由地球内力产生的形变与重力变化,但由于台站建立在地壳表层,恰好位于岩石圈与大气圈、水圈、生物圈的交界面上,大气圈和水圈中的物质转移等周期性的变化会通过多种途径作用于地壳表层、台站介质环境等观测系统中,使观测结果产生相关性响应,而观测值序列既然是多种信息的综合,必然是可分离的[13],基于观测序列的可分性与综合性可对正常环境下实际观测值进行理论模拟。本文对温泉台体应变观测影响因素及特征进行分析,有助于对温泉台体应变观测序列的理论模拟及理解观测序列中包含的各种成分的物理意义,可用于评定台站的观测环境、仪器数据的观测质量及仪器对地形变的监测能力等,也可在一定程度上预估观测序列的变化趋势,为识别异常提供一定的变化背景参考。通过对观测值与模拟值差值的随机波动进行统计分析,也可为异常的识别提供概率上的定量判据和指标。
| [1] |
张凌空, 王广才, 牛安福. 周期气压波对地壳应变场观测影响的若干因素分析[J]. 地震学报, 2011, 33(3): 351-361 (Zhang Lingkong, Wang Guangcai, Niu Anfu. Analysis on Several Factors of Periodic Air Pressure Wave Affecting Crustal Strain Field[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2011, 33(3): 351-361 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2011.03.008)
(  0) 0) |
| [2] |
刘冰冰, 蔡宏雷, 郑国栋, 等. 体应变日常观测资料浅析[J]. 东北地震研究, 2009, 25(3): 28-36 (Liu Bingbing, Cai Honglei, Zheng Guodong, et al. Analysis on the Materials of Daily Observations for Volumetric Strain[J]. Seismological Research of Northeast China, 2009, 25(3): 28-36 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-8565.2009.03.006)
(  0) 0) |
| [3] |
张学阳. 潮汐观测中高精度气压辅助观测的必要性及气压效应的校正[J]. 地壳形变与地震, 1987, 7(4): 273-280 (Zhang Xueyang. A Necessity of High-Precise Assistance Measurement for Atmospheric Pressure and Correction of Atmospheric Pressure Effect in Tidal Observation[J]. Crustal Deformation and Earthquake, 1987, 7(4): 273-280)
(  0) 0) |
| [4] |
周龙寿, 邱泽华, 唐磊. 地壳应变场对气压短周期变化的响应[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2008, 23(6): 1 717-1 726 (Zhou Longshou, Qiu Zehua, Tang Lei. The Response of Crustal Strain Field to Short-Period Atmospheric Pressure Variation[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2008, 23(6): 1 717-1 726)
(  0) 0) |
| [5] |
苏恺之, 李海亮, 张钧, 等. 钻孔地应变观测新进展[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 2003 (Su Kaizhi, Li Hailiang, Zhang Jun, et al. Borehole Strain Observation New Progress[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 2003)
(  0) 0) |
| [6] |
张凌空, 牛安福, 闫伟, 等. 两种应变仪的面应变观测资料的比对研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2011, 31(4): 22-26 (Zhang Lingkong, Niu Anfu, Yan Wei, et al. Compariative Study between Plane Strain Observed Data with YRY-4-Type Component Borehole Strainmeter and TJ-2-Type Volumetric Borehole Strainmeter[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2011, 31(4): 22-26)
(  0) 0) |
| [7] |
王梅. 数字化体应变与气压、水位相关性研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2002, 22(4): 85-88 (Wang Mei. Study on Correlation of Digital Body Strain Data with Atmosphere and Well Water Level[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2002, 22(4): 85-88)
(  0) 0) |
| [8] |
李杰, 刘敏, 邹钟毅, 等. 数字化钻孔体应变干扰机理及异常分析[J]. 地震研究, 2003, 26(3): 230-238 (Li Jie, Liu Min, Zou Zhongyi, et al. Analysis of Disturbance Mechanism and Abnormity of Digital Observation Data of Borehole Body Strain Meters[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 2003, 26(3): 230-238 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2003.03.004)
(  0) 0) |
| [9] |
Moro G D, Zadro M. Subsurface Deformations Induced byRainfall and Atmospheric Pressure:Tilt/Strain Measurements in the NE-Italy Seismic Area[J]. Earth Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 164(1-2): 193-203 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00203-9
(  0) 0) |
| [10] |
Garavaglia M, Moro G D, Zadro M. Radon and Tilt Measurements in a Seismic Area:Temperature Effects[J]. Physics Chemistry of the Earth Part A:Solid Earth and Geodesy, 2000, 25(3): 233-237 DOI:10.1016/S1464-1895(00)00038-7
(  0) 0) |
| [11] |
陈大柱, 张新成, 高守全, 等. 温泉地震台钻孔体应变观测资料分析[J]. 内陆地震, 2014, 28(1): 63-69 (Chen Dazhu, Zhang Xincheng, Gao Shouquan, et al. Analysis on Borehole Body Strain Data in Wenquan Stations[J]. Inland Earthquake, 2014, 28(1): 63-69 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-8956.2014.01.009)
(  0) 0) |
| [12] |
车用太, 鱼金子, 刘成龙, 等. 判别地下水异常的干扰性与前兆性的原则及其应用实例[J]. 地震学报, 2011, 33(6): 800-808 (Che Yongtai, Yu Jinzi, Liu Chenglong, et al. Principles on Distinguishing Interference from Seismic Precursor of Underground Water Variation and Its Application[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2011, 33(6): 800-808 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2011.06.010)
(  0) 0) |
| [13] |
中国地震局监测预报司. 地形变测量[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 2008 (China Earthquake Administration Department of Earthquake Monitoring and Prediction. Topography Change Measurements[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 2008)
(  0) 0) |
2. College of Mathematics and Physics, Xinjiang Institute of Engineering, 1350 Aidinghu Road, Urumqi 830023, China
 2020, Vol. 40
2020, Vol. 40


