2014-11-22四川省甘孜藏族自治州康定县发生MS6.3地震(30.3°N,101.7°E),震源深度18 km,震中位于鲜水河断裂南段。根据四川台网地震目录,截至27日16时,共记录到余震1 544次,其中5.0~5.9级1次,2.0~2.9级6次,最大余震为2014-11-25发生的5.8级地震,余震优势分布方向为NW向。四川省地震局在全省范围内布设的数字强震监测台网记录到了此次地震,最大峰值加速度记录为距震中34.7 km的康定新都台,获取的SN向分量为161.65 cm/s2(台站分布见图 1)。提取和分析康定地震加速度记录的时频特性,对深入研究地震波的传播路径和过程机理具有重要意义[1-2]。

|
图 1 区域断裂分布和台站分布 Fig. 1 Regional fault and the distribution of stations |
要想获取加速度信号记录中的重要信息,需要分析提取加速度信号的时频分布特点。时频分析技术是对非平稳信号频谱随时间的变化进行分析的有力工具。以前都是基于Fourier变换,后一些信号处理技术,如小波变换、CWD分布等分析方法相继出现[3-4],但这些方法都存在一定的缺陷。因此,具备精度分解优势和非线性动态数据刻画能力的希尔伯特-黄变换(HHT)方法逐渐应用于强震记录的时频分析[4-8]。本文在数据处理过程中采用基于聚类经验模态分解(EEMD)的HHT方法,分析和计算不同震中距台站的记录,得到加速度记录信号的Hilbert时频幅值谱、边际谱及相位谱,提取其中心频率、平均周期和Hilbert瞬时能量谱的分布等特性,并与Fourier变换进行对比分析。
1 加速度记录的分析方法基于EEMD的HHT方法已多次应用于强震分析。该方法主要由EEMD和Hilbert变换2部分组成[2, 4],可有效抑制模态混叠问题[8]。本文采用的EEMD具体算法和原理见文献[2, 4, 9-11]。
Hilbert变换和谱分析为:
四川省地震局的数字强震动台网共有211个台站,其中55个台站记录到2014年康定6.3级地震。本文对距震中34.7 km的康定新都台加速度记录进行处理和计算,结果见图 2。图 3为新都台EW向分量经EEMD的结果,每个IMF分量所包含的平均周期、最大振幅、中心频率等信息见表 1。
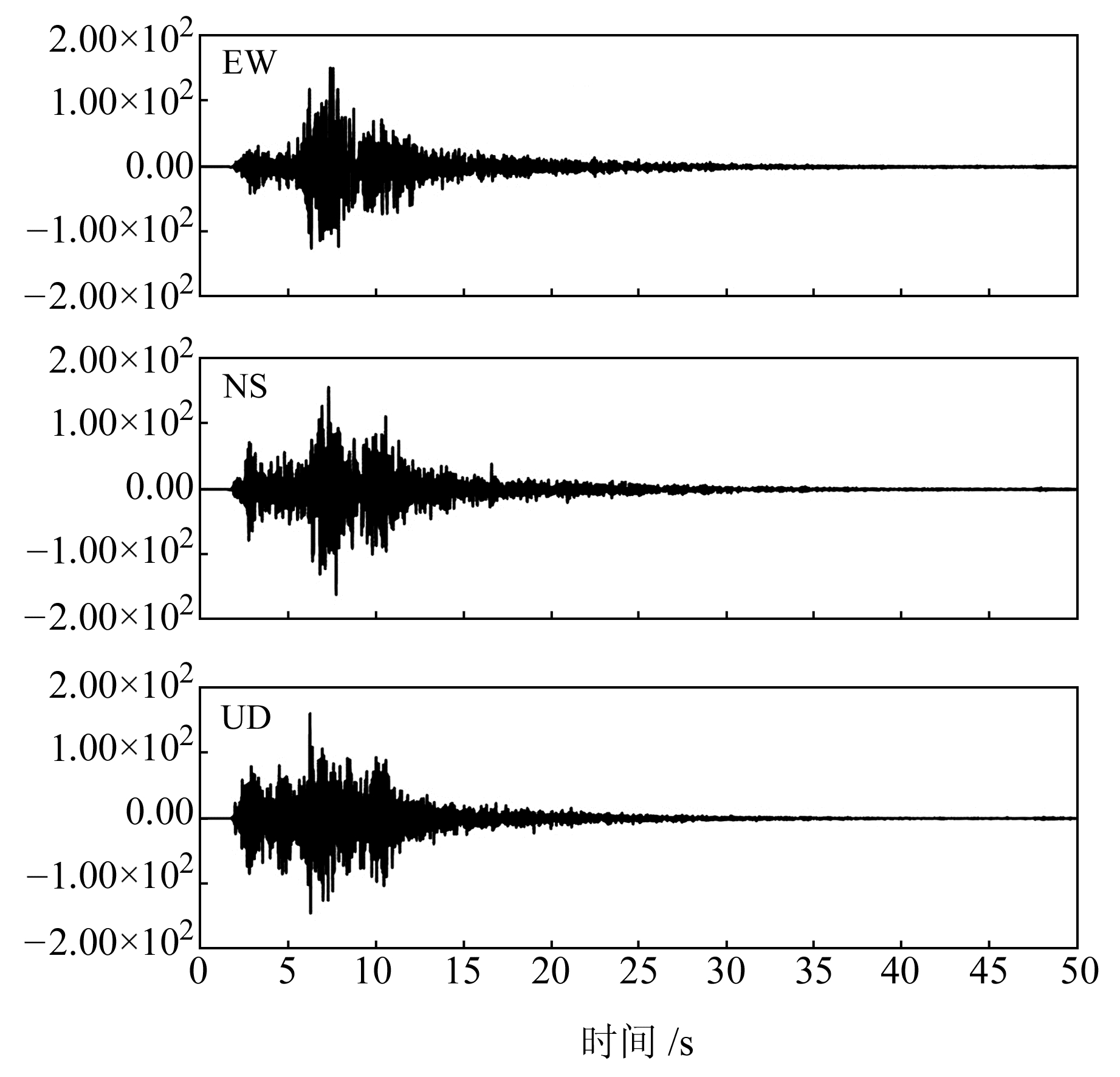
|
图 2 新都台加速度记录 Fig. 2 Acceleration records of Xindu station |

|
图 3 经过EEMD后的各IMF分量 Fig. 3 Each IMF component after EEMD |
|
|
表 1 各个IMF量化统计值 Tab. 1 The statistic of each IMF component |
图 4(a)为康定新都台EW向分量的处理结果。从FFT谱与Hilbert边际谱对比可以看出,在低频段,FFT谱通常会低估正常的地震动幅值,但如果频率增加,FFT谱又高估幅值。同样,对距震中37.6 km的康定专业台和距震中50.3 km的康定姑咱台EW向分量进行FFT谱和边际谱分析,均发现了这一现象,具体结果见图 4(b)和4(c)。

|
图 4 FFT谱和Hilbert边际谱 Fig. 4 Fast Fourier transformation spectrum and Hilbert marginal spectrum |
康定专业台和康定姑咱台的EW向分量数据经HHT变换得到的时频谱(图 5),在不同的时间节点均存在若干不同的频率成分。和小波变换得到的频率不同,EEMD得到的IMF对应的瞬时频率界限范围不是很明显[2, 12]。

|
图 5 不同震中距台站记录的时频谱 Fig. 5 Time-frequency spectrum recorded by stations with different epicentral distances |
对不同震中距台站EW向分量加速度数据进行计算分析,得到的瞬时能量谱见图 6。由图 6(a)和6(b)可知,康定新都台和康定姑咱台大部分能量集中在15 s以内,各能量峰值出现的时刻也清晰可见。对距震中93.5 km的道孚专业台(图 6(c))和距震中143.0 km的炉霍专业台(图 6(d))EW向分量进行HHT瞬时能量谱分析,也验证了该方法的有效性。

|
图 6 瞬时能量谱 Fig. 6 Instantaneous energy spectrum |
对不同震中距台站数据进行Hilbert变换与谱分析得到的能量谱(图 7)揭示了能量集中释放的频段。随着震中距的增大,最大地震动峰值加速度迅速衰减,能量集中分布的主频段逐渐降低。能量谱与瞬时能量谱从不同的方面说明,HHT方法在提取和识别加速度信号的时频特征方面具有广阔的前景。

|
图 7 能量谱 Fig. 7 The energy spectrum |
康定MS6.3地震发生在川滇块体北东边界鲜水河断裂带南段,震区历史最大地震为1786-06-01康定7 3 4级[13]。四川省地震局现场工作队完成了对康定6.3级地震灾区的震害宏观调查工作。在此次地震中,农牧区的“崩科式”建筑房屋损毁严重(图 8(a)),很多都出现墙体开裂甚至局部垮塌的现象;城镇区房屋破坏程度则较轻(图 8(b)、8(c)、8(d)),框架结构房屋仅个别承重梁及填充墙开裂或出现细微裂纹。通过Hilbert边际谱分析可以看出,康定新都台(图 4(a))信号频率集中在10 Hz左右,瞬时能量谱(图 6)反映本次地震的高频成分丰富。另外,由于川西高原的农牧区房屋大多是藏式民居,以“崩科”结构为主,楼高1~3层不等,大多由灰浆粘结块石砌成,底部用石墙承重,抗震性能较差[14-15],这也是造成其在本次地震中损毁严重的原因之一。

|
图 8 康定MS6.3地震典型震害照片 Fig. 8 Typical earthquake damage photographs of Kangding MS6.3 earthquake |
1) 本文选取康定MS6.3地震中不同震中距台站记录的三分量加速度数据,并采用基于EEMD的HHT方法对其进行时频分析。结果表明,EEMD不仅能抑制信号的模态混叠,还能较好地计算数据的时频特性,对能量集中分布的时频段也能较好地体现。
2) 根据地震现场工作科学考察发现,震区崩科藏式建筑房屋表现出震害明显偏重的现象,其原因可能与几个因素有关:首先,通过Hilbert边际谱分析可以看出,康定新都台信号频率集中在10 Hz左右,瞬时能量谱显示高频成分丰富;其次,震害分布特征可能还与房屋建筑结构有关,农牧区的崩科式建筑房屋抗震能力差,损毁较严重,城镇区框架结构房屋损毁程度较轻。目前针对崩科藏式结构房屋抗震设计的研究较少,今后需采用量化分析的方式,从结构动力学角度对房屋结构的刚度、阻尼等基本参数进行研究,记录其在遭遇破坏性地震后相关参数的变化情况和特征,为此类型房屋的抗震设计工作提供可靠的科学依据。
| [1] |
李小军, 周正华, 于海英, 等.汶川8.0级地震强震动观测及记录初步分析[C].汶川地震建筑震害分析与重建研讨会, 北京, 2008 (Li Xiaojun, Zhou Zhenghua, Yu Haiying, et al. Preliminary Analysis of Strong Ground Motion Observation for Wenchuan MS8.0 Earthquake[C]. Seminar on Building Damage Analysis and Reconstruction in Wenchuan Earthquake, Beijing, 2008) http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-OGTY200806001004.htm
(  0) 0) |
| [2] |
李大虎, 赖敏, 何强, 等. 基于聚类经验模态分解(EEMD)的汶川MS8.0强震动记录时频特性分析[J]. 地震学报, 2012, 34(3): 350-362 (Li Dahu, Lai Min, He Qiang, et al. Time-Frequency Characteristics Analysis of Wenchuan MS8.0 Strong Motion Records Based on EEMD Decomposition[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2012, 34(3): 350-362 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-3782.2012.03.007)
(  0) 0) |
| [3] |
Daubechies I. The Wavelet Transform, Time-Frequency Localization and Signal Analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 1990, 36(5): 961-1 005 DOI:10.1109/18.57199
(  0) 0) |
| [4] |
李大虎, 梁明剑, 黎小刚, 等. 011年四川炉霍MS5.3地震加速度记录的时频分析与能量计算[J]. 西北地震学报, 2012, 34(4): 335-341 (Li Dahu, Liang Mingjian, Li Xiaogang, et al. Time-Frequency Analysis and Energy Calculation for Acceleration Records of Luhuo MS5.3 Earthquake in Sichuan Province in 2011[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 2012, 34(4): 335-341)
(  0) 0) |
| [5] |
郝国成, 龚婷, 董浩斌, 等. 基于聚类经验模态分解的地球天然脉冲电磁场时频与能量谱分析:以芦山MS7.0地震为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(5): 231-238 (Hao Guocheng, Gong Ting, Dong Haobin, et al. Time-Frequency Characteristics and Energy Analysis of the Earth's Natural Pulse Electromagnetic Fields Based on Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition: The Lushan MS7.0 Earthquake as an Example[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(5): 231-238)
(  0) 0) |
| [6] |
Krishna B T. Electrocardiogram Signal and Linear Time-Frequency Transforms[J]. Journal of the Institution of Engineers(India): Series B, 2014, 95(4): 377-382 DOI:10.1007/s40031-014-0097-9
(  0) 0) |
| [7] |
Zhou Y H, Chen W C, Gao J H, et al. Application of Hilbert-Huang Transform Based Instantaneous Frequency to Seismic Reflection Data[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2012, 82: 68-74 DOI:10.1016/j.jappgeo.2012.04.002
(  0) 0) |
| [8] |
Wu Z H, Huang N E. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition:A Noise-Assisted Data Analysis Method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(1): 1-41
(  0) 0) |
| [9] |
Wu Z H, Huang N E. A Study of the Characteristics of White Noise Using the Empirical Mode Decomposition Method[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2004, 460(2 046): 1 597-1 611
(  0) 0) |
| [10] |
Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, et al. The Empirical Mode Decomposition and the Hilbert Spectrum for Nonlinear and Non-Stationary Time Series Analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1 971): 903-995
(  0) 0) |
| [11] |
Lu Z, Smith J S, Wu Q H, et al. Empirical Mode Decomposition for Power Quality Monitoring[C]. 2005 IEEE/PES Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition: Asia and Pacific, Dalian, 2005 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1546916/
(  0) 0) |
| [12] |
李大虎, 李军, 邓艳, 等. 云南香格里拉、德钦-四川得荣交界5.9级地震加速度记录的时频分析[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2015, 37(6): 716-723 (Li Dahu, Li Jun, Deng Yan, et al. Time-Frequency Analysis of MS5.9 Earthquake Acceleration Records in Border of Xianggelila between Deqin of Yunnan and Derong of Sichuan[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 37(6): 716-723 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2015.06.08)
(  0) 0) |
| [13] |
易桂喜, 龙锋, 闻学泽, 等. 2014年11月22日康定M6.3级地震序列发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(4): 1 205-1 219 (Yi Guixi, Long Feng, Wen Xueze, et al. Seismogenic Structure of the M6.3 Kangding Earthquake Sequence on 22 Nov. 2014, Southwestern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(4): 1 205-1 219)
(  0) 0) |
| [14] |
周荣军, 赖敏, 李大虎, 等. 2011年4月10日四川炉霍Ms5.3级地震强震记录与震害特点[J]. 成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 40(2): 217-224 (Zhou Rongjun, Lai Min, Li Dahu, et al. Strong-Motion Records and Characteristics of Earthquake Damages of MS5.3 Earthquake Occurred in Luhuo, Sichuan, China, on April 10, 2011[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology: Science and Technology Edition, 2013, 40(2): 217-224)
(  0) 0) |
| [15] |
2014年11月22日四川省甘孜藏族自治州康定县6.3级地震灾害直接损失评估报告[R].四川省地震局, 2011 (Assessment Report on Direct Damage of Earthquake Disaster with MS6.3 in Kangding County, Ganzi Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Sichuan Province, 22 November 2014[R].Sichuan Earthquake Agency, 2011)
(  0) 0) |
 2019, Vol. 39
2019, Vol. 39

