2. 中国地震局第二监测中心,西安市西影路316号,710054;
3. 南阳师范学院环境科学与旅游学院,南阳市卧龙路1638号,473061
断层滑动参数是判断断裂活动性的一个重要手段。在高精度地面观测数据基础上利用多种反演算法研究断层活动特性已取得一定的成果,如Murray等[1]利用Montle Carlo算法反演断层参数;张秀霞等[2]将位错理论模型与遗传算法相结合,采用川西地区2004-2007年GPS数据对龙门山断裂带主要断层的三维滑动速率进行反演;刘杰等[3]将粒子群算法与位错理论模型结合,有效反演了断层滑动参数。本文选取最优非线性反演算法,采用2013-09~2014-09和2014-09~2015-04两期地面重力数据反演鲜水河断裂三维滑动速率,以分析该断层近年来的活动特性及与区域地震的关系。
1 位错模型与地表重力变化的关系用位错理论表示断层参数和地表重力变化的关系。U1、U2、U3分别为断层上盘相对于下盘在走滑方向、倾滑方向、张裂方向的滑动量,其中σ、d、P分别为断层倾角、下底深度、地表面上任意一点。地表自由点(x1,x2,O)处重力变化Δg为[4-5]:
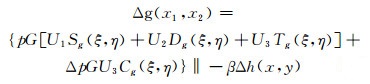
|
(1) |
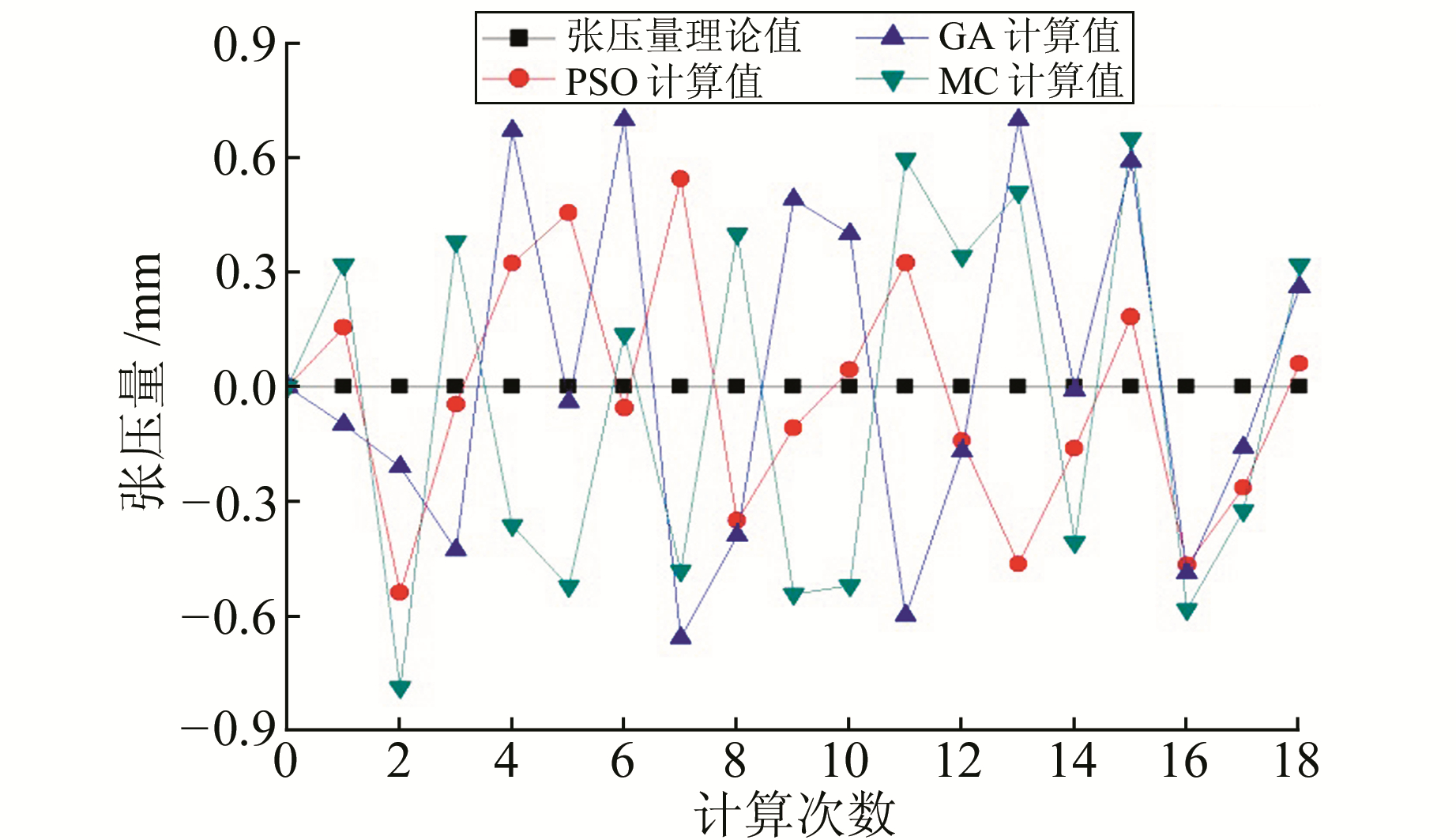
将式(1)由单一断层运动引起的重力变化扩展为复杂多断层运动引起的综合重力变化[4-5]:
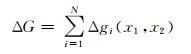
|
(2) |
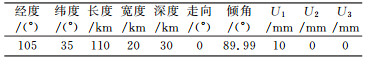
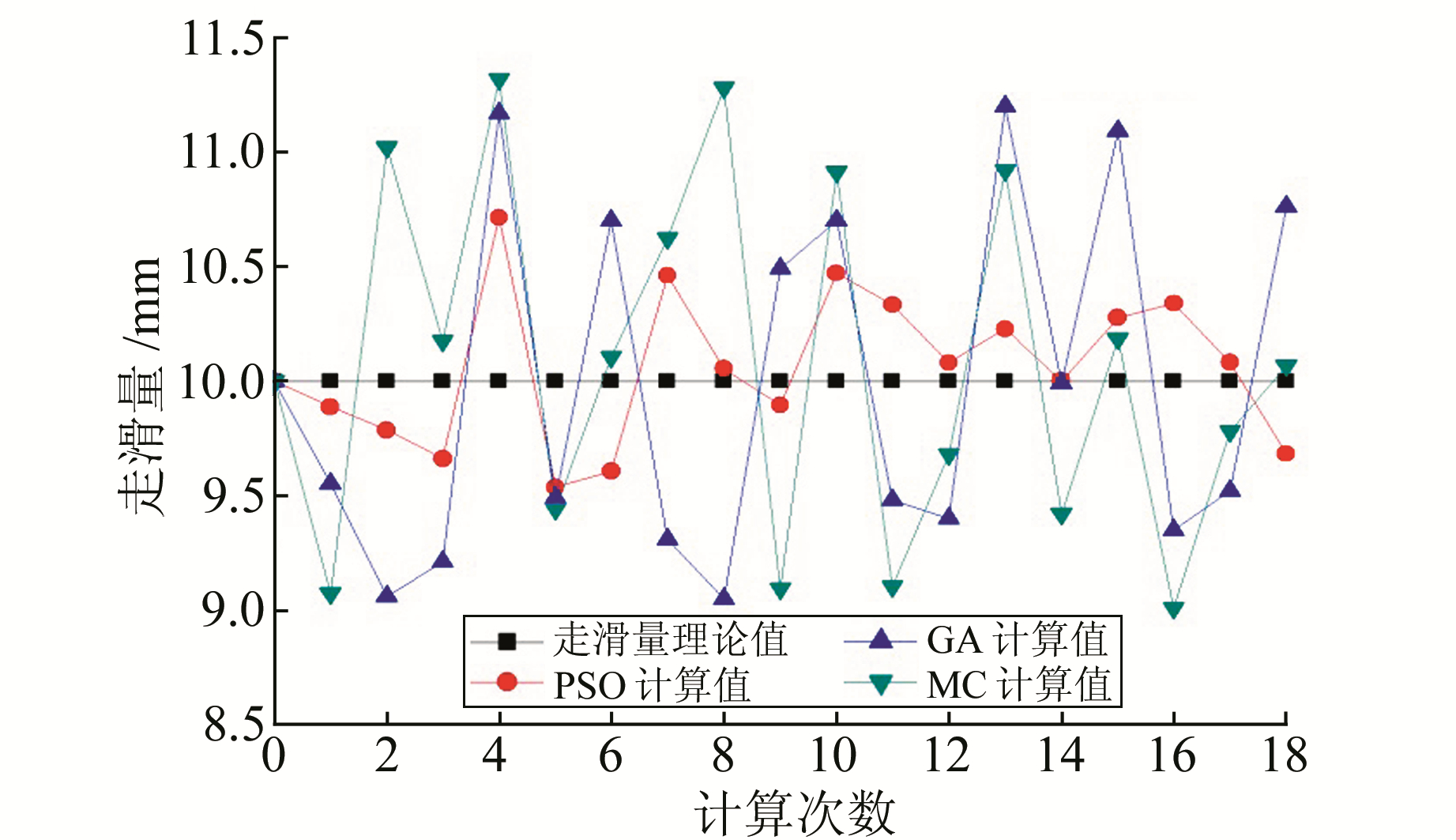
本文基于矩形位错理论模型, 采用表 1给定的断层参数,正演模拟出重力变化数据,并加上一定的扰动误差,然后采用粒子群算法、遗传算法、蒙特卡洛法等3种非线性反演算法分别对已知单断层三维滑动速率(走滑量、倾滑量、张压量)进行反演。各反演方法中,反演值设定范围及计算次数一致,结果见图 1~3。
|
|
表 1 单一模拟断层几何参数 Tab. 1 The geometric parameters of a single fault |
|
图 1 PSO、GA及MC反演走滑量 Fig. 1 The inversion of strike-slip by PSO, GA and MC |

|
图 2 PSO、GA及MC反演倾滑量 Fig. 2 The inversion of dip-slip by PSO, GA and MC |
|
图 3 PSO、GA及MC反演张压量对比 Fig. 3 The inversion of tensile fracture by PSO, GA and MC |
在反演条件相同的情况下,粒子群算法(PSO)、遗传算法(GA)、蒙特卡洛法(MC)反演走滑量范围分别为9.535 97~10.713、9.06~11.2、9.01~11.318, 反演倾滑量范围分别为-0.590 3~0.300 27、-0.59~0.66、-0.723~0.681,反演张压量范围分别为-0.467 23~0.544 8、-0.66~ 0.67、-0.584~0.651 2。显然,粒子群算法在利用重力变化反演断层滑动三维速率方面收敛性较好、稳定性高。
3 鲜水河断裂三维滑动速率反演本文选取粒子群算法,基于位错理论模型,采用鲜水河断裂[6]附近区域2013-09 ~2014-09和2014-09~ 2015-04两期地面重力数据反演该断裂三维滑动速率,见图 4。

|
图 4 重力变化速率等值线(黑色三角形为重力分布点) Fig. 4 The isoline of gravity change rate (The black triangle is gravity distribution points) |
由图 4(a)知,该阶段鲜水河断裂带中段附近断裂两侧重力变化表现为正,南、北段的重力变化正负值基本以鲜水河断裂带为界;由图 4(b)知,鲜水河断裂上重力正负值变化基本以断裂带两侧为界,且中段附近由图 4(a)阶段重力变化值为正逐渐转变为以断裂带为界呈现正负值的现象。
考虑到鲜水河断裂带地质构造复杂,本文利用断层微分思想[7-8]将断裂带分为9段:东谷-朱倭段、炉霍段、仁达段、道孚段、乾宁段、塔公段、康定段、康定-新店子段、磨西段。为尽可能减小模型误差,本文参考文献[9-10]对该断裂带断层几何参数的长度、深度取相同值及近似值。其中断层倾角参数设置为:中北段倾角为85°,中段倾角为60°,中南段倾角为75°[11],见表 2。
|
|
表 2 鲜水河断裂带各子断层几何参数 Tab. 2 Each fault parameters of Xianshuihe fault zone |
利用2013-09~2014-09和2014-09~2015-04两期地面重力数据,基于粒子群算法反演各个子断层三维滑动参数。目标函数为:
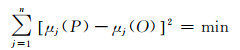
|
(3) |
式中,μj(P)为位错模型模拟的重力数据,μj(O)为地面实测重力数据,n为重力点个数。
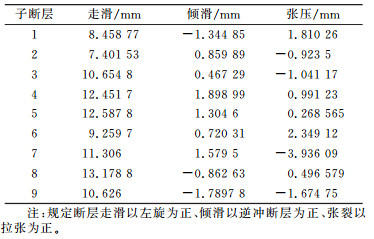
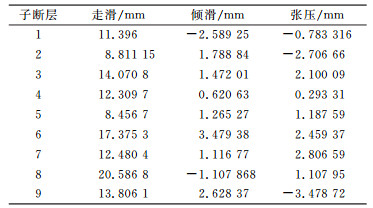
由表 3、表 4可知,鲜水河断裂带滑动速率具有明显的分段性,且表现为以左旋走滑为主,总体呈逆冲断层,局部兼有挤压。两期反演结果整体上东南段平均滑动速率大于西北段,可能与该断裂带东南段与龙门山断裂、安宁河断裂等复杂断裂斜交汇有关。在倾滑方面,该断裂两期倾滑参数在数值上相对于地质结果整体较小,这可能与地质结果是时间尺度上断层累积的综合效应,而重力数据反演的结果与断层活动性实时效应有关。由表 3知,鲜水河断裂平均走滑速率约为10.658 mm/a,最大达13.178 8 mm/a,与已有研究基本一致[12-13],总体上略偏大,原因一方面可能与模型中所取断层几何参数、重力测量误差有关,另一方面可能由于反演所用重力变化是许多动力源共同作用的结果。由表 4知,该阶段鲜水河断裂平均走滑、倾滑速率分别达到19.882 5 mm/a、1.445 7 mm/a,与表 3对比可知,两期反演结果均显示鲜水河断裂滑动速率在空间上表现出一定的不均匀性分布特征,但在断层走滑、倾滑参数方面,2014-09~2015-04相对于2013-09~2014-09反演结果较大,其差异有可能与2014-11-22康定6.3级地震有关。
|
|
表 3 2013-09~2014-09反演结果 Tab. 3 The inversion results by gravity data which from September 2013 to September 2014 |
|
|
表 4 2014-09 ~2015-04反演结果 Tab. 4 The inversion results by gravity data which from October 2014 to April 2015 |
1) 重力资料反演断层滑动参数所用非线性反演算法中,粒子群算法相对于遗传算法、蒙特卡洛法收敛性较好、稳定性强、精确度高;遗传算法次之,蒙特卡洛法相对较差,但总体上均具有一定的应用价值。
2) 鲜水河断裂带具有明显的分段差异性,且不同段处滑动速率大小不同。该断裂以左旋走滑为主,整体呈逆冲断层,局部兼有挤压,两期平均滑动速率分别为10.658 mm/a、19.882 5 mm/a。
3) 相对于2013-09~2014-09反演结果,利用2014-09~2015-04地面重力数据反演的鲜水河断裂断层走滑、倾滑参数较大,这可能与2014-11-22康定6.3级地震有一定的关系。
需要指出的是,重力变化包括断层运动引起的变化和非断层运动引起的变化,是由多种动力源共同作用的结果。论文反演采用相邻两点重力段差,能够从一定程度上剔除一定的重力变化力源的影响。如果想完全剔除外力对重力变化的影响,还需对该断层有更进一步的了解。
| [1] |
Murray M H, Marshall G A, Lisowski M, et al. The 1992 MS=7 Cape Mendocino, California, Earthquake:Coseismic Deformation at the South End of the Cascadia Megathrust[J]. J Geophys Res, 1996, 101(138): 17 707-17 725
(  0) 0) |
| [2] |
张秀霞, 张永志. 遗传算法反演龙门山断裂带断层三维滑动参数研究[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2011, 33(2): 217-220 (Zhang Xiuxia, Zhang Yongzhi. Inversion of Three-Dimensional Slip Parameters of Fault in Longmenshan Fault Zone Using Geneic Algorithm[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2011, 33(2): 217-220 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2011.02.019)
(  0) 0) |
| [3] |
刘杰, 张永志, 张秀霞, 等. 基于GPS数据的粒子群算法反演断层三维滑动速率[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2010, 30(2): 40-42 (Liu Jie, Zhang Yongzhi, Zhang Xiuxia, et al. Fault Slip Velocity Inversion by Using Particl Swarm Optimization Algorithm from GPS Data[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2010, 30(2): 40-42)
(  0) 0) |
| [4] |
Okubo S. Potential and Gravity Changes Raised by Point Dislocations[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2007, 105(3): 573-586
(  0) 0) |
| [5] |
Okubo S. Gravity and Potential Changes Due to Shear and Tensile Faults in Half-Space[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 1992, 97(B5): 7 137-7 144 DOI:10.1029/92JB00178
(  0) 0) |
| [6] |
李大虎, 丁志峰, 吴萍萍, 等. 鲜水河断裂带南东段的深部孕震环境与2014年康定MS6.3地震[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(6): 1941-1953 (Li Dahu, Ding Zhifeng, Wu Pingping, et al. The Deep Seismogenic Environment of the Southeastern Section of the Xianshuihe Fault Zone and the 2014 Kangding MS6.3 Earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(6): 1941-1953)
(  0) 0) |
| [7] |
程佳, 刘杰, 甘卫军, 等. 川滇菱形块体东边界各断层段强震演化特征研究[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2011, 41(9): 1311-1326 (Cheng Jia, Liu Jie, Gan Weijun, et al. Characteristics of Strong Earthquake Evolution around the Eastern Boundary Faults of the Sichuan-Yunnan Rhombic Block[J]. Science China: Earth Science, 2011, 41(9): 1311-1326)
(  0) 0) |
| [8] |
闻学泽. 四川西部鲜水河-安宁河-则木河断裂带的地震破裂分段特征[J]. 地震地质, 2000, 22(3): 239-249 (Wen Xueze. Character of Rupture Segmentation of the Xianshuihe-Anninghe-Zemuhe Fault Zone, Western Sichuan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2000, 22(3): 239-249 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2000.03.005)
(  0) 0) |
| [9] |
申重阳, 王琪, 吴云, 等. 川滇菱形块体主要边界运动模型的GPS数据反演分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 2002, 45(3): 352-361 (Shen Chongyang, Wang Qi, Wu Yun, et al. GPS Inversion of Kinematic Model of the Main Boundaries of the Rhombus Block in Sichuan and Yunnan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2002, 45(3): 352-361 DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2002.03.007)
(  0) 0) |
| [10] |
王阎昭, 王恩宁, 沈正康, 等. 基于GPS资料约束反演川滇地区主要断裂现今活动速率[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2008, 38(5): 582-597 (Wang Yanzhao, Wang Enning, Shen Zhengkang, et al. GPS-Constrained Inversion of Present-Day Slip Rates along Major Faults of the Sichuan-Yunnan Region, China[J]. Science China:Ser D, 2008, 38(5): 582-597)
(  0) 0) |
| [11] |
赵静, 江在森, 牛安福, 等. 川滇菱形块体东边界断层闭锁程度与滑动亏损动态特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(3): 872-885 (Zhao Jing, Jiang Zaisen, Niu Anfu, et al. Study on Dynamic Characteristics of Fault Locking and Fault Slip Deficit in the Eastern Boundery of the Sichuan-Yunnan Rhombic Block[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(3): 872-885)
(  0) 0) |
| [12] |
李乐, 陈棋福, 钮凤林, 等. 鲜水河断裂带南段深部变形的重复地震研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(11): 4 138-4 148 (Li Le, Chen Qifu, Niu Fenglin, et al. Quantitative Study of the Deep Deformation along the Southern of the Xianshuihe Fault Zone Using Repeating Microearthquakes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(11): 4 138-4 148)
(  0) 0) |
| [13] |
熊维, 谭凯, 余鹏飞, 等. 鲜水河断裂近期库仑应力演化及其与康定MW5.9地震的关系[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2016, 36(2): 95-100 (Xiong Wei, Tan Kai, Yu Pengfei, et al. Triggering of MW5.9 Kangding Earthquake by Coulomb Stress Evolution along Xianshuihe Fault Zone since 1955[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2016, 36(2): 95-100)
(  0) 0) |
2. Second Crust Monitoring and Application Center, CEA, 316 Xiying Road, Xi'an 710054, China.;
3. School of Environment Science and Tourism, Nanyang Normal University, 1638 Wolong Road, Nanyang 473061, China
 2017, Vol. 37
2017, Vol. 37