文章信息
- 孙鹏, 李忠芳, 王传刚, 王燕, 崔伟慧, 裴洪昌, 尹晓燕
- SUN Peng, LI Zhong-fang, WANG Chuan-gang, WANG Yan, CUI Wei-hui, PEI Hong-chang, YIN Xiao-yan
- 燃料电池用高温质子交换膜的研究进展
- Research progress of high temperature proton exchange membranes applied in fuel cells
- 材料工程, 2021, 49(1): 23-34
- Journal of Materials Engineering, 2021, 49(1): 23-34.
- http://dx.doi.org/10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2019.001097
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2019-11-27
- 修订日期: 2020-03-17
当前,人类社会的发展仍然面临环境污染和能源短缺等重大问题。要解决这些问题,就要开发低污染或者无污染的新型能源技术。作为一种清洁高效的能源技术,燃料电池(fuel cell)技术得到了广泛的关注[1-3]。燃料电池是一种开放式的能量转换装置,能够直接、连续地将外部供给的燃料和氧化剂中蕴含的化学能转化为电能[4]。内燃机需要经过卡诺循环的热功转换过程才能发电,而燃料电池则可直接将化学能转化为电能,因而具有比内燃机更高的能量转换效率。与传统电池技术相比,燃料电池具有能量转换效率高、比能量密度高、污染小、启动快、结构模块化和噪声低等优势。燃料电池技术是支撑氢能经济的重要技术,可以实现电水热联产。燃料电池根据其电解质和其中传导离子的不同又可分为碱性燃料电池、磷酸燃料电池、熔融碳酸盐燃料电池、固体氧化物燃料电池和质子交换膜燃料电池5种类型[4]。质子交换膜燃料电池(proton exchange membrane fuel cell, PEMFC)具有理论比能量高、能量转化效率高、可实现零排放等优点,得到了极大关注。
质子交换膜燃料电池的单电池由膜电极组(membrane electrode assembly, MEA)、流场板、集流板和端板组成,MEA包括质子交换膜(proton exchange membrane, PEM)、阳极(和阴极)催化层以及阳极(和阴极)扩散层[5-6]。PEMFC所采用的PEM一般以聚合物为主体,可根据需要进行修饰或改性,如掺杂无机材料、与其他高分子材料共混或用活性试剂进行交联,而后经适宜的制膜工艺制得。目前PEMFC所用的阳极催化剂多为铂系金属及其合金,阴极催化剂包括铂系催化剂和过渡金属大环化合物等,双极板多采用导电导热的薄金属板或石墨材料制备。图 1为氢-氧(氢-空)PEMFC单电池的结构和工作原理示意图。
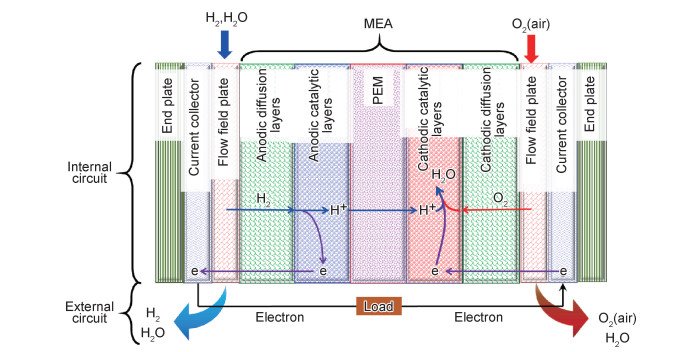
|
图 1 氢-氧(氢-空)PEMFC单电池的结构和工作原理示意图 Fig. 1 Structure and working principle of hydrogen-oxygen (hydrogen-air) PEMFC single cells |
PEMFC在100 ℃以下工作时,往往存在一些难以克服的缺点[7-8]:(1)低温下,电极反应催化活性一般较低;(2)低温下,燃料中的一些杂质会引起催化剂中毒,降低催化效率;(3)电池内气、液两相共存,传质调控十分复杂;(4)水热管理系统复杂,且成本高;(5)以甲醇为燃料时,电催化剂在低温下的催化活性不足,未氧化的甲醇可能穿过催化层到达膜表面,并穿过质子交换膜到达阴极侧,导致电池性能衰减。
针对低温PEMFC面临的问题,提高PEMFC的工作温度到100~200 ℃是一种有效的解决办法[9]:(1)升高温度可以提高电极反应的催化活性;(2)高温下杂质气体在催化剂上的吸附量减少,且有些可被催化氧化,因此,可以提高杂质的耐受能力;(3)电池内的水在高温下主要以气相形式存在,因而仅存在气相传质,传质问题变得简单,传质效率提高;(4)电池反应产生的热用以维持工作温度而不需及时耗散,热管理简化,同时,电池反应生成的水以气态的形式排出,大大降低了水热管理系统的复杂性和成本;(5)高温下阳极催化剂催化甲醇氧化的活性明显提高,因而可以解决甲醇渗透的问题。因此,开发在100~200 ℃下连续稳定工作的高温PEMFC势在必行。低温PEMFC中的其他组件都可耐受100~200 ℃的工作温度,而通常使用的膜材料(Nafion膜)在高温、低相对湿度(relative humidity, RH)下电导率迅速下降,因此,需要开发高温、低湿度下工作的质子交换膜,即高温质子交换膜(high temperature proton exchange membrane,HTPEM)。
近年,HTPEM领域获得了广泛研究,本文首先从HTPEM的主要类型、制备与改性方法和质子传导机制方面进行概述,并指出质子导体掺杂的聚苯并咪唑(PBI)复合HTPEM目前具有较大的潜力,进一步论述复合PBI高温质子交换膜的制备、掺杂的质子导体类型和性能提升方法。最后,本文总结了目前HTPEM面临的挑战,并指出了未来发展的方向。
1 高温质子交换膜的研究进展HTPEM是高温PEMFC中的重要组件。作为一种固态电解质隔膜,HTPEM起传导质子、隔绝阴阳极反应物和阻碍电子通过的作用[10]。传统的Nafion®膜在低相对湿度下100 ℃以上性能严重衰减,所以开发高温PEMFC的关键在于开发HTPEM。对HTPEM的性能要求包括:质子电导率高、电子电导率低、机械性能好、干湿变形小、化学稳定性好、燃料和氧化剂透过率低、使用寿命长、制备过程环保实用等。
1.1 高温质子交换膜的主要类型HTPEM按组成分为纯聚合物膜、聚合物掺杂无机材料制备的有机-无机复合膜以及纯无机膜3种[11]。纯聚合物膜可以由单种聚合物制备或由多种聚合物共混制得,膜内无有机-无机界面。聚合物中亲水链段和疏水链段分别聚集形成微相分离结构,彼此连通的亲水区域形成质子传输通道,疏水区域则起到机械支撑作用。有机-无机复合膜一般是在聚合物中掺杂无机材料制备得到的[8, 12],膜内存在有机-无机界面,因而存在一定程度的相分离。如果无机材料掺杂量过大,会引起团聚,导致严重分相,影响膜的机械性能甚至成膜性能。为改善和解决相分离问题,可以调控掺杂无机材料的掺杂度(即相对含量)、粒径、分布和表面性质,或掺杂有机-无机复合型添加剂,增强其与聚合物间的相容性。纯无机膜一般较脆,研究很少[8, 11]。
从制备HTPEM的聚合物材料方面,可将其分为全氟聚合物质子交换膜材料、部分氟化聚合物质子交换膜材料和非氟化聚合物质子交换膜材料。
全氟聚合物包括全氟磺酸(perfluorinated sulfonic acid, PFSA)聚合物和全氟磺酰亚胺膜[13-14]。其中以PFSA膜最为常见。PFSA聚合物以聚四氟乙烯为骨架,因而膜具有较好的机械性能、热稳定性和化学稳定性;同时,其具有带有磺酸基末端的乙烯基醚侧链,使其具有良好的亲水性,在高湿度下可以吸水形成水化层,质子在电场作用和浓差作用下,结合水分子在膜内连通的亲水区域间进行传导,因而具有良好的质子传导性能[14]。然而在低相对湿度下,PFSA膜的质子电导率衰减严重[14],所以PFSA膜仅适用于低温、高湿度的工作环境,这限制了其在高温和低湿度下的应用。为了使PFSA膜在高温下有理想的质子电导率,可采取如下两类方法对其进行改性:一是向PFSA膜中掺杂吸湿性添加剂,这样水与粒子中亲水基团间形成氢键,以结合水的形式存在于膜内,提高膜在高温条件下的保水能力,但质子的传导仍依赖于水介质,当电池长期在低湿度下工作时,仍可能缓慢失水,导致性能变差;二是向PFSA膜中添加质子导体(在一定温度和湿度范围内具有稳定传导质子能力的物质),如果掺杂的质子导体对相对湿度要求低,那么质子的传导将不再依赖于水介质。
为改善PFSA膜的性能,一些部分氟化的聚合物也被用于制备HTPEM,包括部分氟化的芳香族聚合物和部分氟化的接枝共聚物[14]。前者一般通过α, β, β-三氟苯乙烯或α, β, β-三氟乙氧基苯进行聚合或共聚得到,而后对苯环磺化即可制得具有一定质子电导率的膜材料。后者一般用含芳基磺酸或芳基膦酸的单体进行共聚得到,或在含芳基侧链的烯烃单体共聚后进行芳环磺化来制备。这类膜化学稳定性和机械性能一般较差,不能满足实际使用的需要。
为了同时满足PEM在化学稳定性和机械强度双方面的要求,无氟高温质子交换也被开发出来。这类膜材料一般利用主链上包含苯环结构的无氟芳香族聚合物为原料进行制备,所用无氟芳香聚合物主要包括磺化聚芳醚砜(SPSF)[15]、磺化聚芳(硫)醚(SPAE)[16]、磺化聚醚醚酮(SPEEK)[17]、磺化聚酰亚胺(SPI)[18]和聚苯并咪唑(PBI)[19]等。
1.2 高温质子交换膜的制备和改性方法单层的HTPEM可用流延法、热压法、旋转涂膜法、喷涂法和静电纺丝法来制备[11, 20]。流延法就是将铸膜原料在一定温度下溶解于适宜溶剂得到一定浓度的铸膜液,将铸膜液浇铸到玻璃板或聚四氟乙烯板上,而后在一定温度和真空度下除去溶剂,得到膜或其前驱体,按需要进行热交联或其他修饰,也可同时进行。热压法是将铸膜原料在一定温度下溶解于溶剂或分散于分散剂中得到具有一定黏度的铸膜液,在一定温度和压力下热压一定时间成膜,然后立即用液氮冷淬,使其具有一定的强度,最后用浸渍、高温、真空等方法除去溶剂得到膜材料。旋转涂膜法是将铸膜原料制成具有一定浓度和黏度铸膜液,注射于旋转涂膜机加料口,在一定转速下使铸膜液因离心作用旋涂于基材表面,最后除去溶剂成膜的方法。喷涂法是将铸膜液用喷枪均匀喷涂于基材表面,而后除去溶剂成膜的方法。静电纺丝法是将铸膜原料制成具有一定浓度的纺丝液,在高压直流电场作用下,控制电压、纺丝距离、流速和接收板运动使其在接收板上纺丝成膜的方法。
HTPEM阳极侧和阴极侧的化学环境不同,对膜结构和性能的要求也不同,比如直接甲醇燃料电池在较低温度下存在甲醇从阳极向阴极扩散透过膜的过程, 阴极侧氧还原反应产生的羟基自由基和过氧羟基自由基等物质可能引起膜阴极侧的氧化降解等问题。针对这类问题,可通过表面修饰或制备多层膜的方法进行解决。通过表面修饰,可改善膜的阻醇性能、抗氧化性能和保水能力。多层膜的制备方法包括逐层流延[21-22]、静电层层自组装(即静电交替沉积,layer-by-layer self assembly)[23-24]和逐层喷涂[25]等方法。
改善HTPEM性能的方法包括掺杂功能材料、离子交联(即酸性聚合物与碱性聚合物共混制备离子交联膜,亦称作酸碱共混)、利用交联剂对聚合物进行共价交联、表面修饰和多层复合等,下面按所需改善的性能进行分类论述。改善膜质子电导率的方法包括:掺杂固态酸质子导体[26]、掺杂保水材料[27]和掺杂吸湿材料[28]等;离子交联,即通过离子键和氢键的构筑来构建质子传输通道,改善膜的质子电导率[29-30];通过锚定、吸附、表面修饰或多层复合,可以降低水溶性质子导体或水的流失,从而减缓或避免膜质子电导率的减小[31-33]。天津大学的姜忠义教授课题组通过在膜内掺杂储水微胶囊或金属有机骨架材料(metal-organic frameworks, MOF),降低了膜内水或磷钨酸的流失,为改善高温低湿度下膜的质子电导率提供新的思路[27, 33-36]。
改善膜机械性能的方法包括掺杂增强材料(如高强度纤维材料、碳材料、多孔载体等)[26, 28, 32, 37-41]、共价交联[42-43]和离子交联[44]。其中,非质子导体型增强材料的掺杂会引起质子电导率的降低,因此,掺杂量不宜过高。一般共价交联多使用双官能度交联剂,其在高的交联度下导致膜质子电导率的明显降低,而在低交联度下不能明显提高膜的机械性能。而使用高官能度共价交联剂即可在低交联度下提高膜的机械性能,同时允许较高的质子导体掺杂量,使膜同时具有良好的质子传导性能[42]。
改善膜干湿变形性的方法包括掺杂尺寸稳定性增强材料[26, 31, 38-40, 45]、共价交联[41-43]和离子交联[44]。其中,掺杂非质子导体型材料和交联均可能引起质子电导率的降低。
改善膜抗氧化稳定性的方法包括共价交联[42, 46]、离子交联[44]、端基或侧链修饰[47]、掺杂自由基捕获剂[48-49]和膜阴极侧表面修饰[31]等方法。
1.3 质子传导机制和典型膜材料目前一般认为,质子交换膜的传质机理主要包括运载机理(vehicle mechanism)[50]和跳跃机理(hopping mechanism,又称Grotthuss机理)[51]。从质子传导的驱动力上看,二者并无区别,都是靠电场力和浓度差的协同作用进行质子传导。二者的区别体现在传导的微观过程中,运载机理认为,质子交换膜在工作条件下,膜内存在质子的载体(一般由水分子充当),其结合质子,从阳极侧穿过膜到达阴极侧,而后释放质子,水分子从阴极侧排出。因而,该机理适用于高湿度条件下的质子传导,在低相对湿度下,运载机理受抑制。除相对湿度外,运载机理要求膜内的亲水基团形成贯穿膜的连续的亲水通道,保证质子能够从膜的阳极侧经此通道传输到阴极侧参与氧还原反应。跳跃机理认为,质子交换膜中存在质子的供体和受体(如磺酸基、膦酸基、胺基等),彼此形成氢键,并在膜内形成贯穿膜的连续的氢键网络结构,通过氢键连续的形成-断裂过程完成质子的传导。通过跳跃机理进行质子传导,需要膜内形成贯穿膜的连续氢键网络结构。运载机理的典型聚合物是PFSA,跳跃机理的典型代表是质子导体掺杂的聚苯并咪唑(polybenzimidazole,PBI)复合膜。PBI的芳香性骨架具有刚性,使膜具有良好的热稳定性、机械性能和化学稳定性,且不溶于水,避免膜的过度溶胀,适于作为膜的基体;PBI本身具有弱碱性,便于掺杂酸性质子导体;在咪唑环和亲水端基中同时存在氢键受体和供体,具有一定的质子浓度和构筑质子通道的潜力。图 2分别以PFSA膜和磷酸掺杂的PBI膜为例展示了HTPEM的质子传导机理。

|
图 2 高温质子交换膜的质子传导机理 (a)运载机理;(b)跳跃机理 Fig. 2 Proton conduction mechanism of HTPEMs (a)vehicle mechanism; (b)hopping mechanism |
关于PFSA膜在1.1部分已作介绍,其在低相对湿度下质子传导性能明显衰减。有研究者在Nafion®膜中掺杂吸水性氧化物、质子导体或储水微胶囊[28, 52-53],或制备类似结构的嵌段或接枝聚合物膜以改善其在低相对湿度下的质子传导性能[54-55]。耐温磺化聚合物如磺化聚烯烃[56-57]、磺化聚醚砜(酮)[58]、磺化聚酰亚胺[59]和磺化聚磷腈[60]等也被用于高温PEM的制备。质子导体掺杂到聚合物(如PBI)制备的膜[42, 61]、质子导体填充于多孔载体的膜[62]、磷硅玻璃[63]等材料也受到了广泛关注。在这些工作的基础上,为了进一步提高膜的性能,研究者们开发了一系列对膜进行改性的方法,如磺化[64]、掺杂无机材料[58, 65]、交联(包括离子交联和共价交联)[66]和多层复合[67]等。
与磺化聚合物不同,质子导体掺杂的PBI膜在高温低湿度下可通过跳跃机理传导质子,因而在低相对湿度下具有良好的质子传导性能,是目前高温质子交换膜领域广受关注的一类膜材料。
2 PBI类高温质子交换膜PBI属于特种工程塑料,玻璃化转变温度高、热稳定性好、机械性能好、气体透过率低,成为目前最受关注的HTPEM材料。PBI广义上指结构重复单元中含有苯并咪唑结构的聚合物,狭义上指聚2, 2′-间亚苯基-5, 5′-双苯并咪唑(poly[2, 2′-(m-phenylene)-5, 5′-bibenzimidazole],简称mPBI)[19]。PBI类聚合物的常见结构见图 3,其中mPBI和聚(2, 5-苯并咪唑)(ABPBI)是最常用于HTPEM的PBI[68]。
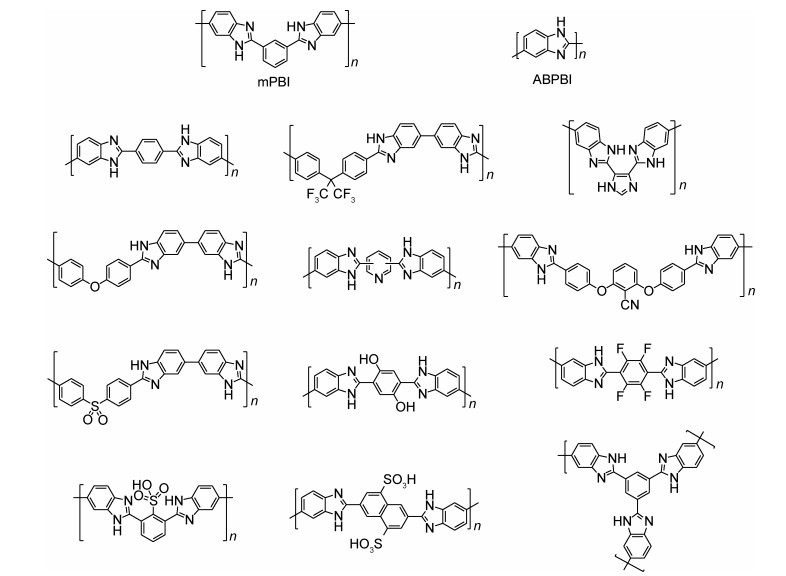
|
图 3 常用于高温质子交换膜的PBI类型 Fig. 3 Common types of PBI used for HTPEMs |
PBI是由芳香族邻二胺基与羧基之间发生缩合聚合反应制备的,反应过程中脱去水分子,主要制备方法为熔融缩聚法和溶液缩聚法[68],前者利用高温除去水分子,后者则利用溶剂或添加的吸水剂(如五氧化二磷)进行脱水。所用反应单体为四胺(含两个邻二胺基苯基的化合物)或其盐酸盐与二酸(或二酯、二腈、二醛、二酰胺)。最常见的是用四胺和二酸经熔融缩聚或溶液缩聚制备。
熔融缩聚法制备PBI一般是在无溶剂、惰性气体保护下,加热到四胺熔点以上进行缩聚反应[69]。反应在无催化剂下需分步进行,在225 ℃和270 ℃下预聚后,取出预聚物研细在300 ℃或更高温度下继续反应得到聚合度较高的PBI。在有机膦或有机硅的催化下,可以省去取出研磨步骤,一步合成PBI。此法适于制备聚合度较低的PBI,产品溶解性好,便于采用流延、喷涂、旋转涂膜等方法铸膜。缺点是PBI聚合度低时机械性能差,尤其是掺杂质子导体后,膜会变脆。熔融聚合法制备mPBI的反应方程式如图 4所示。
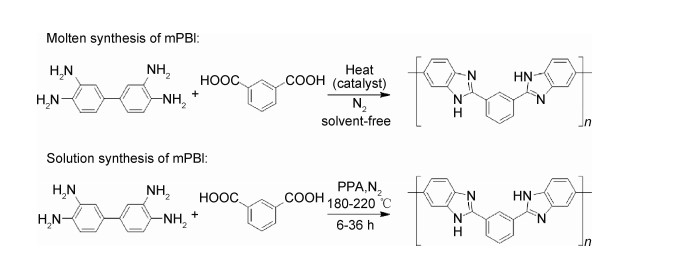
|
图 4 mPBI的制备方法 Fig. 4 Preparation methods of mPBI |
溶液缩聚法制备PBI一般是在多聚磷酸(PPA)或五氧化二磷-甲磺酸中将反应原料溶解后,在惰性气体保护下,加热搅拌进行缩聚,反应时间一般在6~36 h[19]。在PPA中合成PBI时,PPA既充当溶剂,又充当催化剂和吸水剂。此法制得PBI的聚合度与反应温度和时间有关,反应完毕可以直接热压成膜,或倾入大量水中“抽丝”得到PBI固体,研磨洗涤得到PBI。此法一般用于制备高聚合度PBI,且热压后PPA可水解为磷酸,直接得到酸掺杂PBI膜。此法同时存在一些缺点,如反应浓度低,不利于大量合成;对原料纯度要求高,产物溶解性较差;粗产品的中和与洗涤十分耗时,后处理复杂等。溶液聚合法(以PPA为溶剂)制备mPBI的反应方程式如图 4所示。
2.2 复合PBI膜掺杂的质子导体类型PBI本身质子电导率极低,需要掺杂质子导体才能作为质子交换膜使用。硫酸、磷酸(PA)、盐酸、硝酸和高氯酸等液态无机酸都曾作为质子导体掺杂到PBI中[70],其中掺杂硫酸的质子电导率高,而掺杂PA的PBI(PBI/PA)复合膜在高温低湿度下仍能保持较高的质子电导率,因此广受关注[71]。为了使PBI/PA膜具有良好的质子电导率,需要提高浸渍PA浓度、延长PA浸渍时间或提高PA浸渍温度来提高PA掺杂度[72]。另外,PBI/PA膜存在一些缺点限制了其应用:在高PA掺杂度下,PBI/PA膜的机械性能和干湿变形性一般较差,而在低PA掺杂度下,膜的质子电导率不足;另一方面,在中或高RH下工作时,膜中PA容易流失,造成性能衰减[73]。
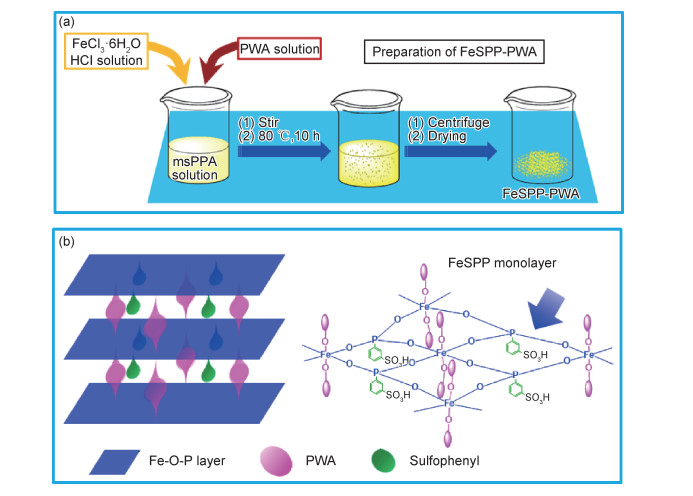
为解决这一问题,可将水溶性无机固态质子导体如杂多酸、超质子导体(可发生超质子相转变的固体酸)等锚定(或吸附)到非水溶性基体材料上,然后掺杂到PBI制备HTPEM[74]。掺杂非水溶性固态质子导体亦可解决这一问题。将金属的磷酸盐[75]、焦磷酸盐[76]、磺化的二氧化硅[77]和官能化多壁碳纳米管[78]等非水溶性无机固态质子导体掺杂到PBI中制得的复合膜,具有较高的质子电导率,同时避免了质子导体流失的问题,但无机质子导体与PBI相容性差,成膜过程中容易出现分相,导致膜的性能衰减[44]。而有机-无机复合质子导体的掺杂则可在一定程度上解决这一问题。常见的有机-无机复合质子导体包括有机磷酸酯(盐)[79]、硅烷基膦酸酯[80]、膦酸基取代的二氧化硅[81]、磺化苯膦酸盐[38-39, 47, 82]等。最近,本课题组发现,在制备层状的磺化苯膦酸铁(FeSPP)时加入水溶性的磷钨酸(PWA)可原位制得PWA插层的FeSPP,制备方法和结构见图 5[83]。进行PWA插层明显提高了质子导体的质子电导率,同时PWA与FeSPP间形成共价键,抑制PWA在高RH下的流失,掺杂到PBI中制备的复合膜具有较高的质子电导率和热稳定性[84]。另外,将酸性聚合物如Nafion [85]、磺化聚芳醚(SPAE)[30]、磺化聚醚醚酮(SPEEK)[44]、磺化聚醚砜[86]、聚乙烯基膦酸(PVPA)[87]、磺化聚苯胺[42]等与PBI进行离子交联制备的复合膜具有高质子电导率和强吸水性,且酸性聚合物与PBI之间形成氢键网络,可提高复合膜在低湿度下的质子电导率和改善其理化性能。有研究者将低RH下质子电导率高且不挥发的离子液体(包括聚离子液体)掺杂到PBI中制备HTPEM[88],但离子液体多溶于水,且可能发生氧化降解。
2.3 复合PBI膜的性能提升方法为进一步改善PBI类HTPEM的性能,可采取的方法包括以下几类:
(1) 改变PBI结构,如改变其聚合度及分布、改变其单体结构、嵌段结构和嵌段长度、侧链结构和分布、端基结构等。为了提高PBI膜的质子电导率,可以对PBI进行磺化或膦酸化[89]。这些质子传导基团可以引入主链或侧链,从自由体积的角度,引入具有一定长度柔性侧链末端可提高链段的运动性,促进质子传导。此外,还可以用具有高咪唑含量或带有吡啶基、三氮唑等结构的单体制备PBI,或通过嵌段或接枝共聚的方法引入碱性基团,这样制得的PBI具有较高的酸掺杂能力,可提高质子导体的掺杂量,抑制质子导体的流失,进而提高质子电导率[90]。改进合成和铸膜方法也可以提高质子电导率[91]。为改善PBI的溶解性使其便于制膜和修饰,可调整其聚合度,使用含醚键、砜基等基团的单体合成PBI或其嵌段、接枝共聚物[92],亦可通过制备支化结构的PBI来实现[93]。如果需要提高膜的机械性能,可以提高PBI的聚合度[94],也可通过嵌段、接枝等共聚手段实现[92]。为改善PBI膜的抗氧化稳定性,可对其进行端基保护[47],或用自由基捕获剂(如CeO2)对PBI膜进行掺杂[95]。
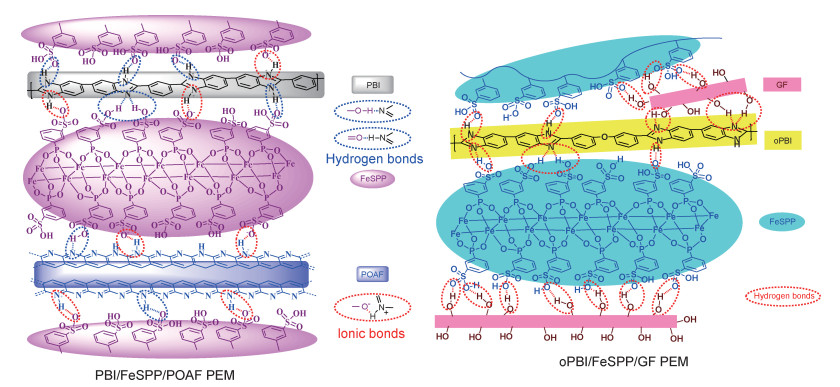
(2) 掺杂无机材料制备PBI复合膜,以调控膜的微观结构,改善膜性能。将亲水性氧化物掺杂到PBI膜中,可以提高膜的吸水能力,从而提高质子电导率,同时还可改善膜的机械性能和干湿变形性[96]。掺杂蒙脱土、黏土等材料可以提高PBI复合膜的PA掺杂度,限制膜的溶胀,降低PA流失[97]。掺杂氧化石墨烯、碳纳米管等碳材料也可以改善PBI膜的性能,如质子电导率、机械性能、化学稳定性等[98]。将PBI嵌入多孔载体制备的复合膜具有良好的机械性能和较小的干湿变形性[36]。近来,本课题组对PBI膜进行了纤维掺杂,以FeSPP为质子导体,分别制备了预氧化聚丙烯腈纤维(POAF)掺杂的PBI/FeSPP/POAF复合膜和玻璃纤维掺杂聚[4, 4′-(二苯醚基)-5, 5′-二苯并咪唑](oPBI)的oPBI/FeSPP/GF复合膜,两种复合膜的结构见图 6[38-39]。在这两种复合膜中,纤维与质子导体和聚合物间可形成致密的氢键网络结构,在较低的纤维掺杂度(3%~10%(质量分数))下,复合膜的干湿变形明显降低,机械性能、热稳定性和抗氧化性能均有改善,同时,质子电导率并未受到明显影响。
(3) 制备PBI交联膜。对PBI进行共价交联或离子交联(酸碱共混)可以改善膜的性能。PBI类HTPEM常用的小分子共价交联剂包括活泼卤代烃类[99]、环氧类[46]、Michael受体类[100]等,其官能团可与PBI分子端基以及链段中的咪唑反应,在膜内形成三维体型聚合物网络结构,同时降低了易受自由基进攻而发生氧化降解的活性位点数目,提高了其抗氧化性能。采用双官能度小分子交联剂可以改善PBI复合膜的机械性能、干湿变形性和抗氧化稳定性,还可降低其甲醇透过率,使之可用于直接甲醇燃料电池。不过,要达到理想的性能提升效果,需要一定的交联度(15%~30%),往往会引起膜质子电导率的降低。最近,本课题组发现,提高交联剂的官能度可以解决这一问题,高官能度交联剂可在较低的交联度下改善膜的性能,同时允许较高的质子导体掺杂量,提高膜的质子电导率[42]。此外,含氯甲基或溴甲基的聚合物也可作为PBI的共价交联剂,对其进行交联共混[101]。
PBI中的咪唑基具有弱碱性,可掺杂酸性聚合物制备离子交联膜,即酸碱共混膜。掺杂的酸性聚合物与PBI间形成静电吸引作用,改善膜的干湿变形性和机械性能,同时,酸性聚合物中的酸性基团往往可以起到促进质子传导的作用,提高膜的质子电导率[83, 102]。
综上,制备具有良好性能的复合PBI高温质子交换膜可从以下方面入手:合理设计PBI分子结构、选取合适的添加剂进行掺杂改性、选用合适的交联剂并优化交联度。需要注意的是,有些合成和改性方法在提高膜某方面性能的同时,可能引起其他性能的降低,因此,需合理设计结构、合理选用制膜材料和工艺,尽量减少改性过程中的“副反应”。
3 结束语HTPEM是高温PEMFC的核心组件,起传导质子、隔绝阴阳极反应物、隔绝电子的作用。高温下电池内相对湿度较低,因此需要开发高温低湿度下性能优越的HTPEM,质子导体掺杂的PBI膜在低相对湿度下可通过跳跃机理进行质子传导,具有良好的热稳定性和机械性能,广受关注。目前,复合PBI类HTPEM仍然面临许多挑战。首先,要设计合成新型质子导体,使PBI膜具有高质子电导率,同时避免质子导体流失以及在较高掺杂度下引起的机械性能降低、干湿变形增大和分相问题。其次,复合PBI膜的端基和咪唑基上的N—H键较为活泼,易发生氧化降解,解决这一问题的方法(交联、端基或侧链修饰、掺杂自由基捕获剂和表面修饰等)往往会引起质子电导率的降低,或效果有限。因此需要开发新的方法或添加剂,有效降低甚至消除氧化降解,同时避免对膜其他性能造成明显影响。另外,进一步研究复合PBI膜的微观结构(微相分离结构和自由体积等)与膜性能之间的关系,调控其膜内微相分离结构、水化区域和自由体积的尺寸与分布等,来有效构筑质子传输通道,综合提升膜的性能。最后,新型聚合物电解质的开发也是值得不断探索和尝试的方向。
| [1] |
LEMMON J P. Energy: reimagine fuel cells[J]. Nature, 2015, 525(7570): 447-449. DOI:10.1038/525447a |
| [2] |
CANO Z P, BANHAM D, YE S, et al. Batteries and fuel cells for emerging electric vehicle markets[J]. Nature Energy, 2018, 3(4): 279-289. DOI:10.1038/s41560-018-0108-1 |
| [3] |
O'HAYRE R, CHA S W, COLELLA W, et al. Fuel cell fundamentals. Chapter 1: introduction[M]. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2016: 1-24.
|
| [4] |
WILBERFORCE T, ALASWAD A, PALUMBO A, et al. Advances in stationary and portable fuel cell applications[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(37): 16509-16522. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.02.057 |
| [5] |
魏成玲, 沈亚云, 杨智, 等. 硫源对Fe/VS/C催化剂氧还原活性的影响研究[J]. 贵州师范大学学院(自然科学版), 2018, 36(6): 58-62. |
| [6] |
KRAYTSBERG A, EIN-ELI Y. Review of advanced materials for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014, 28(12): 7303-7330. |
| [7] |
ZHANG H, SHEN P K. Advances in the high performance polymer electrolyte membranes for fuel cells[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(6): 2382-2394. DOI:10.1039/c2cs15269j |
| [8] |
ZHANG L, CHAE S R, HENDREN Z, et al. Recent advances in proton exchange membranes for fuel cell applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2012, 204/206: 87-97. DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2012.07.103 |
| [9] |
JIANG S P. Functionalized mesoporous structured inorganic materials as high temperature proton exchange membranes for fuel cells[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(21): 7637-7655. DOI:10.1039/C4TA00121D |
| [10] |
BRANCO C M, SHARMA S, DE CAMARGO FORTE M M, et al. New approaches towards novel composite and multilayer membranes for intermediate temperature-polymer electrolyte fuel cells and direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 316: 139-159. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.03.052 |
| [11] |
DUPUIS A C. Proton exchange membranes for fuel cells operated at medium temperatures: materials and experimental techniques[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2011, 56(3): 289-327. DOI:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2010.11.001 |
| [12] |
MORANDI C G, PEACH R, KRIEG H M, et al. Novel imidazolium-functionalized anion-exchange polymer PBI blend membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 476: 256-263. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2014.11.049 |
| [13] |
FECHETE R, DEMCO D E, ZHU X, et al. Water states and dynamics in perfluorinated ionomer membranes by 1H one- and two-dimensional NMR spectroscopy, relaxometry, and diffusometry[J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2014, 597: 6-15. DOI:10.1016/j.cplett.2014.02.024 |
| [14] |
KUSOGLU A, WEBER A Z. New insights into perfluorinated sulfonic-acid ionomers[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(3): 987-1104. DOI:10.1021/acs.chemrev.6b00159 |
| [15] |
OZDEN A, ERCELIK M, DEVRIM Y, et al. Evaluation of sulfonated polysulfone/zirconium hydrogen phosphate composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 256(Suppl C): 196-210. |
| [16] |
XIE H, TAO D, XIANG X, et al. Synthesis and properties of highly branched star-shaped sulfonated block poly(arylene ether)s as proton exchange membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015, 473: 226-236. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2014.09.015 |
| [17] |
SUN H, TANG B, WU P. Two-dimensional zeolitic imidazolate framework/carbon nanotube hybrid networks modified proton exchange membranes for improving transport properties[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(40): 35075-35085. |
| [18] |
YAO Z, ZHANG Z, HU M, et al. Perylene-based sulfonated aliphatic polyimides for fuel cell applications: performance enhancement by stacking of polymer chains[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 547(Suppl C): 43-50. |
| [19] |
LI Q, JENSEN J O, SAVINELL R F, et al. High temperature proton exchange membranes based on polybenzimidazoles for fuel cells[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2009, 34(5): 449-477. DOI:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2008.12.003 |
| [20] |
BOSE S, KUILA T, NGUYEN T X H, et al. Polymer membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell: recent advances and challenges[J]. Progress in Polymer Science, 2011, 36(6): 813-843. DOI:10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2011.01.003 |
| [21] |
LI C, HUANG N, JIANG Z, et al. Sulfonated holey graphene oxide paper with SPEEK membranes on its both sides: a sandwiched membrane with high performance for semi-passive direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 250: 68-76. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2017.08.058 |
| [22] |
LEE J R, WON J H, YOON K S, et al. Multilayer-structured, SiO2/sulfonated poly(phenylsulfone) composite membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012, 37(7): 6182-6188. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.07.085 |
| [23] |
LIU D S, ASHCRAFT J N, MANNARINO M M, et al. Spray layer-by-layer electrospun composite proton exchange membranes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(24): 3087-3095. DOI:10.1002/adfm.201202892 |
| [24] |
XIANG Y, LU S, JIANG S P. Layer-by-layer self-assembly in the development of electrochemical energy conversion and storage devices from fuel cells to supercapacitors[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41(21): 7291-7321. DOI:10.1039/c2cs35048c |
| [25] |
JIANG Y, HOU M, HAO J, et al. Enhanced durability of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketones)-based polymer electrolyte membranes by a multi-layer composite technology[J]. Solid State Ionics, 2017, 309: 33-40. DOI:10.1016/j.ssi.2017.07.003 |
| [26] |
LEE C, PARK J, JEON Y, et al. Phosphate-modified TiO2/ZrO2 nanofibrous web composite membrane for enhanced performance and durability of high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(7): 7645-7652. |
| [27] |
LI Z, YUE X, HE G, et al. Enhanced water retention and low-humidity proton conductivity of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) hybrid membrane by incorporating ellipsoidal microcapsules[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(26): 8398-8406. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.04.138 |
| [28] |
HE X, HE G, ZHAO A, et al. Facilitating proton transport in Nafion-based membranes at low humidity by incorporating multifunctional graphene oxide nanosheets[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(33): 27676-27687. |
| [29] |
RU C, LI Z, ZHAO C, et al. Enhanced proton conductivity of sulfonated hybrid poly(arylene ether ketone) membranes by incorporating an amino-sulfo bifunctionalized metal-organic framework for direct methanol fuel cells[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(9): 7963-7973. |
| [30] |
HAJDOK I, BONA A, WERNER H J, et al. Synthesis and characterization of fluorinated and sulfonated poly(arylene ether-1, 3, 4-oxadiazole) derivatives and their blend membranes[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2014, 52: 76-87. DOI:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2013.12.003 |
| [31] |
ABOUZARI-LOTF E, NASEF M M, GHASSEMI H, et al. Improved methanol barrier property of Nafion hybrid membrane by incorporating nanofibrous interlayer self-immobilized with high level of phosphotungstic acid[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(31): 17008-17015. |
| [32] |
DANG J, ZHAO L, ZHANG J, et al. Imidazole microcapsules toward enhanced phosphoric acid loading of polymer electrolyte membrane for anhydrous proton conduction[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 545: 88-98. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2017.09.062 |
| [33] |
ZHANG B, CAO Y, LI Z, et al. Proton exchange nanohybrid membranes with high phosphotungstic acid loading within metal-organic frameworks for PEMFC applications[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 240: 186-194. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2017.04.087 |
| [34] |
WANG J, YUE X, ZHANG Z, et al. Enhancement of proton conduction at low humidity by incorporating imidazole microcapsules into polymer electrolyte membranes[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(21): 4539-4546. DOI:10.1002/adfm.201201436 |
| [35] |
WANG J, ZHANG H, YANG X, et al. Enhanced water retention by using polymeric microcapsules to confer high proton conductivity on membranes at low humidity[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2011, 21(5): 971-978. DOI:10.1002/adfm.201001793 |
| [36] |
PARK J, WANG L, ADVANI S G, et al. Mechanical stability of H3PO4-doped PBI/hydrophilic-pretreated PTFE membranes for high temperature pemfcs[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2014, 120: 30-38. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2013.12.030 |
| [37] |
PARNIAN M J, ROWSHANZAMIR S, PRASAD A K, et al. High durability sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)-ceria nanocomposite membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 556: 12-22. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2018.03.083 |
| [38] |
SUN P, LI Z, JIN L, et al. Construction of proton channels and reinforcement of physicochemical properties of oPBI/FeSPP/GF high temperature PEM via building hydrogen bonding network[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(21): 14572-14582. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.04.092 |
| [39] |
SUN P, LI Z, JIN L, et al. Pre-oxidized acrylic fiber reinforced ferric sulfophenyl phosphate-doped polybenzimidazole-based high-temperature proton exchange membrane[J]. Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2017, 302(7): 1600468. DOI:10.1002/mame.201600468 |
| [40] |
KALLEM P, DROBEK M, JULBE A, et al. Hierarchical porous polybenzimidazole microsieves: an efficient architecture for anhydrous proton transport via polyionic liquids[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(17): 14844-14857. |
| [41] |
YANG J, JIANG H, GAO L, et al. Fabrication of crosslinked polybenzimidazole membranes by trifunctional crosslinkers for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(6): 3299-3307. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.12.141 |
| [42] |
SUN P, LI Z, WANG S, et al. Performance enhancement of polybenzimidazole based high temperature proton exchange membranes with multifunctional crosslinker and highly sulfonated polyaniline[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 549: 660-669. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2017.10.053 |
| [43] |
LIU X, ZHANG Y, CHEN Y, et al. A superhydrophobic bromomethylated poly(phenylene oxide) as a multifunctional polymer filler in SPEEK membrane towards neat methanol operation of direct methanol fuel cells[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 544: 58-67. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2017.09.013 |
| [44] |
SONG M, LU X, LI Z, et al. Compatible ionic crosslinking composite membranes based on SPEEK and PBI for high temperature proton exchange membranes[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(28): 12069-12081. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.05.227 |
| [45] |
QIU X, UEDA M, HU H, et al. Poly(2, 5-benzimidazole)-grafted graphene oxide as an effective proton conductor for construction of nanocomposite proton exchange membrane[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(38): 33049-33058. |
| [46] |
YANG J, XU Y, LIU P, et al. Epoxides cross-linked hexafluoropropylidene polybenzimidazole membranes for application as high temperature proton exchange membranes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2015, 160: 281-287. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2015.01.094 |
| [47] |
SUN P, LI Z, DONG F, et al. High temperature proton exchange membranes based on cerium sulfophenyl phosphate doped polybenzimidazole by end-group protection and hot-pressing method[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(1): 486-495. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.09.174 |
| [48] |
D'URSO C, OLDANI C, BAGLIO V, et al. Fuel cell performance and durability investigation of bimetallic radical scavengers in aquivion® perfluorosulfonic acid membranes[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(46): 27987-27994. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.07.111 |
| [49] |
SHIN D, HAN M, SHUL Y G, et al. Analysis of cerium-composite polymer-electrolyte membranes during and after accelerated oxidative-stability test[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 378: 468-474. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.12.074 |
| [50] |
KLUMPEN C, GODRICH S, PAPASTAVROU G, et al. Water mediated proton conduction in a sulfonated microporous organic polymer[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(54): 7592-7595. DOI:10.1039/C7CC02117H |
| [51] |
VUILLEUMIER R, BORGIS D. Proton conduction: hopping along hydrogen bonds[J]. Nature Chemistry, 2012, 4(6): 432-433. DOI:10.1038/nchem.1365 |
| [52] |
JIA W, WU P. Stable boron nitride nanocomposites based membranes for high-efficiency proton conduction[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 273: 162-169. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2018.04.017 |
| [53] |
DONNADIO A, D'AMATO R, MARMOTTINI F, et al. On the evolution of proton conductivity of aquivion membranes loaded with CeO2 based nanofillers: effect of temperature and relative humidity[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 574: 17-23. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2018.12.045 |
| [54] |
ZHANG J, ZHANG J, BAI H, et al. A new high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane based on tri-functional group grafted polysulfone for fuel cell application[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 572: 496-503. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2018.11.035 |
| [55] |
SHAHGALDI S, ALAEFOUR I, LI X. The impact of short side chain ionomer on polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell performance and durability[J]. Applied Energy, 2018, 217: 295-302. DOI:10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.02.154 |
| [56] |
TRIGG E B, GAINES T W, MARÉCHAL M, et al. Self-assembled highly ordered acid layers in precisely sulfonated polyethylene produce efficient proton transport[J]. Nature Materials, 2018, 17(8): 725-731. DOI:10.1038/s41563-018-0097-2 |
| [57] |
FENG Z M, ZHAO Y, LI X, et al. Synthesis and characterization of a novel norbornene based copolymer[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(Suppl 2): 439-444. |
| [58] |
WANG L S, LAI A N, ZHUO Y Z, et al. Properties of hybrid SPEK-C/GO composite proton exchange membranes[J]. CIESC Journal, 2015, 66(9): 3605-3610. |
| [59] |
ONO Y, GOTO R, HARA M, et al. High proton conduction of organized sulfonated polyimide thin films with planar and bent backbones[J]. Macromolecules, 2018, 51(9): 3351-3359. DOI:10.1021/acs.macromol.8b00301 |
| [60] |
GAO S, XU H, LUO T, et al. Novel proton conducting membranes based on cross-linked sulfonated polyphosphazenes and poly(ether ether ketone)[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 536: 1-10. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2017.04.065 |
| [61] |
PINGITORE A T, HUANG F, QIAN G, et al. Durable high polymer content m/p-polybenzimidazole membranes for extended lifetime electrochemical devices[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 2(3): 1720-1726. DOI:10.1021/acsaem.8b01820 |
| [62] |
JANKOWSKA A, ZALEWSKA A, SKALSKA A, et al. Proton conductivity of imidazole entrapped in microporous molecular sieves[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(16): 2475-2478. DOI:10.1039/C7CC00690J |
| [63] |
HOSHINO T, HAYASHI K, SAKAMOTO W, et al. One-pot synthesis of proton-conductive inorganic-organic hybrid membranes from organoalkoxysilane and phosphonic acid derivatives[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016, 502: 133-140. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2015.12.045 |
| [64] |
CHEN X, LV H, LIN Q, et al. Partially fluorinated poly(arylene ether)s bearing long alkyl sulfonate side chains for stable and highly conductive proton exchange membranes[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 549: 12-22. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2017.11.066 |
| [65] |
YANG S, KIM D. Antioxidant proton conductive toughening agent for the hydrocarbon based proton exchange polymer membrane for enhanced cell performance and durability in fuel cell[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 393: 11-18. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.05.014 |
| [66] |
BU F, ZHANG Y, HONG L, et al. 1, 2, 4-triazole functionalized poly(arylene ether ketone) for high temperature proton exchange membrane with enhanced oxidative stability[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 545(Suppl C): 167-175. |
| [67] |
LIU J, YU L, CAI X, et al. Sandwiching h-BN monolayer films between sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) and Nafion for proton exchange membranes with improved ion selectivity[J]. ACS Nano, 2019, 13(2): 2094-2102. |
| [68] |
YANG J, HE R, AILI D, et al. Synthesis of polybenzimidazoles[M]. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2016.
|
| [69] |
ASENSIO J A, SANCHEZ E M, GOMEZ-ROMERO P. Proton-conducting membranes based on benzimidazole polymers for high-temperature PEM fuel cells. a chemical quest[J]. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(8): 3210-3239. DOI:10.1039/b922650h |
| [70] |
KORTE C, CONTI F, WACKERL J, et al. Uptake of protic electrolytes by polybenzimidazole-type polymers:absorption isotherms and electrolyte/polymer interactions[J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2015, 45(8): 857-871. DOI:10.1007/s10800-015-0855-7 |
| [71] |
YU T L. Polybenzimidazole/porous poly(tetrafluoro ethylene) composite membranes[M]. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2016.
|
| [72] |
PERRY A K, MORE L K, ANDREW PAYZANT E, et al. A comparative study of phosphoric acid-doped m-PBI membranes[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B, 2014, 52(1): 26-35. DOI:10.1002/polb.23403 |
| [73] |
QUARTARONE E, MUSTARELLI P. Polymer fuel cells based on polybenzimidazole/H3PO4[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(4): 6436-6444. |
| [74] |
WANG S W, DONG F L, LI Z F. Proton-conducting membrane preparation based on SiO2-riveted phosphotungstic acid and poly (2, 5-benzimidazole) via direct casting method and its durability[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2012, 47(11): 4743-4749. DOI:10.1007/s10853-012-6350-1 |
| [75] |
ZHANG Q, LIU H, LI X, et al. Synthesis and characterization of polybenzimidazole/α-zirconium phosphate composites as proton exchange membrane[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2016, 56(6): 622-628. |
| [76] |
KIM T H, LIM T W, PARK Y S, et al. Proton-conducting zirconium pyrophosphate/poly(2, 5-benzimidazole) composite membranes prepared by a PPA direct casting method[J]. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 2007, 208(21): 2293-2302. DOI:10.1002/macp.200700261 |
| [77] |
LINLIN M, MISHRA A K, KIM N H, et al. Poly(2, 5-benzimidazole)-silica nanocomposite membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell[J]. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012, 411-412: 91-98. DOI:10.1016/j.memsci.2012.04.018 |
| [78] |
JHENG L C, HUANG C Y, HSU S L C. Sulfonated MWNT and imidazole functionalized MWNT/polybenzimidazole composite membranes for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(3): 1524-1534. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.10.111 |
| [79] |
SUN P, LI Z, SONG M, et al. Preparation and characterization of zirconium phytate as a novel solid intermediate temperature proton conductor[J]. Materials Letters, 2017, 191: 161-164. DOI:10.1016/j.matlet.2016.12.076 |
| [80] |
JIANG F, PU H, MEYER W H, et al. A new anhydrous proton conductor based on polybenzimidazole and tridecyl phosphate[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2008, 53(13): 4495-4499. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2008.01.022 |
| [81] |
LIN H L, TANG T H, HU C R, et al. Poly(benzimidazole)/silica-ethyl-phosphoric acid hybrid membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 201: 72-80. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2011.10.110 |
| [82] |
DONG F L, LI Z F, WANG S W, et al. Synthesis and characteristics of proton-conducting membranes based on cerium sulfophenyl phosphate and poly (2, 5-benzimidazole) by hot-pressing method[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(17): 11068-11074. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.05.128 |
| [83] |
WANG S, SUN P, HAO X, et al. Ferric sulfophenyl phosphate bonded with phosphotungstic acid as a novel intercalated high-temperature inorganic-organic proton conductor[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2018, 213: 35-43. DOI:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2018.04.009 |
| [84] |
WANG S, SUN P, LI Z, et al. Comprehensive performance enhancement of polybenzimidazole based high temperature proton exchange membranes by doping with a novel intercalated proton conductor[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(21): 9994-10003. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.04.089 |
| [85] |
TANAKA M, TAKEDA Y, WAKIYA T, et al. Acid-doped polymer nanofiber framework: three-dimensional proton conductive network for high-performance fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2017, 342: 125-134. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.12.018 |
| [86] |
KERRES J A, KATZFUß A, CHROMIK A, et al. Sulfonated poly(styrene)s-PBIOO® blend membranes: thermo-oxidative stability and conductivity[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2014, 131(4): 39889. |
| [87] |
BERBER M R, FUJIGAYA T, SASAKI K, et al. Remarkably durable high temperature polymer electrolyte fuel cell based on poly(vinylphosphonic acid)-doped polybenzimidazole[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3: 1764. DOI:10.1038/srep01764 |
| [88] |
REWAR A S, CHAUDHARI H D, ILLATHVALAPPIL R, et al. New approach of blending polymeric ionic liquid with polybenzimidazole (PBI) for enhancing physical and electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(35): 14449-14458. DOI:10.1039/C4TA02184C |
| [89] |
TADAVANI K F, ABDOLMALEKI A, MOLAVIAN M R, et al. Synergistic behavior of phosphonated and sulfonated groups on proton conductivity and their performance for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PENFCs)[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2017, 31(10): 11460-11470. |
| [90] |
YANG J, AILI D, LI Q, et al. Benzimidazole grafted polybenzimidazoles for proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Polymer Chemistry, 2013, 4(17): 4768-4775. DOI:10.1039/c3py00408b |
| [91] |
DIAZ L A, ABUIN G C, CORTI H R. Acid-doped ABPBI membranes prepared by low-temperature casting: Proton conductivity and water uptake properties compared with other polybenzimidazole-based membranes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2016, 163(6): F485-F491. DOI:10.1149/2.0671606jes |
| [92] |
YUAN Q, SUN G H, HAN K F, et al. Copolymerization of 4-(3, 4-diamino-phenoxy)-benzoic acid and 3, 4-diaminobenzoic acid towards H3PO4-doped PBI membranes for proton conductor with better processability[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2016, 85: 175-186. DOI:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.10.002 |
| [93] |
NI J, HU M, LIU D, et al. Synthesis and properties of highly branched polybenzimidazoles as proton exchange membranes for high-temperature fuel cells[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2016, 4(21): 4814-4821. DOI:10.1039/C6TC00862C |
| [94] |
YANG J, CLEEMANN L N, STEENBERG T, et al. High molecular weight polybenzimidazole membranes for high temperature PEMFC[J]. Fuel Cells, 2014, 14(1): 7-15. DOI:10.1002/fuce.201300070 |
| [95] |
LI X, WANG P, LIU Z, et al. Arylether-type polybenzimidazoles bearing benzimidazolyl pendants for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2018, 393: 99-107. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2018.05.011 |
| [96] |
DEVRIM Y, DEVRIM H, EROGLU I. Polybenzimidazole/SiO2 hybrid membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(23): 10044-10052. DOI:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.02.043 |
| [97] |
SINGHA S, JANA T. Influence of interfacial interactions on the properties of polybenzimidazole/clay nanocomposite electrolyte membrane[J]. Polymer, 2016, 98: 20-31. DOI:10.1016/j.polymer.2016.06.007 |
| [98] |
GUERRERO MORENO N, GERVASIO D, GODÍNEZ GARCÍA A, et al. Polybenzimidazole-multiwall carbon nanotubes composite membranes for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 300: 229-237. DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.09.070 |
| [99] |
ÖZDEMIR Y, ÖZKAN N, DEVRIM Y. Fabrication and characterization of cross-linked polybenzimidazole based membranes for high temperature PEM fuel cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 245: 1-13. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2017.05.111 |
| [100] |
AILI D, LI Q, CHRISTENSEN E, et al. Crosslinking of polybenzimidazole membranes by divinylsulfone post-treatment for high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cell applications[J]. Polymer International, 2011, 60(8): 1201-1207. DOI:10.1002/pi.3063 |
| [101] |
YANG J, LI Q, CLEEMANN L N, et al. Crosslinked hexafluoropropylidene polybenzimidazole membranes with chloromethyl polysulfone for fuel cell applications[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2013, 3(5): 622-630. DOI:10.1002/aenm.201200710 |
| [102] |
WANG L, ADVANI S G, PRASAD A K. PBI/Nafion/SiO2 hybrid membrane for high-temperature low-humidity fuel cell applications[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2013, 105: 530-534. DOI:10.1016/j.electacta.2013.05.043 |
 2021, Vol. 49
2021, Vol. 49