粒子滤波(Particle Filter,PF)是由粒子及其权重组成的离散随机测度近似概率分布[1]。由于其在处理非线性非高斯系统的状态滤波问题的优势[2-3],在目标跟踪、卫星导航和故障检测等方面得到了广泛的应用[4-7]。
PF的主要问题是随着迭代次数增加,存在粒子退化现象。Gordon等[8]提出改进方法,解决了粒子退化部分问题,但也带来粒子多样性丧失和计算复杂等问题。为解决这些问题,目前已有的改进PF算法有:改进重采样的PF算法,将PSO(Particle Swarm Optimization,PSO)算法与PF算法结合的PSO-PF算法,将自适应PSO与PF结合的改进算法等[9-13]。将PSO引入到PF算法中,使得粒子分布向高后验概率区域分布,改善粒子退化问题,提高滤波精度。但PSO存在陷入局部最优、计算量大等问题。
本文利用混沌的遍历性、随机性的特点进行搜索,将变量从混沌空间映射到解空间,对当前粒子个体产生混沌扰动,使粒子跳出局部极值区间,提高粒子样本的质量。并给出混沌粒子群优化改进粒子滤波(Chaos Particle Swarm Optimization Particle Filter,CPSO-PF)算法,在高斯噪声和非高斯噪声环境下对算法的性能进行验证,提高了滤波的精度和稳定性,减少了迭代次数。
1 PF算法设非线性系统的状态方程和量测方程为
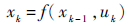
|
(1) |
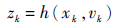
|
(2) |
式中:xk为k时刻的状态;zk为k时刻的量测值;f(·)为状态转移函数;h(·)为量测函数;uk和vk为相互独立的噪声[14]。
基本PF算法的步骤如下:
步骤1 初始化,产生粒子集{x0i}i=1N,粒子的权值为1/N,N为粒子数目。
步骤2 重要性采样,在k时刻,更新粒子权值
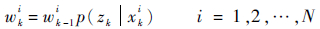
|
(3) |
步骤3 状态预测,利用状态方程预测下一时刻状态参数xk+1i。
步骤4 权值归一化
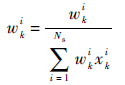
|
(4) |
步骤5 重采样,计算得到新的粒子集为{xki,i=0,1,…,N}。
步骤6 计算状态估计值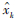
步骤7 时刻k=k+1,转到步骤2。
2 CPSO-PF算法混沌运动具有随机性、遍历性和对初始条件敏感的依赖性等特点[15-16]。Logistic映射是一个典型的混沌系统:
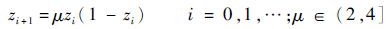
|
(5) |
式中:μ为控制参数,令μ=4,0≤z0≤1,利用产生的混沌序列进行优化搜索。优化搜索是利用Logistic映射系统产生一组混沌序列,将其序列映射到样本空间中,使样本呈现为混沌状态,然后利用混沌变量进行搜索。
2.1 CPSO算法将混沌引入到PSO算法中,得到改进的PSO算法——CPSO算法。求解最优问题的函数为
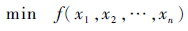
|
(6) |
混沌粒子群优化算法步骤如下:
While(迭代次数k<最大迭代次数)
For i=1:N
1) 按式(5)将随机产生的n组序列混沌化处理,记为u。
2) 将u的各个分量引入扰动,混沌扰动范围为[a,b],扰动量记为Δx。将扰动量和原分量结合在一起。
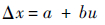
|
(7) |
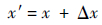
|
(8) |
3) 将式(7)产生的值通过式(5)进行比较,找出最优的一组解,即混沌初始化。
若f′<f,则x′k=xk,否则x′k不变。
End For
k=k+1,计算第i个粒子的适应度值f,若粒子的适应度值大于原来的个体极值,设置当前适应度值为个体极值pbest,根据个体极值找出全局极值gbest。
End While
最后,输出全局极值gbest。
2.2 CPSO-PF算法步骤为优化PF的采样过程,将CPSO算法融入到PF算法中。将最新的观测值引入采样过程,并定义适应度函数为
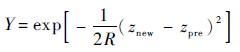
|
(9) |
式中:R为观测噪声;znew为最新量测值;zpre为预测值。文中采用CPSO算法对PF算法进行优化。CPSO-PF算法的步骤如下。
步骤1 初始化,令k=0时刻,粒子数目为N,用{x0:ki,wki}i=1N表示,令每个样本的初始的权值为{wki=1/N,i=1,2,…,N}。
步骤2 利用状态模型计算重要性权值。
步骤3 执行CPSO算法。
① 利用随机数产生函数,产生N个粒子,通过Logistic映射系统进行混沌搜索,并将其映射到解空间,得到N个混沌赋值后的粒子集{xki,1/N}i=1N。
② 利用目标函数式(6),计算出一组最优解作为当前初始粒子集。
③ 计算每个粒子的适应度值,并更新各个粒子的个体极值和全局极值。
④ 更新每个粒子的状态,使粒子逼近真实状态。
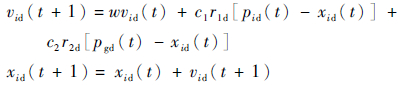
|
式中:vid为粒子的速度;w为惯性因子;c1和c2为加速度;rid和r2d为[0, 1]间的随机数;Pid为最优状态值;Pgd为种群中的目标函数值最大的粒子状态值;xid为粒子的位置。
⑤ 优化是否完成。若没有,则返回第③步。
步骤4 状态预测,利用状态方程预测下一时刻状态参数xk+1i。
步骤5 权值更新,在k时刻更新粒子的权值:
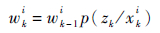
|
归一化权值为
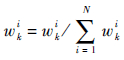
|
步骤6 重采样,当有效粒子数 Neff=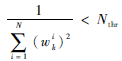
步骤7 计算状态估计值。
步骤8 程序是否结束,若是,结束;否则,k=k+1,返回执行步骤2。
3 算法验证与结果分析算法引用单变量非静态增长模型(Univariate Nonstationary Growth Model,UNGM)进行验证,该模型是研究比较各种PF算法性能的典型验证模型。实验环境为Lenovo E47A,内存为DDR2-4GB,Inter Core i5-2450M。状态模型和量测模型如下:
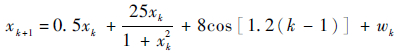
|
(10) |
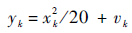
|
(11) |
式中:yk为量测量;wk为噪声。文中用PF、PSO-PF和CPSO-PF不同算法对该非线性系统进行状态估计和跟踪。为验证算法的可行性和有效性,采用均方根误差(RMSE):
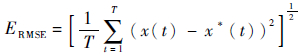
|
(12) |
式中:T为仿真时间长度;x(t)为t时刻真实的状态值;x*(t)为t时刻算法估计的状态值。
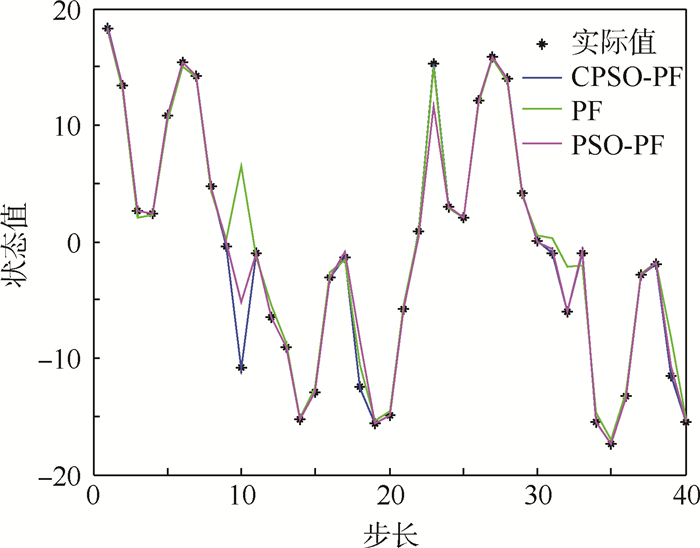
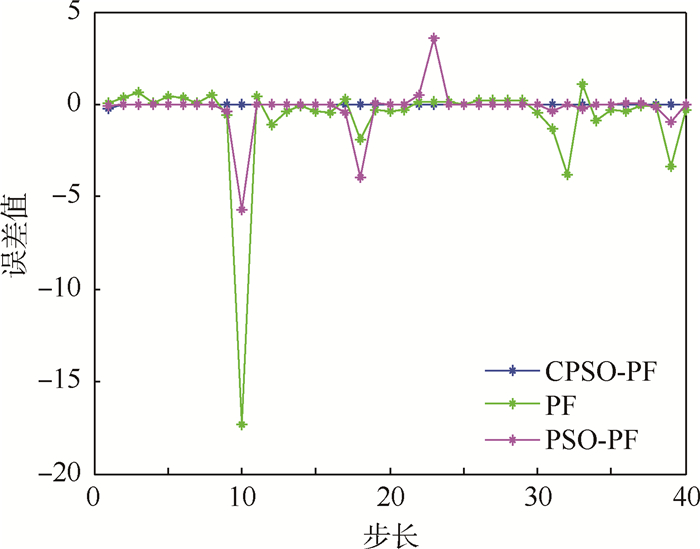
3.1 高斯噪声下算法仿真验证1) 令粒子数N=50,过程噪声wk~(0,1),测量噪声vk~(0,1),均服从零均值高斯分布。仿真结果如图 1所示,跟踪误差曲线如图 2所示。
|
| 图 1 N=50时高斯噪声下不同算法跟踪结果比较 Fig. 1 Comparison of different algorithms’ tracking results under Gaussian noise at N=50 |
|
| 图 2 N=50时高斯噪声下不同算法跟踪误差比较 Fig. 2 Comparison of different algorithms’ tracking error under Gaussian noise at N=50 |
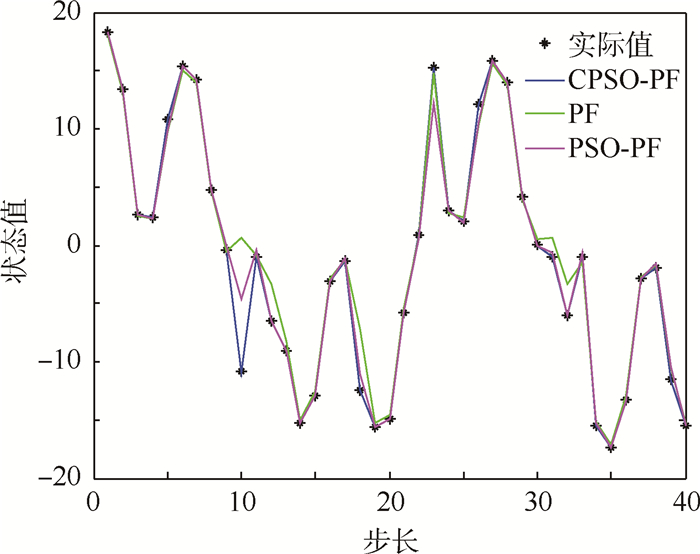
2) 令粒子数N=100,过程噪声wk~(0,1),测量噪声vk~(0,1),均服从零均值高斯分布。仿真结果如图 3所示,跟踪误差曲线如图 4所示。
|
| 图 3 N=100时高斯噪声下不同算法跟踪结果比较 Fig. 3 Comparison of different algorithms’ tracking results under Gaussian noise at N=100 |

|
| 图 4 N=100时高斯噪声下不同算法跟踪误差比较 Fig. 4 Comparison of different algorithms’ tracking error under Gaussian noise at N=100 |
从仿真结果可以看出,PF算法跟踪不是很稳定,在第10个时刻时,PF算法出现了跟踪错误。PSO-PF算法虽然跟踪总体是正确的,但是精度性能不是很理想,CPSO-PF算法跟踪稳定,误差最小。
表 1为高斯噪声下不同算法性能比较,从表中可以看出,PSO-PF算法和CPSO-PF算法的误差明显小于PF算法,CPSO-PF算法的误差较小,且CPSO-PF算法与PSO-PF算法相比减少了运算时间。此外,随着粒子数目的增加,算法跟踪的效果有一定的改善。由于PSO和CPSO算法对迭代的次数敏感,算法通过增加粒子数提高精度会大量增加算法的计算量,应适当选取粒子样本数目。
| 参数 | 算法 | ERMSE | 运行时间/s |
| N=50 | PF | 2.803 4 | 0.141 0 |
| PSO-PF | 1.252 8 | 0.347 6 | |
| CPSO-PF | 0.022 9 | 0.195 8 | |
| N=100 | PF | 2.172 7 | 0.160 5 |
| PSO-PF | 1.172 8 | 0.640 4 | |
| CPSO-PF | 0.022 4 | 0.262 6 |
3) 算法的有效粒子数是用来衡量算法是否出现粒子退化现象的一个标准。Doucet[9]证明退化现象是不可避免的,随着算法的递推,大部分粒子的权值都接近于零而被淘汰。有效粒子数,即有效采样尺度Neff,通常取其近似值,定义为
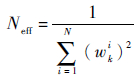
|
(13) |
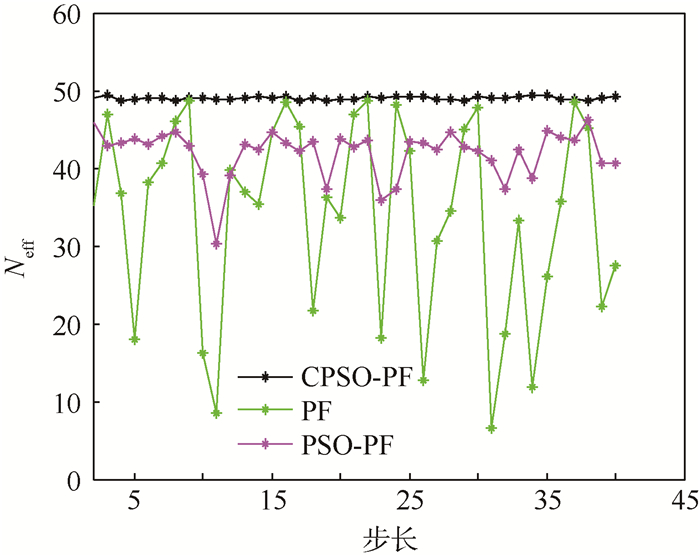
在N=50时,不同算法每个时刻的有效粒子数如图 5所示。
|
| 图 5 不同算法每个时刻的有效粒子数目 Fig. 5 Effective particle number of different algorithms for each step |
从图 5中可以看出,PF算法的有效粒子数较少,PSO-PF算法和CPSO-PF算法的有效粒子数目虽然很接近,但从动态的有效粒子数目可以看出PSO-PF算法的有效粒子数出现明显的波动,而CPSO-PF算法的有效粒子数目更稳定。
3.2 非高斯噪声下算法仿真验证为验证提出的算法具有更普遍的应用范围以及算法的有效性。采用非高斯Alpha稳定分布噪声仿真验证算法的性能。
1) 非高斯Alpha稳定分布
Alpha稳定分布又称为非高斯稳定分布、重尾分布。在实际应用中通常用于描述高斯分布无法描述的噪声。Alpha稳定分布S(α,β,γ,δ)具有4个参数:特征因子α,偏斜因子β,尺度参数γ,中心位置偏移参数δ。图 6为不同α的Alpha分布,α越小噪声分布拖尾越严重。
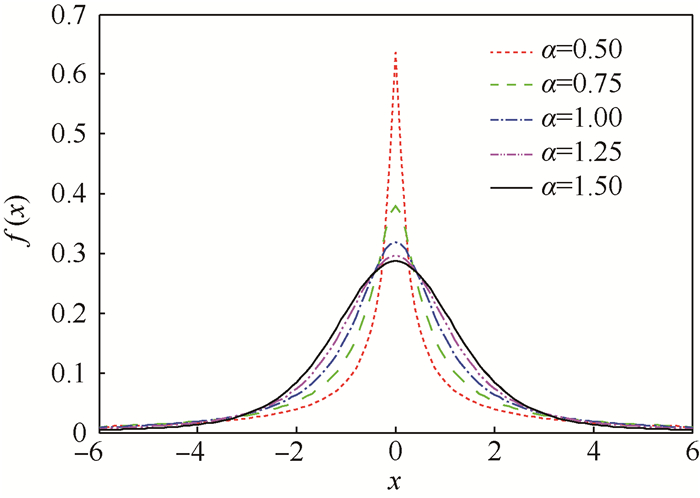
|
| 图 6 不同特征因子的Alpha稳定分布曲线 Fig. 6 Alpha stable distribution curves of different characteristic factors |
2) 算法仿真验证
状态模型和量测模型采用式(10)和式(11)的非线性模型,仿真时选取各参数的值为α=1,β=0,γ=1,δ=0,即S(1,0,1,0)。
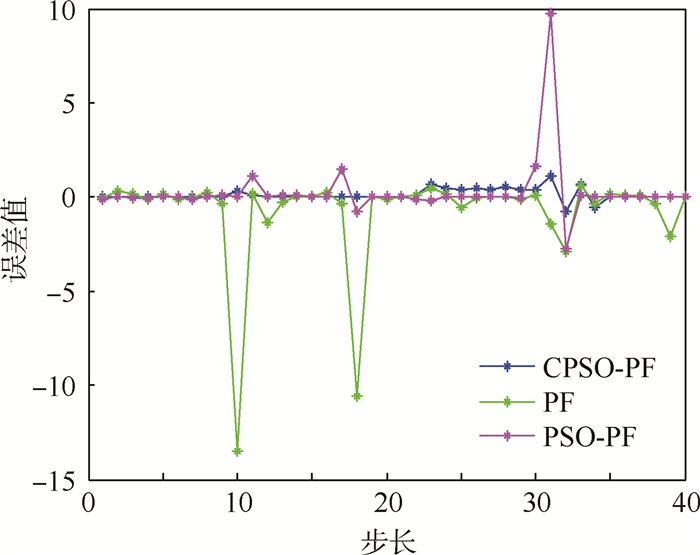
① 令粒子数N=50,过程噪声wk和测量噪声vk符合上述的Alpha稳定分布。仿真结果如图 7所示,跟踪误差曲线如图 8所示。
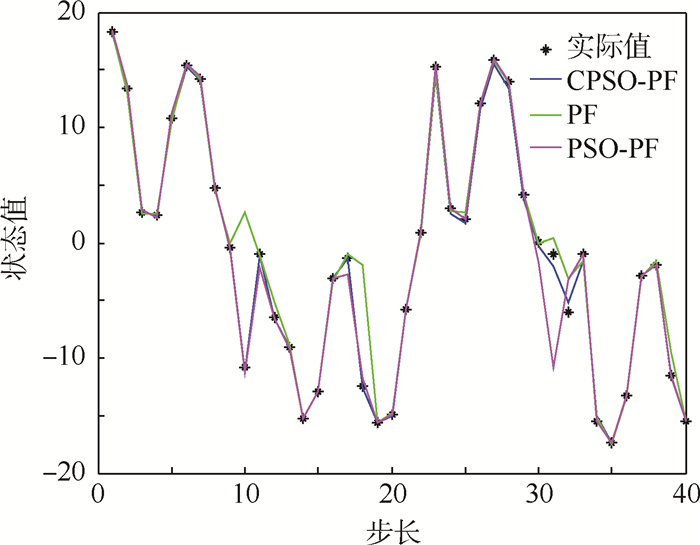
|
| 图 7 N=50时非高斯噪声下不同算法跟踪结果比较 Fig. 7 Comparison of different algorithms’ tracking results under non-Gaussian noise at N=50 |
|
| 图 8 N=50时非高斯噪声下不同算法跟踪误差比较 Fig. 8 Comparison of different algorithms’ tracking error under non-Gaussian noise at N=50 |
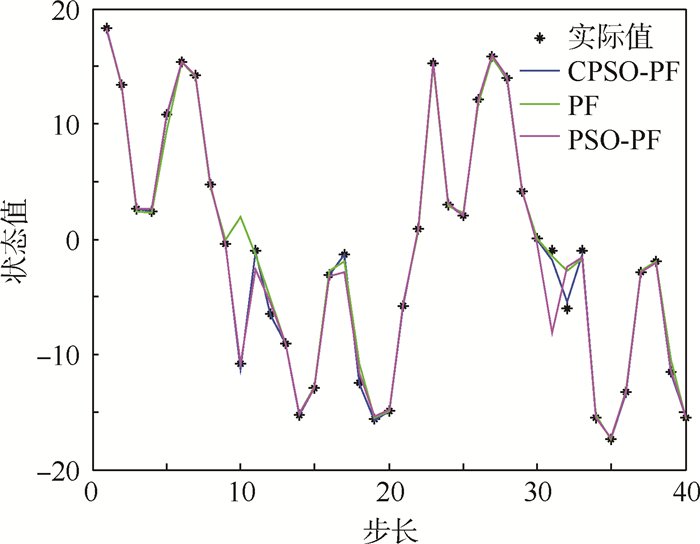
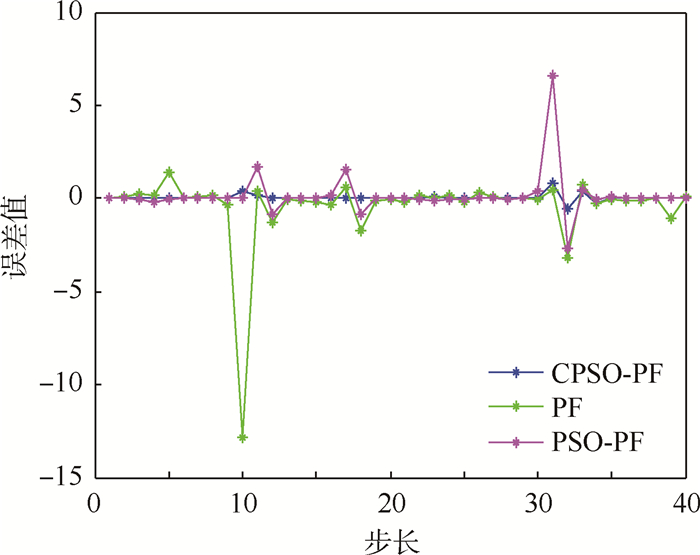
② 令粒子数N=100,过程噪声wk和测量噪声vk符合上述的Alpha稳定分布。仿真结果如图 9所示,跟踪误差结果如图 10所示。
|
| 图 9 N=100时非高斯噪声下不同算法跟踪结果比较 Fig. 9 Comparison of different algorithms’ tracking results under non-Gaussian noise at N=100 |
|
| 图 10 N=100时非高斯噪声下不同算法跟踪误差比较 Fig. 10 Comparison of different algorithms’ tracking error under non-Gaussian noise at N=100 |
从图 7~图 10的结果可以看出,在非高斯噪声下3种算法受到了影响,但与高斯噪声下的结论基本一致。表 2为非高斯噪声下不同算法性能比较,从表中可以看出,在非高斯噪声下PF算法的跟踪误差较大,CPSO-PF算法的均方根误差最小;在运算时间方面,PF算法是最小的,算法的复杂度较小;PSO-PF算法需要迭代多次来寻优,运算时间较长;CPSO-PF算法加入了混沌扰动,减少了迭代次数,运算时间相应的减少。总的来说,CPSO-PF算法跟踪误差较高,稳定性较好。从表中还可以看出,随着粒子数的增加,跟踪误差明显降低,但粒子数N的增加会影响算法的运行效率。
| 参数 | 算法 | RMSE | 运行时间/s |
| N=50 | PF | 3.308 4 | 0.140 9 |
| PSO-PF | 1.652 1 | 0.334 3 | |
| CPSO-PF | 0.289 6 | 0.178 4 | |
| N=100 | PF | 2.542 5 | 0.142 0 |
| PSO-PF | 1.196 5 | 0.651 7 | |
| CPSO-PF | 0.215 9 | 0.274 2 |
4 结 论
本文将混沌序列引入到粒子群算法中,提出了一种混沌粒子群优化粒子滤波算法,利用在粒子群的每次迭代过程中,引入混沌提高样本的质量,通过混沌扰动增加算法的全局寻优能力。在高斯噪声和非高斯噪声下算法仿真验证表明:
1) 提出的算法克服了PSO-PF算法存在的问题,提高了PF算法的跟踪性能,降低了运算时间。
2) 提出的算法提高了有效粒子数目,降低了均方根误差,其整体性能优于基本PF算法和PSO-PF算法。
3) PF算法在Alpha稳定分布的非高斯估计问题中是有效的。
| [1] | CARPENTER J, CLIFFORD P, FEARNHEAD P. Improved particle filter for nonlinear problems[J]. IEEE Proceedings-Radar Sonar and Navigation,1999, 146 (1) : 1 –7. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [2] | 佘黎煌, 张石, 王鸿雁. 非高斯条件下基于粒子滤波的T波交替检测算法[J]. 电子学报,2014, 42 (2) : 223 –229. SHE L H, ZHANG S, WANG H Y. A T-wave alternans detection algotithm based on particle filtering in non-Gaussian environment[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica,2014, 42 (2) : 223 –229. (in Chinese). |
| Cited By in Cnki (0) | Click to display the text | |
| [3] | 张玲霞, 刘志仓, 王辉, 等. 非线性系统故障诊断的粒子滤波方法[J]. 电子学报,2015, 43 (3) : 615 –619. ZHANG L X, LIU Z C, WANG H, et al. Particle filter method for fault diagnosis in nonlinear system[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica,2015, 43 (3) : 615 –619. (in Chinese). |
| Cited By in Cnki (0) | Click to display the text | |
| [4] | GUSTAFSSON F, BERGMAN N, FORSSELL U, et al. Particle filters for positioning,navigation,and tracking[J]. IEEE Transaction on Signal Processing,2002, 50 (2) : 425 –437. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [5] | IBARGUREN A, MAURTUA I, PEREZ M A, et al. Multiple target tracking based on particle filtering for safety in industrial robotic cells[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems,2015, 72 : 105 –113. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [6] | 张华, 张有光, 李国彦. 基于混合粒子滤波的载波估计算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报,2013, 39 (2) : 184 –189. ZHANG H, ZHANG Y G, LI G Y. Carrier estimation algorithm based on novel hybrid particle filtering[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2013, 39 (2) : 184 –189. (in Chinese). |
| Cited By in Cnki (0) | Click to display the text | |
| [7] | KADIRKAMANATHAN V, LI P, JAWARD M H, et al. Particle filtering based fault detection in nonlinear stochastic systems[J]. International Journal of Systems Science,2002, 33 (4) : 259 –265. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [8] | GORDON N, SALMOND D, SMITH A. Novel approach to nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian state estimation[J]. IEEE Proceedings on Radar,Sonar and Navigation,1993, 140 (2) : 107 –113. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [9] | DOUCET A, GODSILL S, ANDRIEU C. On sequential Monte Carlo sampling methods for Bayesian filtering[J]. Statistics and Computing,2000, 10 (3) : 197 –208. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [10] | FU X Y, JIA Y M. An improvement on resampling algorithm of particle filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,2010, 58 (10) : 5414 –5420. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [11] | ZHAO J, LI Z Y. Particle filter based on particle swarm optimization resampling for vision tracking[J]. Expert Systems with Applications,2010, 37 (12) : 8910 –8914. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [12] | ZHAO Z S, FENG X, LIN Y Y, et al. Improved rao-blackwellized particle filter by particle swarm optimization[J]. Journal of Applied Mathematics,2013 (4) : 1 –6. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [13] | 陈志敏, 薄煜明, 吴盘龙, 等. 基于自适应粒子群优化的新型粒子滤波在目标跟踪中的应用[J]. 控制与决策,2013, 28 (2) : 193 –200. CHEN Z M, BO Y M, WU P L, et al. Novel particle filter algorithm based on adaptive particle swarm optimization and its application to radar target tracking[J]. Control and Decision,2013, 28 (2) : 193 –200. (in Chinese). |
| Cited By in Cnki (0) | Click to display the text | |
| [14] | ARULAMPALAM M S, MASKELL S, GORDON N, et al. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing,2002, 50 (2) : 174 –188. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [15] | LORENZ E N. The essence of chaos[M]. Seattle: University of Washington Press, 1993 : 3 -7. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [16] | WAKANO J Y, HAUERT C. Pattern formation and chaos in spatial ecological public goods games[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology,2011, 268 (1) : 30 –38. |
| Click to display the text | |



