2. 福州大学材料科学与工程学院, 福州 350100;
3. 北京航空航天大学材料科学与工程学院, 北京 100083
2. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou 350100, China;
3. School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Beijing 100083, China
Heusler合金是一类包含超过1 500个成员的独特金属间化合物材料,它的化学通式为XYZ(通常称为半Heusler)或者X2YZ(全Heusler),其中X、Y是过渡金属元素,Z为主族元素[1]。很多Heusler合金的性质可以通过简单地计算价电子数来预测[2],例如,价电子数约为27的非磁性Heusler合金是超导体[2]。自从1903年Heusler等[3]发现Heusler合金开始,一个多世纪来Heusler合金仍然受到研究者的广泛关注。近年来,Heusler化合物在半金属铁磁体[4, 5, 6, 7]、补偿铁磁性材料[8]、形状记忆合金[9, 10, 11]、超导体[12, 13]、热电材料[14, 15]和拓扑绝缘体[16, 17]等领域中均表现出了优异的性能。此外,单一Heusler合金可以实现2种甚至多种功能的复合,比如磁光[18]、磁致热[19]和磁构[9]材料。具有独特电子结构的自旋半金属磁电Heusler合金的导带电子的自旋极化率接近100%,是一类非常适合应用于自旋电子学[12]中的新材料[1]。这类自旋半金属材料中,一种自旋方向的电子结构呈现半导体特性,而另一种相反自旋方向的电子结构则会表现出金属性。1983年,Heusler合金MnNiS[20]、Co2MnSn和Co2MnAl[21]先后被研究人员发现具有自旋半金属性。在随后的理论研究中,一些Co基[22]、Mn基[23]、Cr基[24]、V基[25]和Fe基[26]Heusler合金也被预测出具有自旋半金属性。基于这些理论研究,研究者们开展了大量的实验研究,并将Heusler合金应用于自旋电子器件中。例如,Co2FeAl可以应用到磁隧道结中[27],Co2MnGe则被应用到电流垂直平面巨磁阻自旋阀中的铁磁层材料中[28]。
在这些Heusler合金中,Mn2CoAl最初被Xing[29]和Liu[23]等预测为半金属,但是在2013年被Ouardi等[30]证实为一种新型的自旋无带隙半导体(SGS)。与半金属不同,SGS中一个自旋方向的电子结构表现出半导体特性,而另一个自旋方向的导带底和价带顶在费米能级相接触而具有零带隙特征[31]。在SGS中,不仅导带中激发态电子的自旋极化率接近100%,价带中空穴的自旋极化也接近100%。这一特性导致了Heusler合金Mn2CoAl具有高电导率、高居里温度、反常霍尔效应小和大磁矩等独特的输运性能。因此这种Heusler合金是应用于自旋电子学研究的理想材料,有望被应用到自旋探测器、电磁辐射产生器、自旋二极管和自旋图像探测器中[29, 32]。在Heusler合金中,Mn2CoSi[29, 33]、Ti2CoAl[34]和Ti2CoSi[35]被预测为半金属,在自旋电子学应用领域有巨大潜力[33, 36, 37]。由于M2CoA(M=Mn,Ti;A=Al,Si)型Heusler合金在自旋电子学领域中具有巨大应用潜力[38],系统性地研究该系列自旋无带隙Heusler合金的电子结构具有十分重要的意义。
本文采用基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理计算方法,系统性地开展了M2CoA型Heusler合金Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi的自旋无带隙电子结构特征与磁学性质研究,为该系列Heusler合金在自旋电子学中的应用提供理论基础。
1 计算方法本研究基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理方法,采用计算软件包(VASP)进行计算[39]。交换关联能采用基于投影缀加平面波方法(PAW)生成的广义梯度近似(GGA)[40]的Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof(PBE)[41]赝势来处理。Mn、Ti、Co、Al和Si的价电子结构分别为3d64s1、3d34s1、3d84s1、3s23p1和3s23p2。结合能计算采用Blchl四面体法修正。经过收敛性测试,平面波的截断能设置为450 eV,豫驰和静态计算以及态密度和能带结构计算均采用Monkhorst-Pack方法产生的8×8×8 k点网格。离子和电子豫驰收敛标准分别为能量差小于1×10-7和1×10-8eV。
2 结果与讨论 2.1 晶体结构与自旋特性M2CoA型Heusler合金具有Hg2CuTi型非中心对称立方结构[1],其空间群号为216号,空间群符号为F43m,其晶体结构如图 1(a)所示,M原子占据Wyckoff坐标系中的4a(0,0,0)(标为MA)和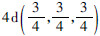 (标为MD)原子位置,而Co和A原子分别占据Wyckoff坐标系中的
(标为MD)原子位置,而Co和A原子分别占据Wyckoff坐标系中的 和
和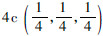 原子位置[30]。M2CoA型Heusler合金的晶体结构也可以看做是4个fcc格子沿(111)方向依次平移
原子位置[30]。M2CoA型Heusler合金的晶体结构也可以看做是4个fcc格子沿(111)方向依次平移 而得到,其原胞可以表示为图 1(b)的形式。
而得到,其原胞可以表示为图 1(b)的形式。
 |
| 图 1 M2CoA型Heusler合金的晶体结构Fig. 1 Crystal structures of M2CoA type Heusler alloy |
经过结构弛豫后M2CoA型Heusler合金的晶格常数a列在表 1中,文献报道Mn2CoAl的晶格常数实验值为0.579 8 nm[30],而Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi仅有理论预测的晶格常数,分别为0.565 nm[29]、0.614 nm[34]和0.603 nm[35],可以看到,本文的计算结果与文献结果十分吻合。表 1中还列出了M2CoA型Heusler合金的原子磁矩。可以看到在这4种合金中,A位原子Al与Si的磁矩很小,可以认为对总磁矩没有贡献。在Mn2CoAl与Mn2CoSi中,2个Mn原子的自旋方向是相反的,而它们的磁矩大小不同,所以Mn2CoAl和Mn2CoSi表现出亚铁磁性的特征。而在Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi中2个Ti原子的自旋方向相同,其中Ti2CoAl中Co原子与Ti原子的磁矩方向不同,表现出亚铁磁性的特征;Ti2CoSi中Co原子与Ti原子的磁矩方向相同,表现出铁磁性的特征。据Skaftouros[42]和Galanakis[43]等报道,Heusler合金的总自旋磁矩遵循Slater-Pauling规则,即Mt=Zt-24或Mt=Zt-18,其中,Mt和Zt分别为单原胞的总自旋磁矩以及总价电子数。Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi的总价电子数为26、27、20和21,计算得到的总自旋磁矩分别为2.0 μB、3.0 μB、2.0 μB和3.0 μB,μB为玻尔磁子,因此,Mn2CoAl和Mn2CoSi的总磁矩遵循Mt=Zt-24,Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi的遵循Mt=Zt-18,即它们遵循Slater-Pauling规则,该结论与Meinert等[44]报道的结果一致。
| 化合物 | a/nm | Ti或Mn A/ μ B | Ti或Mn D/ μ B | Co/ μ B | Si或Al/ μ B | 总磁矩/ μ B |
| Mn 2CoAl | 0.5728 | -1.54 | 2.63 | 0.95 | -0.01 | 2.00 |
| Mn 2CoSi | 0.5615 | -0.51 | 2.62 | 0.86 | 0.01 | 3.00 |
| Ti 2CoAl | 0.6126 | 1.41 | 0.82 | -0.20 | -0.01 | 2.00 |
| Ti 2CoSi | 0.6013 | 1.73 | 0.92 | 0.39 | -0.02 | 3.00 |
为了研究M2CoA型Heusler合金的电子结构,本文计算了沿第一布里渊区高对称点W-L-Γ-X-W-K展开的能带结构。计算得到的Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi的能带结构分别如图 2所示。
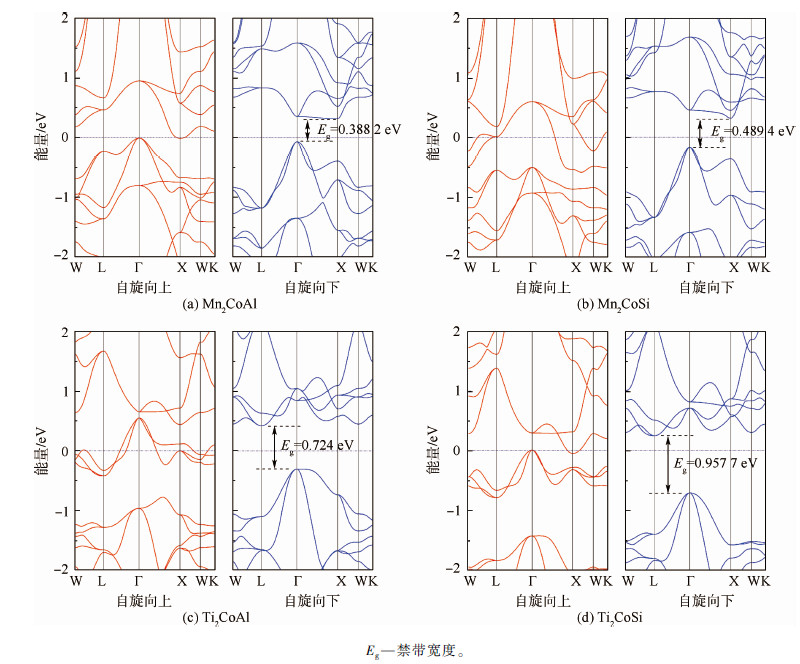 |
| 图 2 Mn2CoAl、 Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和 Ti2CoSi的能带结构Fig. 2 Band structures of Mn2CoAl,Mn2CoSi,Ti2CoAl and Ti2CoSi |
图 2中水平虚线表示费米能级(Ef=0 eV)。从图 2可以看出,M2CoA型Heusler合金在不同自旋态下电子的能带结构分布是不一样的。对于自旋向下的电子,Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi中均具有带隙,表现出半导体的特征,其PBE计算带隙分别为0.388 2、0.489 4、0.724和0.957 7 eV。而对于自旋向上的电子,这几种化合物的能带结构差别较大。如图 2(a)所示,在Mn2CoAl自旋向上的能带结构中可以看到,其价带顶(VBM)在Γ点接触费米能级,而导带底(CBM)则在X点处接触费米能级,最终形成一种间接零带隙半导体。由于具有这种自旋向上能带结构中的零带隙特征与自旋向下能带结构中的开放带隙特征,Mn2CoAl是一种自旋无带隙半导体[31]而不是一种普通的半金属亚铁磁体[23, 29],这与Ouardi等的实验结果[30]一致。根据图 2(b)与图 2(c),Mn2CoSi与Ti2CoAl自旋向上的能带结构均表现出导电的金属特性。结合它们自旋向下的宽阔带隙的能带结构,Mn2CoSi与Ti2CoAl为自旋半金属。图 2(d)中Ti2CoSi自旋向上的能带结构表现出了与Mn2CoAl相似的特征,即其VBM在Γ点接触费米能级,而CBM在X点处穿过费米能级,表现出半金属特性。
为了更加清楚地理解M2CoA型Heusler合金的自旋相关零带隙-宽带隙特性的形成机理,本文计算了Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi的总态密度和分波态密度,如图 3所示。图 3中通过0 eV的垂直虚线表示费米能级Ef,符号↑和↓分别代表自旋向上电子和自旋向下电子。从图 3可以看出,M2CoA型Heusler合金总态密度中的低能量部分(对于Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi分别为-6、-8、-5和-8 eV以下)主要来自A(A=Al,Si)原子的s态电子分波态密度的贡献。因而A原子的s电子对无带隙半导体的零带隙和宽带隙的形成几乎没有影响。总态密度中的部分能量区域(Mn2CoAl的-6~-5 eV能量区域,Mn2CoSi的-7~-6 eV能量区域,Ti2CoAl的-5~-4 eV能量区域,Ti2CoSi的-6~-5 eV能量区域)主要来自A原子的p电子的贡献。而总态密度中-4~4 eV的区域主要由M(M=Mn,Ti)和Co原子的d电子所贡献。在Heusler化合物Mn2CoAl的自旋向上电子的态密度中,费米能级附近存在4个较强杂化峰。其中,位于-2~-0.5 eV能量区域的2个杂化峰主要由MnD-d和Co-d电子的轨道杂化作用贡献,而靠近费米能级附近(-0.5~1 eV)的2个杂化峰则主要由MnA-d电子贡献。在Mn2CoAl的自旋向下电子的态密度中,费米能级附近存在5个较强杂化峰。其中位于费米能级以下(-2~0 eV)的2个杂化峰主要由MnA-d和Co-d电子的轨道杂化作用贡献,另外位于0~1 eV能量区域的2个杂化峰则来自MnA原子、MnD原子和Co原子的d电子间的强烈相互作用,剩下位于1~2 eV能量区域的杂化峰则来自MnD原子的d电子贡献。因此Mn2CoAl无带隙半导体的零带隙和宽带隙的特征源于MnA原子、MnD原子与Co原子的d电子间的强烈相互作用,这与Heusler合金中半金属性带隙的产生类似[23]。对比图 3(b)、图 3(c)和图 3(d),可以看到,在Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi自旋向下电子的态密度中,费米能级附近(-1.5~1.5 eV)存在若干个较强杂化峰。位于费米能级以上(0~1.5 eV)的杂化峰来自Mn/Ti原子与Co的d电子的贡献。而费米能级以下(-1.5~0 eV),Mn2CoSi的杂化峰主要由MnA-d和Co-d电子的轨道杂化作用贡献,Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi的杂化峰则主要由Co-d电子贡献。所以Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi宽阔带隙的形成与Mn2CoAl类似,源于Mn/Ti原子与Co的d电子间的贡献强烈杂化作用。总而言之,M2CoA型Heusler合金的自旋相关零带隙-宽带隙的产生均源于MA原子,MD原子和Co原子的d电子间的强烈相互作用。
 |
| 图 3 Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi的总态密度和分波态密度Fig. 3 Total densities of states and partial densities of states of Mn2CoAl, Mn2CoSi, Ti2CoAl and Ti2CoSi |
为了进一步确定M2CoA型Heusler合金的结构稳定性,本文首先研究了它们的晶格动力学性质,图 4给出了Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi的声子谱。从图中可以看到,Mn2CoAl,Mn2CoSi,Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi具有较为类似的晶格动力学特征,它们的声子谱中均不存在振动频率为负值的虚频。也就是说M2CoA型Heusler合金在晶格动力学上是稳定的。本文进一步采用应力-应变法[45]计算了M2CoA型Heusler合金的弹性常数来表征它们的力学性能稳定性。计算结果列于表 2中。立方晶系的M2CoA型Heusler合金总共有3个独立弹性常数,分别为c11、c12和c44。立方晶系3个独立弹性常数的Born力学稳定性判据[46]分别是:c11>0,c44>0,c11>︱c12︱,(c11+2c12)>0。可以看出,Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi均能够满足立方晶系的Born力学稳定性判据。所以M2CoA型Heusler合金的在力学上也是稳定的。
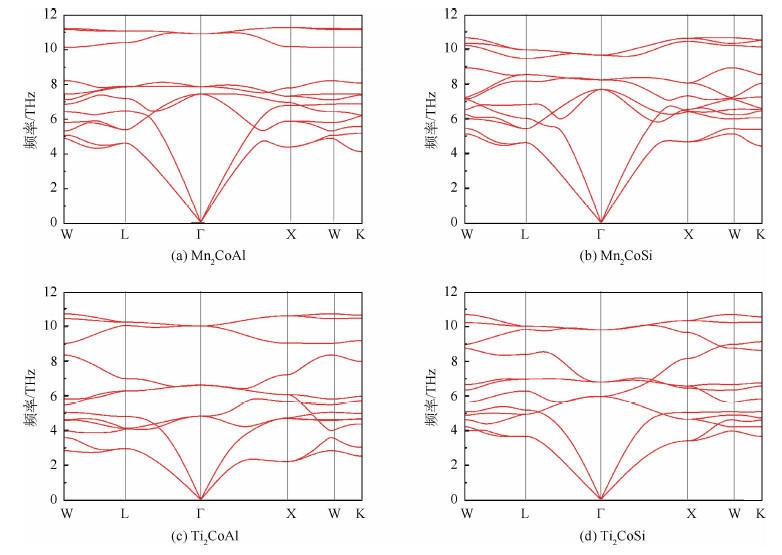 |
| 图 4 Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi的声子谱Fig. 4 Phonon dispersion spectrum of Mn2CoAl, Mn2CoSi, Ti2CoAl and Ti2CoSi |
| GPa | |||
| 化合物 | c 11 | c 12 | c 44 |
| Mn 2CoAl | 241.8 | 112.1 | 153.9 |
| Mn 2CoSi | 285.4 | 181.2 | 154.3 |
| Ti 2CoAl | 185.2 | 111.2 | 96.1 |
| Ti 2CoSi | 236.5 | 120.6 | 93.5 |
本文采用第一性原理方法对M2CoA型Heusler合金Mn2CoAl、Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi进行了系统性的研究,并详细分析了它们的电子结构、磁学性能与晶格动力学稳定性。主要结论如下:
1) 在基态下,Mn2CoAl表现为自旋无带隙半导体,而Mn2CoSi、Ti2CoAl和Ti2CoSi表现为自旋半金属特征。
2) M2CoA型Heusler合金的自旋相关零带隙-宽带隙的产生均源于MA原子,MD原子和Co原子的d电子间的强烈相互作用。
3) 计算得到的M2CoA型Heusler合金的总磁矩符合Slater-Pauling规则。
4) M2CoA型Heusler合金在晶格动力学和力学上均具有良好的稳定性。
| [1] | GRAF T, FELSER C,PARKIN S S P.Simple rules for the understanding of Heusler compounds[J].Progress in Solid State Chemistry,2011,39(1):1-50. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [2] | FELSER C, FECHER G H,BALKE B.Spintronics:A challenge for materials science and solid-state chemistry[J].Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2007,46(5):668-699. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [3] | HEUSLER F, STARCK W,HAUPT E.Magnetisch-chemische studien[J].Verh DPG,1903,5:220-223. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [4] | WU Y, WU B,WEI Z,et al.Structural,half-metallic and elastic properties of the half-Heusler compounds NiMnM(M=Sb,As and Si)and IrMnAs from first-principles calculations[J].Intermetallics,2014,53:26-33. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [5] | AHMADIAN F, SALARY A.Half-metallicity in the inverse Heusler compounds Sc2MnZ(Z=C,Si,Ge,and Sn)[J].Intermetallics,2014,46:243-249. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [6] | SHAN R, SUKEGAWA H,WANG W H,et al.Demonstration of half-metallicity in Fermi-level-tuned Heusler alloy Co2FeAl0.5Si0.5 at room temperature[J].Physical Review Letters,2009,102(24):246601. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [7] | BOMBOR D, BLUM C G F,VOLKONSKIY O,et al.Half-metallic ferromagnetism with unexpectedly small spin splitting in the Heusler compound Co2FeSi[J].Physical Review Letters,2013,110(6):066601. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [8] | PICKETT W E. Single spin superconductivity[J].Physical Review Letters,1996,77(15):3185-3188. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [9] | KAINUMA R, IMANO Y,ITO W,et al.Magnetic-field-induced shape recovery by reverse phase transformation[J].Nature,2006,439(7079):957-960. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [10] | MANOSA L, GONZALEZ-ALONSO D,PLANES A,et al.Giant solid-state barocaloric effect in the Ni-Mn-In magnetic shape-memory alloy[J].Nature Materials,2010,9(6):478-481. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [11] | BISWAS A, SINGH G,SARKAR S K,et al.Hot deformation behavior of Ni-Fe-Ga-based ferromagnetic shape memory alloy-A study using processing map[J].Intermetallics,2014,54:69-78. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [12] | SEAMAN C L, DILLEY N R,DE ANDRADE M C,et al.Superconductivity and magnetism in the Heusler alloys MPd2Pb(M=rare earth,Th,and U)[J].Physical Review B,1996,53(5):2651-2657. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [13] | WINTERLIK J, FECHER G H,FELSER C,et al.Ni-based superconductor:Heusler compound ZrNi2Ga[J].Physical Review B,2008,78(18):184506. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [14] | FU C,XIE H, LIU Y,et al.Thermoelectric properties of FeVSb half-Heusler compounds by levitation melting and spark plasma sintering[J].Intermetallics,2013,32:39-43. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [15] | KIM S W, KIMURA Y,MISHIMA Y.High temperature thermoelectric properties of TiNiSn-based half-Heusler compounds[J].Intermetallics,2007,15(3):349-356. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [16] | CHADOV S, QI X,KUBLER J,et al.Tunable multifunctional topological insulators in ternary Heusler compounds[J].Nature Materials,2010,9(7):541-545. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [17] | LIN H,WRAY L A, XIA Y,et al.Half-Heusler ternary compounds as new multifunctional experimental platforms for topological quantum phenomena[J].Nature Materials,2010,9(7):546-549. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [18] | VAN ENGEN P G, BUSCHOW K H J,JONGEBREUR R.PtMnSb, a material with very high magneto-optical Kerr effect[J].Applied Physics Letters,1983,42(2):202-204. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [19] | KRENKE T, DUMAN E,ACET M,et al.Inverse magnetocaloric effect in ferromagnetic Ni-Mn-Sn alloys[J].Nature Materials,2005,4(6):450-454. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [20] | DE GROOT R A, MUELLER F M,VAN ENGEN P G,et al.New class of materials:Half-metallic ferromagnets[J].Physical Review Letters,1983,50(25):2024-2027. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [21] | KUBLER J, WILLIAMS A R,SOMMERS C B.Formation and coupling of magnetic moments in Heusler alloys[J].Physical Review B,1983,28(4):1745-1755. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [22] | BARTH J, FCHER G H,BALKE B,et al.Itinerant half-metallic ferromagnets Co2TiZ(Z=Si,Ge,Sn):Ab initio calculations and measurement of the electronic structure and transport properties[J].Physical Review B,2010,81(6):064404. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [23] | LIU G D, DAI X F,LIU H Y,et al.Mn2CoZ(Z=Al,Ga,In,Si,Ge,Sn,Sb)compounds:Structural,electronic,and magnetic properties[J].Physical Review B,2008,77(1):014424. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [24] | GALANAKIS I, ÖZDOGAN K, ŞAŞIOGLU E,et al.Ab initio design of half-metallic fully compensated ferrimagnets:The case of Cr2MnZ(Z=P,As,Sb,and Bi)[J].Physical Review B,2007,75(17):172405. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [25] | XING N, GONG Y,ZHANG W,et al.First-principle prediction of half-metallic properties for the Heusler alloys V2YSb(Y=Cr,Mn,Fe,Co)[J].Computational Materials Science,2009,45(2):489-493. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [26] | LUO H,ZHU Z, MA L,et al.Electronic structure and magnetic properties of Fe2YSi(Y=Cr,Mn,Fe,Co,Ni)Heusler alloys:A theoretical and experimental study[J].Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics,2007,40(22):7121-7127. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [27] | WANG W, LIU E,KODZUKA M,et al.Coherent tunneling and giant tunneling magnetoresistance in Co2FeAl/MgO/CoFe magnetic tunneling junctions[J].Physical Review B,2010,81(14):140402. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [28] | NIKOLAEV K, KOLBO P,POKHIL T,et al."All-Heusler alloy" current-perpendicular-to-plane giant magnetoresistance[J].Applied Physics Letters,2009,94(22):222501. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [29] | XING N,LI H, DONG J,et al.First-principle prediction of half-metallic ferrimagnetism of the Heusler alloys Mn2CoZ(Z=Al,Ga,Si,Ge)with a high-ordered structure[J].Computational Materials Science,2008,42(4):600-605. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [30] | OUARDI S, FECHER G H,FELSER C,et al.Realization of spin gapless semiconductors:The Heusler compound Mn2CoAl[J].Physical Review Letters,2013,110(10):100401. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [31] | WANG X L. Proposal for a new class of materials:Spin gapless semiconductors[J].Physical Review Letters,2008,100(15):156404. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [32] | PICOZZI S, CONTINENZA A,FREEMAN A J.Co2MnX(X=Si,Ge,Sn)Heusler compounds:An ab initio study of their structural,electronic,and magnetic properties at zero and elevated pressure[J].Physical Review B,2002,66(9):094421. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [33] | SINGH M, SAINI H S,THAKUR J,et al.Disorder dependent half-metallicity in Mn2CoSi inverse Heusler alloy[J].Journal of Solid State Chemistry,2013,208:71-77. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [34] | BAYAR E, KERVAN N,KERVAN S.Half-metallic ferrimagnetism in the Ti2CoAl Heusler compound[J].Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2011,323(23):2945-2948. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [35] | BIRSAN A, PALADE P,KUNCSER V.Prediction of half metallic properties in Ti2CoSi Heusler alloy based on density functional theory[J].Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2013,331:109-112. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [36] | CHEN Y, WU B,YUAN H,et al.The defect-induced changes of the electronic and magnetic properties in the inverse Heusler alloy Ti2CoAl[J].Journal of Solid State Chemistry,2015,221:311-317. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [37] | FENG Y, WU B,YUAN H,et al.Magnetism and half-metallicity in bulk and (100) surface of Heusler alloy Ti2CoAl with Hg2CuTi-type structure[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2013,557:202-208. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [38] | SKAFTOUROS S, ÖZDOGAN K, ŞAŞIOGLU E,et al.Search for spin gapless semiconductors:The case of inverse Heusler compounds[J].Applied Physics Letters,2013,102(2):022402. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [39] | HAFNER J. Ab-initio simulations of materials using VASP:Density-functional theory and beyond[J].Journal of Computational Chemistry,2008,29(13):2044-2078. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [40] | PERDEW J P, BURKE K,WANG Y.Generalized gradient approximation for the exchange-correlation hole of a many-electron system[J].Physical Review B,1996,54(23):16533-16539. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [41] | PERDEW J P, WANG Y.Accurate and simple analytic representation of the electron-gas correlation energy[J].Physical Review B,1992,45(23):13244-13249. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [42] | SKAFTOUROS S, ÖZDOGAN K, ŞAŞIOGLU E,et al.Generalized Slater-Pauling rule for the inverse Heusler compounds[J].Physical Review B,2013,87(2):024420. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [43] | GALANAKIS I, DEDERICHS P H,PAPANIKOLAOU N.Slater-Pauling behavior and origin of the half-metallicity of the full-Heusler alloys[J].Physical Review B,2002,66(17):174429. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [44] | MEINERT M, SCHMALHORST J-M,REISS G.Exchange interactions and Curie temperatures of Mn2CoZ compounds[J].Journal of Physics:Condensed Matter,2011,23(11):116005. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [45] | SUN Z M, AHUJA R,LOWTHER J E.Mechanical properties of vanadium carbide and a ternary vanadium tungsten carbide[J].Solid State Communications,2010,150(15-16):697-700. |
| Click to display the text | |
| [46] | WU Z,ZHAO E, XIANG H,et al.Crystal structures and elastic properties of superhard IrN2 and IrN3 from first principles[J].Physical Review B,2007,76(5):054115. |
| Click to display the text |



